| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2,3,5,6-Tetrachlorocyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione | |
| Other names p-Chloranil; Tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone; Tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.887 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
| PubChem CID | |
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
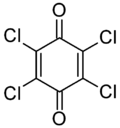
| Chemical formula | C6Cl4O2 |
| Molar mass | 245.86 g·mol |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Melting point | 295 to 296 °C (563 to 565 °F; 568 to 569 K) |
| Magnetic susceptibility (χ) | -112.6·10 cm/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
| Pictograms |  
|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H315, H319, H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P264, P273, P280, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P391, P501 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Chloranil is a quinone with the molecular formula C6Cl4O2. Also known as tetrachloro-1,4-benzoquinone, it is a yellow solid. Like the parent benzoquinone, chloranil is a planar molecule that functions as a mild oxidant.
Synthesis and use as reagent
Chloranil is produced by chlorination of phenol to give hexachlorocyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-one ("hexachlorophenol"). Hydrolysis of the dichloromethylene group in this dienone gives chloranil:
- C6H5OH + 6 Cl2 → C6Cl6O + 6 HCl
- C6Cl6O + H2O → C6Cl4O2 + 2 HCl
Chloroanil serves as a hydrogen acceptor. It is more electrophilic than quinone itself. It is used for the aromatization reactions, such as the conversion of cyclohexadienes to the benzene derivatives.
Chloranil is used to test for free secondary amines. This test is useful for checking for the presence of proline derivatives. It is also a good test for the successful deprotection of a secondary amine. Secondary amines react with chloranil to give a brown/red/orange derivative, the colour depending on the amine. In these reactions, the amine displaces chloride from the ring of the quinone.
Commercial applications
It is a precursor to many dyes, such as pigment violet 23 and diaziquone (AZQ), a cancer chemotherapeutic agent.
See also
References
- Chloranil at Sigma-Aldrich
- J.-M. Lü, S. V. Rosokha, I. S. Neretin and J. K. Kochi, "Quinones as Electron Acceptors. X-Ray Structures, Spectral (EPR, UV-vis) Characteristics and Electron-Transfer Reactivities of Their Reduced Anion Radicals as Separated vs Contact Ion Pairs" Journal of the American Chemical Society 2006 128, 16708-16719.doi:10.1021/ja066471o
- François Muller and Liliane Caillard "Chlorophenols" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2011. doi:10.1002/14356007.a07_001.pub2
- Derek R. Buckle "Chloranil" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, 2001, John Wiley. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rc057
External links
- Chloranil in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)