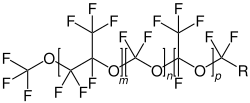
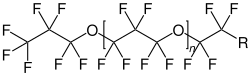
Perfluoropolyethers (PFPEs) are a class of organofluorine compound. Some types are synthetic liquid lubricants that have been used in the aerospace industry for over 30 years. The main properties of PFPE are being temperature resistant between −58 °C (215 K) and 257 °C (530 K) (depending on specific composites), having very low outgassing compared to other fluids (vapour pressure of 6×10 Torr) and having a dielectric strength of around 15.7 MV/m.
Perfluoropolyethers consists of a polymer chain in which monomers consisting of perfluoro-alkyl groups are joined by ether linkages. The bonds between carbon and oxygen or fluorine are strong. Perfluoropolyethers are a type of PFAS.
The thermal and chemical stability of PFPEs along with a vapor–liquid equilibrium of 230 °C when mixed with the right composites make it a suitable candidate for vapor phase soldering technologies.
History
Perfluoropolyethers were developed in the early 1960s for the USAF, who needed a lubricant that would not react with liquid or gaseous oxygen (O2).
Manufacture
Each type of perfluoropolyether is synthesized differently: PFPE-K is obtained from HFPO by anionic polymerization. For PFPE-Y and PFBE-Z, photooxidation of hexafluoropropylene and tetrafluoroethylene, respectively, is applied. PFPE-D is synthesized by anionic ring-opening polymerization of 2,2,3,3-tetrafluorooxetane. PFPE-A is obtained by an initial esterification of polyethylene glycol with a perfluoroacyl fluoride. Then, it is converted into a fully fluorined polymer using direct fluorination.
Properties
PFPEs are chemically inert to many acids and oxidants (like fuming sulfuric acid (oleum, SO3), chlorine gas, oxygen) and solvents, etc.
PFPEs are non-toxic under normal conditions, nonflammable, and exhibit unusually high load carry capabilities. PFPEs can withstand gamma ray degradation.
Electrical resistivity is 10 ohm/cm (20 °C (68 °F))
Applications
Generally, PFPEs may be used as lubricant in all sorts of bearing, plug valves, gaskets, chains, and joint bearing applications, where oxygen inertness of a material is a requirement. Examples include aircraft fuel systems, mechanical components of devices used in airspace, deep space or high vacuum and at cryogenic temperatures.
PFPEs may be used in mold release agent for plastic injection molding.
As top coating lubricant on computer disc drives and Scanning Electron Microscope
As anti-galling compounds.
As fluid medium in ferrofluidic seals.
Semiconductor industry
In the semiconductor industry, PFPEs may be used as a vacuum grease or in plasma etching equipment, or for robots used in semiconductor wafer handling, clean rooms, and other commercial environments.
See also
- Krytox, a PFPE-based lubricant
References
- Bradley Shogrin (August 1995). "Spontaneous Dewetting of a Perfluoropolyether" (PDF). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Retrieved November 29, 2017.
- "Fomblin® PFPE Lubricants".
- ^ Fluorochemie. "Brief Introduction of PFPE Synthesis Methods". Fuzhou Topda New Material Co., Ltd. Retrieved June 27, 2022.
- Kwiatkowski, Carol F.; Andrews, David Q.; Birnbaum, Linda S.; Bruton, Thomas A.; DeWitt, Jamie C.; Knappe, Detlef R. U.; Maffini, Maricel V.; Miller, Mark F.; Pelch, Katherine E.; Reade, Anna; Soehl, Anna; Trier, Xenia; Venier, Marta; Wagner, Charlotte C.; Wang, Zhanyun; Blum, Arlene (11 August 2020). "Scientific Basis for Managing PFAS as a Chemical Class". Environmental Science & Technology Letters. 7 (8): 532–543. doi:10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00255. hdl:20.500.11850/438999.
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-02-27. Retrieved 2020-08-23.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "HUSKEY Specialty lubricants" (PDF). HUSK-ITT Corporation.
- Synthesis Report on Understanding Perfluoropolyethers (PFPEs) and Their Life Cycle (PDF). OECD. 2024.
- ^ Ash, Michael (2004). Handbook of green chemicals. Irene Ash (2 ed.). Endicott, NY: Synapse Information Resources. ISBN 978-1-934764-29-9. OCLC 747426845.