| The neutrality of the style of writing in this article is disputed. Please do not remove this message until conditions to do so are met. (August 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| This article may be too technical for most readers to understand. Please help improve it to make it understandable to non-experts, without removing the technical details. (August 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Peridynamics is a non-local formulation of continuum mechanics that is oriented toward deformations with discontinuities, especially fractures. Originally, bond-based peridynamic has been introduced, wherein, internal interaction forces between a material point and all the other ones with which it can interact, are modeled as a central forces field. This type of force fields can be imagined as a mesh of bonds connecting each point of the body with every other interacting point within a certain distance which depends on material property, called peridynamic horizon. Later, to overcome bond-based framework limitations for the material Poisson’s ratio ( for plane stress and for plane strain in two-dimesional configurations; for three-dimensional ones), state-base peridynamics, has been formulated. Its characteristic feature is that the force exchanged between a point and another one is influenced by the deformation state of all other bonds relative to its interaction zone.
The characteristic feature of peridynamics, which makes it different from classical local mechanics, is the presence of finite-range bond between any two points of the material body: it is a feature that approaches such formulations to discrete meso-scale theories of matter.
Etymology
The term peridynamic, as an adjective, was proposed in the year 2000 and comes from the prefix peri-, which means all around, near, or surrounding; and the root dyna, which means force or power. The term peridynamics, as a noun, is a shortened form of the phrase peridynamic model of solid mechanics.
Purpose
A fracture is a mathematical singularity to which the classical equations of continuum mechanics cannot be applied directly. The peridynamic theory has been proposed with the purpose of mathematically models fractures formation and dynamic in elastic materials. It is founded on integral equations, in contrast with classical continuum mechanics, which is based on partial differential equations. Since partial derivatives do not exist on crack surfaces and other geometric singularities, the classical equations of continuum mechanics cannot be applied directly when such features are present in a deformation. The integral equations of the peridynamic theory hold true also on singularities and can be applied directly, because they do not require partial derivatives. The ability to apply the same equations directly at all points in a mathematical model of a deforming structure helps the peridynamic approach to avoid the need for the special techniques of fracture mechanics like xFEM. For example, in peridynamics, there is no need for a separate crack growth law based on a stress intensity factor.
Definition and basic terminology
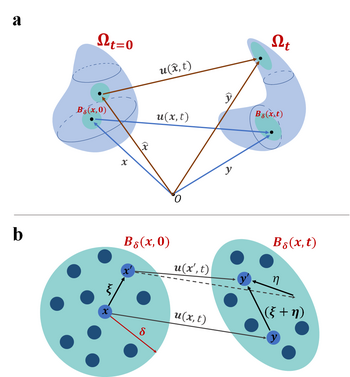
In the context of peridynamic theory, physical bodies are treated as constituted by a continuous points mesh which can exchange long-range mutual interaction forces, within a maximum and well established distance : the peridynamic horizon radius. This perspective approaches much more to molecular dynamics than macroscopic bodies, and as a consequence, is not based on the concept of stress tensor (which is a local concept) and drift toward the notion of pairwise force that a material point exchanges within its peridynamic horizon. With a Lagrangian point of view, suited for small displacements, the peridynamic horizon is considered fixed in the reference configuration and, then, deforms with the body. Consider a material body represented by , where can be either 1, 2 or 3. The body has a positive density . Its reference configuration at the initial time is denoted by . It is important to note that the reference configuration can either be the stress-free configuration or a specific configuration of the body chosen as a reference. In the context of peridynamics, every point in interacts with all the points within a certain neighborhood defined by , where and represents a suitable distance function on . This neighborhood is often referred to as in the literature. It is commonly known as the horizon or the family of .
The kinematics of is described in terms of its displacement from the reference position, denoted as . Consequently, the position of at a specific time is determined by . Furthermore, for each pair of interacting points, the change in the length of the bond relative to the initial configuration is tracked over time through the relative strain , which can be expressed as:
where denotes the Euclidean norm and .
The interaction between any and is referred to as a bond. These pairwise bonds have varying lengths over time in response to the force per unit volume squared, denoted as
.
This force is commonly known as the pairwise force function or peridynamic kernel, and it encompasses all the constitutive (material-dependent) properties. It describes how the internal forces depend on the deformation. It's worth noting that the dependence of on has been omitted here for the sake of simplicity in notation. Additionally, an external forcing term, , is introduced, which results in the following equation of motion, representing the fundamental equation of peridynamics:
where the integral term is the sum of all of the internal and external per-unit-volume forces acting on :
The vector valued function is the force density that exerts on . This force density depends on the relative displacement and relative position vectors between and . The dimension of is .
Bond-based peridynamics
In this formulation of peridynamics, the kernel is determined by the nature of internal forces and physical constraints that governs the interaction between only two material points. For the sake of brevity, the following quantities are defined and so that
Actio et reactio principle
For any and belonging to the neighborhood , the following relationship holds: . This expression reflects the principle of action and reaction, commonly known as Newton's Third Law. It guarantees the conservation of linear momentum in a system composed of mutually interacting particles.
Angular momentum conservation
For any and belonging to the neighborhood , the following condition holds: . This condition arises from considering the relative deformed ray-vector connecting and as . The condition is satisfied if and only if the pairwise force density vector has the same direction as the relative deformed ray-vector. In other words, for all and , where is a scalar-valued function.
Hyperelastic material
An hyperelastic material is a material with constitutive relation such that:
or, equivalently, by Stokes' theorem
,
and, thus,
In the equation above is the scalar valued potential function in . Due to the necessity of satisfying angular momentum conservation, the condition below on the scalar valued function follows
where is a scalar valued function. Integrating both sides of the equation, the following condition on is obtained
,
for a scalar valued function. The elastic nature of is evident: the interaction force depends only on the initial relative position between points and and the modulus of their relative position, , in the deformed configuration at time . Applying the isotropy hypothesis, the dependence on vector can be substituted with a dependence on its modulus ,
Bond forces can, thus, be considered as modeling a spring net that connects each point pairwise with .
Linear elastic material
If , the peridynamic kernel can be linearised around :
then, a second-order micro-modulus tensor can be defined as
where and is the identity tensor. Following application of linear momentum balance, elasticity and isotropy condition, the micro-modulus tensor can be expressed in this form
Therefore for a linearised hyperelastic material, its peridynamic kernel holds the following structure
Expressions for the peridynamic kernel
The peridynamic kernel is a versatile function that characterizes the constitutive behavior of materials within the framework of peridynamic theory. One commonly employed formulation of the kernel is used to describe a class of materials known as prototype micro-elastic brittle (PMB) materials. In the case of isotropic PMB materials, the pairwise force is assumed to be linearly proportional to the finite stretch experienced by the material, defined as
,
so that
where
and where the scalar function is defined as follow
with
The constant is referred to as the micro-modulus constant, and the function serves to indicate whether, at a given time , the bond stretch associated with the pair has surpassed the critical value . If the critical value is exceeded, the bond is considered broken, and a pairwise force of zero is assigned for all .
After a comparison between the strain energy density value obtained under isotropic extension respectively employing peridynamics and classical continuum theory framework, the physical coherent value of micro-modulus can be found
where is the material bulk modulus.
Following the same approach the micro-modulus constant can be extended to , where is now a micro-modulus function. This function provides a more detailed description of how the intensity of pairwise forces is distributed over the peridynamic horizon . Intuitively, the intensity of forces decreases as the distance between and increases, but the specific manner in which this decrease occurs can vary.
The micro-modulus function is expressed as
where the constant is obtained by comparing peridynamic strain density with the classical mechanical theories; is a function defined on with the following properties (given the restrictions of momentum conservation and isotropy)
where is the Dirac Delta function.
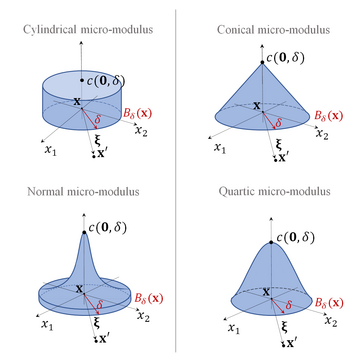
Cylindrical micro-modulus
The simplest expression for the micro-modulus function is
,
where : is the indicator function of the subset , defined as
Triangular micro-modulus
It is characterized by to a be a linear function
Normal micro-modulus
If one wants to reflects the fact that most common discrete physical systems are characterized by a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, in order to include this behavior in peridynamics, the following expression for can be utilized
Quartic micro-modulus
In the literature one can find also the following expression for the function
Overall, depending on the specific material property to be modeled, there exists a wide range of expressions for the micro-modulus and, in general, for the peridynamic kernel. The above list is, thus, not exhaustive.
Damage
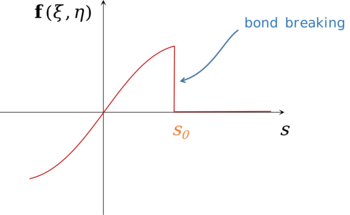
Damage is incorporated in the pairwise force function by allowing bonds to break when their elongation exceeds some prescribed value. After a bond breaks, it no longer sustains any force, and the endpoints are effectively disconnected from each other. When a bond breaks, the force it was carrying is redistributed to other bonds that have not yet broken. This increased load makes it more likely that these other bonds will break. The process of bond breakage and load redistribution, leading to further breakage, is how cracks grow in the peridynamic model.
Analytically, the bond braking is specified inside the expression of peridynamic kernel, by the function
If the graph of versus bond stretching is plotted, the action of bond braking function in fracture formation is clear. However not only abrupt fracture can be modeled in peridynamic framework and more general expression for can be employed.
State-based peridynamics
The theory described above assumes that each peridynamic bond responds independently of all the others. This is an oversimplification for most materials and leads to restrictions on the types of materials that can be modeled. In particular, this assumption implies that any isotropic linear elastic solid is restricted to a Poisson ratio of 1/4.
To address this lack of generality, the idea of peridynamic states was introduced. This allows the force density in each bond to depend on the stretches in all the bonds connected to its endpoints, in addition to its own stretch. For example, the force in a bond could depend on the net volume changes at the endpoints. The effect of this volume change, relative to the effect of the bond stretch, determines the Poisson ratio. With peridynamic states, any material that can be modeled within the standard theory of continuum mechanics can be modeled as a peridynamic material, while retaining the advantages of the peridynamic theory for fracture.
Mathematically the equation of the internal and external force term
used in the bond-based formulations is substituted by
where is the force vector state field.
A general m-order state is a mathematical object similar to a tensor, with the exception that it is
- in general non-linear;
- in general non-continuous;
- is not finite dimensional.
Vector states are states of order equal to 2. For so called simple material, is defined as
where is a Riemann-integrable function on , and is called deformation vector state field and is defined by the following relation
thus is the image of the bond under the deformation
such that
which means that two distinct particles never occupy the same point as the deformation progresses.
It can be proved that balance of linear momentum follow from the definition of , while, if the constitutive relation is such that
the force vector state field satisfy balance of angular momentum.
Applications

The growing interest in peridynamics come from its capability to fill the gap between atomistic theories of matter and classical local continuum mechanics. It is applied effectively to micro-scale phenomena, such as crack formation and propagation, wave dispersion, intra-granular fracture. These phenomena can be described by appropriately adjustment of the peridynamic horizon radius, which is directly linked to the extent of non-local interactions between points within the material.
In addition to the aforementioned research fields, peridynamics' non-local approach to discontinuities has found applications in various other areas. In geo-mechanics, it has been employed to study water-induced soil cracks, geo-material failure, rocks fragmentation, and so on. In biology, peridynamics has been used to model long-range interactions in living tissues, cellular ruptures, cracking of bio-membranes, and more. Furthermore, peridynamics has been extended to thermal diffusion theory, enabling the modeling of heat conduction in materials with discontinuities, defects, inhomogeneities, and cracks. It has also been applied to study advection-diffusion phenomena in multi-phase fluids and to construct models for transient advection-diffusion problems. With its versatility, peridynamics has been used in various multi-physics analyses, including micro-structural analysis, fatigue and heat conduction in composite materials, galvanic corrosion in metals, electricity-induced cracks in dielectric materials and more.
See also
- Continuum mechanics
- Fracture mechanics
- Movable cellular automaton
- Molecular dynamics
- Non-local operator
- Singularity
References
- ^ Silling, S.A. (January 2000). "Reformulation of elasticity theory for discontinuities and long-range forces". Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. 48 (1): 175–209. Bibcode:2000JMPSo..48..175S. doi:10.1016/S0022-5096(99)00029-0. S2CID 122055539.
- Dimola, Nunzio; Coclite, Alessandro; Fanizza, Giuseppe; Politi, Tiziano (2022-10-23). "Bond-based peridynamics, a survey prospecting nonlocal theories of fluid-dynamics". Advances in Continuous and Discrete Models. 2022 (1). arXiv:2207.06194. doi:10.1186/s13662-022-03732-6. ISSN 2731-4235.
- ^ Madenci, Erdogan; Oterkus, Erkan (2014). Peridynamic theory and its applications. New York, NY: Springer. pp. 19–43. ISBN 978-1-4614-8464-6.
- Macek, Richard W.; Silling, Stewart A. (November 2007). "Peridynamics via finite element analysis". Finite Elements in Analysis and Design. 43 (15): 1169–1178. doi:10.1016/j.finel.2007.08.012. ISSN 0168-874X. OSTI 1725746.
- ^ Silling, S. A.; Epton, M.; Weckner, O.; Xu, J.; Askari, E. (2007-08-08). "Peridynamic States and Constitutive Modeling". Journal of Elasticity. 88 (2): 151–184. doi:10.1007/s10659-007-9125-1. ISSN 0374-3535. S2CID 30571789.
- ^ Javili, Ali; Morasata, Rico; Oterkus, Erkan; Oterkus, Selda (November 2019). "Peridynamics review". Mathematics and Mechanics of Solids. 24 (11): 3714–3739. doi:10.1177/1081286518803411. hdl:11693/53217. ISSN 1081-2865. S2CID 162176799.
- ^ Silling, S.A.; Askari, E. (June 2005). "A meshfree method based on the peridynamic model of solid mechanics". Computers & Structures. 83 (17–18): 1526–1535. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2004.11.026.
- Ren, Huilong; Zhuang, Xiaoying; Cai, Yongchang; Rabczuk, Timon (2016-12-21). "Dual-horizon peridynamics: Dual-horizon peridynamics". International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering. 108 (12): 1451–1476. arXiv:1506.05146. doi:10.1002/nme.5257. S2CID 117201049.
- Chen, Ziguang; Bakenhus, Drew; Bobaru, Florin (November 2016). "A constructive peridynamic kernel for elasticity". Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. 311: 356–373. Bibcode:2016CMAME.311..356C. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2016.08.012.
- Bobaru, Florin; Duangpanya, Monchai (September 2010). "The peridynamic formulation for transient heat conduction". International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer. 53 (19–20): 4047–4059. Bibcode:2010IJHMT..53.4047B. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.05.024.
- ^ Huang, Dan; Lu, Guangda; Wang, Chongwen; Qiao, Pizhong (June 2015). "An extended peridynamic approach for deformation and fracture analysis". Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 141: 196–211. doi:10.1016/j.engfracmech.2015.04.036.
- Chen, Zhiyong; Woody Ju, J.; Su, Guoshao; Huang, Xiaohua; Li, Shuang; Zhai, Lianjun (July 2019). "Influence of micro-modulus functions on peridynamics simulation of crack propagation and branching in brittle materials". Engineering Fracture Mechanics. 216: 106498. doi:10.1016/j.engfracmech.2019.106498. S2CID 197621064.
- Ha, Youn Doh; Bobaru, Florin (March 2010). "Studies of dynamic crack propagation and crack branching with peridynamics". International Journal of Fracture. 162 (1–2): 229–244. doi:10.1007/s10704-010-9442-4. ISSN 0376-9429. S2CID 8462707.
- Kilic, Bahattin (2008). "Peridynamic Theory for Progressive Failure Prediction in Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Materials".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Agwai, Abigail; Guven, Ibrahim; Madenci, Erdogan (September 2011). "Predicting crack propagation with peridynamics: a comparative study". International Journal of Fracture. 171 (1): 65–78. doi:10.1007/s10704-011-9628-4. ISSN 0376-9429. S2CID 136475045.
- Lipton, Robert (October 2014). "Dynamic Brittle Fracture as a Small Horizon Limit of Peridynamics". Journal of Elasticity. 117 (1): 21–50. arXiv:1305.4531. doi:10.1007/s10659-013-9463-0. ISSN 0374-3535. S2CID 254462294.
- Silling, S. A.; Weckner, O.; Askari, E.; Bobaru, F. (March 2010). "Crack nucleation in a peridynamic solid". International Journal of Fracture. 162 (1–2): 219–227. doi:10.1007/s10704-010-9447-z. ISSN 0376-9429. S2CID 209225.
- Coclite, G. M.; Dipierro, S.; Fanizza, G.; Maddalena, F.; Romano, M.; Valdinoci, E. (March 2023). "Qualitative Aspects in Nonlocal Dynamics". Journal of Peridynamics and Nonlocal Modeling. 5 (1): 1–19. arXiv:2106.13596. doi:10.1007/s42102-021-00064-z. ISSN 2522-896X. S2CID 235652235.
- Seleson, Pablo; Parks, Michael L.; Gunzburger, Max; Lehoucq, Richard B. (January 2009). "Peridynamics as an Upscaling of Molecular Dynamics". Multiscale Modeling & Simulation. 8 (1): 204–227. doi:10.1137/09074807X. ISSN 1540-3459. OSTI 1678881.
- Behzadinasab, Masoud; Foster, John T. (April 2020). "A semi-Lagrangian constitutive correspondence framework for peridynamics". Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids. 137: 103862. Bibcode:2020JMPSo.13703862B. doi:10.1016/j.jmps.2019.103862. S2CID 212784700.
- Askari, E; Bobaru, F; Lehoucq, R B; Parks, M L; Silling, S A; Weckner, O (2008-07-01). "Peridynamics for multiscale materials modeling". Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 125 (1): 012078. Bibcode:2008JPhCS.125a2078A. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/125/1/012078. ISSN 1742-6596. S2CID 250694017.
- Ni, Tao; Pesavento, Francesco; Zaccariotto, Mirco; Galvanetto, Ugo; Zhu, Qi-Zhi; Schrefler, Bernhard A. (July 2020). "Hybrid FEM and peridynamic simulation of hydraulic fracture propagation in saturated porous media". Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering. 366: 113101. arXiv:2307.10929. Bibcode:2020CMAME.366k3101N. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2020.113101. S2CID 219519506.
- Zhou, Xiao-Ping; Wang, Yun-Teng; Shou, Yun-Dong (August 2020). "Hydromechanical bond-based peridynamic model for pressurized and fluid-driven fracturing processes in fissured porous rocks". International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences. 132: 104383. Bibcode:2020IJRMM.13204383Z. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104383. S2CID 225382857.
- Song, Xiaoyu; Khalili, Nasser (January 2019). "A peridynamics model for strain localization analysis of geomaterials". International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics. 43 (1): 77–96. Bibcode:2019IJNAM..43...77S. doi:10.1002/nag.2854. ISSN 0363-9061. S2CID 125649306.
- Panchadhara, Rohan; Gordon, Peter A.; Parks, Michael L. (March 2017). "Modeling propellant-based stimulation of a borehole with peridynamics". International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences. 93: 330–343. Bibcode:2017IJRMM..93..330P. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.02.006.
- Zhou, Xiao-Ping; Wang, Yun-Teng (January 2021). "State-of-the-Art Review on the Progressive Failure Characteristics of Geomaterials in Peridynamic Theory". Journal of Engineering Mechanics. 147 (1). doi:10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0001876. ISSN 0733-9399. S2CID 228906748.
- Lejeune, Emma; Linder, Christian (August 2017). "Modeling tumor growth with peridynamics". Biomechanics and Modeling in Mechanobiology. 16 (4): 1141–1157. doi:10.1007/s10237-017-0876-8. ISSN 1617-7959. PMID 28124191. S2CID 254169636.
- Taylor, Michael; Gözen, Irep; Patel, Samir; Jesorka, Aldo; Bertoldi, Katia (2016-11-09). van Veen, Hendrik W. (ed.). "Peridynamic Modeling of Ruptures in Biomembranes". PLOS ONE. 11 (11): e0165947. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1165947T. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0165947. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 5102442. PMID 27829001.
- Bobaru, Florin; Duangpanya, Monchai (April 2012). "A peridynamic formulation for transient heat conduction in bodies with evolving discontinuities". Journal of Computational Physics. 231 (7): 2764–2785. Bibcode:2012JCoPh.231.2764B. doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2011.12.017. S2CID 6929467.
- Oterkus, Selda; Madenci, Erdogan; Agwai, Abigail (May 2014). "Peridynamic thermal diffusion". Journal of Computational Physics. 265: 71–96. Bibcode:2014JCoPh.265...71O. doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2014.01.027. S2CID 22835224.
- Foster, John (2019). "Nonlocal and fractional order methods for near-wall turbulence, large-eddy simulation, and fluid-structure interaction". Technical Report, University of Texas at Austin Austin United States.
- Zhao, Jiangming; Chen, Ziguang; Mehrmashhadi, Javad; Bobaru, Florin (November 2018). "Construction of a peridynamic model for transient advection-diffusion problems". International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer. 126: 1253–1266. Bibcode:2018IJHMT.126.1253Z. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.06.075. S2CID 125321481.
- Buryachenko, Valeriy A. (October 2020). "Generalized effective fields method in peridynamic micromechanics of random structure composites". International Journal of Solids and Structures. 202: 765–786. doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2020.06.022. S2CID 225577923.
- Hu, Y.L.; Madenci, E. (January 2017). "Peridynamics for fatigue life and residual strength prediction of composite laminates". Composite Structures. 160: 169–184. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2016.10.010.
- Oterkus, Erkan; Madenci, Erdogan (2012-03-28). "Peridynamic analysis of fiber-reinforced composite materials". Journal of Mechanics of Materials and Structures. 7 (1): 45–84. doi:10.2140/jomms.2012.7.45. ISSN 1559-3959.
- Zhao, Jiangming; Jafarzadeh, Siavash; Rahmani, Mohammad; Chen, Ziguang; Kim, Yong-Rak; Bobaru, Florin (September 2021). "A peridynamic model for galvanic corrosion and fracture". Electrochimica Acta. 391: 138968. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138968.
Further reading
- Bobaru, Florin; Foster, John T.; Geubelle, Philippe H.; Silling, Stewart A., eds. (2016). Handbook of peridynamic modeling. Advances in applied mathematics. Boca Raton London New York: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, a Chapman & Hall book. ISBN 978-1-4822-3044-4.
- Oterkus, Erkan; Oterkus, Selda; Madenci, Erdogan (2021-04-24). Peridynamic Modeling, Numerical Techniques, and Applications. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-12-820441-2.
- Rabczuk, Timon; Ren, Huilong; Zhuang, Xiaoying (2023-02-15). Computational Methods Based on Peridynamics and Nonlocal Operators: Theory and Applications. Springer Nature. ISBN 978-3-031-20906-2.
- D’Elia, Marta; Li, Xingjie; Seleson, Pablo; Tian, Xiaochuan; Yu, Yue (March 2022). "A Review of Local-to-Nonlocal Coupling Methods in Nonlocal Diffusion and Nonlocal Mechanics". Journal of Peridynamics and Nonlocal Modeling. 4 (1): 1–50. arXiv:1912.06668. doi:10.1007/s42102-020-00038-7. ISSN 2522-896X. S2CID 257114051.
- Bobaru, Florin; Chen, Ziguang; Jafarzadeh, Siavash (2023-12-01). Corrosion Damage and Corrosion-Assisted Fracture: Peridynamic Modelling and Computations. Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-12-823174-6.
External links
- Implementation of finite element and finite difference approximation of Nonlocal models
- Peridigm, an open-source computational peridynamics code
- PeriDoX open-source repository for peridynamics and its documentation
- PeriLab open-source repository for peridynamics written in Julia
- Sandia Laboratory-Peridynamics
- Website on peridynamics
 for
for  for
for  within peridynamic theory. (b) Representation of peridynamic horizon of
within peridynamic theory. (b) Representation of peridynamic horizon of  .
. : the peridynamic horizon radius. This perspective approaches much more to
: the peridynamic horizon radius. This perspective approaches much more to  , where
, where  can be either 1, 2 or 3. The body has a positive
can be either 1, 2 or 3. The body has a positive  . Its reference configuration at the initial time is denoted by
. Its reference configuration at the initial time is denoted by  . It is important to note that the reference configuration can either be the
. It is important to note that the reference configuration can either be the  interacts with all the points
interacts with all the points  within a certain neighborhood defined by
within a certain neighborhood defined by  , where
, where  represents a suitable
represents a suitable  . This neighborhood is often referred to as
. This neighborhood is often referred to as  in the literature. It is commonly known as the horizon or the family of
in the literature. It is commonly known as the horizon or the family of  . Consequently, the position of
. Consequently, the position of  is determined by
is determined by  . Furthermore, for each pair of interacting points, the change in the length of the bond relative to the initial configuration is tracked over time through the relative
. Furthermore, for each pair of interacting points, the change in the length of the bond relative to the initial configuration is tracked over time through the relative  , which can be expressed as:
, which can be expressed as:

 denotes the
denotes the  .
.
 is referred to as a bond. These pairwise bonds have varying lengths over time in response to the force per unit volume squared, denoted as
is referred to as a bond. These pairwise bonds have varying lengths over time in response to the force per unit volume squared, denoted as
 .
.
 on
on  , is introduced, which results in the following equation of motion, representing the fundamental equation of peridynamics:
, is introduced, which results in the following equation of motion, representing the fundamental equation of peridynamics:

 is the sum of all of the internal and external per-unit-volume forces acting on
is the sum of all of the internal and external per-unit-volume forces acting on 
 is the force density that
is the force density that  .
.
 and
and  so that
so that

 . This expression reflects the principle of action and reaction, commonly known as
. This expression reflects the principle of action and reaction, commonly known as  belonging to the neighborhood
belonging to the neighborhood  . This condition arises from considering the relative deformed ray-
. This condition arises from considering the relative deformed ray- . The condition is satisfied if and only if the pairwise force density vector has the same direction as the relative deformed ray-vector. In other words,
. The condition is satisfied if and only if the pairwise force density vector has the same direction as the relative deformed ray-vector. In other words,  for all
for all  and
and  , where
, where  is a scalar-valued function.
is a scalar-valued function.

 ,
,

 is the scalar valued
is the scalar valued  . Due to the necessity of satisfying
. Due to the necessity of satisfying  follows
follows

 is a scalar valued function. Integrating both sides of the equation, the following condition on
is a scalar valued function. Integrating both sides of the equation, the following condition on  ,
,
 a scalar valued function. The
a scalar valued function. The  , in the deformed configuration
, in the deformed configuration  can be substituted with a dependence on its modulus
can be substituted with a dependence on its modulus  ,
,

 pairwise with
pairwise with  , the peridynamic kernel can be linearised around
, the peridynamic kernel can be linearised around  :
:


 and
and  is the identity tensor. Following application of linear momentum balance, elasticity and isotropy condition, the micro-modulus tensor can be expressed in this form
is the identity tensor. Following application of linear momentum balance, elasticity and isotropy condition, the micro-modulus tensor can be expressed in this form


 ,
,


 is defined as follow
is defined as follow
 with
with

 is referred to as the micro-modulus constant, and the function
is referred to as the micro-modulus constant, and the function  serves to indicate whether, at a given time
serves to indicate whether, at a given time  , the bond stretch
, the bond stretch  associated with the pair
associated with the pair  has surpassed the critical value
has surpassed the critical value  . If the critical value is exceeded, the bond is considered broken, and a pairwise force of zero is assigned for all
. If the critical value is exceeded, the bond is considered broken, and a pairwise force of zero is assigned for all  .
.

 is the material bulk modulus.
is the material bulk modulus.
 , where
, where  increases, but the specific manner in which this decrease occurs can vary.
increases, but the specific manner in which this decrease occurs can vary.

 is obtained by comparing peridynamic strain density with the classical mechanical theories;
is obtained by comparing peridynamic strain density with the classical mechanical theories;  is a function defined on
is a function defined on 
 is the
is the  .
. ,
,
 :
:  is the
is the  , defined as
, defined as




 with bond-breaking function
with bond-breaking function  versus bond stretching
versus bond stretching  in fracture formation is clear. However not only abrupt fracture can be modeled in peridynamic framework and more general expression for
in fracture formation is clear. However not only abrupt fracture can be modeled in peridynamic framework and more general expression for 
 is the force vector state field.
is the force vector state field.
 is a mathematical object similar to a
is a mathematical object similar to a 
 is a
is a  is called deformation vector state field and is defined by the following relation
is called deformation vector state field and is defined by the following relation

 is the image of the bond
is the image of the bond  under the deformation
under the deformation

 , while, if the constitutive relation is such that
, while, if the constitutive relation is such that
