| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
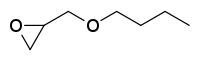
| Preferred IUPAC name 2-(Butoxymethyl)oxirane | |
| Other names
1,2-Epoxy-3-butoxypropane 2,3-Epoxypropyl butyl ether (Butoxymethyl)oxirane 1-Butoxy-2,3-epoxypropane | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.017.616 |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1993 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C7H14O2 |
| Molar mass | 130.187 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Odor | Irritating |
| Density | 0.91 g/cm |
| Boiling point | 164 °C; 327 °F; 437 K |
| Solubility in water | 2% (20 °C) |
| Vapor pressure | 3 mmHg (25 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 130 °F |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
| LD50 (median dose) | 260 mg/m (inhalation, mouse) 1030 ppm (inhalation, rat, 8 hours) |
| LC50 (median concentration) | >3500 ppm (mouse, 4 hr) 1030 ppm (rat, 8 hr) |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
| PEL (Permissible) | TWA 50 ppm (270 mg/m) |
| REL (Recommended) | 5.6 ppm (30 mg/m) |
| IDLH (Immediate danger) | 250 ppm |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
n-Butyl glycidyl ether is an industrial chemical used in adhesives, sealants, and as a paint or coating additive. It is principally used to reduce the viscosity of epoxy resin systems.
Synthesis
n-Butyl alcohol and epichlorohydrin react to form a halohydrin. This is followed by a caustic dehydrochlorination, to form n-butyl glycidyl ether.
Metabolism
n-Butyl glycidyl ether is metabolized renally to butoxyacetic acid, 3-butoxy-2-hydroxypropionic acid and 3-butoxy-2-acetylaminopropionic acid.
Safety
Exposure to n-butyl glycidyl ether through inhalation, eye contact, or skin exposure can cause a cough, sore throat, eye and skin redness, and pain. It is flammable and reacts with strong oxidants, strong bases, strong acids, and amines.
Uses
As an Epoxy modifier it is classed as an epoxy reactive diluent. It is also used to synthesize other molecules. The use of the diluent does effect mechanical properties and microstructure of epoxy resins. It has been used to simultaneously increase cryogenic strength, ductility and impact resistance of epoxy resins.
References
- ^ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0081". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Propane, 1-Butoxy-2,3-epoxy". CDC/NIOSH. 28 March 2018.
- ^ "{{{2}}}". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- Jagtap, Ameya Rajendra; More, Aarti (2022-08-01). "Developments in reactive diluents: a review". Polymer Bulletin. 79 (8): 5667–5708. doi:10.1007/s00289-021-03808-5. ISSN 1436-2449. S2CID 235678040.
- ^ CID 17049 from PubChem
- Eadsforth, C. V.; Hutson, D. H.; Logan, C. J.; Morrison, B. J. (1985). "The metabolism of n-butyl glycidyl ether in the rat and rabbit". Xenobiotica. 15 (7): 579–89. doi:10.3109/00498258509045887. PMID 4049898.
- International Chemical Safety Card 0115
- Monte, Salvatore J. (1998), Pritchard, Geoffrey (ed.), "Diluents and viscosity modifiers for epoxy resins", Plastics Additives: An A-Z reference, Polymer Science and Technology Series, vol. 1, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, pp. 211–216, doi:10.1007/978-94-011-5862-6_24, ISBN 978-94-011-5862-6, retrieved 2022-03-29
- Urata, Kouichi; Takaishi, Naotake (September 1994). "The alkyl glycidyl ether as synthetic building blocks". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 71 (9): 1027–1033. doi:10.1007/BF02542274. S2CID 96776835.
- Pastarnokienė, Liepa; Jonikaitė-Švėgždienė, Jūratė; Lapinskaitė, Neringa; Kulbokaitė, Rūta; Bočkuvienė, Alma; Kochanė, Tatjana; Makuška, Ričardas (2023-07-01). "The effect of reactive diluents on curing of epoxy resins and properties of the cured epoxy coatings". Journal of Coatings Technology and Research. 20 (4): 1207–1221. doi:10.1007/s11998-022-00737-4. ISSN 1935-3804. S2CID 256749849.
- Khalina, Morteza; Beheshty, Mohammad Hosain; Salimi, Ali (2019-08-01). "The effect of reactive diluent on mechanical properties and microstructure of epoxy resins". Polymer Bulletin. 76 (8): 3905–3927. doi:10.1007/s00289-018-2577-6. ISSN 1436-2449. S2CID 105389177.
- Chen, Zhen-Kun; Yang, Guo; Yang, Jiao-Ping; Fu, Shao-Yun; Ye, Lin; Huang, Yong-Gang (2009-02-23). "Simultaneously increasing cryogenic strength, ductility and impact resistance of epoxy resins modified by n-butyl glycidyl ether". Polymer. 50 (5): 1316–1323. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2008.12.048. ISSN 0032-3861.
Further reading
- Epoxy resin technology. Paul F. Bruins, Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn. New York: Interscience Publishers. 1968. ISBN 0-470-11390-1. OCLC 182890.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - Flick, Ernest W. (1993). Epoxy resins, curing agents, compounds, and modifiers : an industrial guide. Park Ridge, NJ. ISBN 978-0-8155-1708-5. OCLC 915134542.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Lee, Henry (1967). Handbook of epoxy resins. Kris Neville ( ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-036997-6. OCLC 311631322.
| Ethers of glycidol | |
|---|---|
| Mono-epoxy | |
| Di-epoxy | |
| Tri-epoxy | |