| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Ratchet" device – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (November 2023) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Red arrows indicate which way force is applied to the gear.

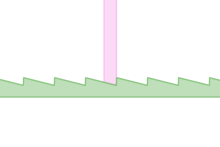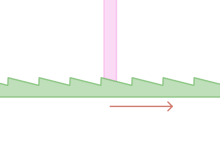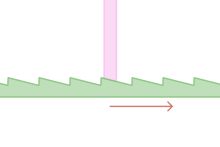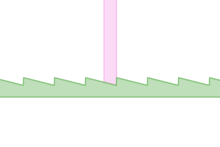
Red arrows indicate which way force is applied to the gear rack. The rack and pawl are both restricted to only linear movement (not shown).
A ratchet (occasionally spelled rachet) is a mechanical device that allows continuous linear or rotary motion in only one direction while preventing motion in the opposite direction. Ratchets are widely used in machinery and tools. The word ratchet is also used informally to refer to a ratcheting socket wrench.
Theory of operation
A ratchet consists of a round gear or a linear rack with teeth, and a pivoting, spring-loaded finger called a pawl (or click, in clocks and watches) that engages the teeth. The teeth are uniform but are usually asymmetrical, with each tooth having a moderate slope on one edge and a much steeper slope on the other edge.
When the teeth are moving in the unrestricted (i.e. forward) direction, the pawl easily slides up and over the gently sloped edges of the teeth, with a spring forcing it (often with an audible 'click') into the depression between the teeth as it passes the tip of each tooth. When the teeth move in the opposite (backward) direction, however, the pawl will catch against the steeply sloped edge of the first tooth it encounters, thereby locking it against the tooth and preventing any further motion in that direction.
Backlash
Because the ratchet can only stop backward motion at discrete points (i.e., at tooth boundaries), a ratchet does allow a limited amount of backward motion. This backward motion—which is limited to a maximum distance equal to the spacing between the teeth—is called backlash. In cases where backlash must be minimized, a smooth, toothless ratchet with a high friction surface such as rubber is sometimes used. The pawl bears against the surface at an angle so that any backward motion will cause the pawl to jam against the surface and thus prevent any further backward motion. Since the backward travel distance is primarily a function of the compressibility of the high friction surface, this mechanism can result in significantly reduced backlash.
Uses
Ratchet mechanisms are used in a wide variety of applications, including these:
- Cable ties
- Capstans
- Caulking guns
- Clocks
- Computer keyboards
- Freewheel (overrunning clutch)
- Grease guns
- Handcuffs
- Jacks
- Anti-rollback devices used in roller coasters
- Looms
- Slacklines
- Socket wrenches
- Tie down straps
- Turnstiles
- Typewriters
Gallery
-
 Ratcheting socket wrench or spanner.
Ratcheting socket wrench or spanner.
-
 A ratchet lever hoist, also known as a 'come-along.'
A ratchet lever hoist, also known as a 'come-along.'
-
The ratchet mechanism of a cable tie.
- Setting the bezel of a diving watch to the start time of a dive. For safety reasons, the ring has a ratchet so it cannot be turned or knocked in the opposite direction.
See also
- Brownian ratchet
- Sprag clutch
- Check valve, a device that allows fluids to flow in only one direction
- Diode, a device that allows electric current to flow in only one direction
References
- hautehorlogerie.org
- "Know your terminology – Clocks". Hints and Tips. British Horological Institute. Archived from the original on 2008-06-07. Retrieved 2008-05-15.