| Tobamovirus tabaci | |
|---|---|
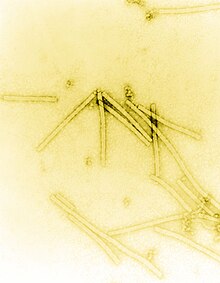
| |
| Transmission electron micrograph of TMV particles negative stained to enhance visibility at 160,000× magnification | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Kitrinoviricota |
| Class: | Alsuviricetes |
| Order: | Martellivirales |
| Family: | Virgaviridae |
| Genus: | Tobamovirus |
| Species: | Tobamovirus tabaci |
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus species in the genus Tobamovirus that infects a wide range of plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteristic patterns, such as "mosaic"-like mottling and discoloration on the leaves (hence the name). TMV was the first virus to be discovered. Although it was known from the late 19th century that a non-bacterial infectious disease was damaging tobacco crops, it was not until 1930 that the infectious agent was determined to be a virus. It is the first pathogen identified as a virus. The virus was crystallised by Wendell Meredith Stanley.
History
In 1886, Adolf Mayer first described the tobacco mosaic disease that could be transferred between plants, similar to bacterial infections. In 1892, Dmitri Ivanovsky gave the first concrete evidence for the existence of a non-bacterial infectious agent, showing that infected sap remained infectious even after filtering through the finest Chamberland filters. Later, in 1903, Ivanovsky published a paper describing abnormal crystal intracellular inclusions in the host cells of the affected tobacco plants and argued the connection between these inclusions and the infectious agent. However, Ivanovsky remained rather convinced, despite repeated failures to produce evidence, that the causal agent was an unculturable bacterium, too small to be retained on the employed Chamberland filters and to be detected in the light microscope. In 1898, Martinus Beijerinck independently replicated Ivanovsky's filtration experiments and then showed that the infectious agent was able to reproduce and multiply in the host cells of the tobacco plant. Beijerinck adopted the term of "virus" to indicate that the causal agent of tobacco mosaic disease was of non-bacterial nature. Tobacco mosaic virus was the first virus to be crystallized. It was achieved by Wendell Meredith Stanley in 1935 who also showed that TMV remains active even after crystallization. For his work, he was awarded 1/4 of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1946, even though it was later shown some of his conclusions (in particular, that the crystals were pure protein, and assembled by autocatalysis) were incorrect. The first electron microscopical images of TMV were made in 1939 by Gustav Kausche, Edgar Pfankuch and Helmut Ruska – the brother of Nobel Prize winner Ernst Ruska. In 1955, Heinz Fraenkel-Conrat and Robley Williams showed that purified TMV RNA and its capsid (coat) protein assemble by themselves to functional viruses, indicating that this is the most stable structure (the one with the lowest free energy). The crystallographer Rosalind Franklin worked for Stanley for about a month at Berkeley, and later designed and built a model of TMV for the 1958 World's Fair at Brussels. In 1958, she speculated that the virus was hollow, not solid, and hypothesized that the RNA of TMV is single-stranded. This conjecture was proven to be correct after her death and is now known to be the + strand. The investigations of tobacco mosaic disease and subsequent discovery of its viral nature were instrumental in the establishment of the general concepts of virology.
Structure

Tobacco mosaic virus has a rod-like appearance. Its capsid is made from 2130 molecules of coat protein and one molecule of genomic single strand RNA, 6400 bases long. The coat protein self-assembles into the rod-like helical structure (16.3 proteins per helix turn) around the RNA, which forms a hairpin loop structure (see the electron micrograph above). The structural organization of the virus gives stability. The protein monomer consists of 158 amino acids which are assembled into four main alpha-helices, which are joined by a prominent loop proximal to the axis of the virion. Virions are ~300 nm in length and ~18 nm in diameter. Negatively stained electron microphotographs show a distinct inner channel of radius ~2 nm. The RNA is located at a radius of ~4 nm and is protected from the action of cellular enzymes by the coat protein. X-ray fiber diffraction structure of the intact virus was studied based on an electron density map at 3.6 Å resolution. Inside the capsid helix, near the core, is the coiled RNA molecule, which is made up of 6,395 ±10 nucleotides. The structure of the virus plays an important role in the recognition of the viral DNA. This happens due to the formation of an obligatory intermediate produced from a protein allows the virus to recognize a specific RNA hairpin structure. The intermediate induces the nucleation of TMV self-assembly by binding with the hairpin structure.
Genome

The TMV genome consists of a 6.3–6.5 kbp single-stranded (ss) RNA. The 3’-terminus has a tRNA-like structure, and the 5’-terminus has a methylated nucleotide cap. (m7G5’pppG). The genome encodes 4 open reading frames (ORFs), two of which produce a single protein due to ribosomal readthrough of a leaky UAG stop codon. The 4 genes encode a replicase (with methyltransferase and RNA helicase domains), an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, a so-called movement protein (MP) and a capsid protein (CP). The coding sequence starts with the first reading frame, which is 69 nucleotides away from the 5' end of the RNA. The noncoding region at the 5' end can be varied in different individual virions, but there hasn't been any variation found between virions in the noncoding region at the 3' end.
Physicochemical properties
TMV is a thermostable virus. On a dried leaf, it can withstand up to 50 °C (120 degree Fahrenheit) for 30 minutes.
TMV has an index of refraction of about 1.57.
Disease cycle
TMV does not have a distinct overwintering structure. Rather, it will over-winter in infected tobacco stalks and leaves in the soil, on the surface of contaminated seed (TMV can even survive in contaminated tobacco products for many years, so smokers can accidentally transmit it by touch, although not in the smoke itself). With the direct contact with host plants through its vectors (normally insects such as aphids and leafhoppers), TMV will go through the infection process and then the replication process.
Infection and transmission
After its multiplication, it enters the neighboring cells through plasmodesmata. The infection does not spread through contact with insects, but instead spreads by direct contact to the neighboring cells. For its smooth entry, TMV produces a 30 kDa movement protein called P30 which enlarges the plasmodesmata. TMV most likely moves from cell-to-cell as a complex of the RNA, P30, and replicate proteins.
It can also spread through phloem for longer distance movement within the plant. Moreover, TMV can be transmitted from one plant to another by direct contact. Although TMV does not have defined transmission vectors, the virus can be easily transmitted from the infected hosts to the healthy plants by human handling.
Replication
Following entry into its host via mechanical inoculation, TMV uncoats itself to release its viral RNA strand. As uncoating occurs, the MetHel:Pol gene is translated to make the capping enzyme MetHel and the RNA Polymerase. Then the viral genome will further replicate to produce multiple mRNAs via a RNA intermediate primed by the tRNAHIS at the RNA 3' end. The resulting mRNAs encode several proteins, including the coat protein and an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), as well as the movement protein. Thus TMV can replicate its own genome.
After the coat protein and RNA genome of TMV have been synthesized, they spontaneously assemble into complete TMV virions in a highly organized process. The protomers come together to form disks or 'lockwashers' composed of two layers of protomers arranged in a helix. The helical capsid grows by the addition of protomers to the end of the rod. As the rod lengthens, the RNA passes through a channel in its center and forms a loop at the growing end. In this way the RNA can easily fit as a spiral into the interior of the helical capsid.
Host and symptoms


Like other plant pathogenic viruses, TMV has a very wide host range and has different effects depending on the host being infected. Tobacco mosaic virus has been known to cause a production loss for flue cured tobacco of up to two percent in North Carolina. It is known to infect members of nine plant families, and at least 125 individual species, including tobacco, tomato, pepper (all members of the Solanaceae), cucumbers, a number of ornamental flowers, and beans including Phaseolus vulgaris and Vigna unguiculata. There are many different strains. The first symptom of this virus disease is a light green coloration between the veins of young leaves. This is followed quickly by the development of a "mosaic" or mottled pattern of light and dark green areas in the leaves. Rugosity may also be seen where the infected plant leaves display small localized random wrinkles. These symptoms develop quickly and are more pronounced on younger leaves. Its infection does not result in plant death, but if infection occurs early in the season, plants are stunted. Lower leaves are subjected to "mosaic burn" especially during periods of hot and dry weather. In these cases, large dead areas develop in the leaves. This constitutes one of the most destructive phases of Tobacco mosaic virus infection. Infected leaves may be crinkled, puckered, or elongated. However, if TMV infects crops like grape and apple, it is almost symptomless. TMV is able to infect and complete its replication cycle in a plant pathogenic fungus, TMV is able to enter and replicate in cells of C. acutatum, C. clavatum, and C. theobromicola, which may not be an exception, although it has neither been found nor probably searched for in nature.
Environment
TMV is one of the most stable viruses and has a wide survival range. As long as the surrounding temperature remains below approximately 40 degrees Celsius, TMV can sustain its stable form. All it needs is a host to infect. If necessary, greenhouses and botanical gardens would provide the most favorable condition for TMV to spread out, due to the high population density of possible hosts and the constant temperature throughout the year. It also could be useful to culture TMV in vitro in sap because it can survive up to 3000 days.
Treatment and management
One of the common control methods for TMV is sanitation, which includes removing infected plants and washing hands in between each planting. Crop rotation should also be employed to avoid infected soil/seed beds for at least two years. As for any plant disease, looking for resistant strains against TMV may also be advised. Furthermore, the cross protection method can be administered, where the stronger strain of TMV infection is inhibited by infecting the host plant with a mild strain of TMV, similar to the effect of a vaccine.
In the past ten years, the application of genetic engineering on a host plant genome has been developed to allow the host plant to produce the TMV coat protein within their cells. It was hypothesized that the TMV genome will be re-coated rapidly upon entering the host cell, thus it prevents the initiation of TMV replication. Later it was found that the mechanism that protects the host from viral genome insertion is through gene silencing.
TMV is inhibited by a product of the myxomycete slime mold Physarum polycephalum. Both tobacco and the beans P. vulgaris and V. sinensis suffered almost no lesioning in vitro from TMV when treated with a P. polycephalum extract.
Research has shown that Bacillus spp. can be used to reduce the severity of symptoms from TMV in tobacco plants. In the study, treated tobacco plants had more growth and less build-up of TMV virions than tobacco plants that hadn't been treated.
A research has been conducted by H.Fraenkel-Conrat to show the influence of acetic acid on the Tobacco Mosaic Virus. According to the research, 67% acetic acid resulted as degradation of the virus.
Another possible source of prevention for TMV is the use of salicylic acid. A study completed by a research team at the University of Cambridge found that treating plants with salicylic acid reduced the amount of TMV viral RNAs and viral coat protein present in the tobacco plants. Their research showed that salicylic acid most likely was disrupting replication and transcription and more specifically, the RdRp complex.
A research was conducted and revealed that humans have antibodies against Tobacco Mosaic Virus.
Scientific and environmental impact

The large amount of literature about TMV and its choice for many pioneering investigations in structural biology (including X-ray diffraction and X-ray crystallography), virus assembly and disassembly, and so on, are fundamentally due to the large quantities that can be obtained, plus the fact that it does not infect animals. After growing several hundred infected tobacco plants in a greenhouse, followed by a few simple laboratory procedures, a scientist can produce several grams of the virus. In fact, tobacco mosaic virus is so proliferate that the inclusion bodies can be seen with only a light microscope.
James D. Watson, in his memoir The Double Helix, cites his x-ray investigation of TMV's helical structure as an important step in deducing the nature of the DNA molecule.
Applications
Plant viruses can be used to engineer viral vectors, tools commonly used by molecular biologists to deliver genetic material into plant cells; they are also sources of biomaterials and nanotechnology devices. Viral vectors based on TMV include those of the magnICON and TRBO plant expression technologies. Due to its cylindrical shape, high aspect ratio, self-assembling nature, and ability to incorporate metal coatings (nickel and cobalt) into its shell, TMV is an ideal candidate to be incorporated into battery electrodes. Addition of TMV to a battery electrode increases the reactive surface area by an order of magnitude, resulting in an increase in the battery's capacity by up to six times compared to a planar electrode geometry. The TMV-based vector also enabled C. acutatum to transiently express exogenous GFP up to six subcultures and for at least 2 mo after infection, without the need to develop transformation technology, RNAi can be expressed in the phytopathogenic fungus Colletotrichum acutatum by VIGS using a recombinant vector based on TMV in which the ORF of the gene encoding the green fluorescent protein (GFP) was transcribed in fungal cells from a duplicate of the TMV coat protein (CP) subgenomic mRNA promoter and demonstrated that the approach could be used to obtain foreign protein expression in fungi.
Notes
- Taxonomical species names were updated by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses in June 2024, with Tobacco mosaic virus being renamed Tobamovirus tabaci.
References
- "Taxon Details | ICTV". ictv.global. Retrieved 2024-10-02.
- Mayer A (1886). "Über die Mosaikkrankheit des Tabaks". Die Landwirtschaftliche Versuchs-stationen (in German). 32: 451–467. Translated into English in Johnson J, ed. (1942). "Concerning the mosaic disease of tobacco" (PDF). Phytopathological Classics. 7. St. Paul, Minnesota: American Phytopathological Society: 11–24.
- ^ Zaitlin M (1998). "The Discovery of the Causal Agent of the Tobacco Mosaic Disease" (PDF). In Kung SD, Yang SF (eds.). Discoveries in Plant Biology. Hong Kong: World Publishing Co. pp. 105–110. ISBN 978-981-02-1313-8.
- Iwanowski D (1892). "Über die Mosaikkrankheit der Tabakspflanze". Bulletin Scientifique Publié Par l'Académie Impériale des Sciences de Saint-Pétersbourg / Nouvelle Serie III (in German and Russian). 35: 67–70. Translated into English in Johnson J, ed. (1942). "Concerning the mosaic disease of the tobacco plant". Phytopathological Classics. 7. St. Paul, Minnesota: American Phytopathological Society: 27–30.
- Iwanowski D (1903). "Über die Mosaikkrankheit der Tabakspflanze". Zeitschrift für Pflanzenkrankheiten und Pflanzenschutz (in German). 13 (1): 1–41. JSTOR 43221892.
- Beijerinck MW (1898). "Über ein Contagium vivum fluidum als Ursache der Fleckenkrankheit der Tabaksblätter" (PDF). Verhandelingen der Koninklijke Akademie van Wetenschappen te Amsterdam (in German). 65: 1–22. Translated into English in Johnson J, ed. (1942). "Contagium vivum fluidum as the cause of spot disease in tobacco leaves". Phytopathological Classics. 7. St. Paul, Minnesota: American Phytopathological Society: 33–52.
- "Wendell M. Stanley – Biographical". nobelprize.org.
- "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1946". NobelPrize.org. Retrieved 2019-12-03.
- Kay LE (September 1986). "W. M. Stanley's crystallization of the tobacco mosaic virus, 1930–1940". Isis; an International Review Devoted to the History of Science and Its Cultural Influences. 77 (288): 450–72. doi:10.1086/354205. JSTOR 231608. PMID 3533840. S2CID 37003363.
- Kausche GA, Pfankuch E, Ruska H (May 1939). "Die Sichtbarmachung von pflanzlichem Virus im Übermikroskop". Naturwissenschaften. 27 (18): 292–9. Bibcode:1939NW.....27..292K. doi:10.1007/BF01493353. S2CID 206795712.
- Maddox B (2002). Rosalind Franklin, the Dark Lady of DNA. Harper Collins. ISBN 978-0-06-018407-0.
- Zaitlin M (1984). Brunt AA, Crabtree K, Dallwitz MJ, Gibbs AJ, Watson L, Zurcher EJ (eds.). "Tobacco mosaic tobamovirus". Plant Viruses Online: Descriptions and Lists from the VIDE Database. Archived from the original on 2009-10-01.
- Caspar DL (January 1964). Anfinsen CB, Anson ML, Edsall JT (eds.). "Assembly and Stability of the Tobacco Mosaic Virus Particle". Advances in Protein Chemistry. 18. Academic Press: 37–121. doi:10.1016/S0065-3233(08)60268-5. ISBN 9780120342181. PMID 14151998.
- Stryer L (1988). Biochemistry. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-1843-7.
- Klug A (March 1999). "The tobacco mosaic virus particle: structure and assembly". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 354 (1383): 531–5. doi:10.1098/rstb.1999.0404. PMC 1692534. PMID 10212932.
- PDB: 1VTM; Namba K, Stubbs G (March 1986). "Structure of tobacco mosaic virus at 3.6 A resolution: implications for assembly". Science. 231 (4744): 1401–6. doi:10.1126/science.3952490. PMID 3952490.
- Goelet P, Lomonossoff GP, Butler PJ, Akam ME, Gait MJ, Karn J (October 1982). "Nucleotide sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 79 (19): 5818–22. Bibcode:1982PNAS...79.5818G. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.19.5818. PMC 347001. PMID 6964389.
- "Sequence: V01408.1". European Nucleotide Archive. EMBL- EBI. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
International central site for archiving nucleic acid sequence. The reference standard in international science.
- Klug A (March 1999). "The tobacco mosaic virus particle: structure and assembly". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 354 (1383): 531–535. doi:10.1098/rstb.1999.0404. PMC 1692534. PMID 10212932.
- Butler PJ (March 1999). "Self-assembly of tobacco mosaic virus: the role of an intermediate aggregate in generating both specificity and speed". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 354 (1383): 537–550. doi:10.1098/rstb.1999.0405. PMC 1692540. PMID 10212933.
- "Tobamovirus". Expasy Viralzone. SIB Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics.
- Gergerich RC, Dolja VV (2006). "Introduction to Plant Viruses, the Invisible Foe". The Plant Health Instructor. doi:10.1094/PHI-I-2006-0414-01.
- ^ Goelet P, Lomonossoff GP, Butler PJ, Akam ME, Gait MJ, Karn J (October 1982). "Nucleotide sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 79 (19): 5818–5822. Bibcode:1982PNAS...79.5818G. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.19.5818. PMC 347001. PMID 6964389.
- Islam W, Qasim M, Ali N, Tayyab M, Chen S, Wang L (Jan 16, 2018). "Management of Tobacco Mosaic Virus through Natural Metabolites" (PDF). Records of Natural Products: 404.
- Ashkin A, Dziedzic JM (March 1987). "Optical trapping and manipulation of viruses and bacteria". Science. 235 (4795): 1517–20. Bibcode:1987Sci...235.1517A. doi:10.1126/science.3547653. PMID 3547653.
- "Is smoking harmful to plants?". OSU Extension Service. Ohio State University. 2018-05-02. Retrieved 2021-03-06.
- "Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV)". Penn State Extension. Penn State College of Agricultural Sciences. Retrieved 2021-03-06.
- ^ Creager, Angela N.H.; Scholthof, Karen-Beth G.; Citovsky, Vitaly; Scholthof, Herman B. (1999). "Tobacco Mosaic Virus: Pioneering Research for a Century". The Plant Cell. 11 (3): 301–308. doi:10.1105/tpc.11.3.301. PMC 1464663. PMID 10072391.
- Woolverton C, Willey J, Sherwood L (2008). Prescott's Microbiology (7th ed.). Boston: McGraw Hill Higher Education. pp. 464–5. ISBN 978-0-07-110231-5.
- Melton TA (2001). "Control of Tobacco Mosaic Virus on Flue-Cured Tobacco". North Carolina Cooperative Extension Service. Archived from the original on 2005-12-01. Retrieved 2009-02-21.
- Pfleger FL, Zeyen RJ. "Tomato-Tobacco Mosaic Virus Disease". University of Minnesota. Archived from the original on 2012-06-14.
- ^ Mayhew DE, Ford RE (1971). "An Inhibitor of Tobacco Mosaic Virus Produced by Physarum polycephalum". Phytopathology. 61 (6). American Phytopathological Society: 636. doi:10.1094/phyto-61-636. ISSN 0031-949X.
- ^ Mascia, Tiziana; Nigro, Franco; Abdallah, Alì; Ferrara, Massimo; De Stradis, Angelo; Faedda, Roberto; Palukaitis, Peter; Gallitelli, Donato (18 March 2014). "Gene silencing and gene expression in phytopathogenic fungi using a plant virus vector". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 111 (11): 4291–4296. Bibcode:2014PNAS..111.4291M. doi:10.1073/pnas.1315668111. PMC 3964105. PMID 24594602.
- Creager AN, Scholthof KB, Citovsky V, Scholthof HB (March 1999). "Tobacco mosaic virus. Pioneering research for a century". The Plant Cell. 11 (3): 301–308. doi:10.1105/tpc.11.3.301. PMC 1464663. PMID 10072391.
- Agrios G (2005). Plant Pathology (5th ed.). Burlington, MA: Elsevier Academic Press. p. 320. ISBN 978-0-12-044565-3.
- Wang S (2009-10-28). "Molecular Mechanism of Plant Growth Promotion and Induced Systemic Resistance to Tobacco Mosaic Virus by Bacillus spp". Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 19 (10): 1250–1258. doi:10.4014/jmb.0901.008. PMID 19884788.
- Fraenkel-Conrat H (August 1957). "Degradation of tobacco mosaic virus with acetic acid". Virology. 4 (1): 1–4. doi:10.1016/0042-6822(57)90038-7. ISSN 0042-6822. PMID 13456355.
- Chivasa S, Murphy AM, Naylor M, Carr JP (April 1997). "Salicylic Acid Interferes with Tobacco Mosaic Virus Replication via a Novel Salicylhydroxamic Acid-Sensitive Mechanism". The Plant Cell. 9 (4): 547–557. doi:10.1105/tpc.9.4.547. PMC 156938. PMID 12237364.
- Liu R, Vaishnav RA, Roberts AM, Friedland RP (2013). "Humans have antibodies against a plant virus: evidence from tobacco mosaic virus". PLOS ONE. 8 (4): e60621. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...860621L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060621. PMC 3615994. PMID 23573274.
- Rollinson, Shirley, personal communication
- Watson JD (2012-11-06). "chapters 16, 18". The Annotated and Illustrated Double Helix. Simon and Schuster. ISBN 978-1-4767-1549-0.
- Pasin F, Menzel W, Daròs JA (June 2019). "Harnessed viruses in the age of metagenomics and synthetic biology: an update on infectious clone assembly and biotechnologies of plant viruses". Plant Biotechnology Journal. 17 (6): 1010–1026. doi:10.1111/pbi.13084. PMC 6523588. PMID 30677208.
- ^ Abrahamian P, Hammond RW, Hammond J (June 2020). "Plant Virus-Derived Vectors: Applications in Agricultural and Medical Biotechnology". Annual Review of Virology. 7 (1): 513–535. doi:10.1146/annurev-virology-010720-054958. PMID 32520661. S2CID 219588089.
- Lindbo JA (December 2007). "TRBO: a high-efficiency tobacco mosaic virus RNA-based overexpression vector". Plant Physiology. 145 (4): 1232–40. doi:10.1104/pp.107.106377. PMC 2151719. PMID 17720752.
- ^ Gerasopoulos K, McCarthy M, Royston E, Culver JN, Ghodssi R (January 13–17, 2008). "Microbatteries with tobacco mosaic virus templated electrodes". 2008 IEEE 21st International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems. pp. 960–963. doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.2008.4443817. ISBN 978-1-4244-1792-6.
- Atanasova P, Rothenstein D, Schneider JJ, Hoffmann RC, Dilfer S, Eiben S, et al. (November 2011). "Virus-templated synthesis of ZnO nanostructures and formation of field-effect transistors". Advanced Materials. 23 (42): 4918–22. Bibcode:2011AdM....23.4918A. doi:10.1002/adma.201102900. PMID 21959928. S2CID 205242233.
Further reading
- Creager AN (2002). The life of a virus: tobacco mosaic virus as an experimental model, 1930–1965. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-12026-3.
- Flue-cured tobacco field manual. Winston-Salem, North Carolina: R.J. Reynolds Tobacco Company. 1995.
External links
- Description of plant viruses – TMV Archived 2007-09-26 at the Wayback Machine – contains information on symptoms, hosts species, purification etc.
- Further information
- Electron microscope image of TM
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Tobacco mosaic virus | |