| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Prince-Bishopric of UtrechtSticht Utrecht (Dutch) Episcopatus Ultraiectensis (Latin) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1024–1528 | |||||||||||
 Flag
Flag
 Coat of arms
Coat of arms
| |||||||||||
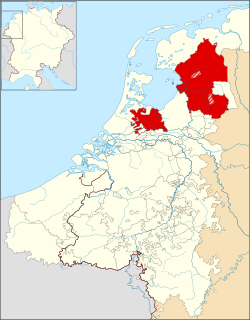 Bishopric of Utrecht c. 1350. Nedersticht is the smaller territory while Oversticht is the larger territory. Bishopric of Utrecht c. 1350. Nedersticht is the smaller territory while Oversticht is the larger territory. | |||||||||||
| Status | State of the Holy Roman Empire | ||||||||||
| Capital | Utrecht | ||||||||||
| Common languages | Middle Dutch, Medieval Latin, Middle Low German | ||||||||||
| Religion | Roman Catholicism (State religion) | ||||||||||
| Government | Ecclesiastical principality | ||||||||||
| Prince-bishop | |||||||||||
| • (1024–1026) | Adalbold II of Utrecht | ||||||||||
| • (1524–1528) | Henry of the Palatinate | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||||
| • Lower Lotharingia divided from Lotharingia | 959 | ||||||||||
| • Established | 1024 | ||||||||||
| • Investiture Controversy | 1075–1122 | ||||||||||
| • Concordat of Worms | 1122 | ||||||||||
| • Joined the Burgundian Circle | 1512 | ||||||||||
| • Guelders Wars | 1502–1543 | ||||||||||
| • Disestablished | 1528 | ||||||||||
| • Union of Utrecht signed | 1579 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | Netherlands | ||||||||||
The Bishopric of Utrecht (Dutch: Sticht Utrecht; Latin: Episcopatus Ultraiectensis) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries, in the present-day Netherlands. From 1024 to 1528, as one of the prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire, it was ruled by the bishops of Utrecht.
The Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht is not to be confused with the Diocese of Utrecht, which covered a larger area. Over the areas outside the Prince-Bishopric, the bishop exercised only spiritual, not temporal, authority.
In 1528, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor secularized the Prince-Bishopric, depriving the bishop of its secular authority.
History
Background
The Diocese of Utrecht was established in 695 when Saint Willibrord was consecrated bishop of the Frisians at Rome by Pope Sergius I. With the consent of the Frankish ruler, Pippin of Herstal, he settled in an old Roman fort in Utrecht. After Willibrord's death the diocese suffered greatly from the incursions of the Frisians, and later on of the Vikings. Whether Willibrord could be called the first bishop of Utrecht is doubtful; as James Palmer points out, "there was no real concept of a well-defined bishopric until at least the days of Alberic (775–84)". And while Saint Boniface is referred to in his hagiographies as the successor of Willibrord (and, in turn, Gregory of Utrecht is referred to as the successor to Willibrord and Boniface), this does not necessarily mean "successor as bishop", but rather that they succeeded each other as missionaries to the Frisians.
Foundation
Better times appeared during the reign of the Saxon emperors, who frequently summoned the Bishops of Utrecht to attend the imperial councils and diets. In 1024 the bishops were made Princes of the Holy Roman Empire and the new Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht was formed. The secular territory over which it ruled was known as Sticht Utrecht or Het Sticht (a sticht was any piece of land governed by a bishop or abbot). This territory was divided into the Nedersticht (Lower Sticht, roughly corresponding to the present day province of Utrecht) and Oversticht (Upper Sticht, encompassing the present-day provinces of Overijssel, Drenthe, and part of Groningen).
In 1122, with the Concordat of Worms, the Emperor's right of investiture was annulled, and the cathedral chapter received the right to elect the bishop. It was, however, soon obligated to share this right with the four other collegiate chapters in the city. The Counts of Holland and Guelders, between whose territories the lands of the Bishops of Utrecht lay, also sought to acquire influence over the filling of the episcopal see. This often led to disputes and consequently the Holy See frequently interfered in the election. After the middle of the 14th century the popes repeatedly appointed the bishop directly without regard to the five chapters.
It was part of the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle, until 1548 when it joined the Burgundian Circle as part of the Habsburg Netherlands.
In 1527, the Bishop sold his territories, and thus his secular authority, to Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and the principality became an integral part of the Habsburg dominions. The chapters transferred their right of electing the bishop to Charles V and his government, a measure to which Pope Clement VII gave his consent, under political pressure after the Sack of Rome.
Dissolution
The Prince-Bishopric of Utrecht was conquered by Habsburg troops in 1528. The southwestern Nedersticht core territory around the city of Utrecht became the Lordship of Utrecht, whilst the southern part of the Oversticht was transformed into the Lordship of Overijssel. The northern parts were annexed in 1536 as the County of Drenthe.
Prince-bishops
This is a list of prince-bishops only. For a full list of bishops and archbishops of Utrecht, see List of bishops and archbishops of Utrecht.- Adalbold II (1010–1026)
- Bernold (1026/7–1054)
- William I (1054–1076)
- Conrad (1076–1099)
- Burchard (1100–1112)
- Godbald (1114–1127)
- Andreas van Cuijk (1127/8–1139)
- Hartbert (1139–1150)
- Herman van Horne (1151–1156)
- Godfrey van Rhenen (1156–1178)
- Baldwin II van Holland (1178–1196)
- Arnold I van Isenburg (1196–1197)
- Dirk I van Holland (1197)
- Dirk II van Are (van Ahr) (1197/8–1212)
- Otto I van Gelre (1212–1215)
- Otto II van Lippe (1216–1227)
- Wilbrand van Oldenburg (1227–1233)
- Otto III van Holland (1233–1249)
- Gozewijn van Amstel (van Randerath) (1249–1250)
- Henry I van Vianden (1250/2–1267)
- John I of Nassau (1267–1290)
- John II van Sierck (1290–1296)
- Willem II Berthout (1296–1301)
- Guy van Avennes (1301–1317)
- Frederik II van Sierck (1317–1322)
- Jacob van Oudshoorn (1322)
- Jan III van Diest (1322–1340)
- Jan IV van Arkel (1342–1364)
- Jan V van Virneburg (1364–1371)
- Arnold II of Horne (1371–1379)
- Floris van Wevelinkhoven (1379–1393)
- Frederik III van Blankenheim (1393–1423)
- Rudolf van Diepholt (1423–1455)
- Zweder van Culemborg (1425–1433)
- Walraven van Meurs (1434–1448)
- Gijsbrecht van Brederode (1455–1456)
- David of Burgundy (1456–1496)
- Frederick IV of Baden (1496–1517)
- Philip of Burgundy (1517–1524)
- Henry of the Palatinate (1524–1529)
Notes
- Adalbold II of Utrecht was bishop of the Diocese of Utrecht from 1010.
- Henry of the Palatinate remained bishop of the Diocese of Utrecht until 1529.
References
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding articles in Dutch and German. (January 2014) Click for important translation instructions.
|
- Palmer, James T. (2009). Anglo-Saxons in a Frankish World (690-900). Studies in the Early Middle Ages. Vol. 19. Turnhout: Brepols. pp. 163–66. ISBN 9782503519111.
Further reading
- Ring, Trudy; Watson, Noelle; Schellinger, Paul, eds. (1995). "Utrecht". International dictionary of historic places. Vol. 2. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn. p. 761. ISBN 188496401X.
- Gosses, Izaak H. (1909). "De Bisschop van Utrecht, het Domkapittel en de Groninger Prefect". Bijdragen voor Vaderlandsche Geschiedenis en Oudheidkunde (in Dutch). ser.4 v.7. 's-Gravenhage: Nijhoff: 25–135. hdl:2027/mdp.39015026699788. OCLC 560305125. Retrieved 2014-09-15.
External links
- Apostolisch vicarissen van de Hollandse Zending (in Dutch)
- Budde, Paul. "Hamaland, Bishopric (Sticht) Utrecht incl. Oversticht (Drente, Overijssel)". PaulBuddeHistory.com. Archived from the original on 2014-01-18. Retrieved 2014-01-18.
| Prince-bishops |  | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prince-abbots | |||||||
| Secular | |||||||
| Counts / Lords |
| ||||||
| Cities | |||||||
| from 1648 until 1648 without seat in Imperial Diet status uncertain
Circles est. 1500: Bavarian, Swabian, Upper Rhenish, Lower Rhenish–Westphalian, Franconian, (Lower) Saxon
| |||||||
- Utrecht (city)
- Medieval history of the Netherlands
- History of Utrecht (province)
- History of Utrecht (city)
- States and territories established in 1024
- States and territories disestablished in 1528
- Former polities in the Netherlands
- Bishops of Utrecht
- Prince-bishoprics of the Holy Roman Empire in the Netherlands
- Lower Rhenish-Westphalian Circle
- History of Overijssel
- History of Drenthe
- 2nd millennium in the Netherlands