| SBe 250 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Fragmentation bomb |
| Place of origin | |
| Service history | |
| Used by | Luftwaffe |
| Wars | World War II |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 250 kg (550 lb) |
| Length | 1.63 m (5 ft 4 in) |
| Diameter | 14 in (36 cm) |
| Warhead | Ammonal |
| Warhead weight | 46 kg (101 lb) |
| Detonation mechanism | TNT |
The SBe 250 (Splitter Beton) or concrete fragmentation in English was a fragmentation bomb used by the Luftwaffe during World War II.
History
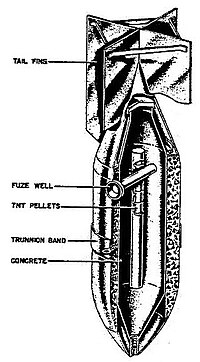
The SBe series of bombs were designed to be semi-armor piercing fragmentation bombs that could act as an adjunct to the SD series of bombs. There were two bombs in this series the SBe 50, and the SBe 250. The number in the bombs designation corresponded to the approximate weight of the bomb. The SBe series was an effort to balance low cost, good fragmentation, and effective explosives. The SBe series achieved its fragmentation by embedding scrap metal in a layer of concrete instead of having a thick steel casing like the SD series. This concept had already been used successfully on the SD 10 A Type II and the SD 10 DW.
Design
The body of the SBe 250 consisted of thin inner and outer steel cases with scrap metal embedded in a 51 mm (2 in) layer of concrete between the cases. The nose was formed from a 5 mm (3/16 in) steel dome and there was a single transverse fuze in the rear 1/3 of the bomb. There was also a central TNT exploder which ran through the ammonal explosive filler. The tail was sheet steel with four single braces and there was a removable trunnion band which was used to horizontally suspend the bomb. Due to its heavy construction its charge to weight ratio was only 18%. The bomb was painted blue green.
See also
References
- ^ United States War Office (1953). German explosive ordnance : (bombs, fuzes, rockets, land mines, grenades and igniters). United States Government Printing Office. OCLC 713755660.
- Visingr, Lukáš. "Německé letecké bomby: Smrticí arzenál Luftwaffe". Vojsko.net (in Czech). Retrieved 2019-03-07.
| German aerial weapons of the Second World War | |
|---|---|
| Machine guns | |
| Autocannons | |
| Anti-tank autocannons | |
| Unguided rockets | |
| Guided bombs and missiles | |
| Anti-personnel bombs | |
| Armor-piercing bombs | |
| Cluster bombs | |
| High-explosive bombs | |
| Incendiary bombs | |
| Anti-ship bombs | |
| Smoke bombs | |
| Experimental weapons | |