
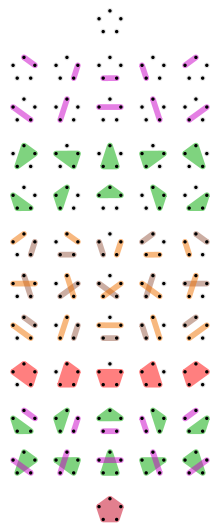
In mathematics, a partition of a set is a grouping of its elements into non-empty subsets, in such a way that every element is included in exactly one subset.
Every equivalence relation on a set defines a partition of this set, and every partition defines an equivalence relation. A set equipped with an equivalence relation or a partition is sometimes called a setoid, typically in type theory and proof theory.
Definition and notation
A partition of a set X is a set of non-empty subsets of X such that every element x in X is in exactly one of these subsets (i.e., the subsets are nonempty mutually disjoint sets).
Equivalently, a family of sets P is a partition of X if and only if all of the following conditions hold:
- The family P does not contain the empty set (that is ).
- The union of the sets in P is equal to X (that is ). The sets in P are said to exhaust or cover X. See also collectively exhaustive events and cover (topology).
- The intersection of any two distinct sets in P is empty (that is ). The elements of P are said to be pairwise disjoint or mutually exclusive. See also mutual exclusivity.
The sets in are called the blocks, parts, or cells, of the partition. If then we represent the cell containing by . That is to say, is notation for the cell in which contains .
Every partition may be identified with an equivalence relation on , namely the relation such that for any we have if and only if (equivalently, if and only if ). The notation evokes the idea that the equivalence relation may be constructed from the partition. Conversely every equivalence relation may be identified with a partition. This is why it is sometimes said informally that "an equivalence relation is the same as a partition". If P is the partition identified with a given equivalence relation , then some authors write . This notation is suggestive of the idea that the partition is the set X divided in to cells. The notation also evokes the idea that, from the equivalence relation one may construct the partition.
The rank of is , if is finite.
Examples
- The empty set has exactly one partition, namely . (Note: this is the partition, not a member of the partition.)
- For any non-empty set X, P = { X } is a partition of X, called the trivial partition.
- Particularly, every singleton set {x} has exactly one partition, namely { {x} }.
- For any non-empty proper subset A of a set U, the set A together with its complement form a partition of U, namely, { A, U ∖ A }.
- The set {1, 2, 3} has these five partitions (one partition per item):
- { {1}, {2}, {3} }, sometimes written 1 | 2 | 3.
- { {1, 2}, {3} }, or 1 2 | 3.
- { {1, 3}, {2} }, or 1 3 | 2.
- { {1}, {2, 3} }, or 1 | 2 3.
- { {1, 2, 3} }, or 123 (in contexts where there will be no confusion with the number).
- The following are not partitions of {1, 2, 3}:
- { {}, {1, 3}, {2} } is not a partition (of any set) because one of its elements is the empty set.
- { {1, 2}, {2, 3} } is not a partition (of any set) because the element 2 is contained in more than one block.
- { {1}, {2} } is not a partition of {1, 2, 3} because none of its blocks contains 3; however, it is a partition of {1, 2}.
Partitions and equivalence relations
For any equivalence relation on a set X, the set of its equivalence classes is a partition of X. Conversely, from any partition P of X, we can define an equivalence relation on X by setting x ~ y precisely when x and y are in the same part in P. Thus the notions of equivalence relation and partition are essentially equivalent.
The axiom of choice guarantees for any partition of a set X the existence of a subset of X containing exactly one element from each part of the partition. This implies that given an equivalence relation on a set one can select a canonical representative element from every equivalence class.
Refinement of partitions

A partition α of a set X is a refinement of a partition ρ of X—and we say that α is finer than ρ and that ρ is coarser than α—if every element of α is a subset of some element of ρ. Informally, this means that α is a further fragmentation of ρ. In that case, it is written that α ≤ ρ.
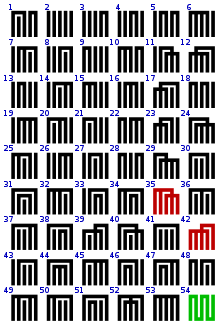
This "finer-than" relation on the set of partitions of X is a partial order (so the notation "≤" is appropriate). Each set of elements has a least upper bound (their "join") and a greatest lower bound (their "meet"), so that it forms a lattice, and more specifically (for partitions of a finite set) it is a geometric and supersolvable lattice. The partition lattice of a 4-element set has 15 elements and is depicted in the Hasse diagram on the left.
The meet and join of partitions α and ρ are defined as follows. The meet is the partition whose blocks are the intersections of a block of α and a block of ρ, except for the empty set. In other words, a block of is the intersection of a block of α and a block of ρ that are not disjoint from each other. To define the join , form a relation on the blocks A of α and the blocks B of ρ by A ~ B if A and B are not disjoint. Then is the partition in which each block C is the union of a family of blocks connected by this relation.
Based on the equivalence between geometric lattices and matroids, this lattice of partitions of a finite set corresponds to a matroid in which the base set of the matroid consists of the atoms of the lattice, namely, the partitions with singleton sets and one two-element set. These atomic partitions correspond one-for-one with the edges of a complete graph. The matroid closure of a set of atomic partitions is the finest common coarsening of them all; in graph-theoretic terms, it is the partition of the vertices of the complete graph into the connected components of the subgraph formed by the given set of edges. In this way, the lattice of partitions corresponds to the lattice of flats of the graphic matroid of the complete graph.
Another example illustrates refinement of partitions from the perspective of equivalence relations. If D is the set of cards in a standard 52-card deck, the same-color-as relation on D – which can be denoted ~C – has two equivalence classes: the sets {red cards} and {black cards}. The 2-part partition corresponding to ~C has a refinement that yields the same-suit-as relation ~S, which has the four equivalence classes {spades}, {diamonds}, {hearts}, and {clubs}.
Noncrossing partitions
A partition of the set N = {1, 2, ..., n} with corresponding equivalence relation ~ is noncrossing if it has the following property: If four elements a, b, c and d of N having a < b < c < d satisfy a ~ c and b ~ d, then a ~ b ~ c ~ d. The name comes from the following equivalent definition: Imagine the elements 1, 2, ..., n of N drawn as the n vertices of a regular n-gon (in counterclockwise order). A partition can then be visualized by drawing each block as a polygon (whose vertices are the elements of the block). The partition is then noncrossing if and only if these polygons do not intersect.
The lattice of noncrossing partitions of a finite set forms a subset of the lattice of all partitions, but not a sublattice, since the join operations of the two lattices do not agree.
The noncrossing partition lattice has taken on importance because of its role in free probability theory.
Counting partitions
The total number of partitions of an n-element set is the Bell number Bn. The first several Bell numbers are B0 = 1, B1 = 1, B2 = 2, B3 = 5, B4 = 15, B5 = 52, and B6 = 203 (sequence A000110 in the OEIS). Bell numbers satisfy the recursion
and have the exponential generating function

The Bell numbers may also be computed using the Bell triangle in which the first value in each row is copied from the end of the previous row, and subsequent values are computed by adding two numbers, the number to the left and the number to the above left of the position. The Bell numbers are repeated along both sides of this triangle. The numbers within the triangle count partitions in which a given element is the largest singleton.
The number of partitions of an n-element set into exactly k (non-empty) parts is the Stirling number of the second kind S(n, k).
The number of noncrossing partitions of an n-element set is the Catalan number
See also
- Exact cover
- Block design
- Cluster analysis
- List of partition topics
- Lamination (topology)
- MECE principle
- Partial equivalence relation
- Partition algebra
- Partition refinement
- Point-finite collection
- Rhyme schemes by set partition
- Weak ordering (ordered set partition)
Notes
- Knuth, Donald E. (2013), "Two thousand years of combinatorics", in Wilson, Robin; Watkins, John J. (eds.), Combinatorics: Ancient and Modern, Oxford University Press, pp. 7–37
- Halmos, Paul (1960). Naive Set Theory R. Springer. p. 28. ISBN 9780387900926.
- Lucas, John F. (1990). Introduction to Abstract Mathematics. Rowman & Littlefield. p. 187. ISBN 9780912675732.
- Brualdi 2004, pp. 44–45.
- Schechter 1997, p. 54.
- Birkhoff, Garrett (1995), Lattice Theory, Colloquium Publications, vol. 25 (3rd ed.), American Mathematical Society, p. 95, ISBN 9780821810255.
- *Stern, Manfred (1999), Semimodular Lattices. Theory and Applications, Encyclopedia of Mathematics and its Applications, vol. 73, Cambridge University Press, doi:10.1017/CBO9780511665578, ISBN 0-521-46105-7
References
- Brualdi, Richard A. (2004). Introductory Combinatorics (4th ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-100119-1.
- Schechter, Eric (1997). Handbook of Analysis and Its Foundations. Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-622760-8.
 ).
). ). The sets in P are said to exhaust or cover X. See also
). The sets in P are said to exhaust or cover X. See also  ). The elements of P are said to be
). The elements of P are said to be  are called the blocks, parts, or cells, of the partition. If
are called the blocks, parts, or cells, of the partition. If  then we represent the cell containing
then we represent the cell containing  by
by  . That is to say,
. That is to say,  , namely the relation
, namely the relation  such that for any
such that for any  we have
we have  if and only if
if and only if  (equivalently, if and only if
(equivalently, if and only if  ). The notation
). The notation  , then some authors write
, then some authors write  . This notation is suggestive of the idea that the partition is the set X divided in to cells. The notation also evokes the idea that, from the equivalence relation one may construct the partition.
. This notation is suggestive of the idea that the partition is the set X divided in to cells. The notation also evokes the idea that, from the equivalence relation one may construct the partition.
 , if
, if  has exactly one partition, namely
has exactly one partition, namely  is the partition whose blocks are the intersections of a block of α and a block of ρ, except for the empty set. In other words, a block of
is the partition whose blocks are the intersections of a block of α and a block of ρ, except for the empty set. In other words, a block of  , form a relation on the blocks A of α and the blocks B of ρ by A ~ B if A and B are not disjoint. Then
, form a relation on the blocks A of α and the blocks B of ρ by A ~ B if A and B are not disjoint. Then  singleton sets and one two-element set. These atomic partitions correspond one-for-one with the edges of a
singleton sets and one two-element set. These atomic partitions correspond one-for-one with the edges of a 

