| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "QM-AM-GM-HM inequalities" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
In mathematics, the QM-AM-GM-HM inequalities, also known as the mean inequality chain, state the relationship between the harmonic mean, geometric mean, arithmetic mean, and quadratic mean (also known as root mean square). Suppose that are positive real numbers. Then
These inequalities often appear in mathematical competitions and have applications in many fields of science.
Proof
There are three inequalities between means to prove. There are various methods to prove the inequalities, including mathematical induction, the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality, Lagrange multipliers, and Jensen's inequality. For several proofs that GM ≤ AM, see Inequality of arithmetic and geometric means.
AM-QM inequality
From the Cauchy–Schwarz inequality on real numbers, setting one vector to (1, 1, ...):
- hence . For positive the square root of this gives the inequality.
HM-GM inequality
The reciprocal of the harmonic mean is the arithmetic mean of the reciprocals , and it exceeds by the AM-GM inequality. implies the inequality:
The n = 2 case

When n = 2, the inequalities become
- for all
which can be visualized in a semi-circle whose diameter is and center D.
Suppose AC = x1 and BC = x2. Construct perpendiculars to at D and C respectively. Join and and further construct a perpendicular to at G. Then the length of GF can be calculated to be the harmonic mean, CF to be the geometric mean, DE to be the arithmetic mean, and CE to be the quadratic mean. The inequalities then follow easily by the Pythagorean theorem.
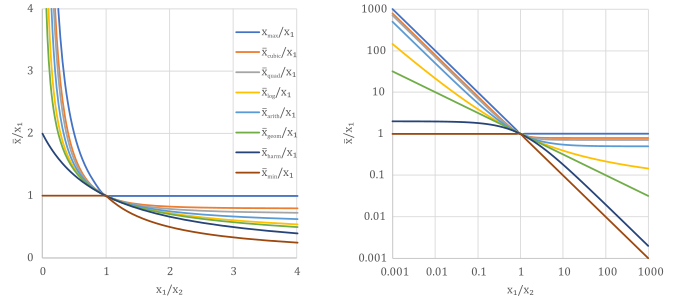
Tests
To infer the correct order, the four expressions can be evaluated with two positive numbers.
For and in particular, this results in .
See also
References
- Djukić, Dušan (2011). The IMO compendium: a collection of problems suggested for the International Mathematical Olympiads, 1959-2009. Problem books in mathematics. International mathematical olympiad. New York: Springer. p. 7. ISBN 978-1-4419-9854-5.
- Sedrakyan, Hayk; Sedrakyan, Nairi (2018), Sedrakyan, Hayk; Sedrakyan, Nairi (eds.), "The HM-GM-AM-QM Inequalities", Algebraic Inequalities, Problem Books in Mathematics, Cham: Springer International Publishing, p. 23, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-77836-5_3, ISBN 978-3-319-77836-5, retrieved 2023-11-26
- Sedrakyan, Hayk; Sedrakyan, Nairi (2018), Sedrakyan, Hayk; Sedrakyan, Nairi (eds.), "The HM-GM-AM-QM Inequalities", Algebraic Inequalities, Problem Books in Mathematics, Cham: Springer International Publishing, p. 21, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-77836-5_3, ISBN 978-3-319-77836-5, retrieved 2023-11-26
External links
- The HM-GM-AM-QM Inequalities
- Useful inequalities cheat sheet entry "means" on the right of page 1
 are positive
are positive 
 hence
hence  . For positive
. For positive  the square root of this gives the inequality.
the square root of this gives the inequality. , and it exceeds
, and it exceeds  by the AM-GM inequality.
by the AM-GM inequality.  implies the inequality:
implies the inequality:

 for all
for all 
 and
and 
 and
and  in particular, this results in
in particular, this results in  .
.