| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Nano-" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Nano (symbol n) is a unit prefix meaning one billionth. Used primarily with the metric system, this prefix denotes a factor of 10 or 0.000000001. It is frequently encountered in science and electronics for prefixing units of time and length.
- Examples
- Three gold atoms lined up are about one nanometer (nm) long.
- If a toy marble were scaled down to one nanometer wide, Earth would scale to about 1 meter (3.3 ft) wide.
- One nanosecond (ns) is about the time required for light to travel 30 cm in air, or 20 cm in an optical fiber.
- One nanometer per second (nm/s) is approximately the speed that a fingernail grows.
The prefix derives from the Greek νᾶνος (Latin nanus), meaning "dwarf". The General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) officially endorsed the usage of nano as a standard prefix in 1960.
When used as a prefix for something other than a unit of measure (as for example in words like "nanoscience"), nano refers to nanotechnology, or means "on a scale of nanometres" (nanoscale).
| Prefix | Base 10 | Decimal | Adoption | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Symbol | |||
| quetta | Q | 10 | 1000000000000000000000000000000 | 2022 |
| ronna | R | 10 | 1000000000000000000000000000 | |
| yotta | Y | 10 | 1000000000000000000000000 | 1991 |
| zetta | Z | 10 | 1000000000000000000000 | |
| exa | E | 10 | 1000000000000000000 | 1975 |
| peta | P | 10 | 1000000000000000 | |
| tera | T | 10 | 1000000000000 | 1960 |
| giga | G | 10 | 1000000000 | |
| mega | M | 10 | 1000000 | 1873 |
| kilo | k | 10 | 1000 | 1795 |
| hecto | h | 10 | 100 | |
| deca | da | 10 | 10 | |
| — | — | 10 | 1 | — |
| deci | d | 10 | 0.1 | 1795 |
| centi | c | 10 | 0.01 | |
| milli | m | 10 | 0.001 | |
| micro | μ | 10 | 0.000001 | 1873 |
| nano | n | 10 | 0.000000001 | 1960 |
| pico | p | 10 | 0.000000000001 | |
| femto | f | 10 | 0.000000000000001 | 1964 |
| atto | a | 10 | 0.000000000000000001 | |
| zepto | z | 10 | 0.000000000000000000001 | 1991 |
| yocto | y | 10 | 0.000000000000000000000001 | |
| ronto | r | 10 | 0.000000000000000000000000001 | 2022 |
| quecto | q | 10 | 0.000000000000000000000000000001 | |
| ||||
Nanometre
This section is an excerpt from Nanometre.
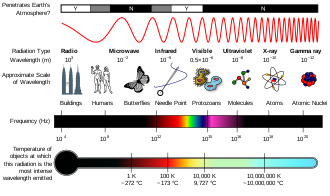
X-rays have a wavelength ranging from the size of 0.01 nm to 10 nm.
Human fingernails grow at approximately one nanometer per second.
Nanosecond
This section is an excerpt from Nanosecond.A nanosecond (ns) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one billionth of a second, that is, 1/1000000000 of a second, or 10 seconds.
The term combines the SI prefix nano- indicating a 1 billionth submultiple of an SI unit (e.g. nanogram, nanometre, etc.) and second, the primary unit of time in the SI.
A nanosecond is to one second, as one second is to approximately 31.69 years.
A nanosecond is equal to 1000 picoseconds or 1/1000 microsecond. Time units ranging between 10 and 10 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of nanoseconds.
Time units of this granularity are commonly found in telecommunications, pulsed lasers, and related aspects of electronics.See also
References
- "Size of the Nanoscale". National Nanotechnology Initiative. Retrieved 2020-05-14.
- ^ "On the extension of the range of SI prefixes". 18 November 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2023.
- "Metric (SI) Prefixes". NIST.
- "Examples of Nanoscale Objects". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 2024-03-16.