A population model is a type of mathematical model that is applied to the study of population dynamics.
Rationale
Models allow a better understanding of how complex interactions and processes work. Modeling of dynamic interactions in nature can provide a manageable way of understanding how numbers change over time or in relation to each other. Many patterns can be noticed by using population modeling as a tool.
Ecological population modeling is concerned with the changes in parameters such as population size and age distribution within a population. This might be due to interactions with the environment, individuals of their own species, or other species.
Population models are used to determine maximum harvest for agriculturists, to understand the dynamics of biological invasions, and for environmental conservation. Population models are also used to understand the spread of parasites, viruses, and disease.
Another way populations models are useful are when species become endangered. Population models can track the fragile species and work and curb the decline.
History
Late 18th-century biologists began to develop techniques in population modeling in order to understand the dynamics of growing and shrinking of all populations of living organisms. Thomas Malthus was one of the first to note that populations grew with a geometric pattern while contemplating the fate of humankind. One of the most basic and milestone models of population growth was the logistic model of population growth formulated by Pierre François Verhulst in 1838. The logistic model takes the shape of a sigmoid curve and describes the growth of a population as exponential, followed by a decrease in growth, and bound by a carrying capacity due to environmental pressures.
Population modeling became of particular interest to biologists in the 20th century as pressure on limited means of sustenance due to increasing human populations in parts of Europe were noticed by biologist like Raymond Pearl. In 1921 Pearl invited physicist Alfred J. Lotka to assist him in his lab. Lotka developed paired differential equations that showed the effect of a parasite on its prey. Mathematician Vito Volterra equated the relationship between two species independent from Lotka. Together, Lotka and Volterra formed the Lotka–Volterra model for competition that applies the logistic equation to two species illustrating competition, predation, and parasitism interactions between species. In 1939 contributions to population modeling were given by Patrick Leslie as he began work in biomathematics. Leslie emphasized the importance of constructing a life table in order to understand the effect that key life history strategies played in the dynamics of whole populations. Matrix algebra was used by Leslie in conjunction with life tables to extend the work of Lotka. Matrix models of populations calculate the growth of a population with life history variables. Later, Robert MacArthur and E. O. Wilson characterized island biogeography. The equilibrium model of island biogeography describes the number of species on an island as an equilibrium of immigration and extinction. The logistic population model, the Lotka–Volterra model of community ecology, life table matrix modeling, the equilibrium model of island biogeography and variations thereof are the basis for ecological population modeling today.
Equations
Logistic growth equation:
Competitive Lotka–Volterra equations:
Examples of individual-based models

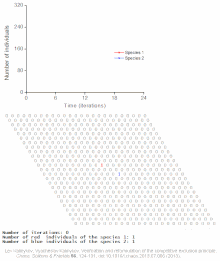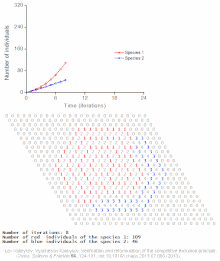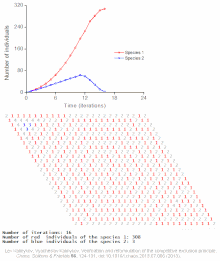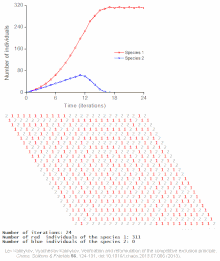
See also
References
- Worster, Donald (1994). Nature's Economy. Cambridge University Press. pp. 398–401.
- ^ Uyenoyama, Marcy (2004). Rama Singh (ed.). The Evolution of Population Biology. Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–19.
- ^ McIntosh, Robert (1985). The Background of Ecology. Cambridge University Press. pp. 171–198.
- Renshaw, Eric (1991). Modeling Biological Populations in Space and Time. Cambridge University Press. pp. 6–9.
- Kingsland, Sharon (1995). Modeling Nature: Episodes in the History of Population Ecology. University of Chicago Press. pp. 127–146.
- Gotelli, Nicholas (2001). A Primer of Ecology. Sinauer.
External links
- GreenBoxes code sharing network. Greenboxes (Beta) is a repository for open-source population modeling code. Greenboxes allows users an easy way to share their code and to search for others shared code.
| Scientific modelling | |
|---|---|
| Biological | |
| Environmental | |
| Sustainability | |
| Social | |
| Related topics | |
| Population | |
|---|---|
| Major topics | |
| Population biology | |
| Population ecology | |
| Society and population | |
| Publications | |
| Lists | |
| Events and organizations |
|
| Related topics | |



