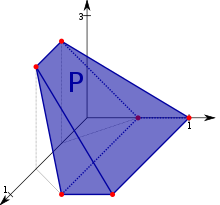
A convex polytope is a special case of a polytope, having the additional property that it is also a convex set contained in the -dimensional Euclidean space . Most texts use the term "polytope" for a bounded convex polytope, and the word "polyhedron" for the more general, possibly unbounded object. Others (including this article) allow polytopes to be unbounded. The terms "bounded/unbounded convex polytope" will be used below whenever the boundedness is critical to the discussed issue. Yet other texts identify a convex polytope with its boundary.
Convex polytopes play an important role both in various branches of mathematics and in applied areas, most notably in linear programming.
In the influential textbooks of Grünbaum and Ziegler on the subject, as well as in many other texts in discrete geometry, convex polytopes are often simply called "polytopes". Grünbaum points out that this is solely to avoid the endless repetition of the word "convex", and that the discussion should throughout be understood as applying only to the convex variety (p. 51).
A polytope is called full-dimensional if it is an -dimensional object in .
Examples
- Many examples of bounded convex polytopes can be found in the article "polyhedron".
- In the 2-dimensional case the full-dimensional examples are a half-plane, a strip between two parallel lines, an angle shape (the intersection of two non-parallel half-planes), a shape defined by a convex polygonal chain with two rays attached to its ends, and a convex polygon.
- Special cases of an unbounded convex polytope are a slab between two parallel hyperplanes, a wedge defined by two non-parallel half-spaces, a polyhedral cylinder (infinite prism), and a polyhedral cone (infinite cone) defined by three or more half-spaces passing through a common point.
Definitions
A convex polytope may be defined in a number of ways, depending on what is more suitable for the problem at hand. Grünbaum's definition is in terms of a convex set of points in space. Other important definitions are: as the intersection of half-spaces (half-space representation) and as the convex hull of a set of points (vertex representation).
Vertex representation (convex hull)
In his book Convex Polytopes, Grünbaum defines a convex polytope as a compact convex set with a finite number of extreme points:
- A set of is convex if, for each pair of distinct points , in , the closed segment with endpoints and is contained within .
This is equivalent to defining a bounded convex polytope as the convex hull of a finite set of points, where the finite set must contain the set of extreme points of the polytope. Such a definition is called a vertex representation (V-representation or V-description). For a compact convex polytope, the minimal V-description is unique and it is given by the set of the vertices of the polytope. A convex polytope is called an integral polytope if all of its vertices have integer coordinates.
Intersection of half-spaces
A convex polytope may be defined as an intersection of a finite number of half-spaces. Such definition is called a half-space representation (H-representation or H-description). There exist infinitely many H-descriptions of a convex polytope. However, for a full-dimensional convex polytope, the minimal H-description is in fact unique and is given by the set of the facet-defining halfspaces.
A closed half-space can be written as a linear inequality:
where is the dimension of the space containing the polytope under consideration. Hence, a closed convex polytope may be regarded as the set of solutions to the system of linear inequalities:
where is the number of half-spaces defining the polytope. This can be concisely written as the matrix inequality:
where is an matrix, is an column vector whose coordinates are the variables to , and is an column vector whose coordinates are the right-hand sides to of the scalar inequalities.
An open convex polytope is defined in the same way, with strict inequalities used in the formulas instead of the non-strict ones.
The coefficients of each row of and correspond with the coefficients of the linear inequality defining the respective half-space. Hence, each row in the matrix corresponds with a supporting hyperplane of the polytope, a hyperplane bounding a half-space that contains the polytope. If a supporting hyperplane also intersects the polytope, it is called a bounding hyperplane (since it is a supporting hyperplane, it can only intersect the polytope at the polytope's boundary).
The foregoing definition assumes that the polytope is full-dimensional. In this case, there is a unique minimal set of defining inequalities (up to multiplication by a positive number). Inequalities belonging to this unique minimal system are called essential. The set of points of a polytope which satisfy an essential inequality with equality is called a facet.
If the polytope is not full-dimensional, then the solutions of lie in a proper affine subspace of and the polytope can be studied as an object in this subspace. In this case, there exist linear equations which are satisfied by all points of the polytope. Adding one of these equations to any of the defining inequalities does not change the polytope. Therefore, in general there is no unique minimal set of inequalities defining the polytope.
