| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Rotation" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Rotation or rotational motion is the circular movement of an object around a central line, known as an axis of rotation. A plane figure can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise sense around a perpendicular axis intersecting anywhere inside or outside the figure at a center of rotation. A solid figure has an infinite number of possible axes and angles of rotation, including chaotic rotation (between arbitrary orientations), in contrast to rotation around a fixed axis.
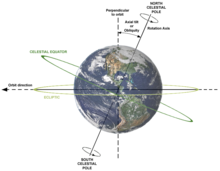
The special case of a rotation with an internal axis passing through the body's own center of mass is known as a spin (or autorotation). In that case, the surface intersection of the internal spin axis can be called a pole; for example, Earth's rotation defines the geographical poles. A rotation around an axis completely external to the moving body is called a revolution (or orbit), e.g. Earth's orbit around the Sun. The ends of the external axis of revolution can be called the orbital poles.
Either type of rotation is involved in a corresponding type of angular velocity (spin angular velocity and orbital angular velocity) and angular momentum (spin angular momentum and orbital angular momentum).
Mathematics
Main article: Rotation (mathematics)

Mathematically, a rotation is a rigid body movement which, unlike a translation, keeps at least one point fixed. This definition applies to rotations in two dimensions (in a plane), in which exactly one point is kept fixed; and also in three dimensions (in space), in which additional points may be kept fixed (as in rotation around a fixed axis, as infinite line).
All rigid body movements are rotations, translations, or combinations of the two.
A rotation is simply a progressive radial orientation to a common point. That common point lies within the axis of that motion. The axis is perpendicular to the plane of the motion.
If a rotation around a point or axis is followed by a second rotation around the same point/axis, a third rotation results. The reverse (inverse) of a rotation is also a rotation. Thus, the rotations around a point/axis form a group. However, a rotation around a point or axis and a rotation around a different point/axis may result in something other than a rotation, e.g. a translation.
Rotations around the x, y and z axes are called principal rotations. Rotation around any axis can be performed by taking a rotation around the x axis, followed by a rotation around the y axis, and followed by a rotation around the z axis. That is to say, any spatial rotation can be decomposed into a combination of principal rotations.
See also: curl (mathematics), cyclic permutation, Euler angles, rigid body, rotation around a fixed axis, rotation group SO(3), rotation matrix, axis angle, quaternion, and isometryFixed axis vs. fixed point
The combination of any sequence of rotations of an object in three dimensions about a fixed point is always equivalent to a rotation about an axis (which may be considered to be a rotation in the plane that is perpendicular to that axis). Similarly, the rotation rate of an object in three dimensions at any instant is about some axis, although this axis may be changing over time.
In other than three dimensions, it does not make sense to describe a rotation as being around an axis, since more than one axis through the object may be kept fixed; instead, simple rotations are described as being in a plane. In four or more dimensions, a combination of two or more rotations about a plane is not in general a rotation in a single plane.
Axis of 2-dimensional rotations
Further information: Rotations in two dimensions2-dimensional rotations, unlike the 3-dimensional ones, possess no axis of rotation, only a point about which the rotation occurs. This is equivalent, for linear transformations, with saying that there is no direction in the plane which is kept unchanged by a 2-dimensional rotation, except, of course, the identity.
The question of the existence of such a direction is the question of existence of an eigenvector for the matrix A representing the rotation. Every 2D rotation around the origin through an angle in counterclockwise direction can be quite simply represented by the following matrix:
A standard eigenvalue determination leads to the characteristic equation
which has
as its eigenvalues. Therefore, there is no real eigenvalue whenever , meaning that no real vector in the plane is kept unchanged by A.
Rotation angle and axis in 3 dimensions
Main article: Rotation around a fixed axisKnowing that the trace is an invariant, the rotation angle for a proper orthogonal 3×3 rotation matrix is found by
Using the principal arc-cosine, this formula gives a rotation angle satisfying . The corresponding rotation axis must be defined to point in a direction that limits the rotation angle to not exceed 180 degrees. (This can always be done because any rotation of more than 180 degrees about an axis can always be written as a rotation having if the axis is replaced with .)
Every proper rotation in 3D space has an axis of rotation, which is defined such that any vector that is aligned with the rotation axis will not be affected by rotation. Accordingly, , and the rotation axis therefore corresponds to an eigenvector of the rotation matrix associated with an eigenvalue of 1. As long as the rotation angle is nonzero (i.e., the rotation is not the identity tensor), there is one and only one such direction. Because A has only real components, there is at least one real eigenvalue, and the remaining two eigenvalues must be complex conjugates of each other (see Eigenvalues and eigenvectors#Eigenvalues and the characteristic polynomial). Knowing that 1 is an eigenvalue, it follows that the remaining two eigenvalues are complex conjugates of each other, but this does not imply that they are complex—they could be real with double multiplicity. In the degenerate case of a rotation angle , the remaining two eigenvalues are both equal to −1. In the degenerate case of a zero rotation angle, the rotation matrix is the identity, and all three eigenvalues are 1 (which is the only case for which the rotation axis is arbitrary).
A spectral analysis is not required to find the rotation axis. If denotes the unit eigenvector aligned with the rotation axis, and if denotes the rotation angle, then it can be shown that . Consequently, the expense of an eigenvalue analysis can be avoided by simply normalizing this vector if it has a nonzero magnitude. On the other hand, if this vector has a zero magnitude, it means that . In other words, this vector will be zero if and only if the rotation angle is 0 or 180 degrees, and the rotation axis may be assigned in this case by normalizing any column of that has a nonzero magnitude.
This discussion applies to a proper rotation, and hence . Any improper orthogonal 3x3 matrix may be written as , in which is proper orthogonal. That is, any improper orthogonal 3x3 matrix may be decomposed as a proper rotation (from which an axis of rotation can be found as described above) followed by an inversion (multiplication by −1). It follows that the rotation axis of is also the eigenvector of corresponding to an eigenvalue of −1.
Rotation plane
Main article: Rotation planeAs much as every tridimensional rotation has a rotation axis, also every tridimensional rotation has a plane, which is perpendicular to the rotation axis, and which is left invariant by the rotation. The rotation, restricted to this plane, is an ordinary 2D rotation.
The proof proceeds similarly to the above discussion. First, suppose that all eigenvalues of the 3D rotation matrix A are real. This means that there is an orthogonal basis, made by the corresponding eigenvectors (which are necessarily orthogonal), over which the effect of the rotation matrix is just stretching it. If we write A in this basis, it is diagonal; but a diagonal orthogonal matrix is made of just +1s and −1s in the diagonal entries. Therefore, we do not have a proper rotation, but either the identity or the result of a sequence of reflections.
It follows, then, that a proper rotation has some complex eigenvalue. Let v be the corresponding eigenvector. Then, as we showed in the previous topic, is also an eigenvector, and and are such that their scalar product vanishes:
because, since is real, it equals its complex conjugate , and and are both representations of the same scalar product between and .
This means and are orthogonal vectors. Also, they are both real vectors by construction. These vectors span the same subspace as and , which is an invariant subspace under the application of A. Therefore, they span an invariant plane.
This plane is orthogonal to the invariant axis, which corresponds to the remaining eigenvector of A, with eigenvalue 1, because of the orthogonality of the eigenvectors of A.
Rotation of vectors
A vector is said to be rotating if it changes its orientation. This effect is generally only accompanied when its rate of change vector has non-zero perpendicular component to the original vector. This can be shown to be the case by considering a vector which is parameterized by some variable for which:
Which also gives a relation of rate of change of unit vector by taking , to be such a vector: showing that vector is perpendicular to the vector, .
From:
,
since the first term is parallel to and the second perpendicular to it, we can conclude in general that the parallel and perpendicular components of rate of change of a vector independently influence only the magnitude or orientation of the vector respectively. Hence, a rotating vector always has a non-zero perpendicular component of its rate of change vector against the vector itself.
In higher dimensions
See also: Rotations in 4-dimensional Euclidean spaceAs dimensions increase the number of rotation vectors increases. Along a four dimensional space (a hypervolume), rotations occur along x, y, z, and w axis. An object rotated on a w axis intersects through various volumes, where each intersection is equal to a self contained volume at an angle. This gives way to a new axis of rotation in a 4d hypervolume, were a 3d object can be rotated perpendicular to the z axis.
Physics
The speed of rotation is given by the angular frequency (rad/s) or frequency (turns per time), or period (seconds, days, etc.). The time-rate of change of angular frequency is angular acceleration (rad/s), caused by torque. The ratio of torque τ to the angular acceleration α is given by the moment of inertia:
The angular velocity vector (an axial vector) also describes the direction of the axis of rotation. Similarly, the torque is an axial vector.
The physics of the rotation around a fixed axis is mathematically described with the axis–angle representation of rotations. According to the right-hand rule, the direction away from the observer is associated with clockwise rotation and the direction towards the observer with counterclockwise rotation, like a screw.
Circular motion
See also: Circular motion and Rotation around a fixed axis
It is possible for objects to have periodic circular trajectories without changing their orientation. These types of motion are treated under circular motion instead of rotation, more specifically as a curvilinear translation. Since translation involves displacement of rigid bodies while preserving the orientation of the body, in the case of curvilinear translation, all the points have the same instantaneous velocity whereas relative motion can only be observed in motions involving rotation.
In rotation, the orientation of the object changes and the change in orientation is independent of the observers whose frames of reference have constant relative orientation over time. By Euler's theorem, any change in orientation can be described by rotation about an axis through a chosen reference point. Hence, the distinction between rotation and circular motion can be made by requiring an instantaneous axis for rotation, a line passing through instantaneous center of circle and perpendicular to the plane of motion. In the example depicting curvilinear translation, the center of circles for the motion lie on a straight line but it is parallel to the plane of motion and hence does not resolve to an axis of rotation. In contrast, a rotating body will always have its instantaneous axis of zero velocity, perpendicular to the plane of motion.
More generally, due to Chasles' theorem, any motion of rigid bodies can be treated as a composition of rotation and translation, called general plane motion. A simple example of pure rotation is considered in rotation around a fixed axis.
Cosmological principle
The laws of physics are currently believed to be invariant under any fixed rotation. (Although they do appear to change when viewed from a rotating viewpoint: see rotating frame of reference.)
In modern physical cosmology, the cosmological principle is the notion that the distribution of matter in the universe is homogeneous and isotropic when viewed on a large enough scale, since the forces are expected to act uniformly throughout the universe and have no preferred direction, and should, therefore, produce no observable irregularities in the large scale structuring over the course of evolution of the matter field that was initially laid down by the Big Bang.
In particular, for a system which behaves the same regardless of how it is oriented in space, its Lagrangian is rotationally invariant. According to Noether's theorem, if the action (the integral over time of its Lagrangian) of a physical system is invariant under rotation, then angular momentum is conserved.
Euler rotations
Main article: Euler angles
Euler rotations provide an alternative description of a rotation. It is a composition of three rotations defined as the movement obtained by changing one of the Euler angles while leaving the other two constant. Euler rotations are never expressed in terms of the external frame, or in terms of the co-moving rotated body frame, but in a mixture. They constitute a mixed axes of rotation system, where the first angle moves the line of nodes around the external axis z, the second rotates around the line of nodes and the third one is an intrinsic rotation around an axis fixed in the body that moves.
These rotations are called precession, nutation, and intrinsic rotation.
Astronomy

In astronomy, rotation is a commonly observed phenomenon; it includes both spin (auto-rotation) and orbital revolution.
Spin
Stars, planets and similar bodies may spin around on their axes. The rotation rate of planets in the solar system was first measured by tracking visual features. Stellar rotation is measured through Doppler shift or by tracking active surface features. An example is sunspots, which rotate around the Sun at the same velocity as the outer gases that make up the Sun.
Under some circumstances orbiting bodies may lock their spin rotation to their orbital rotation around a larger body. This effect is called tidal locking; the Moon is tidal-locked to the Earth.
This rotation induces a centrifugal acceleration in the reference frame of the Earth which slightly counteracts the effect of gravitation the closer one is to the equator. Earth's gravity combines both mass effects such that an object weighs slightly less at the equator than at the poles. Another is that over time the Earth is slightly deformed into an oblate spheroid; a similar equatorial bulge develops for other planets.
Another consequence of the rotation of a planet are the phenomena of precession and nutation. Like a gyroscope, the overall effect is a slight "wobble" in the movement of the axis of a planet. Currently the tilt of the Earth's axis to its orbital plane (obliquity of the ecliptic) is 23.44 degrees, but this angle changes slowly (over thousands of years). (See also Precession of the equinoxes and Pole Star.)
Revolution
Main article: Orbital revolutionWhile revolution is often used as a synonym for rotation, in many fields, particularly astronomy and related fields, revolution, often referred to as orbital revolution for clarity, is used when one body moves around another while rotation is used to mean the movement around an axis. Moons revolve around their planets, planets revolve about their stars (such as the Earth around the Sun); and stars slowly revolve about their galaxial centers. The motion of the components of galaxies is complex, but it usually includes a rotation component.
Retrograde rotation
Main article: Retrograde motionMost planets in the Solar System, including Earth, spin in the same direction as they orbit the Sun. The exceptions are Venus and Uranus. Venus may be thought of as rotating slowly backward (or being "upside down"). Uranus rotates nearly on its side relative to its orbit. Current speculation is that Uranus started off with a typical prograde orientation and was knocked on its side by a large impact early in its history. The dwarf planet Pluto (formerly considered a planet) is anomalous in several ways, including that it also rotates on its side.
Flight dynamics
Main article: Aircraft principal axes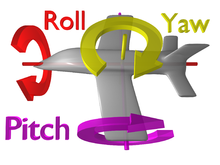
In flight dynamics, the principal rotations described with Euler angles above are known as pitch, roll and yaw. The term rotation is also used in aviation to refer to the upward pitch (nose moves up) of an aircraft, particularly when starting the climb after takeoff.
Principal rotations have the advantage of modelling a number of physical systems such as gimbals, and joysticks, so are easily visualised, and are a very compact way of storing a rotation. But they are difficult to use in calculations as even simple operations like combining rotations are expensive to do, and suffer from a form of gimbal lock where the angles cannot be uniquely calculated for certain rotations.
Amusement rides
Many amusement rides provide rotation. A Ferris wheel has a horizontal central axis, and parallel axes for each gondola, where the rotation is opposite, by gravity or mechanically. As a result, at any time the orientation of the gondola is upright (not rotated), just translated. The tip of the translation vector describes a circle. A carousel provides rotation about a vertical axis. Many rides provide a combination of rotations about several axes. In Chair-O-Planes the rotation about the vertical axis is provided mechanically, while the rotation about the horizontal axis is due to the centripetal force. In roller coaster inversions the rotation about the horizontal axis is one or more full cycles, where inertia keeps people in their seats.
Sports
"Spin move" redirects here. For other uses, see Spin move (disambiguation).Rotation of a ball or other object, usually called spin, plays a role in many sports, including topspin and backspin in tennis, English, follow and draw in billiards and pool, curve balls in baseball, spin bowling in cricket, flying disc sports, etc. Table tennis paddles are manufactured with different surface characteristics to allow the player to impart a greater or lesser amount of spin to the ball.
Rotation of a player one or more times around a vertical axis may be called spin in figure skating, twirling (of the baton or the performer) in baton twirling, or 360, 540, 720, etc. in snowboarding, etc. Rotation of a player or performer one or more times around a horizontal axis may be called a flip, roll, somersault, heli, etc. in gymnastics, waterskiing, or many other sports, or a one-and-a-half, two-and-a-half, gainer (starting facing away from the water), etc. in diving, etc. A combination of vertical and horizontal rotation (back flip with 360°) is called a möbius in waterskiing freestyle jumping.
Rotation of a player around a vertical axis, generally between 180 and 360 degrees, may be called a spin move and is used as a deceptive or avoidance manoeuvre, or in an attempt to play, pass, or receive a ball or puck, etc., or to afford a player a view of the goal or other players. It is often seen in hockey, basketball, football of various codes, tennis, etc.
See also
- Absolute rotation – Rotation independent of any external reference
- Circular motion
- Cyclone – large scale rotating air mass
- Instant centre of rotation – instantaneously fixed point on an arbitrarily moving rigid body
- Mach's principle – speculative hypothesis that a physical law relates the motion of the distant stars to the local inertial frame
- Orientation (geometry)
- Point reflection
- Rolling – motion of two objects in contact with each-other without sliding
- Rotation (quantity) – a unitless scalar representing the number of rotations
- Rotation around a fixed axis
- Rotation formalisms in three dimensions
- Rotating locomotion in living systems
- Top – spinning toy
- Euler angle
References
- ^ Wormeli, R. (2009). Metaphors & Analogies: Power Tools for Teaching Any Subject. Stenhouse Publishers. p. 28. ISBN 978-1-57110-758-9. Retrieved 2023-07-27.
- Brannon, R.M., "Rotation, Reflection, and Frame Change", 2018
- Kumar, N.; Kumar, Naveen (2004). Generalized motion of rigid body. Pangbourne, U.K.: Alpha Science International Ltd. p. 5. ISBN 978-1-84265-160-5.
- Yan, Xiaoqi; Fu, Chi-Wing; Hanson, Andrew J. (September 29, 2012). "Multitouching the Fourth Dimension". Computer. 45 (9): 80–88. doi:10.1109/MC.2012.77 – via Semantic Scholar.
