| This article may be written from a fan's point of view, rather than a neutral point of view. Please clean it up to conform to a higher standard of quality, and to make it neutral in tone. (December 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Sourav Ganguly | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Ganguly in 2008 Ganguly in 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chairman of the ICC Men's Cricket Committee | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Incumbent | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assumed office 17 November 2021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preceded by | Anil Kumble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35th President of the Board of Control for Cricket in India | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In office 23 October 2019 – 18 October 2022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preceded by | C.K. Khanna | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Succeeded by | Roger Binny | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16th President of the Cricket Association of Bengal | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| In office 2015–2019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preceded by | Jagmohan Dalmiya | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Succeeded by | Avishek Dalmiya | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Personal information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Full name | Sourav Chandidas Ganguly | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Born | (1972-07-08) 8 July 1972 (age 52) Behala, Calcutta, West Bengal, India | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nickname | Dada, Prince of Calcutta, Maharaj, Bengal Tiger | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Height | 1.80 m (5 ft 11 in) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Batting | Left-handed | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bowling | Right-arm medium | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Role | Batsman | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Relations |
Dona Ganguly (m. 1997) Sana Ganguly (daughter) Snehasish Ganguly (brother) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | souravganguly | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| National side |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Test debut (cap 206) | 20 June 1996 v England | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last Test | 6 November 2008 v Australia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ODI debut (cap 84) | 11 January 1992 v West Indies | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Last ODI | 15 November 2007 v Pakistan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ODI shirt no. | 99 (previously 21, 24, 1, 2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Domestic team information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Years | Team | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1990–2010 | Bengal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2000 | Lancashire | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | Glamorgan | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 | Northamptonshire | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008–2010 | Kolkata Knight Riders | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011–2012 | Pune Warriors India | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Career statistics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Medal record
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: ESPNcricinfo, 2 January 2013 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Signature |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sourav Chandidas Ganguly (/sʃuːrəv ɡɛnɡuːlj/ ; natively spelled as Gangopadhyay; born 8 July 1972), also known as Dada (meaning "elder brother" in Bengali), is an Indian cricket commentator and former cricketer. He is popularly called the Maharaja of Indian Cricket. He was captain of the Indian national cricket team and is regarded as one of India's most successful cricket captains. As captain, he led Indian national team to win the 2002 ICC Champions Trophy and reach the final of the 2003 Cricket World Cup, the 2000 ICC Champions Trophy and the 2004 Asia Cup.
Ganguly scored 11363 runs in his ODI career which stands at ninth position in the world for most runs scored in ODI matches. He was the third batsman to cross the 10,000 runs in One day cricket, after Sachin Tendulkar and Inzamam Ul Haq. He holds the record for highest score in an innings (183) by an Indian batsman in the ODI Cricket World Cup. In 2002, the Wisden Cricketers' Almanack ranked him the sixth greatest ODI batsman of all time. He announced his retirement from international cricket in 2008 and from all forms of cricket in 2012.
Ganguly was awarded the fourth highest Indian civilian award, Padma Shri in 2004. He was elected as president of the Board of Control for Cricket in India in 2019. He is also a part of the Supreme Court of India appointed probe panel for the IPL Spot fixing and betting scandal's investigations.
Early and personal life
Sourav Ganguly was born on 8 July 1972 in Calcutta, and is the youngest son of Chandidas and Nirupa Ganguly. Chandidas ran a flourishing print business and was one of the richest men in the city. Ganguly had a luxurious childhood and was nicknamed the 'Maharaj', meaning the Great King. Ganguly's father Chandidas Ganguly died at the age of 73 on 21 February 2013 after a long illness.
Ganguly was educated at St. Xavier's Collegiate School, Kolkata. He was then graduated in commerce from the St. Xavier's College, Kolkata.
Since the favourite sport for the people of Calcutta was football, Ganguly was initially attracted to the game. However, academics came in-between his love for sports and Nirupa was not very supportive of Ganguly taking up cricket or any other sport as a career. By then, his elder brother Snehasish was already an established cricketer for the Bengal cricket team. He supported Ganguly's dream to be a cricketer and asked their father to get Ganguly enrolled in a cricket coaching camp during his summer holidays. Ganguly was studying in tenth standard at that time.
Despite being right-handed, Ganguly learnt to bat left-handed so he could use his brother's sporting equipment. After he showed some promise as a batsman, he was enrolled in a cricket academy. An indoor multi-gym and concrete wicket was built at their home, so he and Snehasish could practice the game. They used to watch a number of old cricket match videos, especially the games played by David Gower, whom Ganguly admired. After he scored a century against the Orissa Under–15 side, he was made captain of St Xavier's School's cricket team, where several of his teammates complained against what they perceived to be his arrogance. While touring with a junior team, Ganguly refused his turn as the twelfth man, as he reportedly felt that the duties involved, which included organising equipment and drinks for the players, and delivering messages, were beneath his social status. Ganguly purportedly refused to do such tasks as he considered it beneath his social status to assist his teammates in such a way. However, his playmanship gave him a chance to make his first-class cricket debut for Bengal in 1989, the same year that his brother was dropped from the team.
He is married to Indian classical dancer dancer Dona Ganguly, with whom he has a daughter Sana (b. 2001).
Health
On 2 January 2021, Ganguly complained of chest pain while exercising and was later diagnosed with three blocked coronary arteries which had led to a mild cardiac arrest. He underwent primary angioplasty for one of the blockages on the same day.
Playing career
1990–96: Career beginning and debut success
See also: List of centuries scored on Test cricket debut
Following a prolific Ranji season in 1990–91, Ganguly scored three runs in his One Day International (ODI) debut for India against the West Indies in 1992. He was dropped immediately since he was perceived to be "arrogant" and his attitude towards the game was openly questioned. It was rumoured that Ganguly refused to carry drinks for his teammates, commenting that it was not his job to do so, later denied by him. Consequently, he was removed from the team. He toiled away in domestic cricket, scoring heavily in the 1993–94 and 1994–95 Ranji seasons. Following an innings of 171 in the 1995–96 Duleep Trophy, he was recalled to the Indian team for a tour of England in 1996, in the middle of intense media scrutiny. He played in a single ODI, but was omitted from the team for the first Test. However, after teammate Navjot Singh Sidhu left the touring party, citing ill-treatment by then captain Mohammad Azharuddin, Ganguly made his Test debut against England in the Second Test of a three-match series at Lord's Cricket Ground along with Rahul Dravid. England had won the First Test of the three-match series; however, Ganguly scored a century, becoming only the third cricketer to achieve such a feat on debut at Lord's, after Harry Graham and John Hampshire. Andrew Strauss and Matt Prior have since accomplished this feat, but Ganguly's 131 still remains the highest by any batsman on his debut at the ground. India was not required to bat in the second innings due to the match ending in a draw. In the next Test match at Trent Bridge he made 136, thus becoming only the third batsman to make a century in each of his first two innings (after Lawrence Rowe and Alvin Kallicharran). He shared a 255 run stand with Sachin Tendulkar, which became at that time the highest partnership for India against any country for any wicket outside India. The Test again ended in a draw, handing England a 1–0 series victory; Ganguly scored 48 in the second innings.
1997–99: Marriage, Opening in ODIs and World Cup '99
See also: List of highest individual scores in ODIs
Weeks after his successful tour of England, Ganguly eloped with childhood sweetheart Dona Roy. The bride and groom's family were sworn enemies at that point and this news caused an uproar between them. However, both families reconciled and a formal wedding was held in February 1997. Same year, Ganguly scored his maiden ODI century by hitting 113, opposed to Sri Lanka's team total of 238. Later that year, he won four consecutive man of the match awards, in the Sahara Cup with Pakistan; the second of these was won after he took five wickets for 16 runs off 10 overs, his best bowling in an ODI. After a barren run in Test cricket his form returned at the end of the year with three centuries in four Tests, all against Sri Lanka, and two of these involved stands with Sachin Tendulkar of over 250.
During the third final of the Independence Cup at Dhaka in January 1998, India successfully chased down 315 off 48 overs, and Ganguly won the Man of the Match award. In March 1998 he was part of the Indian team that defeated Australia; in Kolkata, he took three wickets having opened the bowling with his medium pace.
Ganguly was part of the Indian team that competed in the 1999 World Cup in England. During the match against Sri Lanka at Taunton, India chose to bat. After Sadagoppan Ramesh was bowled, Ganguly scored 183 from 158 balls, and hit 17 fours and seven sixes. It was the second highest score in World Cup history and the highest by an Indian in the tournament at the time. His partnership of 318 with Rahul Dravid is the highest overall score in a World Cup and is the second highest in all ODI cricket. In 1999–00, India lost Test series to both Australia and South Africa that involved a combined total of five Tests. Ganguly struggled scoring 224 runs at 22.40; however his ODI form was impressive, with five centuries over the season taking him to the top of the PwC One Day Ratings for batsmen. Around the same time, allegations came that Ganguly was romantically involved with South Indian actress Nagma, something he denied.
2000–05: Ascension to captaincy and accolades
See also: List of players who have scored 10,000 or more runs in One Day International cricketSourav Ganguly to the media"People will support you, people will criticize you. When you cross that rope everything is about you."

In 2000, after the match fixing scandal by some of the players of the team, Ganguly was named the captain of the Indian cricket team. The decision was spurred due to Tendulkar stepping down from the position for his health, and Ganguly being the vice-captain at that time. He began well as a captain, leading India to a series win over South Africa in the five-match one day series and led the Indian team to the finals of the 2000 ICC KnockOut Trophy. He scored two centuries, including one in the final; however, New Zealand still won by four wickets. The same year, Ganguly tried his hand at county cricket career in England but was not successful. In "The Wisden Cricketer", reviewers Steve Pittard and John Stern called him as "The imperious Indian—dubbed 'Lord Snooty'". They commented:
"At the crease it was sometimes uncertain whether his partner was a batsman or a batman being dispatched to take his discarded sweater to the pavilion or carry his kit bag. But mutiny was afoot among the lower orders. In one match Ganguly, after reaching his fifty, raised his bat to the home balcony, only to find it deserted. He did not inspire at Glamorgan or Northamptonshire either. At the latter in 2006 he averaged 4.80 from his four first-class appearances."
His Lancashire teammate Andrew Flintoff thought him to be aloof and compared his attitude to that of Prince Charles. In Australia's three Test and five-match ODI tour of India in early 2001, Ganguly caused controversy by arriving late for the toss on four occasions, something that agitated opposing captain Steve Waugh. In the Fourth ODI, he caused further controversy by failing to wear his playing attire to the toss, something considered unusual in cricket circles. However, India won the Test series 2–1, ending Australia's run of 16 consecutive Test match victories in the Second Test. The match saw India looking set for defeat after conceding a first innings lead of 274. Waugh chose to enforce the follow-on and V. V. S. Laxman (281) and Rahul Dravid (180) batted for the entire fourth day's play to set Australia a target of 384 on a dusty, spinning wicket. The Australians were unable to survive and became only the third team to lose a Test after enforcing the follow-on. In November 2001, Ganguly's wife Dona gave birth to their daughter Sana. During the final match of the 2002 NatWest Series held in Lords after a stunning performance by teammates Yuvraj Singh and Mohammad Kaif, Ganguly took off his shirt in public and brandished it in the air to celebrate India's winning of the match. He was later strongly condemned for tarnishing the "gentleman's game" image of cricket and disrespecting Lord's protocol. Ganguly said that he was only mimicking an act performed by the British all-rounder Andrew Flintoff during a tour of India. In 2003, India reached the World Cup Final for the first time since 1983, where they lost to the Australians. Ganguly had a successful tournament personally, scoring 465 runs at an average of 58.12, including three centuries.

Baichung Bhutia on Sourav Ganguly"Sourav is the sole reason I am a cricket lover"
By 2004, he had achieved significant success as captain and was deemed as India's most successful cricket captains by sections of the media. However, his individual performance deteriorated during his captaincy reign, especially after the World Cup, the tour of Australia in 2003 and the Pakistan series in 2004. In 2004, Australia won a Test series in India for the first time since 1969. It was speculated that Ganguly was in disagreement with the head of cricket in Nagpur over the type of pitch to be used for the Third Test. The groundsmen went against Ganguly, leaving a large amount of grass on the pitch. Some experts indicated that the reason for this was for "spite or revenge" against the Indian captain. When Australia's stand-in-captain, Adam Gilchrist, went to the toss, he noticed Rahul Dravid was waiting instead of Ganguly, leaving him to ask Dravid where Ganguly was. Dravid could not give a definitive answer, saying: "Oh, who knows?"
Following indifferent form in 2004 and poor form in 2005, he was dropped from the team in October 2005. Having been nominated and rejected in 2000, when the game suffered a tarnished reputation due to match fixing scandals, the captaincy was passed to Dravid, his former deputy. Ganguly decided against retiring and attempted to make a comeback to the team. Ganguly was awarded the Padma Shri in 2004, India's fourth highest civilian award, in recognition of his distinguished contribution in the field of sports. He was presented with the award on 30 June 2004, by then President of India, Dr. A. P. J. Abdul Kalam.
2006–07: Comeback and rift with Greg Chappell
Main article: Chappell Ganguly controversy
In September 2005, Greg Chappell became the coach of India for the tour of Zimbabwe. Ganguly's dispute with him resulted in many headlines. Chappell had emailed the Board of Control for Cricket in India, stating that Ganguly was "physically and mentally" unfit to lead India and that his "divide and rule" behaviour was damaging the team. This email was leaked to the media and resulted in huge backlash from Ganguly's fans. Ganguly had enlisted the support from the Indian media and eventually the board had to intervene and order a truce between the pair. BCCI president Ranbir Singh Mahendra issued a statement that,
"In view of the decision that cricket is to go forward, both the coach and the captain have been asked to work out a mutual and professional working relationship. For this, performance will be the criteria, applicable to captain, coach and players. Of course the captain controls the game, the coach does his own job. Mutual trust is important. Henceforth no player/captain/coach will write or have any interaction with the media. Going to the media will lead to disciplinary action."
| Ganguly's results in international matches | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matches | Won | Lost | Drawn | Tied | No result | |
| Test | 113 | 37 | 35 | 41 | 0 | – |
| ODI | 311 | 149 | 145 | - | 1 | 16 |
Ganguly, Chappell and the Indian team manager for the Zimbabwe tour, Amitabh Choudhary, were asked to appear before the BCCI committee, where it was reported that assurance of working together was given by them. Consequently, due to his poor form and differences with the coach, Ganguly was dropped as the captain of the team, with Dravid taking his place. Chandresh Narayan, chief correspondent for The Times of India, commented that "The row with Greg Chappell just added to the mystery, but he was going through a really bad patch then, his only score was a hundred against Zimbabwe and that didn't count for much." Ten months later, during India's tour to South Africa, Ganguly was recalled after his middle order replacements Suresh Raina and Mohammad Kaif suffered poor form.
Following India's poor batting display in the 2006 ICC Champions Trophy and the ODI series in South Africa, in which they were whitewashed 4–0, Ganguly made his comeback to the Test team. Wasim Jaffer, Zaheer Khan and Anil Kumble had earlier been selected for the one-day squad, despite their recent poor performances. Many saw this as an indictment of coach Greg Chappell's youth-first policy. Coming in at 37/4, Ganguly scored 83 in a tour match against the rest of South Africa, modifying his original batting style and taking a middle-stump guard, resulting in India winning the match. During his first Test innings since his comeback, against South Africa in Johannesburg his score of 51 helped India to victory, marking the first Test match win for the team in South Africa. Though India lost the series, Ganguly accumulated the most runs on the scoring chart. After his successful Test comeback he was recalled for the ODI team, as India played host to West Indies and Sri Lanka in back to back ODI tournaments. In his first ODI innings in almost two years, he scored a matchwinning 98. He performed well in both series, averaging almost 70 and won the Man of the Series Award against Sri Lanka.
Ganguly was allotted a place in the official team for the 2007 Cricket World Cup. He was the leading scorer for India in their first round defeat against Bangladesh. After India were knocked out of the tournament in the group stage, there were reports of a rift between certain members of the Indian team and Chappell. Ganguly was alleged to have ignored instructions from the team management to score quickly. After Tendulkar issued a statement saying that what hurt the team most was that "the coach has questioned our attitude", Chappell decided not to renew his contract with the Indian team and left his post as coach, citing "family and personal reasons". On 12 December 2007, Ganguly scored his maiden double century of his career while playing against Pakistan. He scored 239 runs in the first innings of the third and final Test match of the series. He was involved in a 300 run partnership for the fifth wicket with Yuvraj Singh. Ganguly remained prolific in both Test and ODI cricket in the year 2007. He scored 1106 Test runs at an average of 61.44 (with three centuries and four fifties) in 2007 to become the second highest run-scorer in Test matches of that year after Jacques Kallis. He was also the fifth highest run-scorer in 2007 in ODIs, where he scored 1240 runs at an average of 44.28.
For his performances in 2007, he was named in the World Test XI by ESPNcricinfo.
2008–12: International retirement and IPL

In the controversial test vs Australia in January 2008, Ganguly scored half centuries in both the innings in a losing cause. In February 2008, Ganguly joined as the captain of Kolkata Knight Riders (KKR) team, owned by Bollywood actor Shah Rukh Khan, as part of the Indian Premier League (IPL). On 18 April 2008, Ganguly led the KKR, in the IPL Twenty20 cricket match. They had a 140 run victory over Bangalore Royal Challengers (captained by Rahul Dravid and owned by Vijay Mallya). Ganguly opened the innings with Brendon McCullum and scored 10 runs while McCullum remained unbeaten, scoring 158 runs in 73 balls. On 1 May, in a game between the Knight Riders and the Rajasthan Royals, Ganguly made his second T20 half century, scoring 51 runs off of 39 balls at a strike rate of 130.76. In his innings, Ganguly hit four 4s and two sixes, topping the scorers list for the Knight Riders.
On 7 July 2008, media reported that Ganguly was being projected as a candidate for the post of President of the Cricket Association of Bengal (CAB) against his former mentor Jagmohan Dalmiya. Reports also suggested that he could run for the post of BCCI President in 2014 as East Zone's representative. Ganguly himself did not deny the reports and did not rule out any such move. The same year in October, Ganguly announced that the Test series against Australia starting in October 2008 would be his last and stated "o be honest, I didn't expect to be picked for this series. Before coming here, I spoke to my team-mates and hopefully I will go out with a winning knock." Ganguly played in every game of the four-Test series and amassed 324 runs at an average of 54.00. While playing the second Test match of the series in Mohali, Ganguly scored his final test century. In the final test match he played at Nagpur against Australia he scored 85 and 0 in his first and second innings respectively. In the Fourth and final Test, with India needing one wicket to secure a victory, the Indian captain, Mahendra Singh Dhoni, invited Ganguly to lead the side in the field for the final time. India regained the Border–Gavaskar Trophy, winning the series 2–0.
In May 2009, Ganguly was removed from the captaincy of the KKR for the 2009 season of the IPL, and was replaced by McCullum. The decision was questioned by media and other players of the team, when KKR finished at the bottom of the ranking table with three wins and ten losses. After that, Bengali television channel Zee Bangla roped him as the host of the reality quiz show titled Dadagiri Unlimited. It presented participants from the 19 districts of West Bengal, who had to answer questions posed by Ganguly. By August, he was appointed the chairman of CAB's Cricket Development Committee. The job of the committee is to receive a report from the selectors at the end of every cricket season, assess the accountability of the selectors and make necessary recommendations. He played for the Ranji cup in the Bengal team in October 2009. Ganguly scored 110 in the match against Delhi and was involved in a partnership of 222 runs with Wriddhiman Saha.
In the third season of the IPL, Ganguly was once again given the captaincy of KKR, after the team ended at the bottom in the second season. The coach John Buchanan was replaced by Dav Whatmore. In 40 matches and 38 innings for KKR Ganguly scored 1,031 runs and took eight wickets. In the fourth season of the IPL he was signed by the Pune Warriors India, after being unsold in initial bidding process and he made 50 runs of four matches and three innings. In the 2012 season he has been appointed as the Captain cum mentor for Pune Warriors India. On 29 October 2012, he announced that he has decided not to play in next year's IPL and to retire from the game.
2013–present Administration career

Ganguly was part of the Supreme Court of India appointed Justice Mudgal Committee probe panel for the IPL Spot fixing and betting scandal's investigations. From 2015 to October 2019, he was the President of the Cricket association of Bengal. In 2018 his autobiographical book A Century is Not Enough was published. In March 2019, Ganguly was appointed as the advisor of the Delhi Capitals IPL team. In October 2019 he became President of the Board of Control for Cricket in India and President of the editorial board with Wisden India. Ganguly's security cover was upgraded to 'Z' Category by the West Bengal government. He will now have 8 to 10 police personnel guarding him.
Playing style and influences

Ganguly commented that David Gower was the first cricketer to attract him to the game. He loved Gower's style and used to watch old videos of him playing. Other cricketers who had an influence on him are: David Boon, Mohinder Amarnath, Kapil Dev and Allan Border. Ganguly is a left-handed batsman whose runs came primarily from the off-side. Debashish Dutta, author of Sourav Ganguly, the maharaja of cricket, commented that throughout his career, "Ganguly played off-side shots such as the square cut, square drive and cover drive with complete command." Rahul Dravid has called Ganguly "...next to God on the off-side." He used to hit powerful shots to the off-side on front and back foot with equal ease. However, early in his career he was not comfortable with the hook and pull, often giving his wicket away with mistiming such shots. He was also criticised for having difficulty in handling short bouncers, notoriously exploited by the Australians and South Africans. However, after his comeback in 2007, he worked upon these weaknesses to a large extent.
Amrita Daityari, author of Sourav Ganguly: the fire within, noted that in ODIs, where Ganguly usually opened the innings, he used to try to take the advantage of fielding restrictions by advancing down the pitch and hitting pace bowlers over extra cover and mid-off. She commented: "Ganguly was notorious for attacking left-arm spin bowlers. Due to excellent eye–hand coordination, he was noted for picking the length of the ball early, coming down the pitch and hitting the ball aerially over mid-on or midwicket, often for a six. However, he did have a weakness in running between the wickets and judging quick singles." There were many instances where Ganguly's batting partner was run out due to Ganguly's calling for a run, and then sending him back while halfway down the pitch. A situation like this happened in an ODI against Australia where he took a single when on 99, but he coasted and did not ground his bat. Although the bat was past the crease, it was in the air and he was consequently run out. Ganguly said, "I love to watch myself hit a cover drive, to watch myself hit a hundred." Ganguly's relationship with former Indian coach John Wright has been well documented in contemporary media, with them denoting the relationship as a "symbiotic process". They credited Wright and Ganguly with bringing out international class performers, through academic, coaching and scientific fitness regimens. According to Dubey, Ganguly and Wright, along with other members of the team like Tendulkar and Dravid, were the first to understand the importance of a foreign coach for the Indian cricket team and was convinced that the domestic coach has outlived its utility. Ganguly's aggressive style and Wright's importance on fitness ushered in the development of a better cricket team for India.
Ganguly is a right-arm medium pace bowler. He can swing and seam the ball both ways and often chips in with useful wickets to break partnerships. Vinod Tiwari, author of the biography Sourav Ganguly praised him saying "espite not being very athletic as a fielder, Ganguly has taken 100 catches in one-day Internationals. That's something to be proud of!" However he criticised Ganguly's ground fielding, especially his slowness in intercepting the ball to prevent runs and his tendency to get injured during catching the ball.
Legacy
| Opposition | Test | ODI |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | |
| 3 | 3 | |
| 2 | 3 | |
| 3 | 1 | |
| 2 | 2 | |
| 2 | 1 | |
| – | 3 | |
| 1 | 1 | |
| NA | 3 | |
| NA | 1 | |
| Total | 16 | 22 |
Author Pradeep Mandhani commented that in his tenure between 2000 and 2005, Ganguly became India's most successful Test captain. He led his team to victory on 21 occasions – seven times more than Mohammad Azharuddin with the second most wins—and led them for a record 49 matches—twice more than both Azharuddin and Sunil Gavaskar. Compared to his batting average of 45.47 when not captain, Ganguly's Test batting average as captain was a lower 37.66.
Statistics about Ganguly show that he was the seventh Indian cricketer to have played 100 Test matches, the 4th highest overall run scorer for India in Tests, and the fourth Indian to have played in more than 300 ODIs. In terms of overall runs scored in ODIs, Ganguly is the third among Indians after Sachin Tendulkar (who has the most ODI runs) and Virat Kohli and the ninth overall. He has scored 16 centuries in Test matches and 22 in ODIs. He is also one of only ten batsmen to score more than 10,000 runs in ODIs. Along with Tendulkar, Ganguly has formed the most successful opening pair in One Day Cricket, having amassed the highest number of century partnerships (26) for the first wicket. Together, they have scored more than 7000 runs at an average of 48.98, and hold the world record for creating most 50-run partnership in the first wicket (44 fifties). Ganguly became the fourth player to cross 11,000 ODI runs, and was the fastest player to do so in ODI cricket, after Tendulkar. As of 2006, he is the only Indian captain to win a Test series in Pakistan (although two of the three Tests of that series was led by Rahul Dravid). He is also one of the five players in the world to achieve amazing treble of 10,000 runs, 100 wickets and 100 catches in ODI cricket history, the others being Tendulkar, Kallis, Sanath Jayasuriya and Tillakaratne Dilshan.

Author Mihir Bose, in his book, The magic of Indian cricket: cricket and society in India. commented that "The cricket world had gotten too used to the stereotype of the meek Indian cricketer. All that has changed under Ganguly, perhaps for the better." He credits Ganguly for not being shy of taking on responsibility. "He showed that he can be a leader of a team, which has greats like Sachin and Dravid in the side, without any problems. Under Ganguly's leadership, India started winning matches and tournaments, previously lacking from the team considerably." Within a few years of his captaincy, Ganguly rewrote the rules of being a captain of a cricket team. Unlike some of his predecessors, Ganguly was considered impartial, non-parochial, and forever pushed his players to perform better. Off the field, his interactions with the media, his fans, and detractors were uncompromisingly honest and earned him the respect of cricket followers everywhere. However, along with this respect came the criticisms. Ganguly was condemned as a hot-tempered man who refused to listen to other's opinions and abided by his own rules and regulations. Matthew Engel, ICC sport critic, noted that this "turning deaf" to other's opinions would one day harm Ganguly and that it was sheer luck that he existed on the sporting world.
Ganguly believed that his legacy as a captain was that he was able to build a proper Indian team. He added,
" were able to change the face of Indian cricket. That's what I'm proud of, because I think we made a huge difference. People used to think that we would simply roll over when playing out of India, but we changed the image. Absolutely, and that came from self-belief that, that we had the ability to do well outside India."
Bose commented that Ganguly's greatest legacy lay in his influence on the younger and budding generation of cricketers. Ganguly felt that every young player should play two years of domestic cricket before being selected for international assignments. He also said that every newcomer should be given at least five games to prove himself. Later he explained that being at the receiving end of an unfair decision against him, that threatened to ruin his international cricket career, it enabled him to understand the insecurities of other newcomers in the team better than his predecessors. Ganguly had always backed the influence and contribution of younger players of the team.
Despite his contributions, his captaincy and coaching methods came under immense scrutiny from the press as well as other scholars. Engel commented that "He seems like aloof to the problems that his mal-decisions are creating. I don't particularly believe that Ganguly has an 'effing knowledge how to lead his team and tries to counter-pose it with instigating limitless, confrontational behaviours within the younger members of it. the time will come when such shock tactics will cease to work." An article on Cricinfo Magazine pointed out his reckless behaviour. The reporter Rahul Bhattacharya said, "Generally Ganguly fostered angry or reckless young men. To him 'good behaviour', a broad term espoused by the present team management, belonged in school and probably not even there. He himself had been summoned to the match referee no less than 12 times in the last decade. His approach was bound to precipitate what could possibly be termed a cultural conflict in the world of modern sport. For Ganguly, like for Arjuna Ranatunga, competitiveness involved brinksmanship rather than training. As far as they were concerned Australia were not to be aspired to. They were simply to be toppled. England were not to be appeased. Victory lay precisely in their disapproval. In other words, Ganguly and Ranatunga wanted to do things their way."
Overall career performance
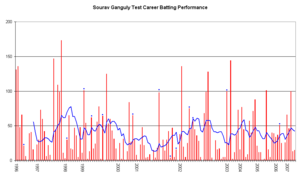
| Test Match Career Performance By Opposition | Batting Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opposition | Matches | Runs | Average | High Score | 100 / 50 |
| 24 | 1403 | 35.07 | 144 | 2 / 7 | |
| 5 | 371 | 61.83 | 100 | 1 / 3 | |
| 12 | 983 | 57.82 | 136 | 3 / 5 | |
| 8 | 563 | 46.91 | 125 | 3 / 2 | |
| 12 | 902 | 47.47 | 239 | 2 / 4 | |
| 17 | 947 | 33.82 | 87 | 0 / 7 | |
| 14 | 1064 | 46.26 | 173 | 3 / 4 | |
| 12 | 449 | 32.07 | 75* | 0 / 2 | |
| 9 | 530 | 44.16 | 136 | 2 / 1 | |
| Overall figures | 113 | 7212 | 42.17 | 239 | 16 / 35 |
| ODI Career Performance By Opposition | Batting Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opposition | Matches | Runs | Average | High Score | 100 / 50 |
| 35 | 774 | 23.45 | 100 | 1 / 5 | |
| 10 | 459 | 57.37 | 135* | 1 / 4 | |
| 26 | 975 | 39.00 | 117* | 1 / 7 | |
| 32 | 1079 | 35.96 | 153* | 3 / 6 | |
| 53 | 1652 | 35.14 | 141 | 2 / 9 | |
| 29 | 1313 | 50.50 | 141* | 3 / 8 | |
| 44 | 1534 | 40.36 | 183 | 4 / 9 | |
| 27 | 1142 | 47.58 | 98 | 0 / 11 | |
| 36 | 1367 | 42.71 | 144 | 3 / 7 | |
| ICC World XI | 1 | 22 | 22.00 | 22 | 0 / 0 |
| Africa XI | 2 | 120 | 60.00 | 88 | 0 / 1 |
| 1 | 89 | 89.00 | 89 | 0 / 1 | |
| 1 | 73 | – | 73* | 0 / 1 | |
| 11 | 588 | 73.50 | 111* | 3 / 2 | |
| 1 | 112 | – | 112* | 1 / 0 | |
| 1 | 8 | 8.00 | 8 | 0 / 0 | |
| 1 | 56 | 56.00 | 56 | 0 / 1 | |
| Overall figures | 311 | 11363 | 41.02 | 183 | 22 / 72 |
Records and achievements

- The only cricketer to win four consecutive man of the match awards in One Day Internationals.
- The ninth highest run-scorer in ODI history and third among the Indians, with 11,363 runs.
- He holds the record for registering the highest individual score by any batsman in a ICC Champions Trophy final (117)
- He was also the first player to score 3 centuries in the history of ICC Champions Trophy
- The second fastest batsman to reach 9,000 ODI runs after AB De Villiers of South Africa who broke Ganguly's record in 2017
- One of the only six cricketers to have achieved the unique treble of 10,000 runs, 100 wickets & 100 catches in ODI cricket. (Others cricketer were Sachin Tendulkar, Sanath Jayasuriya, Jacques Kallis, Chris Gayle, Tillakaratne Dilshan.)
- Has the highest individual score by an Indian batsman (183) in the Cricket World Cup.
- One of the 14 cricketers in the world to have played 100 or more Tests and 300 or more ODIs.
- Sourav Ganguly is the only batsman to score a century on debut and to be dismissed first ball in his final Test innings.
Captaincy record
| Captaincy Record in Test Matches | ||||||
| Venue | Span | Matches | Won | Lost | Tied | Draw |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home | 2000–2005 | 21 | 10 | 3 | 0 | 8 |
| Away | 2000–2005 | 28 | 11 | 10 | 0 | 7 |
| Total | 2000–2005 | 49 | 21 | 13 | 0 | 15 |
| Career summary as captain in Test Matches | ||||||||||||
| Venue | Span | Matches | Runs | HS | Bat Avg | 100 | Wkts | BBI | Bowl Avg | 5 | Ct | St |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home | 2000–2005 | 21 | 868 | 136 | 29.93 | 2 | 3 | 1/14 | 78.00 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Away | 2000–2005 | 28 | 1693 | 144 | 43.41 | 3 | 2 | 2/69 | 193.00 | 0 | 13 | 0 |
| Total | 2000–2005 | 49 | 2561 | 144 | 37.66 | 5 | 5 | 2/69 | 124.00 | 0 | 37 | 0 |
| Captaincy Record in One Day Internationals | ||||||
| Venue | Span | Matches | Won | Lost | Tied | N/R |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home | 2000–2005 | 36 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 0 |
| Away | 2000–2005 | 51 | 24 | 24 | 0 | 3 |
| Neutral | 1999–2005 | 59 | 34 | 23 | 0 | 2 |
| Total | 1999–2005 | 146 | 76 | 65 | 0 | 5 |
| Career summary as captain in One Day Internationals | ||||||||||||
| Venue | Span | Matches | Runs | HS | Bat Avg | 100 | Wkts | BBI | Bowl Avg | 5 | Ct | St |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Home | 2000–2005 | 36 | 1463 | 144 | 43.02 | 2 | 16 | 5/34 | 30.87 | 1 | 14 | 0 |
| Away | 2000–2005 | 51 | 1545 | 135 | 32.18 | 2 | 15 | 3/22 | 39.26 | 0 | 23 | 0 |
| Neutral | 2000–2005 | 60 | 2096 | 141 | 41.92 | 7 | 15 | 3/32 | 43.20 | 0 | 24 | 0 |
| Total | 2000–2005 | 147 | 5104 | 144 | 38.66 | 11 | 46 | 5/34 | 37.63 | 1 | 61 | 0 |
Bibliography
- Ganguly, Sourav; Bhattacharya, Gautam (2018). A Century is Not Enough: My Roller-coaster Ride to Success. Juggernaut Books. ISBN 978-93-86228-56-7.
See also
- List of international cricket centuries by Sourav Ganguly
- List of highest individual scores in ODIs
- Dadagiri Unlimited
- List of Cricket Association of Bengal Presidents
- No Dada No KKR
- Cricket All-Stars
Notes
- Menon, B. N. K. (1999). Myiris Guide to the ICC World Cup, England '99. Marine Sports Pub. Division. p. 132. ISBN 978-81-85361-50-5.
- Jha, Sanjay (2010). 11 Triumphs Trials Turbulence. Orient Paperbacks. p. 23. ISBN 978-81-222-0497-1.
- Bhattacharya, Abhirup (8 July 2018). "Maharaja of Indian Cricket: Why Sourav Ganguly Is An Inspiration". TheQuint. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- "Sourav Ganguly: Inside the mind of India's 'greatest' cricket captain". BBC. 7 March 2018. Archived from the original on 27 December 2022. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- ^ "Former India cricket captain Sourav Ganguly retires". BBC. 29 October 2012. Archived from the original on 26 April 2023. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- "Most runs in career". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 8 June 2023. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- "Sourav Ganguly scores 10,000 ODI run". Hindustan Times. PTI. 10 August 2005. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2023.
- "Records in World Cup". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 8 June 2023. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- "Tendulkar second-best ever: Wisden". Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 23 January 2009. Retrieved 27 November 2008.
- "Padma Awards" (PDF). Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India. 2015. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 October 2015. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- India Today Web Desk (23 October 2019). "Sourav Ganguly formally elected as the 39th president of BCCI". India Today. Retrieved 23 October 2019.
- Times Now (23 October 2019). "Sourav Ganguly takes over as BCCI president, ends 33-month tumultuous CoA reign". Economic Times. Retrieved 23 October 2019.
- "Sourav Ganguly inducted into Mudgal Panel to probe IPL spot-fixing and betting scandal". Economic Times. 9 June 2014. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- ^ "ESPNcricinfo – Players and Officials – Sourav Ganguly". Cricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 20 June 2009. Retrieved 19 May 2008.
- Datta 2007, p. 21.
- ^ Tiwari 2005, p. 16.
- PTI 2 (21 February 2013). "Sourav Ganguly's father Chandidas passes away". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 24 February 2013. Retrieved 1 March 2013.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - "After cricket, time for school". The Times of India. 13 March 2009.
- Ganguly, Sourav (31 December 1999). "My off-side play is just one of the strengths of my batting". Rediff.com (Interview). Interviewed by Haresh Pandya. Archived from the original on 23 January 2022. Retrieved 17 July 2023.
- ^ "Biography of Sourav Ganguly". Official website of Sourav Ganguly. Souravganguly.net. Archived from the original on 30 May 2008. Retrieved 19 May 2008.
- Datta 2007, pp. 22–23.
- Daityari 2003, p. 3.
- ^ Coupar, Paul (27 November 2005). "The Awkward XI". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 8 January 2010. Retrieved 22 May 2008.
- Daityari 2003, p. 15.
- ^ Lilywhite, Jamie (16 July 2007). "Ganguly back in the limelight". BBC. BBC Online. Archived from the original on 7 December 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2010.
- Dubey 2006, p. 205.
- "Sourav Ganguly undergoes angioplasty after suffering a heart attack, is stable". The Times of India. 2 January 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- "Sourav Ganguly undergoes angioplasty in Kolkata hospital, condition stable". Mint. 2 January 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- "Ranji Trophy Statistics: 1990–91". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 22 May 2008.
- "9th Match: India v West Indies at Brisbane, January 11, 1992". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 10 July 2009. Retrieved 22 May 2008.
- "Batting – Most Runs – Ranji Trophy". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2008.
- "Highest Batting Averages in Ranji Trophy". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 4 March 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2008.
- Bose 2006, p. 201.
