| Part of a series on |
| Earthquakes |
|---|
 |
| Types |
| Causes |
| Characteristics |
| Measurement |
| Prediction |
| Other topics |
Induced seismicity is typically earthquakes and tremors that are caused by human activity that alters the stresses and strains on Earth's crust. Most induced seismicity is of a low magnitude. A few sites regularly have larger quakes, such as The Geysers geothermal plant in California which averaged two M4 events and 15 M3 events every year from 2004 to 2009. The Human-Induced Earthquake Database (HiQuake) documents all reported cases of induced seismicity proposed on scientific grounds and is the most complete compilation of its kind.
Results of ongoing multi-year research on induced earthquakes by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) published in 2015 suggested that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma, such as the 1952 magnitude 5.7 El Reno earthquake may have been induced by deep injection of wastewater by the oil industry. A huge number of seismic events in oil and gas extraction states like Oklahoma is caused by increasing the volume of wastewater injection that is generated as part of the extraction process. "Earthquake rates have recently increased markedly in multiple areas of the Central and Eastern United States (CEUS), especially since 2010, and scientific studies have linked the majority of this increased activity to wastewater injection in deep disposal wells."
Induced seismicity can also be caused by the injection of carbon dioxide as the storage step of carbon capture and storage, which aims to sequester carbon dioxide captured from fossil fuel production or other sources in Earth's crust as a means of climate change mitigation. This effect has been observed in Oklahoma and Saskatchewan. Though safe practices and existing technologies can be utilized to reduce the risk of induced seismicity due to injection of carbon dioxide, the risk is still significant if the storage is large in scale. The consequences of the induced seismicity could disrupt pre-existing faults in the Earth's crust as well as compromise the seal integrity of the storage locations.
The seismic hazard from induced seismicity can be assessed using similar techniques as for natural seismicity, although accounting for non-stationary seismicity. It appears that earthquake shaking from induced earthquakes may be similar to that observed in natural tectonic earthquakes, or may have higher shaking at shorter distances. This means that ground-motion models derived from recordings of natural earthquakes, which are often more numerous in strong-motion databases than data from induced earthquakes, may be used with minor adjustments. Subsequently, a risk assessment can be performed, taking into account the increased seismic hazard and the vulnerability of the exposed elements at risk (e.g. local population and the building stock). Finally, the risk can, theoretically at least, be mitigated, either through reductions to the hazard or a reduction to the exposure or the vulnerability.
Causes
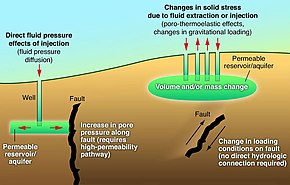
There are many ways in which induced seismicity has been seen to occur. In the 2010s, some energy technologies that inject or extract fluid from the Earth, such as oil and gas extraction and geothermal energy development, have been found or suspected to cause seismic events. Some energy technologies also produce wastes that may be managed through disposal or storage by injection deep into the ground. For example, waste water from oil and gas production and carbon dioxide from a variety of industrial processes may be managed through underground injection.
Artificial lakes
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (January 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
The column of water in a large and deep artificial lake alters in-situ stress along an existing fault or fracture. In these reservoirs, the weight of the water column can significantly change the stress on an underlying fault or fracture by increasing the total stress through direct loading, or decreasing the effective stress through the increased pore water pressure. This significant change in stress can lead to sudden movement along the fault or fracture, resulting in an earthquake. Reservoir-induced seismic events can be relatively large compared to other forms of induced seismicity. Though understanding of reservoir-induced seismic activity is very limited, it has been noted that seismicity appears to occur on dams with heights larger than 330 feet (100 m). The extra water pressure created by large reservoirs is the most accepted explanation for the seismic activity. When the reservoirs are filled or drained, induced seismicity can occur immediately or with a small time lag.
The first case of reservoir-induced seismicity occurred in 1932 in Algeria's Oued Fodda Dam.

The 6.3 magnitude 1967 Koynanagar earthquake occurred in Maharashtra, India with its epicenter, fore- and aftershocks all located near or under the Koyna Dam reservoir. 180 people died and 1,500 were left injured. The effects of the earthquake were felt 140 mi (230 km) away in Bombay with tremors and power outages.
During the beginnings of the Vajont Dam in Italy, there were seismic shocks recorded during its initial fill. After a landslide almost filled the reservoir in 1963, causing a massive flooding and around 2,000 deaths, it was drained and consequently seismic activity was almost non-existent.
On August 1, 1975, a magnitude 6.1 earthquake at Oroville, California, was attributed to seismicity from a large earth-fill dam and reservoir recently constructed and filled.
The filling of the Katse Dam in Lesotho, and the Nurek Dam in Tajikistan is an example. In Zambia, Kariba Lake may have provoked similar effects.
The 2008 Sichuan earthquake, which caused approximately 68,000 deaths, is another possible example. An article in Science suggested that the construction and filling of the Zipingpu Dam may have triggered the earthquake.
Some experts worry that the Three Gorges Dam in China may cause an increase in the frequency and intensity of earthquakes.
Mining
Mining affects the stress state of the surrounding rock mass, often causing observable deformation and seismic activity. A small portion of mining-induced events are associated with damage to mine workings and pose a risk to mine workers. These events are known as rock bursts in hard rock mining, or as bumps in underground coal mining. A mine's propensity to burst or bump depends primarily on depth, mining method, extraction sequence and geometry, and the material properties of the surrounding rock. Many underground hardrock mines operate seismic monitoring networks in order to manage bursting risks, and guide mining practices.
Seismic networks have recorded a variety of mining-related seismic sources including:
- Shear slip events (similar to tectonic earthquakes) which are thought to have been triggered by mining activity. Notable examples include the 1980 Bełchatów earthquake and the 2014 Orkney earthquake.
- Implosional events associated with mine collapses. The 2007 Crandall Canyon mine collapse and the Solvay Mine Collapse are examples of these.
- Explosions associated with routine mining practices, such as drilling and blasting, and unintended explosions such as the Sago mine Disaster. Explosions are generally not considered "induced" events since they are caused entirely by chemical payloads. Most earthquake monitoring agencies take careful measures to identify explosions and exclude them from earthquake catalogs.
- Fracture formation near the surface of excavations, which are usually small magnitude events only detected by dense in-mine networks.
- Slope failures, the largest example being the Bingham Canyon Landslide.
Waste disposal wells

Injecting liquids into waste disposal wells, most commonly in disposing of produced water from oil and natural gas wells, has been known to cause earthquakes. This high-saline water is usually pumped into salt water disposal (SWD) wells. The resulting increase in subsurface pore pressure can trigger movement along faults, resulting in earthquakes.
One of the first known examples was from the Rocky Mountain Arsenal, northeast of Denver. In 1961, waste water was injected into deep strata, and this was later found to have caused a series of earthquakes.
The 2011 Oklahoma earthquake near Prague, of magnitude 5.8, occurred after 20 years of injecting waste water into porous deep formations at increasing pressures and saturation. On September 3, 2016, an even stronger earthquake with a magnitude of 5.8 occurred near Pawnee, Oklahoma, followed by nine aftershocks between magnitudes 2.6 and 3.6 within 3+1⁄2 hours. Tremors were felt as far away as Memphis, Tennessee, and Gilbert, Arizona. Mary Fallin, the Oklahoma governor, declared a local emergency and shutdown orders for local disposal wells were ordered by the Oklahoma Corporation Commission. Results of ongoing multi-year research on induced earthquakes by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) published in 2015 suggested that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma, such as the 1952 magnitude 5.5 El Reno earthquake may have been induced by deep injection of waste water by the oil industry. Prior to April 2015 however, the Oklahoma Geological Survey's position was that the quake was most likely due to natural causes and was not triggered by waste injection. This was one of many earthquakes which have affected the Oklahoma region.
Since 2009, earthquakes have become hundreds of times more common in Oklahoma with magnitude 3 events increasing from 1 or 2 per year to 1 or 2 per day. On April 21, 2015, the Oklahoma Geological Survey released a statement reversing its stance on induced earthquakes in Oklahoma: "The OGS considers it very likely that the majority of recent earthquakes, particularly those in central and north-central Oklahoma, are triggered by the injection of produced water in disposal wells."
Hydrocarbon extraction and storage
Large-scale fossil fuel extraction can generate earthquakes. Induced seismicity can be also related to underground gas storage operations. The 2013 September–October seismic sequence occurred 21 km off the coast of the Valencia Gulf (Spain) is probably the best known case of induced seismicity related to Underground Gas Storage operations (the Castor Project). In September 2013, after the injection operations started, the Spanish seismic network recorded a sudden increase of seismicity. More than 1,000 events with magnitudes (ML) between 0.7 and 4.3 (the largest earthquake ever associated with gas storage operations) and located close the injection platform were recorded in about 40 days. Due to the significant population concern the Spanish Government halted the operations. By the end of 2014, the Spanish government definitively terminated the concession of the UGS plant. Since January 2015 about 20 people who took part in the transaction and approval of the Castor Project were indicted.
Groundwater extraction
The changes in crustal stress patterns caused by the large scale extraction of groundwater has been shown to trigger earthquakes, as in the case of the 2011 Lorca earthquake.
Geothermal energy
Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS), a new type of geothermal power technology that does not require natural convective hydrothermal resources, are known to be associated with induced seismicity. EGS involves pumping fluids at pressure to enhance or create permeability through the use of hydraulic fracturing techniques. Hot dry rock (HDR) EGS actively creates geothermal resources through hydraulic stimulation. Depending on the rock properties, and on injection pressures and fluid volume, the reservoir rock may respond with tensile failure, as is common in the oil and gas industry, or with shear failure of the rock's existing joint set, as is thought to be the main mechanism of reservoir growth in EGS efforts.
HDR and EGS systems are currently being developed and tested in Soultz-sous-Forêts (France), Desert Peak and the Geysers (U.S.), Landau (Germany), and Paralana and Cooper Basin (Australia). Induced seismicity events at the Geysers geothermal field in California has been strongly correlated with injection data. The test site at Basel, Switzerland, has been shut down due to induced seismic events. In November 2017 a Mw 5.5 struck the city of Pohang (South Korea) injuring several people and causing extensive damage. The proximity of the seismic sequence to an EGS site, where stimulation operations had taken place only a few months before the earthquake, raised the possibility that this earthquake had been anthropogenic. According to two different studies it seems plausible that the Pohang earthquake was induced by EGS operations.
| Site | Maximum Magnitude |
|---|---|
| Pohang, South Korea | 5.5 |
| The Geysers, United States | 4.6 |
| Cooper Basin, Australia | 3.7 |
| Basel, Switzerland | 3.4 |
| Rosemanowes Quarry, United Kingdom | 3.1 |
| Soultz-sous-Forêts, France | 2.9 |
Researchers at MIT believe that seismicity associated with hydraulic stimulation can be mitigated and controlled through predictive siting and other techniques. With appropriate management, the number and magnitude of induced seismic events can be decreased, significantly reducing the probability of a damaging seismic event.
Induced seismicity in Basel led to suspension of its HDR project. A seismic hazard evaluation was then conducted, which resulted in the cancellation of the project in December 2009.
Hydraulic fracturing
Main article: Hydraulic fracturingHydraulic fracturing is a technique in which high-pressure fluid is injected into the low-permeable reservoir rocks in order to induce fractures to increase hydrocarbon production. This process is generally associated with seismic events that are too small to be felt at the surface (with moment magnitudes ranging from −3 to 1), although larger magnitude events are not excluded. For example, several cases of larger magnitude events (M > 4) have been recorded in Canada in the unconventional resources of Alberta and British Columbia.
Carbon capture and storage
Risk analysis
Operation of technologies involving long-term geologic storage of waste fluids have been shown to induce seismic activity in nearby areas, and correlation of periods of seismic dormancy with minima in injection volumes and pressures has even been demonstrated for fracking wastewater injection in Youngstown, Ohio. Of particular concern to the viability of carbon dioxide storage from coal-fired power plants and similar endeavors is that the scale of intended CCS projects is much larger in both injection rate and total injection volume than any current or past operation that has already been shown to induce seismicity. As such, extensive modeling must be done of future injection sites in order to assess the risk potential of CCS operations, particularly in relation to the effect of long-term carbon dioxide storage on shale caprock integrity, as the potential for fluid leaks to the surface might be quite high for moderate earthquakes. However, the potential of CCS to induce large earthquakes and CO2 leakage remains a controversial issue.,
Monitoring
Since geological sequestration of carbon dioxide has the potential to induce seismicity, researchers have developed methods to monitor and model the risk of injection-induced seismicity in order to manage better the risks associated with this phenomenon. Monitoring can be conducted with measurements from an instrument such as a geophone to measure the movement of the ground. Generally a network of instruments is used around the site of injection, although many current carbon dioxide injection sites use no monitoring devices. Modelling is an important technique for assessing the potential for induced seismicity and two primary models are used: Physical and numerical. A physical model uses measurements from the early stages of a project to forecast how the project will behave once more carbon dioxide is injected. A numerical model, on the other hand, uses numerical methods to simulate the physics of what is happening within the reservoir. Both modelling and monitoring are useful tools whereby to quantify, understand better and mitigate the risks associated with injection-induced seismicity.
Failure mechanisms due to fluid injection
To assess induced seismicity risks associated with carbon storage, one must understand the mechanisms behind rock failure. The Mohr-Coulomb failure criteria describe shear failure on a fault plane. Most generally, failure will happen on existing faults due to several mechanisms: an increase in shear stress, a decrease in normal stress or a pore pressure increase. The injection of supercritical CO2 will change the stresses in the reservoir as it expands, causing potential failure on nearby faults. Injection of fluids also increases the pore pressures in the reservoir, triggering slip on existing rock weakness planes. The latter is the most common cause of induced seismicity due to fluid injection.
The Mohr-Coulomb failure criteria state that
with the critical shear stress leading to failure on a fault, the cohesive strength along the fault, the normal stress, the friction coefficient on the fault plane and the pore pressure within the fault. When is attained, shear failure occurs and an earthquake can be felt. This process can be represented graphically on a Mohr's circle.
Comparison of risks due to CCS versus other injection methods
While there is risk of induced seismicity associated with carbon capture and storage underground on a large scale, it is currently a much less serious risk than other injection types. Wastewater injection, hydraulic fracturing, and secondary recovery after oil extraction have all contributed significantly more to induced seismic events than carbon capture and storage in the last several years. There have actually not been any major seismic events associated with carbon injection at this point, whereas there have been recorded seismic occurrences caused by the other injection methods. One such example is massively increased induced seismicity in Oklahoma, USA caused by injection of huge volumes of wastewater into the Arbuckle Group sedimentary rock.
Electromagnetic pulses
It has been shown that high-energy electromagnetic pulses can trigger the release of energy stored by tectonic movements by increasing the rate of local earthquakes, within 2–6 days after the emission by the EMP generators. The energy released is approximately six orders of magnitude larger than the EM pulses energy. The release of tectonic stress by these relatively small triggered earthquakes equals to 1-17% of the stress released by a strong earthquake in the area. It has been proposed that strong EM impacts could control seismicity as during the periods of the experiments and long time after, the seismicity dynamics were a lot more regular than usual.
Risk analysis
Risk factors
See also: Seismic riskRisk is defined as the probability of being impacted from an event in the future. Seismic risk is generally estimated by combining the seismic hazard with the exposure and vulnerability at a site or over a region. The hazard from earthquakes depends on the proximity to potential earthquake sources, and the rates of occurrence of different magnitude earthquakes for those sources, and the propagation of seismic waves from the sources to the site of interest. Hazard is then represented in terms of the probability of exceeding some level of ground shaking at a site. Earthquake hazards can include ground shaking, liquefaction, surface fault displacement, landslides, tsunamis, and uplift/subsidence for very large events (ML > 6.0). Because induced seismic events, in general, are smaller than ML 5.0 with short durations, the primary concern is ground shaking.
Ground shaking
Ground shaking can result in both structural and nonstructural damage to buildings and other structures. It is commonly accepted that structural damage to modern engineered structures happens only in earthquakes larger than ML 5.0. In seismology and earthquake engineering, ground shaking can be measured as peak ground velocity (PGV), peak ground acceleration (PGA) or spectral acceleration (SA) at a building's period of excitation. In regions of historical seismicity where buildings are engineered to withstand seismic forces, moderate structural damage is possible, and very strong shaking can be perceived when PGA is greater than 18-34% of g (the acceleration of gravity). In rare cases, nonstructural damage has been reported in earthquakes as small as ML 3.0. For critical facilities like dams and nuclear plants, the acceptable levels of ground shaking is lower than that for buildings.
Probabilistic seismic hazard analysis
Extended reading – An Introduction to Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA)
Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA) is a probabilistic framework that accounts for probabilities in earthquake occurrence and the probabilities in ground motion propagation. Using the framework, the probability of exceeding a certain level of ground shaking at a site can be quantified, taking into account all the possible earthquakes (both natural and induced). PSHA methodology is used to determine seismic loads for building codes in both the United States and Canada, and increasingly in other parts of the world, as well as protecting dams and nuclear plants from the damage of seismic events.
Calculating Seismic Risk
Earthquake source characterization
Understanding the geological background on the site is a prerequisite for seismic hazard estimation. Formations of the rocks, subsurface structures, locations of faults, state of stresses and other parameters that contribute to possible seismic events are considered. Records of past earthquakes of the site are also taken into account.
Recurrence pattern
The magnitudes of earthquakes occurring at a source generally follow the Gutenberg-Richter relation that states that the number of earthquakes decrease exponentially with increase in magnitude, as shown below,
where is the magnitude of seismic events, is the number of events with magnitudes bigger than , is the rate parameter and is the slope. and vary for different sources. In the case of natural earthquakes, historical seismicity is used to determine these parameters. Using this relationship, the number and probability of earthquakes exceeding a certain magnitude can be predicted following the assumptions that earthquakes follow a Poisson process. However, the goal of this analysis is to determine the possibility of future earthquakes. For induced seismicity in contrast to natural seismicity, the earthquake rates change over time as a result of changes in human activity, and hence are quantified as non-stationary processes with varying seismicity rates over time.
Ground motions
At a given site, the ground motion describes the seismic waves that would have been observed at that site with a seismometer. In order to simplify the representation of an entire seismogram, PGV (peak ground velocity), PGA (peak ground acceleration), spectral acceleration (SA) at different period, earthquake duration, arias intensity (IA) are some of the parameters that are used to represent ground shaking. Ground motion propagation from the source to a site for an earthquake of a given magnitude is estimated using ground motion prediction equations (GMPE) that have been developed based on historical records. Since historical records are scarce for induced seismicity, researchers have provided modifications to GMPEs for natural earthquakes in order to apply them to indced earthquakes.
Seismic hazard
The PSHA framework uses the distributions of earthquake magnitudes and ground motion propagation to estimate the seismic hazard – the probability of exceeding a certain level of ground shaking (PGA, PGV, SA, IA, etc.) in the future. Depending on the complexity of the probability distributions, either numerical methods or simulations (such as, Monte Carlo method) may be used to estimate seismic hazard. In the case of induced seismicity, the seismic hazard is not constant, but varies with time due to changes in the underlying seismicity rates.
Exposure and vulnerability
In order to estimate seismic risk, the hazard is combined with the exposure and vulnerability at a site or in a region. For example, if an earthquake occurs where there are no humans or structures, there would be no human impacts despite any level of seismic hazard. Exposure is defined as the set of entities (such as, buildings and people) that exist at a given site or a region. Vulnerability is defined as the potential of impact to those entities, for example, structural or non-structural damage to a building, and loss of well-being and life for people. Vulnerability can also be represented probabilistically using vulnerability or fragility functions. A vulnerability or fragility function specifies the probability of impact at different levels of ground shaking. In regions like Oklahoma without a lot of historical natural seismicity, structures are not engineered to withstand seismic forces, and as a result are more vulnerable even at low levels of ground shaking, as compared to structures in tectonic regions like California and Japan.
Seismic risk
Seismic risk is defined as the probability of exceeding a certain level of impact in the future. For example, it may estimate the exceedance probability of moderate or more damage to a building in the future. Seismic hazard is combined with the exposure and vulnerability to estimate seismic risk. While numerical methods may be used to estimate risk at one site, simulation-based methods are better suited to estimate seismic risk for a region with a portfolio of entities, in order to correctly account for the correlations in ground shaking, and impacts. In the case of induced seismicity, the seismic risk varies over time due to changes in the seismic hazard.
Risk Mitigation
Induced seismicity can cause damage to infrastructure and has been documented to damage buildings in Oklahoma. It can also lead to brine and CO2 leakages.
It is easier to predict and mitigate seismicity caused by explosions. Common mitigation strategies include constraining the amount of dynamite used in one single explosion and the locations of the explosions. For injection-related induced seismicity, however, it is still difficult to predict when and where induced seismic events will occur, as well as the magnitudes. Since induced seismic events related to fluid injection are unpredictable, it has garnered more attention from the public. Induced seismicity is only part of the chain reaction from industrial activities that worry the public. Impressions toward induced seismicity are very different between different groups of people. The public tends to feel more negatively towards earthquakes caused by human activities than natural earthquakes. Two major parts of public concern are related to the damages to infrastructure and the well-being of humans. Most induced seismic events are below M 2 and are not able to cause any physical damage. Nevertheless, when the seismic events are felt and cause damages or injuries, questions arise from the public whether it is appropriate to conduct oil and gas operations in those areas. Public perceptions may vary based on the population and tolerance of local people. For example, in the seismically active Geysers geothermal area in Northern California, which is a rural area with a relatively small population, the local population tolerates earthquakes up to M 4.5. Actions have been taken by regulators, industry and researchers. On October 6, 2015, people from industry, government, academia, and the public gathered together to discuss how effective it was to implement a traffic light system or protocol in Canada to help manage risks from induced seismicity.
Risk assessment and tolerance for induced seismicity, however, is subjective and shaped by different factors like politics, economics, and understanding from the public. Policymakers have to often balance the interests of industry with the interests of the population. In these situations, seismic risk estimation serves as a critical tool for quantifying future risk, and can be used to regulate earthquake-inducing activities until the seismic risk reaches a maximum acceptable level to the population.
Traffic Light System
One of the methods suggested to mitigate seismic risk is a Traffic Light System (TLS), also referred to as Traffic Light Protocol (TLP), which is a calibrated control system that provides continuous and real-time monitoring and management of ground shaking of induced seismicity for specific sites. TLS was first implemented in 2005 in an enhanced geothermal plant in Central America. For oil and gas operations, the most widely implemented one is modified by the system used in the UK. Normally there are two types of TLS – the first one sets different thresholds, usually earthquake local magnitudes (ML) or ground motions from small to large. If the induced seismicity reaches the smaller thresholds, modifications of the operations are implemented by the operators and the regulators are informed. If the induced seismicity reaches the larger thresholds, operations are shut down immediately. The second type of traffic light system sets only one threshold. If this threshold is reached, the operations are halted. This is also called a "stop light system". Thresholds for the traffic light system vary between and within countries, depending on the area.
However, the traffic light system is not able to account for future changes in seismicity. It may take time for changes in human activities to mitigate the seismic activity, and it has been observed that some of the largest induced earthquakes have occurred after stopping fluid injection.
| Country | Location | Major Operation | TSL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Switzerland | Basel | Enhanced Geothermal System | Operate as planned: PGV < 0.5 mm/s, ML < 2.3, no felt report
Inform regulators; no increase in injection rate: PGV ≤ 2.0 mm/s, ML ≥ 2.3, few felt report Reduce injection rate: PGV ≤ 5.0 mm/s, ML ≤ 2.9, many felt reports Suspend pumping; bleeding wells: PGV > 5.0 mm/s, ML > 2.9, generally felt |
| U.K. | Nation-wide | Hydraulic Fracturing of Shale Gas | Operate as planned: ML < 0
Operate with caution; lower the injection rates; increase monitoring: 0 ≤ ML ≤ 0.5 Suspend operation: ML > 0.5 |
| U.S.A | Colorado | Hydraulic Fracturing; Wastewater Disposal | Modify the operation: felt at the surface
Suspend operation: ML ≥ 4.5 |
| U.S.A | Oklahoma | Wastewater Disposal; Hydraulic Fracturing | Escalate review of operators' mitigation procedures : ML ≥ 2.5, ≥ 3.0
Suspend the operation : ML ≥ 3.5 |
| U.S.A | Ohio | Wastewater Disposal; Hydraulic Fracturing | Operate as planned: ML < 1.5
Inform the regulator: ML ≥ 1.5 Modify the operation plan: 2.0 ≤ ML ≤ 2.4 Halt the operations temporarily: ML ≥ 2.5 Suspend the operations: ML ≥ 3.0 |
| Canada | Fox Creek Area, Alberta | Hydraulic Fracturing | Operate as planned: ML < 2.0
Inform the regulator; implement mitigation plans: 2.0 ≤ ML ≤ 4.0 within 5 km of an injection well Inform the regulator; suspend the operations: ML ≥ 4.0 within 5 km of an injection well |
| Canada | Red Deer Area, Alberta | Hydraulic Fracturing | Operate as planned: ML < 1.0
Inform the regulator; implement mitigation plans: 1.0 ≤ ML ≤ 3.0 within 5 km of an injection well Inform the regulator; suspend the operations: ML ≥ 3.0 within 5 km of an injection well |
| Canada | British Columbia | Hydraulic Fracturing | Suspend the operations: ML ≥ 4.0 or a ground motion felt on the surface within 3 km of the drilling pad |
Nuclear explosions
Nuclear explosions can cause seismic activity, but according to USGS, the resulting seismic activity is less energetic than the original nuclear blast, and generally does not produce large aftershocks. Nuclear explosions may instead release the elastic strain energy that was stored in the rock, strengthening the initial blast shockwave.
See also: Tired mountain syndromeU.S. National Research Council report
A 2013 report from the U.S. National Research Council examined the potential for energy technologies—including shale gas recovery, carbon capture and storage, geothermal energy production, and conventional oil and gas development—to cause earthquakes. The report found that only a very small fraction of injection and extraction activities among the hundreds of thousands of energy development sites in the United States have induced seismicity at levels noticeable to the public. However, although scientists understand the general mechanisms that induce seismic events, they are unable to accurately predict the magnitude or occurrence of these earthquakes due to insufficient information about the natural rock systems and a lack of validated predictive models at specific energy development sites.
The report noted that hydraulic fracturing has a low risk for inducing earthquakes that can be felt by people, but underground injection of wastewater produced by hydraulic fracturing and other energy technologies has a higher risk of causing such earthquakes. In addition, carbon capture and storage—a technology for storing excess carbon dioxide underground—may have the potential for inducing seismic events, because significant volumes of fluids are injected underground over long periods of time.
List of induced seismic events
Table
| Date | Cause | Details | Mag. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1951 | Underground nuclear test | Operation Buster–Jangle was a series of seven (six atmospheric, one cratering) nuclear weapons tests conducted by the United States in late 1951 at the Nevada Test Site. This was the first underground nuclear weapons test ever conducted. | Unknown |
| 1952 | Wastewater injection wells | Results of ongoing multi-year research on induced earthquakes by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) published in 2015 suggested that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma, such as the 1952 magnitude 5.7 El Reno earthquake may have been induced by deep injection of waste water by the oil industry. "Earthquake rates have recently increased markedly in multiple areas of the Central and Eastern United States (CEUS), especially since 2010, and scientific studies have linked the majority of this increased activity to wastewater injection in deep disposal wells." | 5.7 |
| 1967 December 11 | Artificial lake | The 1967 Koynanagar earthquake occurred near Koynanagar town in Maharashtra, India on 11 December local time. The magnitude 6.6 shock hit with a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (Severe). It occurred near the site of Koyna dam, raising questions about induced seismicity, and claimed at least 177 lives and injured over 2,200. | 6.6 |
| 1971 November 6 | Underground nuclear test | Occurred on Amchitka island, Alaska, by the United States Atomic Energy Commission. The experiment, part of the Operation Grommet nuclear test series, tested the warhead design for the LIM-49 Spartan anti-ballistic missile. With an explosive yield of almost 5-megatons TNT equivalent, the test was the largest underground explosion ever detonated. The campaigning environmental organization Greenpeace grew out of efforts to oppose the test. | 7.1 mb |
| 1973 | Geothermal power plant | Studies have shown that injecting water into The Geysers field produces earthquakes from magnitude 0.5 to 3.0, although a 4.6 occurred in 1973 and magnitude four events increased thereafter. | 4.6 |
| 2006 October 9 | Underground nuclear test | 2006 North Korean nuclear test | 4.3 mb |
| 2009 May 25 | Underground nuclear test | 2009 North Korean nuclear test | 4.7 mb |
| 2011 November 5 | Wastewater injection wells | 2011 Oklahoma earthquake | 5.8 |
| 2013 February 12 | Underground nuclear test | 2013 North Korean nuclear test | 5.1 |
| 2016 January 6 | Underground nuclear test | January 2016 North Korean nuclear test | 5.1 |
| 2016 September 9 | Underground nuclear test | September 2016 North Korean nuclear test | 5.3 |
| 2017 September 3 | Underground nuclear test | 2017 North Korean nuclear test | 6.3 |
References
- "Man-made geothermal earthquakes". Anderson Springs Community Alliance. 2009. Archived from the original on March 4, 2016. Retrieved April 28, 2016.
- Wilson, M.P.; Foulger, G.R; Gluyas, J.G.; Davies, R.D.; Julian, B.R. (2017). "HiQuake: The Human-Induced Earthquake Database". Seismological Research Letters. 88 (6): 1560–1565. Bibcode:2017SeiRL..88.1560W. doi:10.1785/0220170112.
- Foulger, G.R.; Wilson, M.P.; Gluyas, J.G.; Julian, B.R.; Davies, R.J. (2018). "Global review of human-induced earthquakes". Earth-Science Reviews. 178: 438–514. Bibcode:2018ESRv..178..438F. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.07.008.
- D. Atoufi, Hossein; Lampert, David J. (2020). "Membrane Desalination to Prepare Produced Water for Reuse". World Environmental and Water Resources Congress 2020. Henderson, Nevada (Conference Cancelled): American Society of Civil Engineers: 8–15. doi:10.1061/9780784482988.002. ISBN 978-0-7844-8298-8. S2CID 219430591 – via American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE).
- ^ Hough, Susan E.; Page, Morgan (October 20, 2015). "A Century of Induced Earthquakes in Oklahoma?". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
Several lines of evidence further suggest that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma during the 20th century may also have been induced by oil production activities. Deep injection of waste water, now recognized to potentially induce earthquakes, in fact began in the state in the 1930s.
- Ellsworth, W.L. (2013). "Injection-induced earthquakes". Science. 341 (6142): 7. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.460.5560. doi:10.1126/science.1225942. PMID 23846903. S2CID 206543048.
- Keranen, K.M.; Weingarten, Matthew; Abers, G.A.; Bekins, B.A.; Ge, Shemin (2014). "Sharp increase in central Oklahoma seismicity since 2008 induced by massive wastewater injection". Science. 345 (6195): 448–451. Bibcode:2014Sci...345..448K. doi:10.1126/science.1255802. PMID 24993347. S2CID 206558853.
- Walsh, F.R.; Zoback, M.D. (2015). "Oklahoma's recent earthquakes and saltwater disposal". Science Advances. 1 (5): e1500195. Bibcode:2015SciA....1E0195W. doi:10.1126/sciadv.1500195. PMC 4640601. PMID 26601200.
- Weingarten, Matthew; Ge, Shemin; Godt, J.W.; Bekins, B.A.; Rubinstein, J.L. (2015). "High-rate injection is associated with the increase in U.S. mid-continent seismicity". Science. 348 (6241): 1336–1340. Bibcode:2015Sci...348.1336W. doi:10.1126/science.aab1345. PMID 26089509. S2CID 206637414.
- Petersen, Mark D.; Mueller, Charles S.; Moschetti, Morgan P.; Hoover, Susan M.; Llenos, Andrea L.; Ellsworth, William L.; Michael, Andrew J.; Rubinstein, Justin L.; McGarr, Arthur F.; Rukstales, Kenneth S. (April 1, 2016). "2016 One-Year Seismic Hazard Forecast for the Central and Eastern United States from Induced and Natural Earthquakes" (PDF). Open-File Report (Report). Reston, Virginia. p. 58. doi:10.3133/ofr20161035. ISSN 2331-1258. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 14, 2016. Retrieved April 29, 2016.
- Keranen, Katie M.; Savage, Heather M.; Abers, Geoffrey A.; Cochran, Elizabeth S. (2013). "Potentially induced earthquakes in Oklahoma, USA: Links between wastewater injection and the 2011 Mw 5.7 earthquake sequence". Geology. 41 (6): 699–702. Bibcode:2013Geo....41..699K. doi:10.1130/G34045.1. Retrieved April 28, 2016.via EBSCO
- ^ Verdon, J.P. (2016). "Carbon capture and storage, geomechanics and induced seismicity activity". Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering. 8 (6): 928935. Bibcode:2016JRMGE...8..928V. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.06.004.
- ^ Zoback, M.D. (2012). "Earthquake triggering and large-scale geologic storage of carbon dioxide". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 109 (26): 10164–8. Bibcode:2012PNAS..10910164Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.1202473109. PMC 3387039. PMID 22711814.
- ^ Gupta, Abhineet, and Jack W. Baker. "A Framework for Time-Varying Induced Seismicity Risk Assessment, with Application in Oklahoma". Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering 17, no. 8 (August 2019): 4475–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10518-019-00620-5.
- ^ Bourne, S. J.; Oates, S. J.; Bommer, J. J.; Dost, B.; Elk, J. van; Doornhof, D. (2015). "A Monte Carlo Method for Probabilistic Hazard Assessment of Induced Seismicity due to Conventional Natural Gas Production". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 105 (3): 1721–1738. Bibcode:2015BuSSA.105.1721B. doi:10.1785/0120140302. hdl:10044/1/56262.
- Douglas, J.; Edwards, B.; Convertito, V.; Sharma, N.; Tramelli, A.; Kraaijpoel, D.; Cabrera, B. M.; Maercklin, N.; Troise, C. (2013). "Predicting Ground Motion from Induced Earthquakes in Geothermal Areas". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 103 (3): 1875–1897. Bibcode:2013BuSSA.103.1875D. doi:10.1785/0120120197.
- Atkinson, Gail M.; Assatourians, Karen (2017-03-01). "Are Ground-Motion Models Derived from Natural Events Applicable to the Estimation of Expected Motions for Induced Earthquakes?". Seismological Research Letters. 88 (2A): 430–441. Bibcode:2017SeiRL..88..430A. doi:10.1785/0220160153. ISSN 0895-0695.
- ^ Gupta, Abhineet, Jack W. Baker, and William L. Ellsworth. "Assessing Ground‐Motion Amplitudes and Attenuation for Small‐to‐Moderate Induced and Tectonic Earthquakes in the Central and Eastern United States". Seismological Research Letters 88, no. 5 (June 28, 2017). https://doi.org/10.1785/0220160199.
- Akkar, S.; Sandıkkaya, M. A.; Şenyurt, M.; Sisi, A. Azari; Ay, B. Ö; Traversa, P.; Douglas, J.; Cotton, F.; Luzi, L. (2014-02-01). "Reference database for seismic ground-motion in Europe (RESORCE)" (PDF). Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering. 12 (1): 311–339. Bibcode:2014BuEE...12..311A. doi:10.1007/s10518-013-9506-8. ISSN 1570-761X. S2CID 17906356.
- Mignan, A.; Landtwing, D.; Kästli, P.; Mena, B.; Wiemer, S. (2015-01-01). "Induced seismicity risk analysis of the 2006 Basel, Switzerland, Enhanced Geothermal System project: Influence of uncertainties on risk mitigation". Geothermics. 53: 133–146. Bibcode:2015Geoth..53..133M. doi:10.1016/j.geothermics.2014.05.007.
- Bommer, Julian J.; Oates, Stephen; Cepeda, José Mauricio; Lindholm, Conrad; Bird, Juliet; Torres, Rodolfo; Marroquín, Griselda; Rivas, José (2006-03-03). "Control of hazard due to seismicity induced by a hot fractured rock geothermal project". Engineering Geology. 83 (4): 287–306. Bibcode:2006EngGe..83..287B. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2005.11.002.
- Douglas, John; Aochi, Hideo (2014-08-01). "Using Estimated Risk to Develop Stimulation Strategies for Enhanced Geothermal Systems" (PDF). Pure and Applied Geophysics. 171 (8): 1847–1858. Bibcode:2014PApGe.171.1847D. doi:10.1007/s00024-013-0765-8. ISSN 0033-4553. S2CID 51988824.
- Bommer, Julian J.; Crowley, Helen; Pinho, Rui (2015-04-01). "A risk-mitigation approach to the management of induced seismicity". Journal of Seismology. 19 (2): 623–646. Bibcode:2015JSeis..19..623B. doi:10.1007/s10950-015-9478-z. ISSN 1383-4649. PMC 5270888. PMID 28190961.
- Simpson, D. W.; Leith, W. S.; Scholz, C.H. (1988). "Two Types of Reservoir-Induced Seismicity". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 78 (6): 2025–2040. Bibcode:1988BuSSA..78.2025S. doi:10.1785/BSSA0780062025.
- "Dam–Induced Seismicity". International Rivers. 1967-12-11. Archived from the original on 2012-04-23. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
- "Reservoir-Induced Seismicity". Internationalrivers.org. 1967-12-11. Archived from the original on 2012-04-19. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
- "International Rivers". International Rivers. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
- Kerr, RA; Stone, R (2009). "A Human Trigger for the Great Quake of Sichuan?". Science. 323 (5912): 322. doi:10.1126/science.323.5912.322. PMID 19150817. S2CID 206583866.
- Chinese earthquake may have been man-made, say scientists, Telegraph, February 3, 2009
- Naik, Gautam; Oster, Shai (February 6, 2009). "Scientists Link China's Dam to Earthquake, Renewing Debate". The Wall Street Journal.
- Chen, L.; Talwani, P. (1998). "Seismicity in China". Pure and Applied Geophysics. 153 (1): 133–149. Bibcode:1998PApGe.153..133C. doi:10.1007/s000240050188. S2CID 33668765.
- ^ Gibowicz, Sławomir J.; Kijko, Andrzej (1994). An introduction to mining seismology. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-282120-3. OCLC 28255842.
- Mendecki, A. J.; Lynch, R. A.; Malovichko, D. A. (2010-11-01). Routine micro-seismic monitoring in mines. Australian Earthquake Engineering Society Annual Conference. Perth, Australia. pp. 1–33.
- "Seismicity induced by surface mining: the Belchatow, Poland, earthquake of 29 November 1980". International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts (in Polish). 21 (1): A8. 1984-02-01. doi:10.1016/0148-9062(84)90072-x. ISSN 0148-9062.
- Swanson, P.; Zipf, R. K. (1999-01-01). Description of a large catastrophic failure in a southwestern Wyoming Trona Mine. 37th U.S. Symposium on Rock Mechanics. Vail, Colorado: American Rock Mechanics Association.
- Murphy, Michael M.; Westman, Erik C.; Barczak, Thomas M. (2012-12-01). "Attenuation and duration of seismic signals generated from controlled methane and coal dust explosions in an underground mine". International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences. 56: 112–120. Bibcode:2012IJRMM..56..112M. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2012.07.022.
- "Routine United States Mining Seismicity". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2019-05-28.
- Conners, Deanna (2019-04-10). "Bingham Canyon landslide". EarthSky. Retrieved 2019-05-28.
- Frohlich, Cliff; Hayward, Chris; Stump, Brian; Potter, Eric (2011-02-01). "The Dallas–Fort Worth Earthquake Sequence: October 2008 through May 2009". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 101 (1): 327–340. Bibcode:2011BuSSA.101..327F. doi:10.1785/0120100131. hdl:2152/43249.
- Madrigal, Alexis (June 4, 2008). "Top 5 Ways to Cause a Man-Made Earthquake". Wired.
- Hsieh, Paul A.; Bredehoeft, John D. (10 February 1981). "A reservoir analysis of the Denver earthquakes: A case of induced seismicity". Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 86 (B2): 903–920. Bibcode:1981JGR....86..903H. doi:10.1029/JB086iB02p00903. hdl:10150/191695. Retrieved 17 November 2022.
- U.S. Geological Survey, Oklahoma – Magnitude 5.8.
- Henry Fountain (March 28, 2013). "Study Links 2011 Quake to Technique at Oil Wells". The New York Times. Retrieved March 29, 2013.
- Record tying Oklahoma earthquake felt as far away as Arizona, Associated Press, Ken Miller, September 3, 2016. Retrieved 3 September 2016.
- USGS calls for shut down of wells, governor declares emergency in wake of 5.6 quake in Oklahoma, Enid News & Eagle, Sally Asher & Violet Hassler, September 3, 2016. Retrieved 4 September 2016.
- Keller, G. Randy; Holland, Austin A. (March 22, 2013). Statement about the cause of 2011 Prague Earthquake Sequence (PDF). Oklahoma Geological Survey (Report). Archived from the original (PDF) on May 14, 2015. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- Pérez-Peña, Richard (April 23, 2015). "U.S. Maps Pinpoint Earthquakes Linked to Quest for Oil and Gas". The New York Times. Retrieved November 8, 2015.
- Andrews, Richard D.; Holland, Austin A. (April 21, 2015). Statement on Oklahoma Seismicity (PDF). Oklahoma Geological Survey (Report). University of Oklahoma. Retrieved April 30, 2015.
- "Induced Seismicity – Home". Esd.lbl.gov. Archived from the original on 2011-08-22. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
- Van Eijsa, R.M.H.E; Muldersa, F.M.M; Nepveua, M; Kenterb, C.J; Scheffers, B.C. (2006). "Correlation between hydrocarbon reservoir properties and induced seismicity in the Netherlands". Engineering Geology. 84 (3–4): 99–111. Bibcode:2006EngGe..84...99V. doi:10.1016/j.enggeo.2006.01.002.
- Cesca, S.; Grigoli, F.; Heimann, S.; Gonzalez, A.; Buforn, E.; Maghsoudi, S.; Blanch, E.; Dahm, T. (2014-08-01). "The 2013 September–October seismic sequence offshore Spain: a case of seismicity triggered by gas injection?". Geophysical Journal International. 198 (2): 941–953. Bibcode:2014GeoJI.198..941C. doi:10.1093/gji/ggu172. hdl:10261/113734. ISSN 0956-540X.
- Gaite, Beatriz; Ugalde, Arantza; Villaseñor, Antonio; Blanch, Estefania (2016-05-01). "Improving the location of induced earthquakes associated with an underground gas storage in the Gulf of Valencia (Spain)". Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors. 254: 46–59. Bibcode:2016PEPI..254...46G. doi:10.1016/j.pepi.2016.03.006. hdl:10261/132539.
- González, P.J.; Tiampo K.F.; Palano M.; Cannavó F.; Fernández J. (2012). "The 2011 Lorca earthquake slip distribution controlled by groundwater crustal unloading". Nature Geoscience. 5 (11): 821–825. Bibcode:2012NatGe...5..821G. doi:10.1038/ngeo1610. hdl:10261/73773.
- Tester, Jefferson W. (Massachusetts Institute of Technology); et al. (2006). The Future of Geothermal Energy – Impact of Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS) on the United States in the 21st Century (PDF). Idaho Falls: Idaho National Laboratory. pp. 4–10. ISBN 978-0-615-13438-3. Archived from the original (14MB PDF) on 2011-03-10. Retrieved 2007-02-07.
- Majer, Ernest L.; Peterson, John E. (2007-12-01). "The impact of injection on seismicity at The Geysers, California Geothermal Field". International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences. 44 (8): 1079–1090. Bibcode:2007IJRMM..44.1079M. doi:10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.07.023. S2CID 54575780.
- Grigoli, F.; Cesca, S.; Rinaldi, A. P.; Manconi, A.; López-Comino, J. A.; Clinton, J. F.; Westaway, R.; Cauzzi, C.; Dahm, T. (2018-04-26). "The November 2017 Mw 5.5 Pohang earthquake: A possible case of induced seismicity in South Korea" (PDF). Science. 360 (6392): 1003–1006. Bibcode:2018Sci...360.1003G. doi:10.1126/science.aat2010. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 29700226. S2CID 13778707.
- Kim, Kwang-Hee; Ree, Jin-Han; Kim, YoungHee; Kim, Sungshil; Kang, Su Young; Seo, Wooseok (2018-04-26). "Assessing whether the 2017 Mw 5.4 Pohang earthquake in South Korea was an induced event". Science. 360 (6392): 1007–1009. Bibcode:2018Sci...360.1007K. doi:10.1126/science.aat6081. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 29700224. S2CID 13876371.
- Bromley, C.J. & Mongillo, M.A. (February 2007), "All Geothermal Energy from Fractured Reservoirs – Dealing with Induced Seismicity" (PDF), IEA Open Journal, 48 (7): 5, archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-06-09, retrieved 2010-01-07
- Tester 2006, pp. 5–6
- Castro-Alvarez, Fernando; Marsters, Peter; Barido, Diego Ponce de León; Kammen, Daniel M. (2018). "Sustainability lessons from shale development in the United States for Mexico and other emerging unconventional oil and gas developers". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 82: 1320–1332. Bibcode:2018RSERv..82.1320C. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2017.08.082. S2CID 56351664.
- Rutqvist, Jonny; Rinaldi, Antonio P.; Cappa, Frédéric; Moridis, George J. (2015-03-01). "Modeling of fault activation and seismicity by injection directly into a fault zone associated with hydraulic fracturing of shale-gas reservoirs". Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering. 127: 377–386. Bibcode:2015JPSE..127..377R. doi:10.1016/j.petrol.2015.01.019.
- Atkinson, Gail M.; Eaton, David W.; Ghofrani, Hadi; Walker, Dan; Cheadle, Burns; Schultz, Ryan; Shcherbakov, Robert; Tiampo, Kristy; Gu, Jeff (2016-05-01). "Hydraulic Fracturing and Seismicity in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin". Seismological Research Letters. 87 (3): 631–647. Bibcode:2016SeiRL..87..631A. doi:10.1785/0220150263. ISSN 0895-0695.
- Kim, Won-Young (2013). "Induced seismicity associated with fluid injection into a deep well in Youngstown, Ohio". Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 118 (7): 3506–3518. Bibcode:2013JGRB..118.3506K. doi:10.1002/jgrb.50247.
- Verdon, James P (2014). "Significance for secure CO2 storage of earthquakes induced by fluid injection". Environmental Research Letters. 9 (6): 064022. Bibcode:2014ERL.....9f4022V. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/9/6/064022.
- Vilarrasa, Victor; Carrera, Jesus (2015). "Geologic carbon storage is unlikely to trigger large earthquakes and reactivate faults through which CO2 could leak". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (19): 5938–5943. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112.5938V. doi:10.1073/pnas.1413284112. PMC 4434732. PMID 25902501.
- Zoback, Mark D.; Gorelick, Steven M. (2015). "To prevent earthquake triggering, pressure changes due to CO2 injection need to be limited". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (33): E4510. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112E4510Z. doi:10.1073/pnas.1508533112. PMC 4547280. PMID 26240342.
- Vilarrasa, Victor; Carrera, Jesus (2015). "Reply to Zoback and Gorelick: Geologic carbon storage remains a safe strategy to significantly reduce CO2 emissions". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 112 (33): E4511. Bibcode:2015PNAS..112E4511V. doi:10.1073/pnas.1511302112. PMC 4547211. PMID 26240341.
- Davis, S. D.; Frohlich, C. (1993). "Did (or will) fluid injection cause earthquakes? – criteria for a rational assessment" (PDF). Seismological Research Letters. 64 (3–4): 207–224. Bibcode:1993SeiRL..64..207D. doi:10.1785/gssrl.64.3-4.207.
- Riffault, J., Dempsey, D., Archer, R., Kelkar, S. and Karra, S. (2011), Understanding Poroelastic Stressing and Induced Seismicity with a Stochastic/Deterministic Model: an Application to an EGS Stimulation at Paralana, South Australia, 2011. 41st Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering, Stanford University.
- NRC – National Research Council (2013). Induced Seismicity Potential in Energy Technologies. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. doi:10.17226/13355.
- "FAQs." Earthquakes in Oklahoma. N.p., n.d. Web. 27 Apr. 2017. https://earthquakes.ok.gov/faqs/ Archived 2017-05-04 at the Wayback Machine .
- Tarasov, N. T.; Tarasova, N. V. (2009-12-18). "Spatial-temporal structure of seismicity of the North Tien Shan and its changeunder effect of high energy electromagnetic pulses". Annals of Geophysics. 47 (1). doi:10.4401/ag-3272.
- Tarasov, N. T.; Tarasova, N. V. (October 2011). "Influence of electromagnetic fields on the seismotectonic strain rate; relaxation and active monitoring of elastic stresses". Izvestiya, Physics of the Solid Earth. 47 (10): 937–950. Bibcode:2011IzPSE..47..937T. doi:10.1134/S1069351311100120. ISSN 1069-3513. S2CID 128622959.
- Novikov, Victor A.; Okunev, Vladimir I.; Klyuchkin, Vadim N.; Liu, Jing; Ruzhin, Yuri Ya.; Shen, Xuhui (2017-08-01). "Electrical triggering of earthquakes: results of laboratory experiments at spring-block models". Earthquake Science. 30 (4): 167–172. Bibcode:2017EaSci..30..167N. doi:10.1007/s11589-017-0181-8. ISSN 1867-8777. S2CID 133812017.
- Zeigarnik, Vladimir A.; Novikov, Viktor A.; Avagimov, A. A.; Tarasov, N. T.; Bogomolov, Leonid (2007). "Discharge of Tectonic Stresses in the Earth Crust by High-power Electric Pulses for Earthquake Hazard Mitigation". 2nd International Conference on Urban Disaster Reduction. Taipei. S2CID 195726703.
- Wijesinghe, Nelka (July 16, 2018). "Induced Seismicity Associated with Oil & Gas Development". HARCresearch.org. Archived from the original on 2019-04-18. Retrieved 2019-04-18.
- ^ Megalooikonomou, Konstantinos G.; Parolai, Stefano; Pittore, Massimiliano (2018). "Toward performance-driven seismic risk monitoring for geothermal platforms: development of ad hoc fragility curves". Geothermal Energy. 6 (1): 8. Bibcode:2018GeoE....6....8M. doi:10.1186/s40517-018-0094-3. S2CID 49366266.
- Bommer, Julian J.; Crowley, Helen; Pinho, Rui (2015-04-01). "A risk-mitigation approach to the management of induced seismicity". Journal of Seismology. 19 (2): 623–646. Bibcode:2015JSeis..19..623B. doi:10.1007/s10950-015-9478-z. ISSN 1383-4649. PMC 5270888. PMID 28190961.
- ^ American Society of Civil Engineers, ed. Minimum Design Loads and Associated Criteria for Buildings and Other Structures. Reston, Virginia: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2017.
- ^ Atkinson, Gail M. (2017-04-27). "Strategies to prevent damage to critical infrastructure due to induced seismicity". FACETS. 2: 374–394. doi:10.1139/facets-2017-0013.
- ^ Baker, Jack W. "An Introduction to Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA)" (PDF).
- Cornell, C. Allin (1968-10-01). "Engineering seismic risk analysis". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America. 58 (5): 1583. Bibcode:1968BuSSA..58.1583C. doi:10.1785/BSSA0580051583. ISSN 0037-1106.
- McGuire, R (2004). Seismic hazard and risk analysis. Oakland, California: Earthquake Engineering Research Institute.
- ACB, CDA /. "Dam Safety Publications". cda.ca. Retrieved 2018-04-17.
- Baker, Jack W. "An Introduction to Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA),” 2015. https://web.stanford.edu/~bakerjw/Publications/Baker_(2015)_Intro_to_PSHA.pdf.
- van der Elst, Nicholas J.; Page, Morgan T.; Weiser, Deborah A.; Goebel, Thomas H.W.; Hosseini, S. Mehran (2016-06-01). "Induced earthquake magnitudes are as large as (statistically) expected". Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth. 121 (6): 4575–4590. Bibcode:2016JGRB..121.4575V. doi:10.1002/2016jb012818. ISSN 2169-9356. S2CID 132187915.
- Gupta, Abhineet, and Jack W. Baker. "Estimating Spatially Varying Event Rates with a Change Point Using Bayesian Statistics: Application to Induced Seismicity". Structural Safety 65 (March 2017): 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2016.11.002.
- Goulet, Christine A., Tadahiro Kishida, Timothy D. Ancheta, Chris H. Cramer, Robert B. Darragh, Walter J. Silva, Youssef M. A. Hashash, et al. "PEER NGA-East Database". University of California, Berkeley: Pacific Earthquake Engineering Research Center, October 2014.
- Atkinson, Gail M., and David M. Boore. "Modifications to Existing Ground-Motion Prediction Equations in Light of New Data". Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America 101, no. 3 (June 1, 2011): 1121–35. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120100270.
- Backer, Jack W. "An Introduction to Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis (PSHA)" (PDF).
- Krawinkler, H., J. D. Osteraas, B. M. McDonald, and J. P. Hunt. "Development of Damage Fragility Functions for URM Chimneys and Parapets". In 15th World Conference in Earthquake Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 2012. http://www.iitk.ac.in/nicee/wcee/article/WCEE2012_4622.pdf.
- Holmes, William, Roger Borcherdt, David Brookshire, Richard Eisner, Robert Olson, Michael O’Rourke, Henry Lagorio, Robert Reitherman, and Robert Whitman. "Hazus-MR4 Technical Manual – Earthquake Model". Hazus-MR4 Technical Manual. Washington, DC: Department of Homeland Security, Federal Emergency Management Agency, July 14, 2014. http://www.fema.gov/media-library-data/20130726-1716-25045-6422/hazus_mr4_earthquake_tech_manual.pdf
- "Oklahoma Earthquakes: Who Pays?". 30 March 2016.
- Green, Kenneth P. (December 2014). "Managing the Risk of Hydraulic Fracturing" (PDF). fraserinstitute.org.
- ^ "Survey Responses on the Public Perception of Induced Seismicity". CSEG RECORDER Magazine. Retrieved 2018-04-10.
- McComas, Katherine A.; Lu, Hang; Keranen, Katie M.; Furtney, Maria A.; Song, Hwansuck (2016). "Public perceptions and acceptance of induced earthquakes related to energy development". Energy Policy. 99: 27–32. Bibcode:2016EnPol..99...27M. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2016.09.026.
- "Why are there so many earthquakes in the Geysers area in Northern California?". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2019-04-17.
- Kao, H; Eaton, D W; Atkinson, G M; Maxwell, S; Mahani, A Babaie (2016). "Technical meeting on the traffic light protocols (TLP) for induced seismicity: summary and recommendations". doi:10.4095/299002.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Walters, Randi Jean; Zoback, Mark D.; Baker, Jack W.; Beroza, Gregory C. (2015-07-01). "Characterizing and Responding to Seismic Risk Associated with Earthquakes Potentially Triggered by Fluid Disposal and Hydraulic Fracturing". Seismological Research Letters. 86 (4): 1110–1118. Bibcode:2015SeiRL..86.1110W. doi:10.1785/0220150048. ISSN 0895-0695.
- Rubinstein, Justin L., and Alireza Babaie Mahani. "Myths and Facts on Wastewater Injection, Hydraulic Fracturing, Enhanced Oil Recovery, and Induced Seismicity". Seismological Research Letters, June 10, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220150067.
- Kao, Hong (2019-04-09). "A Review of Traffic Light Protocol for Induced Seismicity and Its Effectiveness in Canada" (PDF).
- "Can nuclear explosions cause earthquakes?". United States Geological Survey. 2016-09-09. Retrieved 2018-06-05.
- U.S. National Research Council Report, Induced Seismicity Potential in Energy Technologies, https://www.nap.edu/catalog/13355/induced-seismicity-potential-in-energy-technologies
- ^ , Induced Seismicity Potential in Energy Technologies
- Hough, Susan E.; Page, Morgan (October 20, 2015). "A Century of Induced Earthquakes in Oklahoma?". U.S. Geological Survey. Retrieved November 8, 2015. "Several lines of evidence further suggest that most of the significant earthquakes in Oklahoma during the 20th century may also have been induced by oil production activities. Deep injection of waste water, now recognized to potentially induce earthquakes, in fact began in the state in the 1930s."
- Goldblat, Jozef; Cox, David, eds. (1988). Nuclear Weapon Tests: Prohibition or Limitation?. SIPRI Monograph Series. Stockholm International Peace Research Institute. p. 80. ISBN 978-0-19-829120-6.
- "Induced Seismicity – Home". esd1.lbl.gov. Archived from the original on 2018-07-11. Retrieved 2017-09-04.
- "M 4.3 Nuclear Explosion – North Korea". 2014-04-27. Retrieved 2017-12-30.
- "M 4.7 Nuclear Explosion – North Korea". 2009-05-28. Retrieved 2017-12-30.
- "Magnitudes for Oklahoma Earthquakes Shift Upward". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2017-09-04.
- "M 5.1 Nuclear Explosion – 24 km ENE of Sungjibaegam, North Korea". United States Geological Survey. Retrieved 2017-09-04.
- ^ (http://www.dw.com), Deutsche Welle. "North Korea claims successful hydrogen bomb test | News | DW | 03.09.2017". Deutsche Welle. Retrieved 2017-09-04.
{{cite web}}: External link in|last= - "North Korea claims success in fifth nuclear test". BBC News. 2016-09-09. Retrieved 2017-09-04.
Further reading
- Kisslinger, C (1976). "A review of theories of mechanisms of induced seismicity". Engineering Geology. 10 (2–4): 85–98. Bibcode:1976EngGe..10...85K. doi:10.1016/0013-7952(76)90014-4. ISSN 0013-7952.
- Talwani, P. (1997). "On the Nature of Reservoir-induced Seismicity". Pure and Applied Geophysics. 150 (3–4): 473–492. Bibcode:1997PApGe.150..473T. doi:10.1007/s000240050089. ISSN 0033-4553. S2CID 32397341.
- Foulger, G.R.; Wilson, M.P.; Gluyas, J.G.; Julian, B.R.; Davies, R.J. (2018). "Global review of human-induced earthquakes". Earth-Science Reviews. 178: 438–514. Bibcode:2018ESRv..178..438F. doi:10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.07.008.
External links
- The Human-Induced Earthquake Database
- Map of reservoir-induced earthquakes at International Rivers
- WEBINAR: Yes, Humans Really Are Causing Earthquakes – IRIS Consortium
- One-year seismic hazard forecast for the Central and Eastern United States from induced and natural earthquakes – United States Geological Survey, 2016 (with maps)
- Induced Earthquakes – United States Geological Survey website

 the critical
the critical  the
the  the normal stress,
the normal stress,  the friction coefficient on the fault plane and
the friction coefficient on the fault plane and  the pore pressure within the fault. When
the pore pressure within the fault. When 
 is the magnitude of seismic events,
is the magnitude of seismic events,  is the number of events with magnitudes bigger than
is the number of events with magnitudes bigger than  is the rate parameter and
is the rate parameter and  is the slope.
is the slope.