- Kageyama, Akira (August 1, 2016). "A visualization method of four-dimensional polytopes by oval display of parallel hyperplane slices". Journal of Visualization. 19 (3): 417–422. arXiv:1607.01102. doi:10.1007/s12650-015-0319-5 – via Springer Link.
- ^ Harrison, H.; Nettleton, T. (1997-08-01). "Rigid body motion in three dimensions". Advanced Engineering Dynamics. Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 55. ISBN 978-0-08-052335-4.
- Hibbeler, R. C. (2007). "Planar kinematics of a rigid body: Instantaneous center of zero velocity". Engineering Mechanics: Statics & dynamics. Prentice-Hall. ISBN 978-0-13-221509-1.
- "An Oasis, or a Secret Lair?". ESO Picture of the Week. Archived from the original on 11 October 2013. Retrieved 8 October 2013.
External links
- "Rotation", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001
- Product of Rotations at cut-the-knot.
- When a Triangle is Equilateral at cut-the-knot.
- Rotate Points Using Polar Coordinates, howtoproperly.com
- Rotation in Two Dimensions by Sergio Hannibal Mejia after work by Roger Germundsson and Understanding 3D Rotation by Roger Germundsson, Wolfram Demonstrations Project. demonstrations.wolfram.com
- Brannon, R. M. (2018). Rotation, Reflection, and Frame Changes. IOP Publishing. doi:10.1088/978-0-7503-1454-1. ISBN 978-0-7503-1454-1.
 in counterclockwise direction can be quite simply represented by the following
in counterclockwise direction can be quite simply represented by the following 


 , meaning that no real vector in the plane is kept unchanged by A.
, meaning that no real vector in the plane is kept unchanged by A.
 for a proper orthogonal 3×3 rotation matrix
for a proper orthogonal 3×3 rotation matrix  is found by
is found by

 . The corresponding rotation axis must be defined to point in a direction that limits the rotation angle to not exceed 180 degrees. (This can always be done because any rotation of more than 180 degrees about an axis
. The corresponding rotation axis must be defined to point in a direction that limits the rotation angle to not exceed 180 degrees. (This can always be done because any rotation of more than 180 degrees about an axis  can always be written as a rotation having
can always be written as a rotation having  .)
.)
 that is aligned with the rotation axis will not be affected by rotation. Accordingly,
that is aligned with the rotation axis will not be affected by rotation. Accordingly,  , and the rotation axis therefore corresponds to an eigenvector of the rotation matrix associated with an eigenvalue of 1. As long as the rotation angle
, and the rotation axis therefore corresponds to an eigenvector of the rotation matrix associated with an eigenvalue of 1. As long as the rotation angle  , the remaining two eigenvalues are both equal to −1. In the degenerate case of a zero rotation angle, the rotation matrix is the identity, and all three eigenvalues are 1 (which is the only case for which the rotation axis is arbitrary).
, the remaining two eigenvalues are both equal to −1. In the degenerate case of a zero rotation angle, the rotation matrix is the identity, and all three eigenvalues are 1 (which is the only case for which the rotation axis is arbitrary).
 denotes the unit eigenvector aligned with the rotation axis, and if
denotes the unit eigenvector aligned with the rotation axis, and if  . Consequently, the expense of an eigenvalue analysis can be avoided by simply normalizing this vector if it has a nonzero magnitude. On the other hand, if this vector has a zero magnitude, it means that
. Consequently, the expense of an eigenvalue analysis can be avoided by simply normalizing this vector if it has a nonzero magnitude. On the other hand, if this vector has a zero magnitude, it means that  . In other words, this vector will be zero if and only if the rotation angle is 0 or 180 degrees, and the rotation axis may be assigned in this case by normalizing any column of
. In other words, this vector will be zero if and only if the rotation angle is 0 or 180 degrees, and the rotation axis may be assigned in this case by normalizing any column of  that has a nonzero magnitude.
that has a nonzero magnitude.
 . Any improper orthogonal 3x3 matrix
. Any improper orthogonal 3x3 matrix  may be written as
may be written as  , in which
, in which  is also an eigenvector, and
is also an eigenvector, and  and
and  are such that their scalar product vanishes:
are such that their scalar product vanishes:

 is real, it equals its complex conjugate
is real, it equals its complex conjugate  , and
, and  and
and  are both representations of the same scalar product between
are both representations of the same scalar product between  which is parameterized by some variable
which is parameterized by some variable  for which:
for which:

 showing that
showing that  vector is perpendicular to the vector,
vector is perpendicular to the vector,  ,
,