In general the intersection of arbitrary half-spaces need not be bounded. However if one wishes to have a definition equivalent to that as a convex hull, then bounding must be explicitly required.
Equivalence to the vertex representation
By requiring that the intersection of half-spaces results in a bounded set, the definition becomes equivalent to the vertex-representation. An outline of the proof, that the bounded intersection of half-spaces results in a polytope in vertex-representation, follows:
The bounded intersection of closed half-spaces of is clearly compact and convex. A compact and convex set with a finite number of extreme points must be a polytope, where those extreme points form the set of vertices. It remains to show that the set of extreme points (of the bounded intersection of a finite set of half-spaces) is also finite:
Let be an extreme point of , the bounded intersection of closed half-spaces . We consider the intersection of all the corresponding hyperplanes (which divide the space into the half-spaces) that contain . This yields an affine subspace . For each half-space where the hyperplane does not contain , we consider the intersection of the interior of those half-spaces. This yields an open set . Clearly, . Since is an extreme point of and is relatively open, it follows that must be 0-dimensional and . If was not 0-dimensional, would be the inner point of (at least) a line, which contradicts being an extreme point. Since every construction of chooses either the interior or the boundary of one of the closed half-spaces, there are only finitely many different sets . Every extreme point lies in one of these sets, which means that the amount of extreme points is finite.
Using the different representations
The two representations together provide an efficient way to decide whether a given vector is included in a given convex polytope: to show that it is in the polytope, it is sufficient to present it as a convex combination of the polytope vertices (the V-description is used); to show that it is not in the polytope, it is sufficient to present a single defining inequality that it violates.
A subtle point in the representation by vectors is that the number of vectors may be exponential in the dimension, so the proof that a vector is in the polytope might be exponentially long. Fortunately, Carathéodory's theorem guarantees that every vector in the polytope can be represented by at most d+1 defining vectors, where d is the dimension of the space.
Representation of unbounded polytopes
For an unbounded polytope (sometimes called: polyhedron), the H-description is still valid, but the V-description should be extended. Theodore Motzkin (1936) proved that any unbounded polytope can be represented as a sum of a bounded polytope and a convex polyhedral cone. In other words, every vector in an unbounded polytope is a convex sum of its vertices (its "defining points"), plus a conical sum of the Euclidean vectors of its infinite edges (its "defining rays"). This is called the finite basis theorem.
Properties
Every (bounded) convex polytope is the image of a simplex, as every point is a convex combination of the (finitely many) vertices. However, polytopes are not in general isomorphic to simplices. This is in contrast to the case of vector spaces and linear combinations, every finite-dimensional vector space being not only an image of, but in fact isomorphic to, Euclidean space of some dimension (or analog over other fields).
The face lattice
Main article: abstract polytopeA face of a convex polytope is any intersection of the polytope with a halfspace such that none of the interior points of the polytope lie on the boundary of the halfspace. Equivalently, a face is the set of points giving equality in some valid inequality of the polytope.
If a polytope is d-dimensional, its facets are its (d − 1)-dimensional faces, its vertices are its 0-dimensional faces, its edges are its 1-dimensional faces, and its ridges are its (d − 2)-dimensional faces.
Given a convex polytope P defined by the matrix inequality , if each row in A corresponds with a bounding hyperplane and is linearly independent of the other rows, then each facet of P corresponds with exactly one row of A, and vice versa, as long as equality holds. Each point on a given facet will satisfy the linear equality of the corresponding row in the matrix. (It may or may not also satisfy equality in other rows). Similarly, each point on a ridge will satisfy equality in two of the rows of A.

In general, an (n − j)-dimensional face satisfies equality in j specific rows of A. These rows form a basis of the face. Geometrically speaking, this means that the face is the set of points on the polytope that lie in the intersection of j of the polytope's bounding hyperplanes.
The faces of a convex polytope thus form an Eulerian lattice called its face lattice, where the partial ordering is by set containment of faces. The definition of a face given above allows both the polytope itself and the empty set to be considered as faces, ensuring that every pair of faces has a join and a meet in the face lattice. The whole polytope is the unique maximum element of the lattice, and the empty set, considered to be a (−1)-dimensional face (a null polytope) of every polytope, is the unique minimum element of the lattice.
Two polytopes are called combinatorially isomorphic if their face lattices are isomorphic.
The polytope graph (polytopal graph, graph of the polytope, 1-skeleton) is the set of vertices and edges of the polytope only, ignoring higher-dimensional faces. For instance, a polyhedral graph is the polytope graph of a three-dimensional polytope. By a result of Whitney the face lattice of a three-dimensional polytope is determined by its graph. The same is true for simple polytopes of arbitrary dimension (Blind & Mani-Levitska 1987, proving a conjecture of Micha Perles). Kalai (1988) gives a simple proof based on unique sink orientations. Because these polytopes' face lattices are determined by their graphs, the problem of deciding whether two three-dimensional or simple convex polytopes are combinatorially isomorphic can be formulated equivalently as a special case of the graph isomorphism problem. However, it is also possible to translate these problems in the opposite direction, showing that polytope isomorphism testing is graph-isomorphism complete.
Topological properties
A convex polytope, like any compact convex subset of R, is homeomorphic to a closed ball. Let m denote the dimension of the polytope. If the polytope is full-dimensional, then m = n. The convex polytope therefore is an m-dimensional manifold with boundary, its Euler characteristic is 1, and its fundamental group is trivial. The boundary of the convex polytope is homeomorphic to an (m − 1)-sphere. The boundary's Euler characteristic is 0 for even m and 2 for odd m. The boundary may also be regarded as a tessellation of (m − 1)-dimensional spherical space — i.e. as a spherical tiling.
Simplicial decomposition
A convex polytope can be decomposed into a simplicial complex, or union of simplices, satisfying certain properties.
Given a convex r-dimensional polytope P, a subset of its vertices containing (r+1) affinely independent points defines an r-simplex. It is possible to form a collection of subsets such that the union of the corresponding simplices is equal to P, and the intersection of any two simplices is either empty or a lower-dimensional simplex. This simplicial decomposition is the basis of many methods for computing the volume of a convex polytope, since the volume of a simplex is easily given by a formula.
Scissors-congruency
Every convex polyhedron is scissors-congruent to an orthoscheme. Every regular convex polyhedron (Platonic solid) can be dissected into some even number of instances of its characteristic orthoscheme.
Algorithmic problems for a convex polytope
Construction of representations
Different representations of a convex polytope have different utility, therefore the construction of one representation given another one is an important problem. The problem of the construction of a V-representation is known as the vertex enumeration problem and the problem of the construction of a H-representation is known as the facet enumeration problem. While the vertex set of a bounded convex polytope uniquely defines it, in various applications it is important to know more about the combinatorial structure of the polytope, i.e., about its face lattice. Various convex hull algorithms deal both with the facet enumeration and face lattice construction.
In the planar case, i.e., for a convex polygon, both facet and vertex enumeration problems amount to the ordering vertices (resp. edges) around the convex hull. It is a trivial task when the convex polygon is specified in a traditional way for polygons, i.e., by the ordered sequence of its vertices . When the input list of vertices (or edges) is unordered, the time complexity of the problems becomes O(m log m). A matching lower bound is known in the algebraic decision tree model of computation.
Volume computation
The task of computing the volume of a convex polytope has been studied in the field of computational geometry. The volume can be computed approximately, for instance, using the convex volume approximation technique, when having access to a membership oracle. As for exact computation, one obstacle is that, when given a representation of the convex polytope as an equation system of linear inequalities, the volume of the polytope may have a bit-length which is not polynomial in this representation.
See also
- Oriented matroid
- Nef polyhedron
- Steinitz's theorem for convex polyhedra
References
- ^ Branko Grünbaum, Convex Polytopes, 2nd edition, prepared by Volker Kaibel, Victor Klee, and Günter M. Ziegler, 2003, ISBN 0-387-40409-0, ISBN 978-0-387-40409-7, 466pp.
- ^ Ziegler, Günter M. (1995), Lectures on Polytopes, Graduate Texts in Mathematics, vol. 152, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag.
- ^ Mathematical Programming, by Melvyn W. Jeter (1986) ISBN 0-8247-7478-7, p. 68
- Hug, Daniel; Weil, Wolfgang (2020). Lectures on convex geometry. Graduate texts in mathematics. Cham, Switzerland: Springer. pp. 30–35. ISBN 978-3-030-50180-8.
- ^ Lovász, László; Plummer, M. D. (1986), Matching Theory, Annals of Discrete Mathematics, vol. 29, North-Holland, ISBN 0-444-87916-1, MR 0859549
- Motzkin, Theodore (1936). Beitrage zur Theorie der linearen Ungleichungen (Ph.D. dissertation). Jerusalem.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Whitney, Hassler (1932). "Congruent graphs and the connectivity of graphs". Amer. J. Math. 54 (1): 150–168. doi:10.2307/2371086. hdl:10338.dmlcz/101067. JSTOR 2371086.
- Blind, Roswitha; Mani-Levitska, Peter (1987), "Puzzles and polytope isomorphisms", Aequationes Mathematicae, 34 (2–3): 287–297, doi:10.1007/BF01830678, MR 0921106, S2CID 120222616.
- Kalai, Gil (1988), "A simple way to tell a simple polytope from its graph", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Ser. A, 49 (2): 381–383, doi:10.1016/0097-3165(88)90064-7, MR 0964396.
- Kaibel, Volker; Schwartz, Alexander (2003). "On the Complexity of Polytope Isomorphism Problems". Graphs and Combinatorics. 19 (2): 215–230. arXiv:math/0106093. doi:10.1007/s00373-002-0503-y. S2CID 179936. Archived from the original on 2015-07-21.
- Glen E. Bredon, Topology and Geometry, 1993, ISBN 0-387-97926-3, p. 56.
- Büeler, B.; Enge, A.; Fukuda, K. (2000). "Exact Volume Computation for Polytopes: A Practical Study". Polytopes — Combinatorics and Computation. pp. 131–154. doi:10.1007/978-3-0348-8438-9_6. ISBN 978-3-7643-6351-2.
- Cormen, Thomas H.; Leiserson, Charles E.; Rivest, Ronald L.; Stein, Clifford (2001) . "33.3 Finding the convex hull". Introduction to Algorithms (2nd ed.). MIT Press and McGraw-Hill. pp. 947–957. ISBN 0-262-03293-7.
- Yao, Andrew Chi Chih (1981), "A lower bound to finding convex hulls", Journal of the ACM, 28 (4): 780–787, doi:10.1145/322276.322289, MR 0677089, S2CID 13846330; Ben-Or, Michael (1983), "Lower Bounds for Algebraic Computation Trees", Proceedings of the Fifteenth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing (STOC '83), pp. 80–86, doi:10.1145/800061.808735.
- Lawrence, Jim (1991). "Polytope volume computation". Mathematics of Computation. 57 (195): 259–271. Bibcode:1991MaCom..57..259L. doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-1991-1079024-2. ISSN 0025-5718.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Convex polygon". MathWorld.
- Weisstein, Eric W. "Convex polyhedron". MathWorld.
- Komei Fukuda, Polyhedral computation FAQ.
 -dimensional Euclidean space
-dimensional Euclidean space  . Most texts use the term "polytope" for a
. Most texts use the term "polytope" for a  of
of  ,
,  in
in 

 is the number of half-spaces defining the polytope. This can be concisely written as the
is the number of half-spaces defining the polytope. This can be concisely written as the 
 is an
is an  matrix,
matrix,  is an
is an  column vector whose coordinates are the variables
column vector whose coordinates are the variables  to
to  , and
, and  column vector whose coordinates are the right-hand sides
column vector whose coordinates are the right-hand sides  to
to  of the scalar inequalities.
of the scalar inequalities.
 be an extreme point of
be an extreme point of  , the bounded intersection of closed half-spaces
, the bounded intersection of closed half-spaces  . We consider the intersection of all the corresponding hyperplanes (which divide the space into the half-spaces) that contain
. We consider the intersection of all the corresponding hyperplanes (which divide the space into the half-spaces) that contain  . For each half-space where the hyperplane does not contain
. For each half-space where the hyperplane does not contain  . Clearly,
. Clearly,  . Since
. Since  and
and  is
is  must be 0-dimensional and
must be 0-dimensional and  . If
. If  closed half-spaces, there are only finitely many different sets
closed half-spaces, there are only finitely many different sets  . When the input list of vertices (or edges) is unordered, the
. When the input list of vertices (or edges) is unordered, the