| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Chemical polarity" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry.
Polar molecules interact through dipole-dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points.
Polarity of bonds

 In a molecule of hydrogen fluoride (HF), the more electronegative atom (fluorine) is shown in yellow. Because the electrons spend more time by the fluorine atom in the H−F bond, the red represents partially negatively charged regions, while blue represents partially positively charged regions.
In a molecule of hydrogen fluoride (HF), the more electronegative atom (fluorine) is shown in yellow. Because the electrons spend more time by the fluorine atom in the H−F bond, the red represents partially negatively charged regions, while blue represents partially positively charged regions.
Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativities – such as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogen – exert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline earth metals. In a bond, this leads to unequal sharing of electrons between the atoms, as electrons will be drawn closer to the atom with the higher electronegativity.
Because electrons have a negative charge, the unequal sharing of electrons within a bond leads to the formation of an electric dipole: a separation of positive and negative electric charge. Because the amount of charge separated in such dipoles is usually smaller than a fundamental charge, they are called partial charges, denoted as δ+ (delta plus) and δ− (delta minus). These symbols were introduced by Sir Christopher Ingold and Edith Hilda (Usherwood) Ingold in 1926. The bond dipole moment is calculated by multiplying the amount of charge separated and the distance between the charges.
These dipoles within molecules can interact with dipoles in other molecules, creating dipole-dipole intermolecular forces.
Classification
Bonds can fall between one of two extremes – completely nonpolar or completely polar. A completely nonpolar bond occurs when the electronegativities are identical and therefore possess a difference of zero. A completely polar bond is more correctly called an ionic bond, and occurs when the difference between electronegativities is large enough that one atom actually takes an electron from the other. The terms "polar" and "nonpolar" are usually applied to covalent bonds, that is, bonds where the polarity is not complete. To determine the polarity of a covalent bond using numerical means, the difference between the electronegativity of the atoms is used.
Bond polarity is typically divided into three groups that are loosely based on the difference in electronegativity between the two bonded atoms. According to the Pauling scale:
- Nonpolar bonds generally occur when the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms is less than 0.5
- Polar bonds generally occur when the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms is roughly between 0.5 and 2.0
- Ionic bonds generally occur when the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms is greater than 2.0
Pauling based this classification scheme on the partial ionic character of a bond, which is an approximate function of the difference in electronegativity between the two bonded atoms. He estimated that a difference of 1.7 corresponds to 50% ionic character, so that a greater difference corresponds to a bond which is predominantly ionic.
As a quantum-mechanical description, Pauling proposed that the wave function for a polar molecule AB is a linear combination of wave functions for covalent and ionic molecules: ψ = aψ(A:B) + bψ(AB). The amount of covalent and ionic character depends on the values of the squared coefficients a and b.
Bond dipole moments

The bond dipole moment uses the idea of electric dipole moment to measure the polarity of a chemical bond within a molecule. It occurs whenever there is a separation of positive and negative charges.
The bond dipole μ is given by:
- .
The bond dipole is modeled as δ — δ with a distance d between the partial charges δ and δ. It is a vector, parallel to the bond axis, pointing from minus to plus, as is conventional for electric dipole moment vectors.
Chemists often draw the vector pointing from plus to minus. This vector can be physically interpreted as the movement undergone by electrons when the two atoms are placed a distance d apart and allowed to interact, the electrons will move from their free state positions to be localised more around the more electronegative atom.
The SI unit for electric dipole moment is the coulomb–meter. This is too large to be practical on the molecular scale. Bond dipole moments are commonly measured in debyes, represented by the symbol D, which is obtained by measuring the charge in units of 10 statcoulomb and the distance d in Angstroms. Based on the conversion factor of 10 statcoulomb being 0.208 units of elementary charge, so 1.0 debye results from an electron and a proton separated by 0.208 Å. A useful conversion factor is 1 D = 3.335 64×10 C m.
For diatomic molecules there is only one (single or multiple) bond so the bond dipole moment is the molecular dipole moment, with typical values in the range of 0 to 11 D. At one extreme, a symmetrical molecule such as bromine, Br
2, has zero dipole moment, while near the other extreme, gas phase potassium bromide, KBr, which is highly ionic, has a dipole moment of 10.41 D.
For polyatomic molecules, there is more than one bond. The total molecular dipole moment may be approximated as the vector sum of the individual bond dipole moments. Often bond dipoles are obtained by the reverse process: a known total dipole of a molecule can be decomposed into bond dipoles. This is done to transfer bond dipole moments to molecules that have the same bonds, but for which the total dipole moment is not yet known. The vector sum of the transferred bond dipoles gives an estimate for the total (unknown) dipole of the molecule.
Polarity of molecules
See also: Dipole § Molecular dipolesA molecule is composed of one or more chemical bonds between molecular orbitals of different atoms. A molecule may be polar either as a result of polar bonds due to differences in electronegativity as described above, or as a result of an asymmetric arrangement of nonpolar covalent bonds and non-bonding pairs of electrons known as a full molecular orbital.
While the molecules can be described as "polar covalent", "nonpolar covalent", or "ionic", this is often a relative term, with one molecule simply being more polar or more nonpolar than another. However, the following properties are typical of such molecules.
Boiling point
When comparing a polar and nonpolar molecule with similar molar masses, the polar molecule in general has a higher boiling point, because the dipole–dipole interaction between polar molecules results in stronger intermolecular attractions. One common form of polar interaction is the hydrogen bond, which is also known as the H-bond. For example, water forms H-bonds and has a molar mass M = 18 and a boiling point of +100 °C, compared to nonpolar methane with M = 16 and a boiling point of –161 °C.
Solubility
Due to the polar nature of the water molecule itself, other polar molecules are generally able to dissolve in water. Most nonpolar molecules are water-insoluble (hydrophobic) at room temperature. Many nonpolar organic solvents, such as turpentine, are able to dissolve nonpolar substances.
Surface tension
Polar compounds tend to have higher surface tension than nonpolar compounds.
Capillary action
Polar liquids have a tendency to rise against gravity in a small diameter tube.
Viscosity
Polar liquids have a tendency to be more viscous than nonpolar liquids. For example, nonpolar hexane is much less viscous than polar water. However, molecule size is a much stronger factor on viscosity than polarity, where compounds with larger molecules are more viscous than compounds with smaller molecules. Thus, water (small polar molecules) is less viscous than hexadecane (large nonpolar molecules).
Examples
Polar molecules

A polar molecule has a net dipole as a result of the opposing charges (i.e. having partial positive and partial negative charges) from polar bonds arranged asymmetrically. Water (H2O) is an example of a polar molecule since it has a slight positive charge on one side and a slight negative charge on the other. The dipoles do not cancel out, resulting in a net dipole. The dipole moment of water depends on its state. In the gas phase the dipole moment is ≈ 1.86 debye (D), whereas liquid water (≈ 2.95 D) and ice (≈ 3.09 D) are higher due to differing hydrogen-bonded environments. Other examples include sugars (like sucrose), which have many polar oxygen–hydrogen (−OH) groups and are overall highly polar.
If the bond dipole moments of the molecule do not cancel, the molecule is polar. For example, the water molecule (H2O) contains two polar O−H bonds in a bent (nonlinear) geometry. The bond dipole moments do not cancel, so that the molecule forms a molecular dipole with its negative pole at the oxygen and its positive pole midway between the two hydrogen atoms. In the figure each bond joins the central O atom with a negative charge (red) to an H atom with a positive charge (blue).
The hydrogen fluoride, HF, molecule is polar by virtue of polar covalent bonds – in the covalent bond electrons are displaced toward the more electronegative fluorine atom.

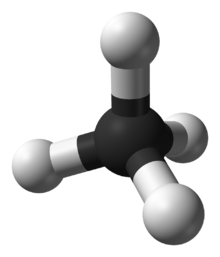
Ammonia, NH3, is a molecule whose three N−H bonds have only a slight polarity (toward the more electronegative nitrogen atom). The molecule has two lone electrons in an orbital that points towards the fourth apex of an approximately regular tetrahedron, as predicted by the VSEPR theory. This orbital is not participating in covalent bonding; it is electron-rich, which results in a powerful dipole across the whole ammonia molecule.

In ozone (O3) molecules, the two O−O bonds are nonpolar (there is no electronegativity difference between atoms of the same element). However, the distribution of other electrons is uneven – since the central atom has to share electrons with two other atoms, but each of the outer atoms has to share electrons with only one other atom, the central atom is more deprived of electrons than the others (the central atom has a formal charge of +1, while the outer atoms each have a formal charge of −1⁄2). Since the molecule has a bent geometry, the result is a dipole across the whole ozone molecule.
Nonpolar molecules
A molecule may be nonpolar either when there is an equal sharing of electrons between the two atoms of a diatomic molecule or because of the symmetrical arrangement of polar bonds in a more complex molecule. For example, boron trifluoride (BF3) has a trigonal planar arrangement of three polar bonds at 120°. This results in no overall dipole in the molecule.

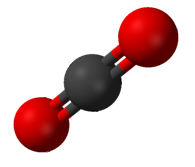
Carbon dioxide (CO2) has two polar C=O bonds, but the geometry of CO2 is linear so that the two bond dipole moments cancel and there is no net molecular dipole moment; the molecule is nonpolar.
Examples of household nonpolar compounds include fats, oil, and petrol/gasoline.
In the methane molecule (CH4) the four C−H bonds are arranged tetrahedrally around the carbon atom. Each bond has polarity (though not very strong). The bonds are arranged symmetrically so there is no overall dipole in the molecule. The diatomic oxygen molecule (O2) does not have polarity in the covalent bond because of equal electronegativity, hence there is no polarity in the molecule.
Amphiphilic molecules
Large molecules that have one end with polar groups attached and another end with nonpolar groups are described as amphiphiles or amphiphilic molecules. They are good surfactants and can aid in the formation of stable emulsions, or blends, of water and fats. Surfactants reduce the interfacial tension between oil and water by adsorbing at the liquid–liquid interface.
-
 This amphiphilic molecule has several polar groups (hydrophilic, water-loving) on the right side and a long nonpolar chain (lipophilic, fat-loving) at the left side. This gives it surfactant properties
This amphiphilic molecule has several polar groups (hydrophilic, water-loving) on the right side and a long nonpolar chain (lipophilic, fat-loving) at the left side. This gives it surfactant properties
-
 A micelle – the lipophilic ends of the surfactant molecules dissolve in the oil, while the hydrophilic charged ends remain outside in the water phase, shielding the rest of the hydrophobic micelle. In this way, the small oil droplet becomes water-soluble.
A micelle – the lipophilic ends of the surfactant molecules dissolve in the oil, while the hydrophilic charged ends remain outside in the water phase, shielding the rest of the hydrophobic micelle. In this way, the small oil droplet becomes water-soluble.
-
 Phospholipids are effective natural surfactants that have important biological functions
Phospholipids are effective natural surfactants that have important biological functions
-
 Cross section view of the structures that can be formed by phospholipids. They can form a micelle and are vital in forming cell membranes
Cross section view of the structures that can be formed by phospholipids. They can form a micelle and are vital in forming cell membranes
Predicting molecule polarity
| Formula | Description | Example | Name | Dipole moment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polar | AB | Linear molecules | CO | Carbon monoxide | 0.112 |
| HAx | Molecules with a single H | HF | Hydrogen fluoride | 1.86 | |
| AxOH | Molecules with an OH at one end | C2H5OH | Ethanol | 1.69 | |
| OxAy | Molecules with an O at one end | H2O | Water | 1.85 | |
| NxAy | Molecules with an N at one end | NH3 | Ammonia | 1.42 | |
| Nonpolar | A2 | Diatomic molecules of the same element | O2 | Dioxygen | 0.0 |
| CxAy | Most hydrocarbon compounds | C3H8 | Propane | 0.083 | |
| CxAy | Hydrocarbon with center of inversion | C4H10 | Butane | 0.0 |
Determining the point group is a useful way to predict polarity of a molecule. In general, a molecule will not possess dipole moment if the individual bond dipole moments of the molecule cancel each other out. This is because dipole moments are euclidean vector quantities with magnitude and direction, and a two equal vectors that oppose each other will cancel out.
Any molecule with a centre of inversion ("i") or a horizontal mirror plane ("σh") will not possess dipole moments. Likewise, a molecule with more than one Cn axis of rotation will not possess a dipole moment because dipole moments cannot lie in more than one dimension. As a consequence of that constraint, all molecules with dihedral symmetry (Dn) will not have a dipole moment because, by definition, D point groups have two or multiple Cn axes.
Since C1, Cs,C∞h Cn and Cnv point groups do not have a centre of inversion, horizontal mirror planes or multiple Cn axis, molecules in one of those point groups will have dipole moment.
Electrical deflection of water
Contrary to popular misconception, the electrical deflection of a stream of water from a charged object is not based on polarity. The deflection occurs because of electrically charged droplets in the stream, which the charged object induces. A stream of water can also be deflected in a uniform electrical field, which cannot exert force on polar molecules. Additionally, after a stream of water is grounded, it can no longer be deflected. Weak deflection is even possible for nonpolar liquids.
See also
- Chemical properties
- Colloid
- Detergent
- Electronegativities of the elements (data page)
- Polar point group
References
- Jensen, William B. (2009). "The Origin of the "Delta" Symbol for Fractional Charges". J. Chem. Educ. 86 (5): 545. Bibcode:2009JChEd..86..545J. doi:10.1021/ed086p545.
- Ingold, C. K.; Ingold, E. H. (1926). "The Nature of the Alternating Effect in Carbon Chains. Part V. A Discussion of Aromatic Substitution with Special Reference to Respective Roles of Polar and Nonpolar Dissociation; and a Further Study of the Relative Directive Efficiencies of Oxygen and Nitrogen". J. Chem. Soc. 129: 1310–1328. doi:10.1039/jr9262901310.
- Pauling, L. (1960). The Nature of the Chemical Bond (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 98–100. ISBN 0801403332.
- Pauling, L. (1960). The Nature of the Chemical Bond (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 66. ISBN 0801403332.
- Blaber, Mike (2018). "Dipole_Moments". Libre Texts. California State University.
- IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "electric dipole moment, p". doi:10.1351/goldbook.E01929
- Hovick, James W.; Poler, J. C. (2005). "Misconceptions in Sign Conventions: Flipping the Electric Dipole Moment". J. Chem. Educ. 82 (6): 889. Bibcode:2005JChEd..82..889H. doi:10.1021/ed082p889.
- Atkins, Peter; de Paula, Julio (2006). Physical Chemistry (8th ed.). W.H. Freeman. p. 620 (and inside front cover). ISBN 0-7167-8759-8.
- Physical chemistry 2nd Edition (1966) G.M. Barrow McGraw Hill
- Van Wachem, R.; De Leeuw, F. H.; Dymanus, A. (1967). "Dipole Moments of KF and KBr Measured by the Molecular-Beam Electric-Resonance Method". J. Chem. Phys. 47 (7): 2256. Bibcode:1967JChPh..47.2256V. doi:10.1063/1.1703301.
- Clough, Shepard A.; Beers, Yardley; Klein, Gerald P.; Rothman, Laurence S. (1 September 1973). "Dipole moment of water from Stark measurements of H2O, HDO, and D2O". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 59 (5): 2254–2259. Bibcode:1973JChPh..59.2254C. doi:10.1063/1.1680328.
- Gubskaya, Anna V.; Kusalik, Peter G. (27 August 2002). "The total molecular dipole moment for liquid water". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 117 (11): 5290–5302. Bibcode:2002JChPh.117.5290G. doi:10.1063/1.1501122.
- Batista, Enrique R.; Xantheas, Sotiris S.; Jónsson, Hannes (15 September 1998). "Molecular multipole moments of water molecules in ice Ih". The Journal of Chemical Physics. 109 (11): 4546–4551. Bibcode:1998JChPh.109.4546B. doi:10.1063/1.477058.
- Ziaei-Moayyed, Maryam; Goodman, Edward; Williams, Peter (2000-11-01). "Electrical Deflection of Polar Liquid Streams: A Misunderstood Demonstration". Journal of Chemical Education. 77 (11): 1520. Bibcode:2000JChEd..77.1520Z. doi:10.1021/ed077p1520. ISSN 0021-9584.
External links
| Chemical solutions | |
|---|---|
| Solution | |
| Concentration and related quantities | |
| Solubility | |
| Solvent | |
| Chemical bonds | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intramolecular (strong) |
|    | ||||||
| Intermolecular (weak) |
| |||||||
| Bond cleavage | ||||||||
| Electron counting rules | ||||||||
 .
. in units of 10
in units of 10