| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Mecklenburg" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2019) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Mecklenburg | |
|---|---|
| Historical region of Germany | |
 Flag Flag Coat of arms Coat of arms | |
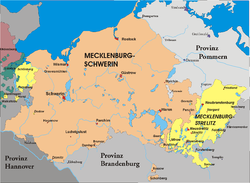 Mecklenburg, divided between Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz, from 1866 to 1934. Mecklenburg, divided between Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz, from 1866 to 1934. | |
| Coordinates: 53°50′14″N 11°28′16″E / 53.83722°N 11.47111°E / 53.83722; 11.47111 | |
| Largest city | Rostock |
| Demonym | Mecklenburgian • Mecklenburger |
Mecklenburg (German pronunciation: [ˈmeːklənbʊʁk]; Low German: Mękel(n)borg [ˈmɛːkəl(n)bɔrx]) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow.
The name Mecklenburg derives from a castle named Mikilenburg (Old Saxon for "big castle", hence its translation into Neo-Latin and Greek as Megalopolis), located between the cities of Schwerin and Wismar. In Slavic languages it was known as Veligrad, which also means "big castle". It was the ancestral seat of the House of Mecklenburg; for a time the area was divided into Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz among the same dynasty.
Linguistically Mecklenburgers retain and use many features of Low German vocabulary or phonology.
The adjective for the region is Mecklenburgian or Mecklenburgish (German: mecklenburgisch); inhabitants are called Mecklenburgians or Mecklenburgers (German: Mecklenburger).
Geography
Mecklenburg is known for its mostly flat countryside. Much of the terrain is boggy, with ponds, marshes and fields as common features, with small forests interspersed. The terrain changes as one moves north towards the Baltic Sea.
Under the peat of Mecklenburg are sometimes found deposits of ancient lava flows. Traditionally, at least in the countryside, the stone from these flows is cut and used in the construction of homes, often in joint use with cement, brick and wood, forming a unique look to the exterior of country houses.
Mecklenburg has productive farming, but the land is most suitable for grazing for livestock.
List of urban centers in Mecklenburg
See also: List of cities in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern| Town/ municipality |
District | Population as of December 31, 2012 |
Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rostock | district-free city | 206,011 (12-31-2015) | 
|
| Schwerin | district-free city | 91,264 | 
|
| Neubrandenburg | Mecklenburgische Seenplatte | 63,509 | 
|
| Wismar | Nordwestmecklenburg | 42,433 | 
|
| Güstrow | Rostock | 28,586 | 
|
| Neustrelitz | Mecklenburgische Seenplatte | 20,322 | 
|
| Waren (Müritz) | Mecklenburgische Seenplatte | 21,074 | 
|
| Parchim | Ludwigslust-Parchim | 17,174 | 
|
| Ludwigslust | Ludwigslust-Parchim | 11,998 | 
|
| Bad Doberan | Rostock | 11,427 | 
|
| Hagenow | Ludwigslust-Parchim | 11,324 | 
|
| Grevesmühlen | Nordwestmecklenburg | 10,621 | 
|
| Boizenburg/Elbe | Ludwigslust-Parchim | 10,169 | 
|
| Teterow | Rostock | 8,733 | 
|
| Malchin | Mecklenburgische Seenplatte | 7,657 | 
|
History
See also: Partitions of MecklenburgEarly history
Mecklenburg is the site of many prehistoric dolmen tombs. Its earliest organised inhabitants may have had Celtic origins. By no later than 100 BC the area had been populated by pre-Christian Germanic peoples.
The traditional symbol of Mecklenburg, the grinning steer's head (Low German: Ossenkopp, lit.: 'oxen's head', with osse being a synonym for steer and bull in Middle Low German), with an attached hide, and a crown above, may have originated from this period. It represents what early peoples would have worn, i.e. a steers's head as a helmet, with the hide hanging down the back to protect the neck from the sun, and overall as a way to instill fear in the enemy.
From the 7th through the 12th centuries, Mecklenburg was inhabited by Western Slavs who migrated there from what is now eastern Poland and north-western Ukraine. Among them were the Obotrites and other tribes that Frankish sources referred to as "Wends". The 11th-century founder of the Mecklenburger dynasty of Dukes and later Grand Dukes, which lasted until 1918, was Nyklot of the Obotrites.
