| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Process variable" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In control theory, a process variable (PV; also process value or process parameter) is the current measured value of a particular part of a process which is being monitored or controlled. An example of this would be the temperature of a furnace. The current temperature is the process variable, while the desired temperature is known as the set-point (SP).
Control system use
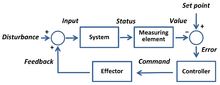
Measurement of process variables is essential in control systems to controlling a process. The value of the process variable is continuously monitored so that control may be exerted.
Four commonly measured variables that affect chemical and physical processes are: pressure, temperature, level and flow. but there are in fact a large number of measurement quantities which for international purposes use the International System of Units (SI)
The SP-PV error is used to exert control on a process so that the value of PV equals the value of the SP. A classic use of this is in the PID controller.
References
- B. Wayne Bequette (2003). Process Control: Modeling, Design, and Simulation. Prentice Hall Professional. p. 5. ISBN 9780133536409.
This technology-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |