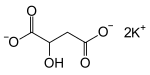
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name dipotassium 2-hydroxybutanedioate | |
| Other names Dipotassium malate; E351 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.683 |
| E number | E351 (antioxidants, ...) |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C4H4K2O5 |
| Molar mass | 210.268 g·mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium malate is a compound with formula K2(C2H4O(COO)2). It is the potassium salt of malic acid.
As a food additive, it has the E number E351. It is used as acidity regulator or acidifier for use in, for example, canned vegetables, soups, sauces, fruit products, and soft drinks. It also acts as an antioxidant and a food flavoring agent.
It is an important compound in the transport of nitrate from the roots of a plant to the leaves of the plant. Potassium malate is the salt that transports from the leaves to the root. At the root, the potassium malate oxidizes to potassium carbonate, then is converted to potassium nitrate by soil nitrate and transported back to the leaves.
References
- "Approved additives and E numbers". UK Food Standards Agency.
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |