



Natural gas was the United States' largest source of energy production in 2016, representing 33 percent of all energy produced in the country. Natural gas has been the largest source of electrical generation in the United States since July 2015.
In 2012, the United States produced 25.3 trillion cubic feet of marketed natural gas, with an average wellhead value of $2.66 per thousand cubic feet, for a total wellhead value of $67.3 billion. In 2013, the country produced 30.0 trillion cubic feet (TCF) of marketed gas. With 7,545 billion cubic feet (BCF), the leading gas-producing area in the United States in 2013 was Texas, followed by Pennsylvania (3,259 BCF), and Louisiana (2,407 BCF). US natural gas production achieved new record highs for each year from 2011 through 2015. Marketed natural gas production in 2015 was 28.8 trillion cubic feet, a 5.4 percent increase over 2014, and a 52 percent increase over the production of 18.9 trillion cubic feet in 2005. The natural gas industry includes exploration for, production, processing, transportation, storage, and marketing of natural gas and natural gas liquids. The exploration for and production of natural gas and petroleum form a single industry, and many wells produce both oil and gas.
Because of the greater supply, consumer prices for natural gas are significantly lower in the United States than in Europe and Japan. The low price of natural gas, together with its smaller carbon footprint compared to coal, has encouraged a rapid growth in electricity generated from natural gas.
Between 2005 and 2014, US production of natural gas liquids (NGLs) increased 70 percent, from 1.74 million barrels per day in 2005 to 2.96 million barrels per day in 2014.
Although the United States leads the world in natural gas production, it is only fifth in proved reserves of natural gas, behind Russia, Iran, Qatar, and Turkmenistan.
Industry structure
Main article: Petroleum in the United StatesThe United States oil and gas industry is often informally divided into "upstream" (exploration and production), "midstream" (transportation and refining), and "downstream" (distribution and marketing). Petroleum and natural gas share a common upstream (exploration and production) sector, but the midstream and downstream sectors are largely separate. All large oil companies in the US produce both oil and gas. However, the relative amounts of oil and gas produced vary greatly. Of the top ten natural gas-producing companies in the US 2009, only three (BP, ConocoPhiillips, and XTO) were also among the top ten oil producers.
Top natural gas producers in the United States, 2009
| Rank | Company | Billion cubic ft./Year |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BP | 907 |
| 2 | XTO Energy | 855 |
| 3 | ConocoPhillips | 850 |
| 4 | Chesapeake Energy | 835 |
| 5 | Anadarko Petroleum | 817 |
| 6 | Devon Energy | 743 |
| 7 | Encana | 590 |
| 8 | ExxonMobil | 566 |
| 9 | Williams Companies | 435 |
| 10 | EOG Resources | 422 |
| Annual owned production, 2009. Source: | ||
In 2009, the production owned by the top ten companies was 31% of total US natural gas production.
Natural gas exploration
In 2010, the industry drilled and completed 16,696 wells primarily for gas, slightly more than the number of wells drilled primarily for oil (15,753). Many wells produced both oil and gas, and oil wells produced 18 percent of US gas production in 2013. Of the gas wells, 1,105 were exploratory wells, and 15,591 development wells.
The number of actively drilling gas rigs was once regarded as a reliable leading indicator of near-future gas production. However, the average number of active gas drill rigs has fallen each year for four straight years from 2010 (942 rigs) to 2014 (332 rigs), a drop of 65 percent, even while gas production rose each year for the same period, from 21.3 trillion cubic feet (TCF) in 2010 to 25.7 TCF in 2014, an increase of 21 percent. Remaining proved reserves increased overall, from 301 TCF in 2013 to 338 TCF in 2013 (the last year for which reserves are available), an increase of 11 percent. The rise in gas production despite fewer rigs drilling has been explained by the greater efficiency in drilling, and the greater productivity of shale gas wells.
Natural gas production
| Graphs are unavailable due to technical issues. Updates on reimplementing the Graph extension, which will be known as the Chart extension, can be found on Phabricator and on MediaWiki.org. |
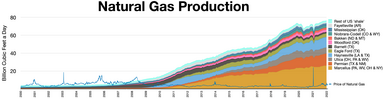
| Rank | Field | State | Discovery Year | Billion cubic ft./Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Marcellus Shale | Pennsylvania and West Virginia | 2008 | 2,836 |
| 2 | Newark East Barnett Shale | Texas | 1981 | 1,952 |
| 3 | Haynesville Shale | Louisiana and Texas | 2008 | 1,426 |
| 4 | Eagle Ford Formation | Texas | 1962 | 1,112 |
| 5 | Fayetteville Shale | Arkansas | 2005 | 1,025 |
| 6 | San Juan Basin | New Mexico and Colorado | 1927 | 1,025 |
| 7 | Carthage | Texas | 1936 | 653 |
| 8 | Pinedale Gas Field | Wyoming | 1955 | 568 |
| 9 | Spraberry | Texas | 1949 | 307 |
| 10 | Wattenberg Gas Field | Colorado | 1970 | 305 |
The U.S. Energy Information Administration publishes annual natural gas production data in aggregate by well type: traditional oil wells and gas wells, coalbed methane wells, and shale gas wells.

Oil and gas
See also: Petroleum in the United StatesMost oil fields produce some gas, and vice versa, but the ratio of oil and gas varies considerably. In fields developed to produce oil, the natural gas is in a raw form called associated gas. Some fields, called "dry gas" fields, produce only gas. Of the top ten gas-producing fields in the US, only one, the Eagle Ford, is also among the top ten oil fields. The number of wells classified as traditional gas wells has been declining in recent years as they are replaced by shale gas wells.
The associated gas from oil wells is utilized similar to other sources of natural gas, or may be re-injected for storage and to enhance oil production. In some cases the well operator may designate the gas as a waste product, and large amounts of gas may be intentionally vented or flared depending on local regulations.
Coalbed methane
Main article: Coalbed methane in the United StatesCoalbed methane production in the US peaked at 1.97 TCF in 2008, when it made up 7.8 percent of US gas production. By 2018, coalbed methane production had declined to 0.95 TCF.
Shale gas
Main article: Shale gas in the United StatesSince 2000, shale gas has become a key source of natural gas in the US. Production rose more than tenfold from 2007 to 2018, when shale gas contributed 23.6 TCF, 63 percent of US gas production, and was still increasing.
Gas prices



In February 2003 there was a similar spike in natural gas prices because of shortages.
The most commonly quoted producer price for natural gas is the Louisiana-based Henry Hub price, which is futures-traded on NYMEX.
A barrel of oil releases about 5.8 million BTU when burned, so that 5.8 MCF of gas (at the standard one thousand BTU per cubic foot) releases about the same energy as a barrel of oil. Sometimes gas containing 5.8 million BTU is defined as a "barrel of oil equivalent for energy calculation purposes. When describing reserves or production, however, the oil and gas industry more commonly uses the rounded number of 6 MCF of gas (or 6 million BTU in the natural gas) as equal to one barrel of oil equivalent.
Since the price of natural gas was deregulated in the 1990s, its price has tended to parallel that of oil, with oil usually at a premium on a BTU basis. But starting in the late 2000s, an abundance of natural gas in North America has caused the price of a unit of energy from gas to be much lower than the price of energy from oil.
Natural gas pipelines
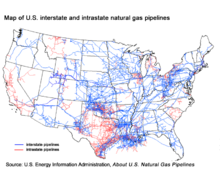
When oil and natural gas are brought to the surface, they are usually separated at the wellhead, after which the oil and the gas are treated separately. Gas flows through a gathering system into a pipeline to a gas processing plant. As of 2014, there were 189,000 miles of interstate natural gas pipelines in the United States
Gas processing


Natural gas has a variety of chemical constituents that must be removed or diluted with other gas to achieve consistent pipeline quality. Pipeline gas specifications vary from line to line, but generally the gas must contain no appreciable hydrogen sulfide (which is toxic), less than a few percent carbon dioxide (carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which is corrosive to iron and steel pipe), and a British thermal unit (BTU) content of 900 or more. Natural gas delivered to consumers generally has a BTU content of about 1020 to 1050 per standard cubic foot, slightly higher than that of pure methane (1010 BTU).
Natural gas liquids
Natural gas is composed primarily of methane, but often contains longer-chain hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbon compounds from hexane (each molecule of which is a simple chain containing six carbon atoms, hence called C6) and heavier generally separate out ("condense") from the gas at the wellhead; this mixture is called condensate, and is usually reported as oil production, and sold to refineries the same as oil. The C2 through C5 hydrocarbons (ethane, propane, butane, and pentane) are known as natural gas liquids (NGLs), and remain in gaseous form until they are extracted at a gas processing plant. The division between the two classes is not perfect: some hexane, and heptane remain in the gas to be separated out as NGLs, while some butane and pentane, may separate out with the condensate.
Natural gas which contains NGLs is called "wet gas." Gas which naturally contains no NGLs, or gas from which the NGLs have been removed, is called "dry gas."
Natural gas liquids are used either for fuel (sold as propane, or liquid petroleum gas (LPG), or for feedstock to the petrochemical industry.
The United States has been the world's top producer of NGLs since 2010, and is far above second place Saudi Arabia, which produced 1.82 million barrels per day in 2015.
Increased production of NGLs since 2000 has lowered the price of NGLs in the North American market, leading to a surge in construction and expansion of petrochemical plants to convert ethane and propane into ethylene and propylene, which are used to make plastics. The United States has the world's largest ethylene-manufacturing capacity, 28.4 million tons per year in 2015, with projects to add another 7.6 million tons from 2015 through 2017. As of 2015, the reduction in NGL prices had turned North America from one of the high-cost places to manufacture petrochemical, into the lowest-cost area outside the Middle East.
Other byproducts
Main articles: Helium production in the United States and Sulfur production in the United StatesSome natural gas contains enough helium to be extracted as a byproduct.
Sulfur, which must be removed from natural gas for safety, aesthetic, and environmental reasons, is recovered and sold as a byproduct. In 2013, natural gas processing plants recovered 1.02 million metric tons of sulfur, which was 12 percent of US supply of elemental sulfur (the remaining sulfur production came from oil refineries).
Gas storage
See also: Natural gas storage and Strategic natural gas reserve


Consumption of natural gas in the US is strongly seasonal, higher in the winter than the summer by between 50% and 90%, depending on severity of the winter. To make larger volumes of gas available in the winter, companies have established underground gas storage facilities. There are three types of natural gas storage units currently in service in the US: salt domes, depleted gas reservoirs, and deep aquifers.
The largest volume held in storage was 8.29 trillion cubic feet in October 2012. This was equivalent to 26 percent of the total US production in 2014. The small mid-summer increase shown on the consumption graph is due to increased gas use for electrical power in the summer. Unlike residential, commercial, and industrial use, all of which are higher in winter, electrical power generation uses more gas in the summer.
Natural gas marketing
From the processing plant, natural gas is sold mostly to gas utility companies. In 2014, 46% of the marketed gas was used by commercial and industrial users, 33% by electrical power generators, and 21% by residential consumers.
Natural gas electricity generation
Main article: Natural gas power plantSince 2009, electricity generation has been the largest use of natural gas in the US. Electricity generated by natural gas has been by far the fastest-growing source of electricity in the US since the 1990s. Natural gas became the second-largest source of US electricity in 2006, when it surpassed nuclear power. In late 2015, natural gas surpassed coal as the largest source of electricity generated in the United States.
In the decade 2005 to 2015, electricity generated by natural gas increased by 574 billion kilowatt-hours, more than triple the increase of the second-fastest-growing source, wind energy, which increased 173 billion kilowatt-hours over the same period. Natural gas-generated electricity increased its share of total US electricity from 18.8 percent in 2005, to 32.6 percent in 2015. The increase in gas-generated electricity was mostly at the expense of coal power, which fell from 49.6 percent of US electricity in 2005, to 33.2 percent in 2015. Natural gas surpassed coal as the number one generator of US electricity in late 2015. During the 12-month period through August 2016, natural gas generated 34.5 percent of US electricity, versus 29.8 percent for coal.
Unlike the other sectors of natural gas consumption, the electrical power industry uses more natural gas in the summer, when electricity demand is increased by air conditioning, and when natural gas prices are at seasonal lows.
The increased use of natural gas for electricity is driven by three factors. First, pressure on utilities to decrease greenhouse gas emissions has favored the substitution of coal generation by natural gas generation, which, according to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, and the IPCC, has significantly less life-cycle GHG emissions than coal-powered electricity. Second, gas power plants are able to ramp up and down quickly, making them well suited to complement intermittent power sources such as wind and solar. Third, since late 2008, the price of natural gas has been relatively cheap on the North American market, especially compared to oil. Electricity from oil-powered generators in the US declined 81 percent from 2005 to 2014.
