| Ribonuclease PH | |
|---|---|
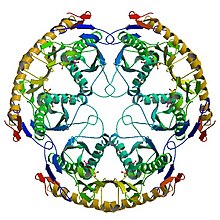 Structure of the RNase PH hexamer Structure of the RNase PH hexamer | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | RNASEPH |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 2.7.7.56 |
RNase PH is a tRNA nucleotidyltransferase, present in archaea and bacteria, that is involved in tRNA processing. Contrary to hydrolytic enzymes, it is a phosphorolytic enzyme, meaning that it uses inorganic phosphate as a reactant to cleave nucleotide-nucleotide bonds, releasing diphosphate nucleotides. The active structure of the proteins is a homohexameric complex, consisting of three ribonuclease (RNase) PH dimers. RNase PH has homologues in many other organisms, which are referred to as RNase PH-like proteins. The part of another larger protein with a domain that is very similar to RNase PH is called an RNase PH domain (RPD).
See also
Two highly related exoribonuclease complexes:
References
- Ishii R, Nureki O, Yokoyama S (August 2003). "Crystal structure of the tRNA processing enzyme RNase PH from Aquifex aeolicus". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (34): 32397–404. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300639200. PMID 12746447.
External links
| Transferases: phosphorus-containing groups (EC 2.7) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.7.1-2.7.4: phosphotransferase/kinase (PO4) |
| ||||||||||||||
| 2.7.6: diphosphotransferase (P2O7) | |||||||||||||||
| 2.7.7: nucleotidyltransferase (PO4-nucleoside) |
| ||||||||||||||
| 2.7.8: miscellaneous |
| ||||||||||||||
| 2.7.10-2.7.13: protein kinase (PO4; protein acceptor) |
| ||||||||||||||
| Enzymes | |
|---|---|
| Activity | |
| Regulation | |
| Classification | |
| Kinetics | |
| Types |
|
This genetics article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |