| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (June 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Posterior interosseous nerve | |
|---|---|
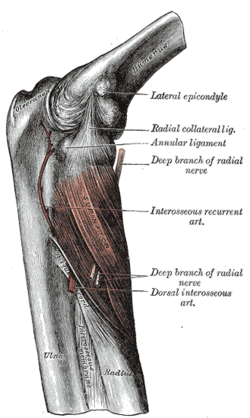 The supinator. (Deep branch of radial nerve labeled at upper right and lower right. Dorsal interosseous is this nerve after passing the supinator, at lower right.) The supinator. (Deep branch of radial nerve labeled at upper right and lower right. Dorsal interosseous is this nerve after passing the supinator, at lower right.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Deep branch of the radial nerve |
| Innervates | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus interosseus antebrachii posterior |
| TA98 | A14.2.03.055 |
| TA2 | 6437 |
| FMA | 77559 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy[edit on Wikidata] | |
The posterior interosseous nerve (or dorsal interosseous nerve/deep radial nerve) is a nerve in the forearm. It is the continuation of the deep branch of the radial nerve, after this has crossed the supinator muscle. It is considerably diminished in size compared to the deep branch of the radial nerve. The nerve fibers originate from cervical segments C7 and C8 in the spinal column.
Structure
Course
It descends along the interosseous membrane, anterior to the extensor pollicis longus muscle, to the back of the carpus, where it presents a gangliform enlargement from which filaments are distributed to the ligaments and articulations of the carpus.
Supply
The posterior interosseous nerve supplies all the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm, except anconeus muscle, brachioradialis muscle, and extensor carpi radialis longus muscle. In other words, it supplies the following muscles:
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle — deep branch of radial nerve
- Extensor digitorum muscle
- Extensor digiti minimi muscle
- Extensor carpi ulnaris muscle
- Supinator muscle — deep branch of radial nerve
- Abductor pollicis longus muscle
- Extensor pollicis brevis muscle
- Extensor pollicis longus muscle
- Extensor indicis muscle
The posterior interosseous nerve provides proprioception to the joint capsule of the distal radioulnar articulation, but not pain sensation.
Clinical significance
The posterior interosseous nerve may be entrapped at the arcade of Frohse, which is part of the supinator muscle. This nerve can be injured in Monteggia fracture due to dislocation of the proximal head of radius bone.
Posterior interosseous neuropathy is purely a motor syndrome resulting in finger drop due to no extension of IP joints and radial wrist deviation on extension.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 944 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918).
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 944 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918).
- Slutsky, David J. (2006). "Chapter 4 - A Practical Approach to Nerve Grafting in the Upper Extremity". Peripheral Nerve Surgery - Practical Applications in the Upper Extremity. Elsevier, Churchill Livingstone. pp. 61–80. doi:10.1016/B978-0-443-06667-2.50009-5. ISBN 978-0-443-06667-2.
| Nerve supply of the human arm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supraclavicular | |||||||
| Infraclavicular |
| ||||||
| Other | |||||||
This neuroanatomy article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |