
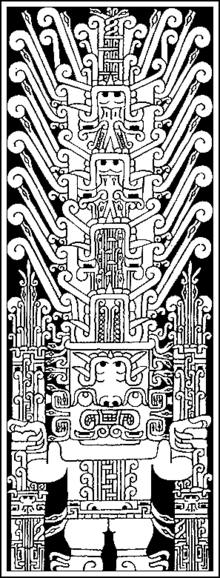
The Raimondi Stele is a sacred object and significant piece of art of the Chavín culture of the central Andes in present-day Peru. The Chavín were named after Chavín de Huantar, the main structure found in ruin at this archaeological site. The Chavín are believed to have occupied this space from 1500 BCE to 300 BCE, which places them in the Early Horizon period of Andean cultures. The Early Horizon came to rise after the spread and domination of Chavín art styles, namely the hanging pendant eye and anthropomorphism/zoomorphism of feline, serpent, and crocodilian creatures. The stele is seven feet high, made of highly polished granite, with a lightly incised design featuring these key artistic choices shown in the depiction of the Staff God. After not being found in situ (in its original intended position), the stele now is housed in the courtyard of the Museo Nacional de Arqueología Antropología e Historia del Perú in Lima.
Finding
The first modern record of someone writing about their finding of the stele was José Toribio Polo in 1871, but his sights at the time were more set on the Lanzón. Two years later in 1873, Antonio Raimondi, an Italian-Peruvian naturalist, visited Chavín de Huantar and described the structure as a "fortress," taking note of the stele in the ceremonial center. As mentioned previously, the Raimondi Stele was not found in situ, but instead in the home of Timoteo Espinoza, a local farmer. According to Raimondi and other accounts of travelers at the time, the local people of Peru would collect and display objects representative of the past in their homes, aligning themselves with the past while also protecting their history.
Once the modern world knew about the existence of the stele, Polo returned and focused his 1891/1892 study on the monolith. After excavations done by Julio C. Tello years later, it was confirmed that structures like the Raimondi Stele existed elsewhere on the grounds (the Tello Obelisk, for example) and led to further investigations of the purposes of these monoliths.
Visual analysis
Chavin artists frequently used the technique of contour rivalry in their art forms, and the Raimondi Stele shows this technique through dualism in the imagery of an indigenous god and its adornments. Contour rivalry means that the lines in an image can be read in multiple ways, depending on which way the object is being viewed, and in Chavín culture it is often used to enlighten those who can understand the iconography and exclude those who can not.
When the Raimondi Stela is viewed one way, the image depicts a fearsome deity, the Staff God, holding a staff in each hand that also double as Huachuma (or San Pedro) cactus. Spiritual leaders and elite would drink the juice from the San Pedro Cactus that would elicit a hallucinogenic response, allowing them to become closer to the deities that they honored. The eyes of the figure look upward toward his large, elaborate headdress of snakes and volutes. Contour rivalry is found not only in the physical transformation of the monolith, but also in the iconography. The Staff God's staffs are also vegetation, his belt is also a face, the ears of the face on the belt are snakes, and his headdress is made up of caiman.
When flipped upside-down, the same image can be seen differently. The headdress can be "read" as a stacked row of smiling, fanged faces, while the deity's face has turned into the face of a smiling reptile. The deity's staffs also appear to be rows of stacked faces. This technique speaks to larger Andean concerns of the duality and reciprocal nature of nature, life, and society. The idea of transformation (through flipping a stone structure, making an image out of other images, or taking hallucinogens) is intrinsic to the Chavín cosmology. This theme is found in the art of many other Andean indigenous civilizations.
In total, there are 10 sets of eyes, 11 mouths, and 50 snakes within the figure and staffs. As common in Chavin art, there is extreme attention paid to maintaining bilateral symmetry, this naturally creates further contour rivalry in all orientations of the Raimondi Stele. A classic response to taking hallucinogens, the Chavin were interested in the interconnectedness of all things. The entire composition utilizes similar forms and line work to represent flora, fauna, and the human. The enter-locking mouth motif, common throughout Chavin art, is seen on the torso of the figure.
Cosmology
The main figure in the image on the Raimondi Stele is the Staff God, an anthropomorphic creature that exhibits human, feline, reptilian, and avian characteristics. The animals represented were highly mythologized and rumored in Andean cultures because of their geographic location. They are all apex predators and lived in the jungles just above the mountain ranges, using their power and prowess to thrive. These characteristics of strength reflect on what was thought of the Staff God, considering he was the main deity of the Chavín, showing his all-encompassing power and rule.
The duality of the Raimondi Stele is shown throughout the entire structure. The image is perfectly symmetrical, placing an emphasis on the mirroring and double-imaging shown. Part of understanding the stele is in the looking; the whole structure would have to be turned upside down to see the other image. Because the Staff God is so paramount to the Chavín worldview, the image was made difficult to see to separate those within the community from those outside. The interaction with the stone is not passive, it requires the viewer to become active in the knowing of this deity by either moving their head and body to see the other side, physically lifting the stone to flip the double image, or simply just focusing on the low relief that the stele was carved in to really observe all that is happening in the imagery. The transformation of the stone object reflects the transformation that the viewers of the Raimondi Stele would so often undergo. The duality shown through double meaning and contour rivalry is indicative of the importance of duality in their everyday lives: night and day, rainy and dry season, life and death, etc.
See also
References
- "Chavin (Archaeological Site)".
- ^ Fux, Peter, ed. (2013). Chavín : Peru's enigmatic temple in the Andes. Zurich. ISBN 9783858817310. OCLC 834407719.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Gänger, Stefanie (May 2014). Relics of the past : the collecting and study of pre-Columbian antiquities in Peru and Chile, 1837-1911 (First ed.). Oxford, United Kingdom. ISBN 9780199687695. OCLC 879398377.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - "Chavín de Huántar". Khan Academy. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
- ^ Stone, Rebecca (2012). Art of the Andes : from Chavin to Inca. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 9780500204153. OCLC 792747356.
- ^ Weismantel, Mary J. / Inhuman eyes : Looking at Chavín de Huantar. Relational Archaeologies: Humans, Animals, Things. Taylor and Francis, 2014. pp. 21-41
- ^ "Complexity and vision: the Staff God at Chavín de Huántar and beyond – Smarthistory". smarthistory.org. Retrieved 2019-04-30.
External links
- Raimondi Stele Full Image