The states which use the most natural gas for electricity production are, in descending order, Texas, Florida, California, and New York.
| Year | Total | % of total | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | 639,129 | 17.1% | 42,389 | 37,967 | 44,364 | 45,843 | 50,934 | 57,603 | 73,030 | 78,410 | 60,181 | 56,376 | 44,491 | 47,541 |
| 2002 | 691,006 | 17.91% | 48,413 | 44,308 | 51,214 | 49,146 | 50,275 | 65,631 | 83,917 | 84,477 | 68,161 | 54,201 | 45,161 | 46,100 |
| 2003 | 649,908 | 16.74% | 50,176 | 43,547 | 46,699 | 45,195 | 49,373 | 54,453 | 76,938 | 83,250 | 59,090 | 51,824 | 45,328 | 44,035 |
| 2004 | 710,100 | 17.88% | 48,253 | 50,320 | 49,801 | 51,822 | 62,022 | 64,686 | 79,290 | 77,821 | 67,854 | 57,229 | 49,693 | 51,310 |
| 2005 | 760,960 | 18.76% | 51,338 | 44,913 | 51,897 | 52,016 | 54,826 | 75,635 | 96,819 | 100,787 | 73,355 | 55,941 | 49,440 | 53,993 |
| 2006 | 816,441 | 20.09% | 43,807 | 47,409 | 54,922 | 56,091 | 65,586 | 81,060 | 108,094 | 106,592 | 72,673 | 70,640 | 53,440 | 56,128 |
| 2007 | 896,590 | 21.57% | 61,475 | 57,622 | 56,204 | 60,153 | 66,470 | 81,511 | 97,483 | 121,338 | 88,532 | 78,358 | 60,637 | 66,808 |
| 2008 | 882,981 | 21.43% | 72,600 | 60,042 | 62,171 | 63,046 | 62,270 | 84,620 | 100,321 | 99,673 | 79,136 | 73,283 | 61,454 | 64,364 |
| 2009 | 920,979 | 23.31% | 66,390 | 62,139 | 68,203 | 61,159 | 68,146 | 84,205 | 101,894 | 109,240 | 92,127 | 72,603 | 63,285 | 71,590 |
| 2010 | 987,697 | 23.94% | 74,173 | 66,198 | 63,431 | 64,644 | 73,665 | 92,268 | 114,624 | 121,151 | 93,004 | 77,738 | 69,227 | 77,573 |
| 2011 | 1,013,689 | 24.72% | 74,254 | 65,924 | 65,947 | 70,029 | 75,243 | 90,691 | 119,624 | 119,856 | 91,739 | 78,819 | 75,441 | 86,122 |
| 2012 | 1,225,894 | 30.29% | 90,761 | 90,610 | 92,251 | 94,829 | 107,352 | 115,598 | 138,863 | 131,736 | 108,012 | 91,725 | 80,169 | 83,989 |
| 2013 | 1,124,836 | 27.66% | 88,559 | 80,283 | 84,275 | 78,036 | 83,816 | 99,615 | 120,771 | 121,156 | 102,063 | 88,587 | 84,287 | 92,936 |
| 2014 | 1,126,635 | 27.52% | 91,016 | 75,942 | 78,151 | 76,782 | 89,120 | 98,460 | 115,081 | 122,348 | 106,582 | 97,683 | 84,354 | 91,038 |
| 2015 | 1,334,668 | 32.72% | 101,687 | 91,315 | 99,423 | 92,806 | 101,516 | 121,478 | 141,119 | 139,084 | 123,036 | 110,005 | 102,236 | 109,777 |
| 2016 | 1,379,271 | 33.83% | 110,044 | 98,552 | 103,890 | 98,876 | 110,430 | 131,395 | 151,554 | 154,760 | 125,603 | 102,898 | 93,942 | 96,364 |
| 2017 | 1,297,703 | 32.16% | 95,572 | 82,768 | 95,074 | 88,455 | 98,019 | 117,236 | 146,929 | 141,201 | 118,036 | 106,826 | 94,928 | 111,398 |
| 2018 | 1,471,843 | 35.2% | 110,293 | 98,512 | 106,524 | 98,371 | 115,284 | 130,826 | 164,749 | 161,676 | 141,786 | 123,142 | 108,168 | 109,802 |
| 2019 | 1,588,533 | 38.46% | 121,589 | 112,142 | 115,813 | 104,059 | 117,059 | 137,836 | 171,955 | 174,968 | 149,697 | 130,948 | 117,910 | 131,839 |
| 2020 | 1,626,790 | 40.57% | 136,084 | 128,018 | 126,187 | 110,564 | 117,186 | 143,055 | 181,568 | 173,644 | 141,397 | 131,413 | 109,811 | 127,863 |
| 2021 | 1,579,190 | 38.43% | 126,530 | 111,183 | 107,019 | 107,416 | 114,676 | 149,376 | 170,189 | 172,716 | 138,214 | 131,852 | 122,433 | 127,586 |
| 2022 | 1,687,067 | 39.88% | 134,948 | 114,945 | 112,477 | 105,506 | 127,094 | 155,517 | 189,042 | 188,860 | 156,948 | 133,492 | 127,523 | 140,716 |
| 2023 | 1,802,062 | 43.13% | 137,541 | 123,921 | 132,153 | 120,478 | 137,795 | 161,693 | 200,507 | 199,993 | 164,466 | 140,962 | 135,212 | 146,174 |
| 2024 | 1,582,696 | 43.76% | 160,450 | 130,990 | 130,423 | 122,441 | 143,917 | 168,803 | 209,033 | 203,094 | 169,382 | 146,370 | ||
| Last entry, % of Total | 42.25% | 40.9% | 40.3% | 39.51% | 41.62% | 43.31% | 48.56% | 47.97% | 47.16% | 43.86% | 42.02% | 42.2% | ||
Liquified petroleum gas
Liquefied petroleum gas includes the butane and propane natural gas liquids removed in gas processing. They are sold for home heating, cooking, and increasingly for motor fuel. The industry segment is represented by the National Propane Gas Association.
Vehicle fuel
Main article: Natural gas vehicleNatural gas, in the forms of compressed natural gas, liquified natural gas, and liquified petroleum gas, is being increasingly used for motor vehicle fuel, especially in fleet vehicles. It has the advantages over gasoline and diesel fuel of being cheaper and emitting less air pollution. It has the disadvantage of having few retail outlets. As of 2011, 262,000 vehicles in the US ran on natural gas. Although natural gas used for vehicle fuel increased 60 percent in the decade 2004-2014, in 2014 it still made up only 3.7 percent on a BTU-basis of fossil fuel use (gasoline, diesel, and natural gas) as transportation fuel in the US. Transportation fuel made up 0.13 percent of natural gas consumption in 2014.
History
Main article: History of the petroleum industry in the United StatesPipeline technology
The natural gas industry in the United States goes back to 1821, when natural gas was discovered and used in Fredonia, New York. From the start, the market for natural gas was limited by pipeline technology. The gas for Fredonia, New York in 1821 was supplied through wooden pipes, which were incapable of carrying gas for long distances.
In the 1800s, residences in most cities were supplied with town gas generated from coal at local "gashouses." The gas was carried in cast iron pipes, introduced in 1843, typically with bell-and-spigot joints sealed with rope and molten lead.
In the 1800s and early 1900s, most natural gas discoveries were made while exploring for oil. Natural gas was usually an unwanted byproduct of oil production. In the 1870s steel pipe replaced cast iron. In 1883, Pittsburgh became the first major city supplied with natural gas. Other cities followed, but only if they were close to natural gas wells. Because natural gas was a byproduct, it was priced cheaply, and, where available, undercut the market for town gas. In 1891, one of the longest pipelines of the time was built, a 120-mile long pipeline from the gas fields of Indiana to Chicago, without compression.
Long-distance high-pressure gas pipelines became feasible after oxyacetylene welding was introduced in 1911, and especially after electric arc welding became popular in the 1920s This allowed remote gas deposits to be supplied to big cities. Natural gas increasingly became a sought-for commodity.
Price regulation
The prices charged by utilities delivering natural gas to customers have always been subject to state regulation. With the construction of interstate gas pipelines in the 1920s and 1930s, city utilities became dependent on natural gas supplies beyond the regulatory power of state and local governments. In 1935, the federal trade commission, believing that interstate pipelines had too much power to control the downstream gas market, recommended federal controls. Congress passed the Natural Gas Act of 1938 to regulate the rates charged by interstate pipelines.
Federal regulations at first included only the rates interstate pipelines charged to carry gas. When the market price of natural gas at the wellhead increased in the 1950s, gas utilities complained that the gas producers should be regulated as well. In 1954, the US Supreme Court ruled in Phillips Petroleum Co. v. Wisconsin that regulation of the wellhead price was within the intent of the Natural Gas Act of 1938 to control prices to utilities, and therefore the federal government could control wellhead prices of any natural gas going into an interstate pipeline.
By the early 1970s, the artificially low price set by the federal government had created a shortage, but only of interstate gas. Gas consumed within the state where it was produced was plentiful, but more expensive. By 1975, about half the natural gas produced went to the intrastate market. In 1975 and 1976, some schools and factories in the Midwest shut down periodically when the local utility could not find any natural gas to buy at the controlled price. The Federal Power Commission tried to allocate the scarce gas by identifying "high-priority" and "low-priority" customers, but this caused extensive litigation.
The federal government responded to gas shortages with the Natural Gas Policy Act of 1978, which both increased federal regulation by extended price controls to all existing natural gas wells, and promised to end price controls on all new wells by 1985. Under the new rules, natural gas was subject to a complicated set of prices, depending on when the well was drilled, the size of the company that owned the well, the permeability of the formation, and the distance of the well from previous wells. Gas production from some types of gas reservoirs received tax subsidies. In 1976, the federal government established the Eastern Gas Shales Project, a large research effort to find ways to produce gas from shale.
Price controls grew even more complex with the Energy Act of 1980, which exempted Devonian gas shales (shales deposited during the Devonian geologic period) from price controls (but not gas shales deposited during other geologic periods), as well as low-permeability formations and coalbed methane. In addition, production from these sources earned tax credits for the producers for qualified wells drilled before January 1, 1992; the tax credits expired at the end of 2002.
The Natural Gas Wellhead Decontrol Act of 1989 mandated that all remaining price controls on natural gas were to be eliminated as of January 1, 1993.
Shortages and surplus

As with petroleum, the future supply of natural gas has long been the subject of concern, and predictions of shortages. In 1952, Dr. Edward Steidle, Dean of the School of Mineral Industries at Pennsylvania State College, predicted that gas production would soon decline significantly from 1952 rates, so that gas would cease to be a significant energy source by 2002, and possibly as early as 1975.
In 1956, M. King Hubbert used an estimated ultimate recovery (EUR) of 850 trillion cubic feet (24,000 km) (an amount postulated by geologist Wallace Pratt) to predict a US production peak of about 14 trillion cubic feet (400 km) per year to occur "approximately 1970". Pratt, in his EUR estimate (p. 96), explicitly included what he called the "phenomenal discovery rate" that the industry was then experiencing in the offshore Gulf of Mexico.
US marketed gas production reached a peak in 1973 at about 22.6 trillion cubic feet (640 km), and declined to a low of 16.9 trillion cubic feet (480 km) in 1986. But then instead of declining further, as predicted by the Hubbert curve, natural gas production rose slowly but steadily for the next 15 years, and reached 20.6 TCF in 2001. Then it dropped again for a few years, and in 2005 was down to 18.9 TCF.
After 2005, natural gas production rose rapidly, exceeded its old 1973 peak, and set new records for high production in each year 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, and 2015, when marketed production was 28.8 trillion cubic feet (820 km).
International trade





In 2017, the United States became a net exporter of natural gas on an annual basis for the first time since 1957. Net exports averaged 0.4 billion cubic feet per day. The US Energy Information Administration projected that net exports would grow to 4.6 billion cubic feet per day in 2019. Export growth was driven by pipeline exports to Mexico and Canada, although the US continued to import more from Canada than it exports to that country. In addition, exports of liquefied natural gas increased.
Natural gas depends on pipelines for economical transport. Without pipeline connections, natural gas must be transported as liquefied natural gas (LNG), an expensive process. For this reason, the price of natural gas tends to differ between regions not connected by gas pipelines. The North American market, consisting of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, all connected by a common pipeline network, has had much lower gas prices in recent years than some other major world gas markets, such as Europe (since 2010), Japan (since 2008), and Korea.
The United States is connected by pipeline to Canada and Mexico. The US has long imported large quantities of gas from Canada, and exported smaller quantities to some parts of eastern Canada. In 2014, the US imported 2,634 BCF from Canada, and exported 769 BCF, so that net imports from Canada totaled 1,865 BCF. The United States has exported increasing volumes to Mexico over the past decade. In 2014, the US exported 728.5 BCF to Mexico, and imported 1.4 BCF, so that net exports to Mexico totaled 727 BCF.
The cost of net imports peaked at US$29.7 billion in 2005; the cost of net imports was $5.9 billion in 2014.
Liquified natural gas


The United States became a net exporter of liquified natural gas in 2016. Principal markets for US LNG are Mexico, South Korea, China, and Japan. In late 2021, U.S. producer Venture Global LNG signed three long-term supply deals with China's state-owned Sinopec to supply liquefied natural gas. China's imports of U.S. natural gas will more than double. U.S. exports of liquefied natural gas to China and other Asian countries surged in 2021, with Asian buyers willing to pay higher prices than European importers.
In past years, when experts were projecting gas shortages in North America, utility companies built liquified natural gas (LNG) import terminals along the coast. Net imports of LNG peaked in 2007, but have since decreased. In 2014, the US imported 59 BCF of LNG gas, and exported 16 BCF, so that net LNG imports amounted to 43 BCF. Most imported LNG was from Trinidad and Tobago.
Long-term LNG contracts usually tie the price of LNG to the oil price.
In 2010, after the price of US natural gas fell below that of world markets, US companies have proposed establishing a number of LNG export terminals. A number of these proposals involve converting inactive LNG import terminals to handle LNG exports. Any proposals to export natural gas must be approved by the US Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), which gives its approval only if the project receives a satisfactory environmental review, and if FERC finds that the export terminal would be in the public interest. As of August 2015, 24 new LNG export terminals have been proposed, of which FERC has so far approved 6. Cheniere Energy expects to begin exporting LNG through its Sabine Pass terminal in January 2016.
As of 2014, the only active LNG export terminal in the US was in Kenai, Alaska. The plant, with a capacity of 0.2 BCF per day, is owned by ConocoPhillips, and has been exporting LNG since 1969. Most exported LNG went to Japan.
The New England States are connected by pipeline to the rest of the US and to Canada, but the existing pipelines are insufficient to supply the winter demand. For this reason, a quarter of New England's demand for gas is supplied by more-expensive LNG. Four LNG import terminals serve New England, but most LNG imported to New England arrives through the Everett terminal in Boston, and the Canaport terminal in New Brunswick, Canada. As of 2015, pipelines were under construction to carry cheaper gas from Pennsylvania to New England.
In 2023, exports of liquefied natural gas (LNG) from the United States increased by 12% from the previous year, reaching an average of 13.6 billion cubic feet per day (Bcf/d) in December, and contributing to a record annual total of 20.9 Bcf/d for all natural gas exports. This increase in LNG exports played a significant role, with the U.S. providing nearly half of Europe's LNG imports for the year. Meanwhile, overall U.S. natural gas imports decreased by 3% to 8.0 Bcf/d, largely due to milder winter temperatures and disruptions from wildfires in western Canada, which led to a 9% reduction in imports during April and May compared to the same months in 2022. Additionally, U.S. LNG imports remained minimal, below 0.1 Bcf/d, primarily servicing the New England market during peak demand periods, especially in the winter.
See also
- Energy in the United States
- Fracking in the United States
- Petroleum in the United States
- Shale gas in the United States
References
- US Energy Information Administration,Overview, accessed 13 February 2017.
- Marketed natural gas production, and average wellhead price, US EIA.
- "US Energy Information Administration". Archived from the original on 2010-11-04. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- "US Energy Information Administration". Archived from the original on 2019-11-16. Retrieved 2015-09-13.
- US EIA, Natural gas wellhead value and marketed production, accessed 25 April 2015.
- American Petroleum Institute, , accessed 20 February 2010.
- "Global natural gas prices vary considerably - Today in Energy - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)".
- ^ US Energy Information Administration, Top 100 Operators, 2009, accessed 2 August 2015.
- Crude oil and natural gas exploratory and development wells, US Energy Information Administration.
- Rethinking rig count as a predictor of natural gas production, US Energy Information Administration, 28 Oct. 2013.
- ^ "Natural Gas Gross Withdrawals and Production Data". U.S. Energy Information Administration. Retrieved 2019-12-28.
- US Energy Information Administration, Top 100 U.S. oil and gas fields, Mar. 2015
- "Natural Gas Flaring and Venting: State and Federal Regulatory Overview, Trends, and Impacts" (PDF). U.S. Department of Energy. 2019-06-01. Retrieved 2019-12-29.
- "Henry Hub Natural Gas Spot Price (Dollars per Million Btu)".
- https://www.ferc.gov/sites/default/files/2020-05/The-Price-Spike-Report-07-23-03.pdf
- Energy units Archived 2007-03-21 at the Wayback Machine.
- , US Geological Survey.
- Christopher E. Smith, "Oil pipelines lead way in strong 2014," Oil & Gas Journal, 7 Sept. 2015, p.111.
- US EIA, BTU content, accessed 2 August 2015.
- Schlumberger, Natural gas liquids accessed 2 August 2015
- Growing US HGL production spurs petrochemical industry investment, US Energy Information Administration, 29 Jan. 2015,
- Robert Brelsford, "Low-cost feed supports North American ethylene expansion plans," Oil & Gas Journal, 6 July 2015.
- Mapping North America's petrochemical construction projects, Petrochemical Update, 23 Apr. 2015.
- Lori E Apodaca, Sulfur, US Geological Survey, Minerals Yearbook, 2013.
- gas/natural gas/analysis publications/storagebasics/storagebasics.htmlEIA-The Basics of Underground Natural Gas Storage
- US EIA, The basics of underground natural gas storage, Aug. 2014.
- US EIA, Natural gas consumption, accessed 4 August 2015.
- Net generation by energy source, all sectors, US Energy Information Administration, accessed 15 Mar. 2016.
- Natural gas consumption has two peaks, US EIA, 11 Sept. 2015.
- US National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Life-cycle analysis harmonization, results and findings Archived 2017-05-06 at the Wayback Machine, NREL estimates life-cycle greenhouse gas emissions cor coal-fired electricity to be 979 grams CO2 equivalent per kWhr, compared to 450 grams for electricity from conventional gas, and 465 grams for electricity fueled by gas from massive hydraulic fractured gas wells.
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, , The IPCC estimates life-cycle GHG emissions for coal plants to be between 710 and 950 grams CO2 equivalent per kWhr, and the emissions from gas-fired plants between 410 and 650 grams.
- April Lee and others, Opportunities for Synergy Between Natural Gas and Renewable Energy in the Electric Power and Transportation Sectors, US National Renewable Energy Laboratory, NREL/TP-6A50-56324, Dec, 2012.
- "Electric Power Monthly" (PDF). Report. U.S. Department of Energy, Energy Information Administration. 26 Apr 2021.
- "Table 1.1. Net Generation by Energy Source: Total (All Sectors), 2014 – July 2024". U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Retrieved October 11, 2024.
- "Table 3.1.A. Net Generation by Energy Source: Total (All Sectors), 2001–2011". U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Retrieved October 25, 2023.
- Transportation sector, US Energy Information Administration.
- ^ http://www.penspen.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/past-present-future.pdf
- http://corridoreis.anl.gov/documents/docs/technical/apt_61034_evs_tm_08_5.pdf
- Daniel Yergin, The Prize (New York: Simon & Schuster, 1991) 76.
- .
- Dan Seward and Brad Curtis, "Comparison of the Appalachian Basin Devonian shales and Fort Worth Basin Mississippian shale," AAPG Southwest Section, Annual Convention, 13 April 2015.
- Edward Steidle, Mineral Forecast, 2000 A.D. (State College, Penn.: Pennsylvania State College, 1952) 74.
- M. King Hubbert (June 1956). "Nuclear Energy and the Fossil Fuels 'Drilling and Production Practice'" (PDF). API. p. figure 22 and p.25,36. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 May 2008. Retrieved 18 April 2008.
- Wallace E. Pratt (1956) "The impact of the peaceful uses of atomic energy on the petroleum industry," in Peaceful Uses of Atomic Energy, US Congress Joint Committee on Atomic Energy, p.89-103.
- US natural gas production by year, 1900-2014, US EIA.
- US Energy Information Administration, EIA expects 2018 and 2019 natural gas prices to remain relatively flat, 25 Jan. 2018.
- ^ US Energy Information Administration, The United States exported more natural gas than it imported in 2017, 19 March 2018.
- "Sinopec signs China's largest long-term LNG contract with U.S. firm". Reuters. November 4, 2021.
- "Sinopec signs huge LNG deals with US producer Venture Global". Financial Times. 20 October 2021.
- "Asian buyers outbid Europe for spot supplies of US natural gas". Financial Times. 21 September 2021.
- , Government Accountability Office.
- Approved LNG terminals Archived 2015-09-05 at the Wayback Machine Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, 6 Aug. 2015.
- "LNG tanker streams toward U.S. Sabine Pass for inaugural loading," Reuters, 9 Nov. 2015.
- Kenai liquified natural gas plant and Cook Inlet gas fields, Alaska Archived 2015-09-22 at the Wayback Machine, ConocoPhillips, April 2014.
- Alaska LNG terminals, FERC.
- , US Energy Information Administration.
- "The United States exported a record volume of natural gas in 2023 - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA)". www.eia.gov. Retrieved 2024-04-16.
External links
- America's Natural Gas Alliance – Natural gas producers
- American Gas Association
- American Public Gas Association – Publicly owned gas utilities
- Interstate Natural Gas Association of America – Interstate gas pipelines
- Natural Gas Supply Association
- "Natural gas leakage in USA". Global Energy Monitor. 15 December 2020.