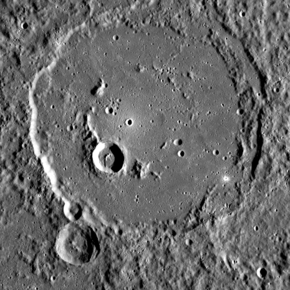
 An image of Polygnotus. Its central peak ring has been partially submerged by smooth plains material An image of Polygnotus. Its central peak ring has been partially submerged by smooth plains material | |
| Feature type | Peak-ring impact basin |
|---|---|
| Location | Kuiper quadrangle, Mercury |
| Coordinates | 0°08′S 69°16′W / 0.13°S 69.26°W / -0.13; -69.26 |
| Diameter | 124 km (77 mi) |
| Eponym | Polygnotus |
Polygnotus is a crater on Mercury, named by the IAU in 1976, after ancient Greek painter Polygnotus. The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.
Polygnotus has a central peak ring which is embayed with smooth plains material, which is very different in texture from the surrounding terrain. It is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury.
Boethius crater is west of Polygnotus. Tansen is to the northwest, and Motonobu is to the east.
-
 Exaggerated color image with Polygnotus near center
Exaggerated color image with Polygnotus near center
-
 Distant oblique view showing Polygnotus at right and Motonobu at top center
Distant oblique view showing Polygnotus at right and Motonobu at top center
References
- "Polygnotus". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. IAU/NASA/USGS. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- Davies, M. E.; Dwornik, S. E.; Gault, D. E.; Strom, R. G. (1978). Atlas of Mercury. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. pp. 1–128. ISBN 978-1-114-27448-8. Special Publication SP-423.
- MESSENGER Gathers Unprecedented Data about Mercury's Surface, Release Date: October 7, 2008. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington
- Chapman, C. R., Baker, D. M. H., Barnouin, O. S., Fassett, C. I., Marchie, S., Merline, W. J., Ostrach, L. R., Prockter, L. M., and Strom, R. G., 2018. Impact Cratering of Mercury. In Mercury: The View After MESSENGER edited by Sean C. Solomon, Larry R. Nittler, and Brian J. Anderson. Cambridge Planetary Science. Chapter 9.
This article about an impact crater on Mercury is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |