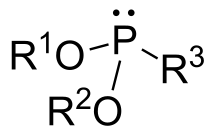
In organic chemistry, phosphonites are organophosphorus compounds with the formula P(OR)2R. They are found in some pesticides and are used as ligands.
Preparation
Although they are derivatives of phosphonous acid (RP(OH)2), they are not prepared from such precursors. Phosphonites are prepared by alcoholysis of organophosphinous chlorides. For example, treatment of dichlorophenylphosphine with methanol and base gives dimethyl phenylphosphonite:
- Cl2PPh + 2 CH3OH → (CH3O)2PPh + 2 HCl
Reactions
Oxidation of phosphonites gives phosphonates:
- 2 P(OR)2R + O2 → 2 OP(OR)2R
Phosphonites can function as ligands in homogeneous catalysis.
References
- D. E. C. Corbridge "Phosphorus: An Outline of its Chemistry, Biochemistry, and Technology" 5th Edition Elsevier: Amsterdam 1995. ISBN 0-444-89307-5.
- IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "phosphonous acids". doi:10.1351/goldbook.P04565
- T. V. (Babu) Rajanbabu “Phosphinite and Phosphonite Ligands” in Phosphorus(III) Ligands in Homogeneous Catalysis: Design and Synthesis Paul C. J. Kamer and Piet W. N. M. van Leeuwen, Eds., John Wiley & Sons 2012. doi:10.1002/9781118299715.ch5
| Organophosphorus | |
|---|---|
| Functional groups | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocarbons (only C and H) | |||||||||||||||
| Only carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (only C, H and O) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Only one element, not being carbon, hydrogen, or oxygen (one element, not C, H or O) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Other | |||||||||||||||