| This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. Please help improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (January 2025) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Project Galileo is an educational astronomy project based at Clifton College in Bristol in the United Kingdom.
History
Project Galileo started in December 2000, as a result of a telescope being donated to a Bristol school, with the overall aim of making the system available for other schools in the area to use. The system became operational in July 2005, and achieved full on-line capability by the autumn of 2008, running until the main project co-ordinator left teaching.
Aims
Project Galileo aims to provide a curriculum resource for Science and Technology at Key Stages 3 & 4 and AS/A2 levels, including ICT & Design & Technology courses at post-16 level, to inspire teenagers to "learn the art as well as science of research and research teams, how scientific research is practiced, how physical ideas become mainstream, how collaboration between scientific disciplines fosters greater understanding, and to encourage links and collaboration between schools of different age-ranges and traditions in the city of Bristol." (Project FAQ)
The project focuses on the issues surrounding the maintenance and successful operation of a remote-controlled observatory. It is built around a remote-controlled telescope with a 1.3 metre dome and CCD camera located in Bristol, which enables imaging and searches of comets, asteroids, supernovae, deep-sky and planetary objects.
How it works
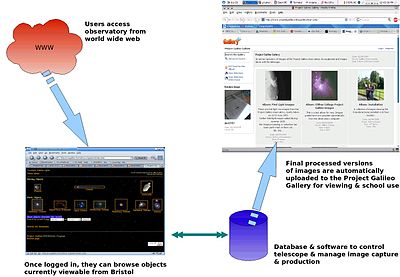
Schools registered via the main Project Galileo website, and then logged in to the telescope to order images, much in the same way as is done with other online school observatories. One important feature of the software being developed for the project is that it comes under the GPL, so other schools or institutions who want to develop similar systems will be able to modify the code rather than having to spend vital educational budgets for proprietary software.
Here is a simplified diagram of how the system works:
Results so far
-
 M13 Globular Cluster, July 2005
M13 Globular Cluster, July 2005
-
 M27 Planetary Nebula, July 2005
M27 Planetary Nebula, July 2005
-
 M42, Orion Nebula, December 2005
M42, Orion Nebula, December 2005
-
 Saturn, raw rgb images, December 2005
Saturn, raw rgb images, December 2005
See also
References
- Physics Education (January2003) (Institute of Physics, UK. )
- Models, Kits, and Astronomy Projects ] (Particle Physics and Astronomy Research Council, UK. )
External links
- Official website
- Clifton College Project Galileo page
- Sourceforge software developer's page for Project Galileo