| Part of a series on the |
| Wireless network technologies |
|---|
 |
| Analog |
| Digital |
| Mobile telecommunications |


Mobile telephony is the provision of wireless telephone services to mobile phones, distinguishing it from fixed-location telephony provided via landline phones. Traditionally, telephony specifically refers to voice communication, though the distinction has become less clear with the integration of additional features such as text messaging and data services.
Modern mobile phones connect to a terrestrial cellular network of base stations (commonly referred to as cell sites), using radio waves to facilitate communication. Satellite phones use wireless links to orbiting satellites, providing an alternative in areas lacking local terrestrial communication infrastructure, such as landline and cellular networks. Cellular networks, satellite networks, and landline systems are all linked to the public switched telephone network (PSTN), enabling calls to be made to and from nearly any telephone worldwide.
As of 2010, global estimates indicated approximately five billion mobile cellular subscriptions, highlighting the significant role of mobile telephony in global communication systems.
History
Main articles: History of mobile phones and History of the prepaid mobile phoneAccording to internal memos, American Telephone & Telegraph discussed developing a wireless phone in 1915, but were afraid that deployment of the technology could undermine its monopoly on wired service in the U.S.

Public mobile phone systems were first introduced in the years after the Second World War and made use of technology developed before and during the conflict. The first system opened in St. Louis, Missouri, United States in 1946 whilst other countries followed in the succeeding decades. The UK introduced its 'System 1' manual radiotelephone service as the South Lancashire Radiophone Service in 1958. Calls were made via an operator using handsets identical to ordinary phone handsets. The phone itself was a large box located in the boot (trunk) of the vehicle containing valves and other early electronic components. Although an uprated manual service ('System 3') was extended to cover most of the UK, automation did not arrive until 1981 with 'System 4'. Although this non-cellular service, based on German B-Netz technology, was expanded rapidly throughout the UK between 1982 and 1985 and continued in operation for several years before finally closing in Scotland, it was overtaken by the introduction in January 1985 of two cellular systems - the British Telecom/Securicor 'Cellnet' service and the Racal/Millicom/Barclays 'Vodafone' (from voice + data + phone) service. These cellular systems were based on US Advanced Mobile Phone Service (AMPS) technology, the modified technology being named Total Access Communication System (TACS).

In 1947, Bell Labs was the first to propose a cellular radio telephone network. The primary innovation was the development of a network of small overlapping cell sites supported by a call switching infrastructure that tracks users as they move through a network and passes their calls from one site to another without dropping the connection. In 1956, the MTA system was launched in Sweden. The early efforts to develop mobile telephony faced two significant challenges: allowing a great number of callers to use the comparatively few available frequencies simultaneously and allowing users to seamlessly move from one area to another without having their calls dropped. Both problems were solved by Bell Labs employee Amos Joel who, in 1970 applied for a patent for a mobile communications system. However, a business consulting firm calculated the entire U.S. market for mobile telephones at 100,000 units and the entire worldwide market at no more than 200,000 units based on the ready availability of pay telephones and the high cost of constructing cell towers. As a consequence, Bell Labs concluded that the invention was "of little or no consequence," leading it not to attempt to commercialize the invention. The invention earned Joel induction into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 2008.
The development of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) large-scale integration (LSI) technology, information theory and cellular networking led to the development of affordable mobile communications. The first call on a handheld mobile phone was made on April 3, 1973, by Martin Cooper, then of Motorola to his opposite number in Bell Labs who were also racing to be first. Bell Labs went on to install the first trial cellular network in Chicago in 1978. This trial system was licensed by the FCC to ATT for commercial use in 1982 and, as part of the divestiture arrangements for the breakup of ATT, the AMPS technology was distributed to local telcos. The first commercial system opened in Chicago in October 1983. A system designed by Motorola also operated in the Washington D.C./Baltimore area from summer 1982 and became a full public service later the following year. Japan's first commercial radiotelephony service was launched by NTT in 1979.
The first fully automatic first generation cellular system was the Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT) system, simultaneously launched in 1981 in Denmark, Finland, Norway and Sweden. NMT was the first mobile phone network featuring international roaming. The Swedish electrical engineer Östen Mäkitalo started to work on this vision in 1966, and is considered as the father of the NMT system and some also consider him the father of the cellular phone.
There was a rapid growth of wireless telecommunications towards the end of the 20th century, primarily due to the introduction of digital signal processing in wireless communications, driven by the development of low-cost, very large-scale integration (VLSI) RF CMOS (radio-frequency complementary MOS) technology. The advent of cellular technology encouraged European countries to co-operate in the development of a pan-European cellular technology to rival those of the US and Japan. This resulted in the GSM system, the initials originally from the Groupe Spécial Mobile that was charged with the specification and development tasks but latterly as the 'Global System for Mobile Communications'. The GSM standard eventually spread outside Europe and is now the most widely used cellular technology in the world and the de facto standard. The industry association, the GSMA, now represents 219 countries and nearly 800 mobile network operators. There are now estimated to be over 5 billion phone subscriptions according to the "List of countries by number of mobile phones in use" (although some users have multiple subscriptions, or inactive subscriptions), which also makes the mobile phone the most widely spread technology and the most common electronic device in the world.
The first mobile phone to enable internet connectivity and wireless email, the Nokia Communicator, was released in 1996, creating a new category of multi-use devices called smartphones. In 1999 the first mobile internet service was launched by NTT DoCoMo in Japan under the i-Mode service. By 2007 over 798 million people around the world accessed the internet or equivalent mobile internet services such as WAP and i-Mode at least occasionally using a mobile phone rather than a personal computer.
Cellular systems
Main articles: Cellular network and Cellular frequencies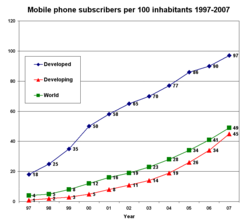
Mobile phones receive and send radio signals with any number of cell site base stations fitted with microwave antennas. These sites are usually mounted on a tower, pole or building, located throughout populated areas, then connected to a cabled communication network and switching system. The phones have a low-power transceiver that transmits voice and data to the nearest cell sites, normally not more than 8 to 13 km (approximately 5 to 8 miles) away. In areas of low coverage, a cellular repeater may be used, which uses a long-distance high-gain dish antenna or yagi antenna to communicate with a cell tower far outside of normal range, and a repeater to rebroadcast on a small short-range local antenna that allows any cellphone within a few meters to function properly.
When the mobile phone or data device is turned on, it registers with the mobile telephone exchange, or switch, with its unique identifiers, and can then be alerted by the mobile switch when there is an incoming telephone call. The handset constantly listens for the strongest signal being received from the surrounding base stations, and is able to switch seamlessly between sites. As the user moves around the network, the "handoffs" are performed to allow the device to switch sites without interrupting the call.
Cell sites have relatively low-power (often only one or two watts) radio transmitters which broadcast their presence and relay communications between the mobile handsets and the switch. The switch in turn connects the call to another subscriber of the same wireless service provider or to the public telephone network, which includes the networks of other wireless carriers. Many of these sites are camouflaged to blend with existing environments, particularly in scenic areas.
The dialogue between the handset and the cell site is a stream of digital data that includes digitised audio (except for the first generation analog networks). The technology that achieves this depends on the system which the mobile phone operator has adopted. The technologies are grouped by generation. The first-generation systems started in 1979 with Japan, are all analog and include AMPS and NMT. Second-generation systems, started in 1991 in Finland, are all digital and include GSM, CDMA and TDMA.
The GSM standard is a European initiative expressed at the CEPT ("Conférence Européenne des Postes et Telecommunications", European Postal and Telecommunications conference). The Franco-German R&D cooperation demonstrated the technical feasibility, and in 1987 a Memorandum of Understanding was signed between 13 European countries who agreed to launch a commercial service by 1991. The first version of the GSM (=2G) standard had 6,000 pages. The IEEE/RSE awarded to Thomas Haug and Philippe Dupuis the 2018 James Clerk Maxwell medal for their contributions to the first digital mobile telephone standard. In 2018, the GSM was used by over 5 billion people in over 220 countries. The GSM (2G) has evolved into 3G, 4G and 5G. The standardisation body for GSM started at the CEPT Working Group GSM (Group Special Mobile) in 1982 under the umbrella of CEPT. In 1988, ETSI was established and all CEPT standardization activities were transferred to ETSI. Working Group GSM became Technical Committee GSM. In 1991, it became Technical Committee SMG (Special Mobile Group) when ETSI tasked the committee with UMTS (3G).

The nature of cellular technology renders many phones vulnerable to 'cloning': anytime a cell phone moves out of coverage (for example, in a road tunnel), when the signal is re-established, the phone sends out a 're-connect' signal to the nearest cell-tower, identifying itself and signalling that it is again ready to transmit. With the proper equipment, it is possible to intercept the re-connect signal and encode the data it contains into a 'blank' phone—in all respects, the 'blank' is then an exact duplicate of the real phone and any calls made on the 'clone' will be charged to the original account. This problem was widespread with the first generation analogue technology, however the modern digital standards such as GSM greatly improve security and make cloning hard to achieve.
In an effort to limit the potential harm from having a transmitter close to the user's body, the first fixed/mobile cellular phones that had a separate transmitter, vehicle-mounted antenna, and handset (known as car phones and bag phones) were limited to a maximum 3 watts Effective Radiated Power. Modern handheld cellphones which must have the transmission antenna held inches from the user's skull are limited to a maximum transmission power of 0.6 watts ERP. Regardless of the potential biological effects, the reduced transmission range of modern handheld phones limits their usefulness in rural locations as compared to car/bag phones, and handhelds require that cell towers are spaced much closer together to compensate for their lack of transmission power.
Usage
By civilians

An increasing number of countries, particularly in Europe, now have more mobile phones than people. According to the figures from Eurostat, the European Union's in-house statistical office, Luxembourg had the highest mobile phone penetration rate at 158 mobile subscriptions per 100 people, closely followed by Lithuania and Italy. In Hong Kong the penetration rate reached 139.8% of the population in July 2007. Over 50 countries have mobile phone subscription penetration rates higher than that of the population and the Western European average penetration rate was 110% in 2007 (source Informa 2007).
There are over five hundred million active mobile phone accounts in China, as of 2007, but the total penetration rate there still stands below 50%. The total number of mobile phone subscribers in the world was estimated at 2.14 billion in 2005. The subscriber count reached 2.7 billion by end of 2006 according to Information, and 3.3 billion by November, 2007, thus reaching an equivalent of over half the planet's population. Around 80% of the world's population has access to mobile phone coverage, as of 2006. This figure is expected to increase to 90% by 2010.
In some developing countries with little "landline" telephone infrastructure, mobile phone use has quadrupled in the last decade. The rise of mobile phone technology in developing countries is often cited as an example of the leapfrog effect. Many remote regions in the third world went from having no telecommunications infrastructure to having satellite based communications systems. At present, Africa has the largest growth rate of cellular subscribers in the world, its markets expanding nearly twice as fast as Asian markets. The availability of prepaid or 'pay-as-you-go' services, where the subscriber is not committed to a long-term contract, has helped fuel this growth in Africa as well as in other continents.
On a numerical basis, India is the largest growth market, adding about 6 million mobile phones every month. It currently has a mobile subscriber base of 937.06 million mobile phones.
Traffic
Since the world is operating quickly to 3G and 4G networks, mobile traffic through video is heading high. It is expected that by the end of 2018, the global traffic will reach an annual rate of 190 exabytes/year. This is the result of people shifting to smartphones. It is predicted by 2018, mobile traffic will reach by 10 billion connections with 94% traffic comes from smartphones, laptops and tablets. Also 69% of mobile traffic will be from videos since we have high definition screens available in smart phones and 176.9 wearable devices to be at use. Apparently, 4G will be dominating the traffic by 51% of total mobile data by 2018.
By government agencies
Law enforcement
Main article: Lawful interceptionLaw enforcement have used mobile phone evidence in a number of different ways. Evidence about the physical location of an individual at a given time can be obtained by triangulating the individual's cellphone between several cellphone towers. This triangulation technique can be used to show that an individual's cellphone was at a certain location at a certain time. The concerns over terrorism and terrorist use of technology prompted an inquiry by the British House of Commons Home Affairs Select Committee into the use of evidence from mobile phone devices, prompting leading mobile telephone forensic specialists to identify forensic techniques available in this area. NIST have published guidelines and procedures for the preservation, acquisition, examination, analysis, and reporting of digital information present on mobile phones can be found under the NIST Publication SP800-101.
In the UK in 2000 it was claimed that recordings of mobile phone conversations made on the day of the Omagh bombing were crucial to the police investigation. In particular, calls made on two mobile phones which were tracked from south of the Irish border to Omagh and back on the day of the bombing, were considered of vital importance.
Further example of criminal investigations using mobile phones is the initial location and ultimate identification of the terrorists of the 2004 Madrid train bombings. In the attacks, mobile phones had been used to detonate the bombs. However, one of the bombs failed to detonate, and the SIM card in the corresponding mobile phone gave the first serious lead about the terrorists to investigators. By tracking the whereabouts of the SIM card and correlating other mobile phones that had been registered in those areas, police were able to locate the terrorists.
Disaster response
The Finnish government decided in 2005 that the fastest way to warn citizens of disasters was the mobile phone network. In Japan, mobile phone companies provide immediate notification of earthquakes and other natural disasters to their customers free of charge. In the event of an emergency, disaster response crews can locate trapped or injured people using the signals from their mobile phones. An interactive menu accessible through the phone's web browser notifies the company if the user is safe or in distress. In Finland rescue services suggest hikers carry mobile phones in case of emergency even when deep in the forests beyond cellular coverage, as the radio signal of a cellphone attempting to connect to a base station can be detected by overflying rescue aircraft with special detection gear. Also, users in the United States can sign up through their provider for free text messages when an AMBER Alert goes out for a missing person in their area.
However, most mobile phone networks operate close to capacity during normal times, and spikes in call volumes caused by widespread emergencies often overload the system just when it is needed the most. Examples reported in the media where this has occurred include the September 11, 2001 attacks, the 2003 Northeast blackouts, the 2005 London Tube bombings, Hurricane Katrina, the 2006 Kiholo Bay earthquake, and the 2007 Minnesota bridge collapse.
Under FCC regulations, all mobile telephones must be capable of dialing emergency telephone numbers, regardless of the presence of a SIM card or the payment status of the account.
Impact on society
Human health
Main article: Mobile phone radiation and healthSince the introduction of mobile phones, concerns (both scientific and public) have been raised about the potential health impacts from regular use. But by 2008, American mobile phones transmitted and received more text messages than phone calls. Numerous studies have reported no significant relationship between mobile phone use and health, but the effect of mobile phone usage on health continues to be an area of public concern.
For example, at the request of some of their customers, Verizon created usage controls that meter service and can switch phones off, so that children could get some sleep. There have also been attempts to limit use by persons operating moving trains or automobiles, coaches when writing to potential players on their teams, and movie theater audiences. By one measure, nearly 40% of automobile drivers aged 16 to 30 years old text while driving, and by another, 40% of teenagers said they could text blindfolded.
18 studies have been conducted on the link between cell phones and brain cancer; A review of these studies found that cell phone use of 10 years or more "give a consistent pattern of an increased risk for acoustic neuroma and glioma". The tumors are found mostly on the side of the head that the mobile phone is in contact with. In July 2008, Dr. Ronald Herberman, director of the University of Pittsburgh Cancer Institute, warned about the radiation from mobile phones. He stated that there was no definitive proof of the link between mobile phones and brain tumors but there was enough studies that mobile phone usage should be reduced as a precaution. To reduce the amount of radiation being absorbed hands free devices can be used or texting could supplement calls. Calls could also be shortened or limit mobile phone usage in rural areas. Radiation is found to be higher in areas that are located away from mobile phone towers.
According to Reuters, The British Association of Dermatologists is warning of a rash occurring on people's ears or cheeks caused by an allergic reaction from the nickel surface commonly found on mobile devices’ exteriors. There is also a theory it could even occur on the fingers if someone spends a lot of time text messaging on metal menu buttons. In 2008, Lionel Bercovitch of Brown University in Providence, Rhode Island, and his colleagues tested 22 popular handsets from eight different manufacturers and found nickel on 10 of the devices.
Human behaviour
Culture and customs

Between the 1980s and the 2000s, the mobile phone has gone from being an expensive item used by the business elite to a pervasive, personal communications tool for the general population. In most countries, mobile phones outnumber land-line phones, with fixed landlines numbering 1.3 billion but mobile subscriptions 3.3 billion at the end of 2007.
In many markets from Japan and South Korea, to Europe, to Malaysia, Singapore, Taiwan and Hong Kong, most children age 8-9 have mobile phones and the new accounts are now opened for customers aged 6 and 7. Where mostly parents tend to give hand-me-down used phones to their youngest children, in Japan already new cameraphones are on the market whose target age group is under 10 years of age, introduced by KDDI in February 2007. The USA also lags on this measure, as in the US so far, about half of all children have mobile phones. In many young adults' households it has supplanted the land-line phone. Mobile phone usage is banned in some countries, such as North Korea and restricted in some other countries such as Burma.
Given the high levels of societal mobile phone service penetration, it is a key means for people to communicate with each other. The SMS feature spawned the "texting" sub-culture amongst younger users. In December 1993, the first person-to-person SMS text message was transmitted in Finland. Currently, texting is the most widely used data service; 1.8 billion users generated $80 billion of revenue in 2006 (source ITU). Many phones offer Instant Messenger services for simple, easy texting. Mobile phones have Internet service (e.g. NTT DoCoMo's i-mode), offering text messaging via e-mail in Japan, South Korea, China, and India. Most mobile internet access is much different from computer access, featuring alerts, weather data, e-mail, search engines, instant messages, and game and music downloading; most mobile internet access is hurried and short.
Because mobile phones are often used publicly, social norms have been shown to play a major role in the usage of mobile phones. Furthermore, the mobile phone can be a fashion totem custom-decorated to reflect the owner's personality and may be a part of their self-identity. This aspect of the mobile telephony business is, in itself, an industry, e.g. ringtone sales amounted to $3.5 billion in 2005. Mobile phone use on aircraft is starting to be allowed with several airlines already offering the ability to use phones during flights. Mobile phone use during flights used to be prohibited and many airlines still claim in their in-plane announcements that this prohibition is due to possible interference with aircraft radio communications. Shut-off mobile phones do not interfere with aircraft avionics. The recommendation why phones should not be used during take-off and landing, even on planes that allow calls or messaging, is so that passengers pay attention to the crew for any possible accident situations, as most aircraft accidents happen on take-off and landing.
Etiquette
Main article: Cell Phone EtiquetteMobile phone use can be an important matter of social discourtesy: phones ringing during funerals or weddings; in toilets, cinemas and theatres. Some book shops, libraries, bathrooms, cinemas, doctors' offices and places of worship prohibit their use, so that other patrons will not be disturbed by conversations. Some facilities install signal-jamming equipment to prevent their use, although in many countries, including the US, such equipment is illegal.
Many US cities with subway transit systems underground are studying or have implemented mobile phone reception in their tunnels for their riders, and trains, particularly those involving long-distance services, often offer a "quiet carriage" where phone use is prohibited, much like the designated non-smoking carriage of the past. Most schools in the United States and Europe and Canada have prohibited mobile phones in the classroom, or in school in an effort to limit class disruptions.
A working group made up of Finnish telephone companies, public transport operators and communications authorities has launched a campaign to remind mobile phone users of courtesy, especially when using mass transit—what to talk about on the phone, and how to. In particular, the campaign wants to impact loud mobile phone usage as well as calls regarding sensitive matters.
Use by drivers
Main articles: Mobile phones and driving safety and HandsfreeThe use of mobile phones by people who are driving has become increasingly common, for example as part of their job, as in the case of delivery drivers who are calling a client, or socially as for commuters who are chatting with a friend. While many drivers have embraced the convenience of using their cellphone while driving, some jurisdictions have made the practice against the law, such as Australia, the Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Quebec, Ontario, Nova Scotia, and Newfoundland and Labrador as well as the United Kingdom, consisting of a zero-tolerance system operated in Scotland and a warning system operated in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Officials from these jurisdictions argue that using a mobile phone while driving is an impediment to vehicle operation that can increase the risk of road traffic accidents.
Studies have found vastly different relative risks (RR). Two separate studies using case-crossover analysis each calculated RR at 4, while an epidemiological cohort study found RR, when adjusted for crash-risk exposure, of 1.11 for men and 1.21 for women.
A simulation study from the University of Utah Professor David Strayer compared drivers with a blood alcohol content of 0.08% to those conversing on a cell phone, and after controlling for driving difficulty and time on task, the study concluded that cell phone drivers exhibited greater impairment than intoxicated drivers. Meta-analysis by The Canadian Automobile Association and The University of Illinois found that response time while using both hands-free and hand-held phones was approximately 0.5 standard deviations higher than normal driving (i.e., an average driver, while talking on a cell phone, has response times of a driver in roughly the 40th percentile).
Driving while using a hands-free device is not safer than driving while using a hand-held phone, as concluded by case-crossover studies. epidemiological studies, simulation studies, and meta-analysis. Even with this information, California initiated new Wireless Communications Device Law (effective January 1, 2009) makes it an infraction to write, send, or read text-based communication on an electronic wireless communications device, such as a cell phone, while driving a motor vehicle. Two additional laws dealing with the use of wireless telephones while driving went into effect July 1, 2008. The first law prohibits all drivers from using a handheld wireless telephone while operating a motor vehicle. The law allows a driver to use a wireless telephone to make emergency calls to a law enforcement agency, a medical provider, the fire department, or other emergency services agency. The base fine for the FIRST offense is $20 and $50 for subsequent convictions. With penalty assessments, the fine can be more than triple the base fine amount. According to California Vehicle Code §23123, Motorists 18 and over may use a “hands-free device". The second law effective July 1, 2008, prohibits drivers under the age of 18 from using a wireless telephone or hands-free device while operating a motor vehicle (VC §23124). The consistency of increased crash risk between hands-free and hand-held phone use is at odds with legislation in over 30 countries that prohibit hand-held phone use but allow hands-free. Scientific literature is mixed on the dangers of talking on a phone versus those of talking with a passenger, with the Accident Research Unit at the University of Nottingham finding that the number of utterances was usually higher for mobile calls when compared to blindfolded and non-blindfolded passengers, but the University of Illinois meta-analysis concluding that passenger conversations were just as costly to driving performance as cell phone ones.
Use on aircraft
Main article: Mobile phones on aircraftAs of 2007, several airlines are experimenting with base station and antenna systems installed on the airplane, allowing low power, short-range connection of any phones aboard to remain connected to the aircraft's base station. Thus, they would not attempt connection to the ground base stations as during takeoff and landing. Simultaneously, airlines may offer phone services to their travelling passengers either as full voice and data services, or initially only as SMS text messaging and similar services. The Australian airline Qantas is the first airline to run a test aeroplane in this configuration in the autumn of 2007. Emirates has announced plans to allow limited mobile phone usage on some flights. However, in the past, commercial airlines have prevented the use of cell phones and laptops, due to the assertion that the frequencies emitted from these devices may disturb the radio waves contact of the airplane.
On March 20, 2008, an Emirates flight was the first time voice calls have been allowed in-flight on commercial airline flights. The breakthrough came after the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and the United Arab Emirates-based General Civil Aviation Authority (GCAA) granted full approval for the AeroMobile system to be used on Emirates. Passengers were able to make and receive voice calls as well as use text messaging. The system automatically came into operation as the Airbus A340-300 reached cruise altitude. Passengers wanting to use the service received a text message welcoming them to the AeroMobile system when they first switched their phones on. The approval by EASA has established that GSM phones are safe to use on airplanes, as the AeroMobile system does not require the modification of aircraft components deemed "sensitive," nor does it require the use of modified phones.
In any case, there are inconsistencies between practices allowed by different airlines and even on the same airline in different countries. For example, Delta Air Lines may allow the use of mobile phones immediately after landing on a domestic flight within the US, whereas they may state "not until the doors are open" on an international flight arriving in the Netherlands. In April 2007 the US Federal Communications Commission officially prohibited passengers' use of cell phones during a flight.
In a similar vein, signs are put up in many countries, such as Canada, the UK and the U.S., at petrol stations prohibiting the use of mobile phones, due to possible safety issues. However, it is unlikely that mobile phone use can cause any problems, and in fact "petrol station employees have themselves spread the rumour about alleged incidents."
Environmental impacts
See also: Electronic waste
Like all high structures, cellular antenna masts pose a hazard to low flying aircraft. Towers over a certain height or towers that are close to airports or heliports are normally required to have warning lights. There have been reports that warning lights on cellular masts, TV-towers and other high structures can attract and confuse birds. US authorities estimate that millions of birds are killed near communication towers in the country each year.
Some cellular antenna towers have been camouflaged to make them less obvious on the horizon, and make them look more like a tree.
An example of the way mobile phones and mobile networks have sometimes been perceived as a threat is the widely reported and later discredited claim that mobile phone masts are associated with the Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD) which has reduced bee hive numbers by up to 75% in many areas, especially near cities in the US. The Independent newspaper cited a scientific study claiming it provided evidence for the theory that mobile phone masts are a major cause in the collapse of bee populations, with controlled experiments demonstrating a rapid and catastrophic effect on individual hives near masts. Mobile phones were in fact not covered in the study, and the original researchers have since emphatically disavowed any connection between their research, mobile phones, and CCD, specifically indicating that the Independent article had misinterpreted their results and created "a horror story". While the initial claim of damage to bees was widely reported, the corrections to the story were almost non-existent in the media.
There are more than 500 million used mobile phones in the US sitting on shelves or in landfills, and it is estimated that over 125 million will be discarded this year alone. The problem is growing at a rate of more than two million phones per week, putting tons of toxic waste into landfills daily. Several companies offer to buy back and recycle mobile phones from users. In the United States many unwanted but working mobile phones are donated to women's shelters to allow emergency communication.
Tariff models
See also: GSM services § Voice charges, Mobile Internet, and flat rate
Payment methods
There are two principal ways to pay for mobile telephony: the 'pay-as-you-go' model where conversation time is purchased and added to a phone unit via an Internet account or in shops or ATMs, or the contract model where bills are paid by regular intervals after the service has been consumed. It is increasingly common for a consumer to purchase a basic package and then bolt-on services and functionality to create a subscription customised to the users needs.
Pay as you go (also known as "pre-pay" or "prepaid") accounts were invented simultaneously in Portugal and Italy and today form more than half of all mobile phone subscriptions. USA, Canada, Costa Rica, Japan, Israel and Finland are among the rare countries left where most phones are still contract-based.
Incoming call charges
In the early days of mobile telephony, the operators (carriers) charged for all air time consumed by the mobile phone user, which included both outbound and inbound telephone calls. As mobile phone adoption rates increased, competition between operators meant that some decided not to charge for incoming calls in some markets (also called "calling party pays").
The European market adopted a calling party pays model throughout the GSM environment and soon various other GSM markets also started to emulate this model.
In Hong Kong, Singapore, Canada, and the United States, it is common for the party receiving the call to be charged per minute, although a few carriers are beginning to offer unlimited received phone calls. This is called the "Receiving Party Pays" model. In China, it was reported that both of its two operators were to adopt the caller-pays approach as early as January 2007.
One disadvantage of the receiving party pays systems is that phone owners keep their phones turned off to avoid receiving unwanted calls, which results in the total voice usage rates (and profits) in Calling Party Pays countries outperforming those in Receiving Party Pays countries. To avoid the problem of users keeping their phone turned off, most Receiving Party Pays countries have either switched to Calling Party Pays, or their carriers offer additional incentives such as a large number of monthly minutes at a sufficiently discounted rate to compensate for the inconvenience.
When a user roams in another country, international roaming tariffs apply to all calls received, regardless of the model adopted in the home country.
Technologies used
The list below is a non-comprehensive attempt at listing the technologies used in mobile telephony:
0G (mobile radio telephone)
1G networks (analog networks)
2G networks (the first digital networks):
- Digital AMPS
- cdmaOne
- GSM
- GPRS
- EDGE(IMT-SC)
- Evolved EDGE
3G networks:
4G networks:
- LTE (TD-LTE)
- LTE Advanced
- LTE Advanced Pro
- WiMAX
- WiMAX-Advanced (WirelessMAN-Advanced)
- Ultra Mobile Broadband (never commercialized)
5G networks:
Starting with EVDO the following techniques can also be used to improve performance:
- MIMO, SDMA and Beamforming
See also
References
- Wu, Tim (June 10, 2008). "iSurrender: Apple's new iPhone augurs the inevitable return of the Bell telephone monopoly". Slate.
- "Asset Bank | Image Details". Imagelibrary.btplc.com. Archived from the original on May 6, 2016. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- "Asset Bank | Image Details". Imagelibrary.btplc.com. Archived from the original on May 6, 2016. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Patent No. 3,663,762, issued May 16, 1972.
- List of National Inventors Hall of Fame inductees
- ^ Srivastava, Viranjay M.; Singh, Ghanshyam (2013). MOSFET Technologies for Double-Pole Four-Throw Radio-Frequency Switch. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 1. ISBN 9783319011653.
- "30th Anniversary of First Wireless Cell Phone Call". 3g.co.uk. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Article by Larry Kahaner and Alan Green in the Chicago Tribune of December 22, 1983 Reach out and touch someone--by land, sea or air
- Phil Ament. "Mobile Phone History - Invention of the Mobile Phone". Ideafinder.com. Archived from the original on July 13, 2011. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Visited and evaluated by a group of (soon-to-be) British Telecoms staff (including writer) in September 1982.
- "Swedish National Museum of Science and Technology". Tekniskamuseet.se. Archived from the original on October 22, 2008. Retrieved July 29, 2009.
- "Mobile and technology: The Basics of Mobile Phones". Sharelie-download.com. Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- "Facts about the Mobile" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on August 13, 2010. Retrieved 2011-07-11.
- "Full Members ~ GSM World". Gsmworld.com. Archived from the original on July 11, 2011. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- ^ "Global cellphone penetration reaches 50 pct". Reuters. Archived from the original on April 26, 2023.
- "Duke of Cambridge Presents Maxwell Medals to GSM Developers". IEEE United Kingdom and Ireland Section. September 1, 2018. Retrieved December 10, 2020.
- "Europeans hang up on fixed lines". BBC News. November 28, 2007. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Office of the Telecommunications Authority in Hong Kong Archived March 9, 2009, at the Wayback Machine.
- "500 mln cell phone accounts in China". ITFacts Mobile usage. Retrieved September 5, 2007.
- "Total mobile subscribers top 1.8 billion".
- "Up to 90 percent of globe to have mobile coverage". Textually.org. October 17, 2006. Archived from the original on July 16, 2011. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- "Cell phone use booming worldwide". September 15, 2007. Retrieved September 15, 2007.
- "Mobile growth fastest in Africa". BBC News. March 9, 2005.
- Rice, Xan (March 4, 2006). "Phone revolution makes Africa upwardly mobile". The Times. UK. Archived from the original on October 13, 2008. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- "The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on February 25, 2009. Retrieved February 8, 2009. (444 KB)
- "The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on February 8, 2015. Retrieved February 2, 2015.
- "Mobile Network 2018". www.Phoneam.com. Archived from the original on April 29, 2015. Retrieved September 8, 2015.
- The Committee Office, House of Commons. "Supplementary memorandum submitted by Gregory Smith". Publications.parliament.uk. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Ayers, Richard; Jansen, Wayne (May 30, 2007). "Guidelines on Cell Phone Forensics" (PDF). doi:10.6028/NIST.SP.800-101.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) (1.44 MB), Recommendations of the National Institute of Standards and Technology, May 2007. - "Mobile phones key to Omagh probe". BBC News. October 10, 2000. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- "Communication safety". Nokia-n98.org. Archived from the original on December 24, 2008. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- "New Japanese phones offer Earthquake early warning alerts". Archived from the original on January 21, 2008. Retrieved January 8, 2008.
- Campbell, Jonathan. "Cellular Phones and Cancer". Archived from the original on January 20, 1998. Retrieved March 2, 2007.
- ^ Steinhauser, Jennifer & Holson, Laura M. (September 19, 2008). "Text Messages Seen as Dangerously Distracting". The New York Times. Retrieved September 19, 2008.
- Hamilton, Tyler. "Listening to Cell Phone Warnings: Researchers Working Overtime to Find Out If the Greatest Tool of Business is Causing Brian Cancer in Those Who Use it Constantly" Toronto Star. May 31, 2008. Retrieved November 20, 2008.
- "The BBC. "US Cancer Boss in Mobiles Warning." BBC News 24 July 2008. Retrieved November 20, 2008". BBC News. July 24, 2008. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Rachel Lieberman, Brandel France de Bravo, MPH, and Diana Zuckerman, Ph.D. "Can Cell Phones Harm Our Health? Archived February 24, 2015, at the Wayback Machine" National Research Center for Women and Families. August 2008. Retrieved August 13, 2013. /
- Doctors warn of rash from mobile phone use Reuters.com. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- "Mobile Phones for Kids Under 15: a Responsible Question". Point.com. April 13, 2006. Archived from the original on July 15, 2011. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- "Rise in executions for mobile use". ITV News. June 15, 2007. Archived from the original on August 17, 2007. Retrieved June 23, 2007.
- ^ Burger, Christoph; Riemer, Valentin; Grafeneder, Jürgen; Woisetschläger, Bianca; Vidovic, Dragana; Hergovich, Andreas (2010). "Reaching the Mobile Respondent: Determinants of High-Level Mobile Phone Use Among a High-Coverage Group" (PDF). Social Science Computer Review. 28 (3): 336–349. doi:10.1177/0894439309353099. S2CID 61640965.
- Aquino, Grace (April 28, 2006). "Cell Phone Fashion Show". PC World. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Gundersen, Edna, "Mastertones ring up profits", USA Today, 11/29/2006
- campaign to promote cell phone manners (in finish)
- ^ Redelmeier, Donald; Tibshirani, Robert (February 13, 1997). "Association Between Cellular-Telephone Calls And Motor Vehicle Collisions" (PDF). The New England Journal of Medicine. 336 (7): 453–458. doi:10.1056/NEJM199702133360701. PMID 9017937. S2CID 23723296. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 18, 2009.
- ^ McEvoy, Suzanne; Stevenson, MR; McCartt, AT; Woodward, M; Haworth, C; Palamara, P; Cercarelli, R (2005). "Role of mobile phones in motor vehicle crashes resulting in hospital attendance: a case-crossover study". BMJ. 331 (7514): 428. doi:10.1136/bmj.38537.397512.55. PMC 1188107. PMID 16012176.
- ^ Laberge-Nadeau, Claire (September 2003). "Wireless telephones and the risk of road crashes". Accident Analysis & Prevention. 35 (5): 649–660. doi:10.1016/S0001-4575(02)00043-X. PMID 12850065.
- ^ Strayer, David; Drews, Frank; Crouch, Dennis (2003). "Fatal Distraction? A Comparison Of The Cell-Phone Driver And The Drunk Driver" (PDF). University of Utah Department of Psychology. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 11, 2009. Retrieved June 27, 2009.
- ^ Jeffrey K. Caird; et al. (October 25, 2004). "Effects of Cellular Telephones on Driving Behaviour and Crash Risk: Results of Meta-Analysis" (PDF). Ama.ab.ca. CAA Foundation for Traffic Safety. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 16, 2008.
- ^ Horrey, William; Christopher Wickens (Spring 2006). "Examining the Impact of Cell Phone Conversations on Driving Using Meta-Analytic Techniques" (PDF). Human Factors. 38 (1). Human Factors and Ergonomics Society: 196–205. doi:10.1518/001872006776412135. PMID 16696268. S2CID 3918855. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 25, 2009. Retrieved June 27, 2009.
- Domain, Public. "Text Messaging Law Effective January 1, 2009 Cellular Phone Laws Effective July 1, 2008". California Department of Motor Vehicles. California, USA: State of California. Archived from the original on August 7, 2013. Retrieved August 19, 2013.
- videos about California cellular phone laws; with caption
- David Crundall; Manpreet Bains; Peter Chapman; Geoffrey Underwood (2005). "Regulating conversation during driving: a problem for mobile telephones?" (PDF). Transportation Research Part F: Traffic Psychology and Behaviour. 8F (3): 197–211. Bibcode:2005TRPF....8..197C. doi:10.1016/j.trf.2005.01.003. S2CID 143502056. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 16, 2007.
- "Europe closer to allowing in-flight cellphone use". Engadget. October 18, 2007. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Clark, Amy (April 3, 2007). "FCC Says No To Cell Phones On Planes". CBS News. Retrieved December 9, 2017.
- Mobile Phones and Service Stations: Rumour, Risk and Precaution, by Adam Burgess (2007) Diogenes 213 54: 1
- "Communication Towers and the Fish and Wildlife Service". U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Archived from the original on August 5, 2007. Retrieved September 26, 2007.
- Lean, Geoffrey; Shawcross, Harriet (April 15, 2007). "Are mobile phones wiping out our bees?". The Independent. UK. Archived from the original on July 6, 2008. Retrieved May 12, 2010.
- Eric Sylvers (April 22, 2007). "Wireless: Case of the disappearing bees creates a buzz about cellphones". International Herald Tribune.
- Chloe Johnson (April 22, 2007). "Researchers: Often-cited study doesn't relate to bee colony collapse". Foster's Online.
- "Study: Cell Phone Waste Harmful". Wired. Associated Press. May 7, 2002. Retrieved July 11, 2011.
- Amy Gu, "Mainland mobile services to be cheaper", South China Morning Post, December 18, 2006, Page A1.
- OECD.org
- REGULATORY AND MARKET ENVIRONMENT
Further reading
- Chen, Adrian, "The Confidence Game: How Silicon Valley broke the economy", The Nation, vol. 309, no. 11 (4 November 2019), pp. 27–30. The multifarious abuses perpetrated by individuals, organizations, corporations, and governments, using the Internet and mobile telephony, prompt Adrian Chen to muse whether "a technical complex born... of Cold War militarism and mainstreamed in a free-market frenzy might not be fundamentally always at odds with human flourishing." (p. 30.)
| Mobile phones | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile networks, protocols |
| ||||||
| General operation | |||||||
| Mobile devices |
| ||||||
| Mobile specific software |
| ||||||
| Culture | |||||||
| Environment and health | |||||||
| Law | |||||||
| Cellular network standards | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| List of mobile phone generations | |||||||||
| 0G radio telephones (1946) | |||||||||
| 1G (1979) |
| ||||||||
| 2G (1991) |
| ||||||||
| 2G transitional (2.5G, 2.75G, 2.9G) |
| ||||||||
| 3G (1998) IMT-2000 (2001) |
| ||||||||
| 3G transitional (3.5G, 3.75G, 3.9G) |
| ||||||||
| 4G (2009) IMT Advanced (2013) |
| ||||||||
| 5G (2018) IMT-2020 (2021) |
| ||||||||
| Related articles | |||||||||