| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (July 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Overheating is a phenomenon of rising temperatures in an electrical circuit. Overheating causes damage to the circuit components and can cause fire, explosion, and injury. Damage caused by overheating is usually irreversible; the only way to repair it is to replace some components.
Causes
When overheating, the temperature of the part rises above the operating temperature. Overheating can take place:
- if heat is produced in more than expected amount (such as in cases of short-circuits, or applying more voltage than rated), or
- if heat dissipation is poor, so that normally produced waste heat does not drain away properly.
Overheating may be caused from any accidental fault of the circuit (such as short-circuit or spark-gap), or may be caused from a wrong design or manufacture (such as the lack of a proper heat dissipation system). Due to accumulation of heat, the system reaches an equilibrium of heat accumulation vs. dissipation at a much higher temperature than expected.
Preventive measures
Main article: Thermal management (electronics)Use of circuit breaker or fuse


 Glitched and garbled display on a workstation laptop with a defective graphics card that underwent extensive overheating from use in a hot environment.
Glitched and garbled display on a workstation laptop with a defective graphics card that underwent extensive overheating from use in a hot environment.The second image shows the same laptop failing to operate properly due to a graphics card defect, crashing the operating system and displaying a blue screen of death on the screen.
Circuit-breakers can be placed at portions of a circuit in series to the path of current it will affect. If more current than expected goes through the circuit-breaker, the circuit breaker "opens" the circuit and stops all current. A fuse is a common type of circuit breaker that involves direct effect of Joule-overheating. A fuse is always placed in series with the path of current it will affect. Fuses usually consist of a thin strand of wire of definite-material. When more that the rated current flows through the fuse, the wire melts and breaks the circuit.
Use of heat-dissipating systems
Many systems use ventilation holes or slits kept on the box of equipment to dissipate heat. Heat sinks are often attached to portions of the circuit that produce most heat or are vulnerable to heat. Fans are also often used. Some high-voltage instruments are kept immersed in oil. In some cases, to remove unwanted heat, a cooling system like air conditioning or refrigerating heat-pumps may be required.
Control within circuit-design
Sometimes, special circuits are built for the purpose of sensing and controlling the temperature or voltage status. Devices such as thermistors, voltage-dependent resistors, thermostats and sensors such as infrared thermometers are used to modify the current upon different conditions such as circuit-temperature and input voltage.
Proper manufacture
Main article: Building codeFor certain purposes in an item of electrical equipment or a portion of it, definite type and size of materials with proper rating for voltage, current and temperature, are used. The circuit resistance never kept too low. Sometimes some parts placed inside the board and box, maintaining a proper distance from each other, to avoid heat damage and short-circuit damage. To prevent short circuit, appropriate types of electrical connectors and mechanical fasteners are used.
Gallery
Gallery: Circuit breakers and fuses used to stop current.-
 Miniature time-delay fuse to interrupt 0.3 A current at 250 V after 100 s, and 15 A current at 250 V in 0.1 s
Miniature time-delay fuse to interrupt 0.3 A current at 250 V after 100 s, and 15 A current at 250 V in 0.1 s
-
 MEM rewirable fuse holders (30 A and 15 A)
MEM rewirable fuse holders (30 A and 15 A)
-
 A 115 kV high-voltage fuse near a hydroelectric power plant
A 115 kV high-voltage fuse near a hydroelectric power plant
-
 Pin-, straight- and flared-fin heat sink types
Pin-, straight- and flared-fin heat sink types
-
 Pin fin heat sink with thermal profile and air flow movement
Pin fin heat sink with thermal profile and air flow movement
-
Oil transformer with air convection cooled heat exchangers
-
 Power resistor
Power resistor
-
 Bimetallic thermostat for buildings
Bimetallic thermostat for buildings
-
 Millivolt thermostat interior mechanism
Millivolt thermostat interior mechanism
-
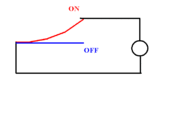 Bimetallic strip-thermostat working principle schematic
Bimetallic strip-thermostat working principle schematic
-
 working principle of bimetallic strip.
working principle of bimetallic strip.
-
 Bimetal coil reacts to lighter
Bimetal coil reacts to lighter
-
 Thermistors. They can be NTC or PTC according response to warming.
Thermistors. They can be NTC or PTC according response to warming.
-
 Metal-oxide varistor (voltage-dependent resistor)
Metal-oxide varistor (voltage-dependent resistor)
-
 High voltage varistor
High voltage varistor
-
 An infrared thermometer
An infrared thermometer
-
 A short circuit caused by overvoltage destroys an integrated circuit.
A short circuit caused by overvoltage destroys an integrated circuit.
-
Joule heating or resistive heating is sometimes helpful such as in a heating coil. But Joule heating occurs, to some extent, in all the conductive parts of a circuit.
-
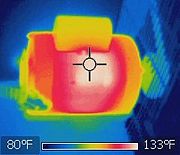 infrared-thermal image of a motor
infrared-thermal image of a motor
-
 Electric arc (spark) between two wires. This can cause overheating and ignition.
Electric arc (spark) between two wires. This can cause overheating and ignition.
-
On un-insulated wires, trees facilitated short-circuit in storms.
-
 Electricity applied to deliberately start up a fire (ignite) wastes in an incinerator. The same could happen in a circuit or building.
Electricity applied to deliberately start up a fire (ignite) wastes in an incinerator. The same could happen in a circuit or building.
See also
- Active cooling
- Air-cooling with fan
- Computer cooling
- Conflagration
- Coolant
- Heat exchanger
- Heat pipe
- Heat pump
- Heat sink
- Heat spreader
- Oil cooling
- Radiator
- Thermal design power
- Thermal management of electronic devices and systems
- Thermal management of high-power LEDs
- Thermal resistance in electronics
- Thermal runaway
- Thermoelectric cooling
- Transformer oil
- Wire gauge
References
- http://www.ufba.org.nz/images/documents/hazardsandsafeguards.pdf Archived 2016-10-09 at the Wayback Machine
- "Classification of Electrical Overheating Modes - Electro-Mechanical Recertifiers, Inc". Retrieved 27 August 2016.
- ElectroTechnik. "What are the reasons for transformer overheating?". Retrieved 27 August 2016.
- "The Basics of Electrical Overheating". Retrieved 27 August 2016.
- http://www.testequipmentdepot.com/application-notes/pdf/power-quality/case-study-the-overheating-transformer_an.pdf
- "Protectowire | The Global Leader In Linear Heat Detection Systems". Protectowire.
- http://www.mirusinternational.com/downloads/hmt_faq10.pdf
- http://www.learnabout-electronics.org/Downloads/ac_theory_module11.pdf
- "Power Transformers". Retrieved 27 August 2016.
- http://sound.whsites.net/xfmr.htm Archived 2019-07-21 at the Wayback Machine
- http://sound.whsites.net/xfmr-6.jpg Archived 2016-10-08 at the Wayback Machine
- "Top 14 Reasons Electrical Service Installations Get Red Tagged". Retrieved 27 August 2016.
- http://ecmweb.com/site-files/ecmweb.com/files/uploads/2016/03/Electrical-Service-Meltdown-6.jpg