| Poronay 幌内 | |
|---|---|
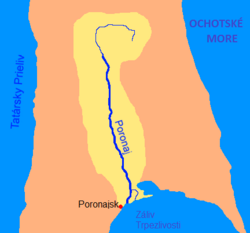 Map of the Poronay watershed Map of the Poronay watershed | |
 Location of the mouth of the Poronay within Sakhalin Oblast Location of the mouth of the Poronay within Sakhalin Oblast | |
| Etymology | Ainu for "big river" |
| Native name | Поронай (Russian) |
| Location | |
| Country | Russia |
| State | Sakhalin Oblast |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Mount Nevel |
| • location | East Sakhalin Mountains |
| • coordinates | 50°22′19.30″N 143°10′56.33″E / 50.3720278°N 143.1823139°E / 50.3720278; 143.1823139 |
| Mouth | Gulf of Patience |
| • location | Sea of Okhotsk |
| • coordinates | 49°13′31.77″N 143°07′23.44″E / 49.2254917°N 143.1231778°E / 49.2254917; 143.1231778 |
| Length | 350 km (220 mi) |
| Basin size | 7,990 km (3,080 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Pacific Ocean |
| • average | 120 m/s (4,200 cu ft/s) |
The Poronay (Russian: Поронай, Japanese: 幌内川) is the longest river on the island of Sakhalin in Russia. It flows in a southerly direction through Tym, Smirnykhovsky and Poronaysky Districts.
Geography
The river begins on Mt. Nevel in the East Sakhalin Mountains, flows south through the swampy wetlands of the Tym-Poronay Valley, and enters the Sea of Okhotsk in the Gulf of Patience. 10 km (6 mi) before it enters the sea, the river divides into two arms, which flow into the sea 5 km (3 mi) apart from each other. The two branches create a marshy river island in the middle. The town of Poronaysk is located near the western mouth of the river.
The Poronay is crossed by only two bridges, one rail and one road bridge. Both bridges are next to each other, in the middle of the river between the towns of Pobedino and Pervomaysk. The river valley, especially the area between the downstream Poronay and the Deer River (a small river to the east), has many lakes. The Poronay river system is a rich breeding ground for salmon and other anadromous fish, as well as freshwater fish such as Amur pike.
Hydrology
The river is fed by both snowmelt and rain. Average water flow is 120 m³/s. The highest level of flow has been observed in early May, and the lowest in the second half of September. The river usually freezes in the second half of November, while the ice thaws in late April.
List of tributaries
The length of each tributary is given in parentheses:
- Right tributaries
- Leonidovka (95)
- Orlovka (83)
- Onorka (77)
- Kamenka (Nizhnyaya Matrosovka) (71)
- Buyuklinka (63)
- Yelnaya (61)
- Longari (55 )
- Severnaya Khandasa (54)
- Yuzhnaya Khandasa (51)
- Pobedinka (49)
- Taulan (41)
- Tumannaya (34)
- Daldaganka (31)
- Tayozhnaya (31)
- Left tributaries
- Zhitnitsa (Muyka) (61)
- Valza (50)
- Borisovka (38)
- Kresty (36)
References
- Poronay in the "Dictionary of Modern Geographical Names" (in Russian, retrieved 2012-08-27)
- "Государственный водный реестр РФ: Поронай". Archived from the original on 2016-02-06.
- ^ Poronay Archived 2013-09-22 at the Wayback Machine - an article in the Great Soviet Encyclopedia. (In Russian, retrieved 2012-08-28.)
- Skopets, Mikhail. "Sakhalin Island, Poronai River, Part 1." Flyfishing Russia. Blog post, 16 August 2009. Retrieved 28 August 2012.