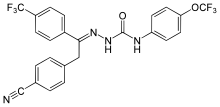
Pharmaceutical compound
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | ProMeris, Alverde |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.107.480 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H16F6N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 506.408 g·mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Metaflumizone is a semicarbazone broad-spectrum insecticide developed by Nihon Nohyaku with activity on Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, and certain Hemiptera. It is also used for the veterinary treatment of fleas and ticks, marketed under the brand name ProMeris. A discontinued variant of ProMeris, called ProMeris Duo or Promeris for Dogs, was indicated for canine use and was a formulated blend of metaflumizone and amitraz. The metaflumizone-only formulation is waterproof and typically remain effective for 30–45 days in a cutaneous application at the base of the neck.
Similar insecticides
Metaflumizone is chemically similar to pyrazoline sodium channel blocker insecticides (SCBIs) discovered at Philips-Duphar in the early 1970s, but is less dangerous to mammals than earlier compounds.
Action
Metaflumizone belongs to IRAC group 22B and works by blocking sodium channels in target insects, resulting in flaccid paralysis. Metaflumizone blocks sodium channels by binding selectively to the slow-inactivated state, which is characteristic of the SCBIs. The toxin has been tested for efficacy against Spodoptera eridania moths and is indicated for control of fleas and ticks. However, in a cross comparison with other veterinary flea control substances, Metaflumizone was not shown to result in a significant reduction in the number of engorged adult female Culex mosquitoes. Therefore, its usefulness as a heartworm control treatment is likely to be insignificant when compared with comparable treatments such as selamectin that do impact the mosquito disease vector.
Adverse effects reported
In 2011, Pfizer Animal Care decided to cease production of the drug based on findings which linked its use to an elevated incidence of the autoimmune disorder pemphigus foliaceus.
References
- Jeschke P, Witschel M, Krämer W, Schirmer U (25 January 2019). "33.4.2 Semicarbazone Insecticides: Metaflumizone". Modern Crop Protection Compounds (3rd ed.). Wiley‐VCH. pp. 1440–1448. ISBN 9783527699261.
- "Metaflumizone (ProMeris and ProMeris Duo) for Dogs and Cats". PetPlace Drug Library.
- ^ Salgado VL, Hayashi JH (December 2007). "Metaflumizone is a novel sodium channel blocker insecticide". Veterinary Parasitology. 150 (3): 182–9. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2007.08.032. PMID 17959312.
- Bouhsira E, Fysikopoulos A, Franc M (August 2009). "Efficacy of fipronil-(S)-methoprene, metaflumizone combined with amitraz, and pyriprole commercial spot-on products in preventing Culex pipiens pipiens from feeding on dogs". The Veterinary Record. 165 (5): 135–7. doi:10.1136/vr.165.5.135. PMID 19648637.
- Tremayne J (18 April 2011). "Study Links ProMeris to Pemphigus Foliaceus; Pfizer Stopping Its Production". Veterinary Practice News. California, United States: BowTie. Retrieved 26 April 2011.
External links
- Metaflumizone in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)