In the late 12th century, Henry the Lion, Duke of the Saxons, reconquered the region, took oaths from its local lords, and Christianized its people, in a precursor to the Northern Crusades. From the 12th to 14th centuries, large numbers of Germans and Flemings settled the area (Ostsiedlung), importing German law and improved agricultural techniques. The Wends who survived all warfare and devastation of the centuries before, including invasions of and expeditions into Saxony, Denmark and Liutizic areas as well as internal conflicts, were assimilated in the centuries thereafter. However, elements of certain names and words used in Mecklenburg speak to the lingering Slavic influence. An example would be the city of Schwerin, which was originally called Zuarin in Slavic. Another example is the town of Bresegard, the 'gard' portion of the town name deriving from the Slavic word 'grad', meaning city or town.
Since the 12th century, the territory remained stable and relatively independent of its neighbours; one of the few German territories for which this is true. During the Reformation, the Duke in Schwerin would convert to Protestantism and so would follow the Duchy of Mecklenburg in 1549.

History, 1621–1933
Like many German territories, Mecklenburg was sometimes partitioned and re-partitioned among different members of the ruling dynasty. In 1621 it was divided into the two duchies of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Güstrow. With the extinction of the Güstrow line in 1701, the Güstrow lands were redivided, part going to the Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, and part going to the new line of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
In 1815, the two Mecklenburgian duchies were raised to Grand Duchies, the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin and the Grand Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, and subsequently existed separately as such in Germany under enlightened but absolute rule (constitutions being granted on the eve of World War I) until the revolution of 1918. Life in Mecklenburg could be quite harsh. Practices such as having to ask for permission from the Grand Duke to get married, or having to apply for permission to emigrate, would linger late into the history of Mecklenburg (i.e. 1918), long after such practices had been abandoned in other German areas. Even as late as the later half of the 19th century the Grand Duke personally owned half of the countryside. The last Duke abdicated in 1918, as monarchies fell throughout Europe. The Duke's ruling house reigned in Mecklenburg uninterrupted (except for two years) from its incorporation into the Holy Roman Empire until 1918. From 1918 to 1933, the duchies were free states in the Weimar Republic.
Traditionally Mecklenburg has always been one of the poorer German regions. The reasons for this may be varied, but one factor stands out: agriculturally the land is poor and can not produce at the same level as other parts of Germany. The two Mecklenburgs made attempts at being independent states after 1918, but eventually failed as their dependence on the rest of the German lands became apparent.
History since 1934
After three centuries of partition, Mecklenburg was united on 1 January 1934 by the German government. During World War II the Wehrmacht assigned Mecklenburg and Pomerania to Wehrkreis II under the command of General der Infanterie Werner Kienitz, with the headquarters at Stettin. Mecklenburg was assigned to an Area headquartered at Schwerin, which was responsible for military units in Schwerin, Rostock, Parchim, and Neustrelitz.
After World War II, the Soviet government occupying eastern Germany merged Mecklenburg with the smaller neighbouring region of Western Pomerania (German Vorpommern) to form the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Mecklenburg contributed about two-thirds of the geographical size of the new state and the majority of its population. Also, the new state became temporary or permanent home for many refugees expelled from former German territories seized by the Soviet Union and Poland after the war. The Soviets changed the name from "Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania" to "Mecklenburg" in 1947.
In 1952, the East German government ended the independent existence of Mecklenburg, creating three districts ("Bezirke") out of its territory: Rostock, Schwerin and Neubrandenburg.
During German reunification in 1990, the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern was revived, and is now one of the 16 states of the Federal Republic of Germany.
Coat of arms of the duchies of Mecklenburg

The House of Mecklenburg was founded by Niklot, prince of the Obotrites, Chizzini and Circipani on the Baltic Sea, who died in 1160. His Christian progeny was recognized as prince of the Holy Roman Empire 1170 and Duke of Mecklenburg 8 July 1348. On 27 February 1658 the ducal house divided in two branches: Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz.
The flag of both Mecklenburg duchies is traditionally made of the colours blue, yellow and red. The sequence however changed more than once in the past 300 years. In 1813 the duchies used yellow-red-blue. 23 December 1863 for Schwerin and 4 January 1864 for Strelitz blue-yellow-red was ordered. Mecklenburg-Schwerin however used white instead of yellow for flags on sea by law of 24 March 1855.
Siebmachers Wappenbuch gives therefore (?) blue-white-red for Schwerin and blue-yellow-red for Strelitz. According to this source, the grand ducal house of Schwerin used a flag of 3.75 to 5.625 M with the middle arms on a white quadrant (1.75 M) in the middle.
The middle arms show the shield of Mecklenburg as arranged in the 17th century. The county of Schwerin in the middle and in the quartering Mecklenburg (bull's head with hide), Rostock (griffin), principality of Schwerin (griffin surmounting green rectangle), Ratzeburg (cross surmounted by crown), Stargard (arm with hand holding ring) and Wenden (bull's head). The shield is supported by a bull and a griffin and surmounted by a royal crown.
The dukes of Strelitz used according to Siebmachers the blue-yellow-red flag with just the (oval) shield of Mecklenburg in the yellow band.
Ströhl in 1897 and Bulgaria show another arrangement: The grand-duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin flows a flag (4:5) with the arms of the figures from the shield of arms.
The former Schwerin standard with the white quadrant is now ascribed to the grand dukes of Strelitz. Ströhl mentions a flag for the grand ducal house by law of 23 December 1863 with the middle arms in the yellow band. And he mentions a special sea flag, the same but with a white middle band. 'Berühmte Fahnen' shows furthermore a standard for grand duchess Alexandra of Mecklenburg-Schwerin, princess of Hannover (1882–1963), showing her shield and that of Mecklenburg joined by the order of the Wendic Crown in a white oval. On sea the yellow band in her flag was of course white. The princes (dukes) of Mecklenburg-Schwerin had according to this source their own standard, showing the griffin of Rostock.
Economy
Agriculture
A flat landscape, Mecklenburg is known for its farmlands—which produces quinoa, wheat, barley and maize—and its animal husbandry, notably its cattle and the Mecklenburger breed of horse. Recently, given the upheavals and environmental disruptions created by globalisation, German farmers have become concerned about potentially invasive species such as the Greater rhea and the Asian hornet.
Tourism
See also: Tourism in GermanyMecklenburg has seen a huge increase in tourism since German reunification in 1990, particularly with its beaches and seaside resorts at the Baltic Sea ("German Riviera", Warnemünde, Boltenhagen, Heiligendamm, Kühlungsborn, Rerik and others), the Mecklenburg Lakeland (Mecklenburgische Seenplatte) and the Mecklenburg Switzerland (Mecklenburgische Schweiz) with their pristine nature, the old Hanseatic towns of Rostock, Greifswald, Stralsund and Wismar (the latter two being World Heritage) well known for their medieval Brick Gothic buildings, and the former royal residences of Schwerin, Güstrow, Ludwigslust and Neustrelitz.
Notable Mecklenburgers

- Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher (1742–1819), Prussian army leader
- Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (1744–1818), wife of George III of the United Kingdom and grandmother of Queen Victoria.
- Fritz Reuter (1810–1874), poet and novelist
- Ludwig Jacoby, (1813–1874), born in Altstrelitz, an author and Methodist clergyman
- Heinrich Schliemann (1822–1890), classical archaeologist
- Siegfried Marcus (1831–1898), automobile pioneer
- Gottlob Frege (1848–1925) a German philosopher, logician, and mathematician.
- Johannes Gillhoff (1861–1930), teacher, author of book on Mecklenburg emigrants to the US
- Michael Buddrus (born 1957), historian
- Jan Ullrich (born 1973) a German former professional road bicycle racer.
See also
- Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
- Duchy of Mecklenburg-Schwerin
- Duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
- List of rulers of Mecklenburg
- Mecklenburg County, North Carolina
- Mecklenburg County, Virginia
References
- (Ströhl, Deutsche Wappenrolle, Stuttgart, 1897, p. 89)
- (Ströhl, 86)
- Siebmachers Wappenbuch (Nuremberg, 1878)
- Berühmte Fahnen Deutscher Geschichte (Dresden, 1922)
- "Asian Hornet Invading Europe, German Specimen Shows Species is Spreading North". International Business Times. 6 February 2020. Archived from the original on 25 May 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2020.
Literature
- Grewolls, Grete (2011). Wer war wer in Mecklenburg und Vorpommern. Das Personenlexikon (in German). Rostock: Hinstorff Verlag. ISBN 978-3-356-01301-6.
External links
![]() Media related to Mecklenburg at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Mecklenburg at Wikimedia Commons
- Government portal of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
- Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Mecklenburg" . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- "Mecklenburg" . Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 17 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 1018–1020.
- Virtual State Museum of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
| Ecclesiastical |  | |
|---|---|---|
| Secular | ||
| Cities | ||
| until 1648. until 1701. from 1648. until 1731. until 1705. until 1596. from 1708. until 1773. until 1640. until 1695. from 1701. until 1734.
Circles est. 1500: Bavarian, Swabian, Upper Rhenish, Lower Rhenish–Westphalian, Franconian, (Lower) Saxon Circles est. 1512: Austrian, Burgundian, Upper Saxon, Electoral Rhenish · Unencircled territories | ||