- "ESPNcricinfo – 3rd ODI: England v India at Manchester, May 26–27, 1996". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 24 September 2009. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- ^ Bose 2006, p. 258.
- "2nd Test: England v India at Lord's, June 20–24, 1996". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. 24 June 1996. Archived from the original on 10 July 2009. Retrieved 23 May 2008.
- "Statsguru – List of test centuries on debut at Lord's". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 20 July 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2008.
- "3rd Test: England v India at Nottingham, July 4–9, 1996". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 18 June 2009. Retrieved 19 May 2008.
- Datta 2007, p. 99.
- Pandey, Jhimli Mukherjee (29 May 2001). "Saurav and Donna happy at last". The Times of India. The Times Group. Archived from the original on 16 March 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Ramchand, Partab (22 September 2009). "Independence Cup final, Dhaka, 1998". Sify. Archived from the original on 4 April 2010. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- James, Claudia (19 October 2008). "Vintage Sourav Ganguly puts Australia to the sword". The Times. London: News Corporation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Mandhani 2008, p. 134.
- Reporter, Post (23 September 2001). "Ganguly and Dravid storm the World Cup 1999". Thats Cricket. Oneindia.in. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "India in Australia, 1999/00 Test Series Best Innings". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "South Africa in India Test Series 1999/00 / Results". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Coopers, Pricewaterhouse (19 March 2000). "PwC Ratings: Ganguly claims Number One spot". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Basu, Surajit (19 September 2009). "History: Past, Present and coming". India Today. 2 (1–13). Mumbai, India: Living Media: 78. ISSN 0254-8399. Retrieved 5 February 2010.
- "Ganguly?s career was at stake, so we parted: Nagma". Rediff.com. 6 March 2003. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- ^ Reporter, BBC (26 January 2001). "In Depth: Corruption in Cricket". BBC. BBC Online. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "Coca-Cola Champions' Trophy, 2000–01". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Dubey 2006, p. 123.
- Pittard, Steve; Stern, John (24 May 2007). "Dodgy overseas signings". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- ^ Swanton, Will (19 November 2008). "Hero or villain, Ganguly made his mark". The Age. Melbourne: Fairfax Digital. Archived from the original on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- Waugh 2001, p. 71.
- Waugh 2001, pp. 52–53.
- "2nd Test: India v Australia at Calcutta 11–15 March 2001". ESPNcricinfo. ESPN. Archived from the original on 6 February 2007. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "Incredible India defeat Australia". BBC Sport. 15 March 2001. Archived from the original on 16 September 2009. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "Tests – Victory after Following-On". ESPNcricinfo. ESPN. Archived from the original on 16 January 2010. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Tharakan, Tony (10 November 2008). "Ganguly takes off his shirt one last time". Reuters. Archived from the original on 27 July 2018. Retrieved 27 July 2018.
- Kavoori 2009, p. 54.
- Reporter, BBC (23 February 2003). "Ruthless Aussies lift World Cup". BBC. BBC Online. Archived from the original on 28 March 2015. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "SC Ganguly / One-Day Internationals / Series averages". ESPNcricinfo. ESPN. Archived from the original on 19 January 2013. Retrieved 25 January 2010.
- Reporter, BBC (19 February 2003). "Ganguly hits back at critics". BBC. BBC Online. Archived from the original on 7 April 2008. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Gilchrist 2008, pp. 423–424.
- Singh, Onkar (15 December 2005). "Ganguly cried on being dropped". Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Bhandari, Sunita (26 January 2004). "Ganguly, Dravid and Anju get Padma Shri". The Times of India. The Times Group. Archived from the original on 22 February 2009. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "Winning Padma Shri a great honour: Ganguly". Rediff.com. Press Trust of India. 30 June 2004. Archived from the original on 7 June 2011. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Rajaraman, G. "A Temporary And Tenuous Truce". www.outlookindia.com. Retrieved 8 December 2020.
- "Statistics / Statsguru / SC Ganguly /Test Matches". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 20 September 2012. Retrieved 4 January 2013.
- "List of Test victories". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 19 January 2014. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
- "List of ODI victories". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 31 October 2013. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
- Majumdar, Boria (26 January 2018). "When Greg Chappell told Sourav Ganguly: You have no place in the team". The Economic Times. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- Reporter, BBC (13 October 2005). "Ganguly dropped as India captain". BBC. BBC Online. Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Reporter, BBC (30 November 2006). "Ganguly recalled for Test series". BBC. BBC Online. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "ESPNcricinfo Statsguru – India – Champions Trophy 2006 – Team analysis". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- "ESPNcricinfo Statsguru – India Vs. South Africa 2006–07 – Team analysis". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Reporter, ESPNcricinfo (30 November 2006). "Ganguly in, Laxman appointed vice-captain". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 24 December 2009. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Reporter, ESPNcricinfo (25 March 2006). "Jaffer, Zaheer and Kumble added to ODI squad". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Srikkanth, Kris (30 October 2006). "Raina's inclusion a big surprise". The Times of India. The Times Group. Archived from the original on 21 February 2009. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Alter, Jaime (13 December 2006). "Exorcising the demons". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 1 January 2010. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- "Tour Match: Rest of South Africa v Indians at Potchefstroom, December 7–9, 2006". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- "1st Test: South Africa v India at Johannesburg, December 15–18, 2006". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 14 October 2008. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Patwardhan, Deepti (18 December 2006). "India score maiden Test win in South Africa". Rediff.com. Archived from the original on 1 May 2010. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- "India in South Africa Test Series, 2006/07 – Most runs". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 23 February 2009. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Vasu, Anand (12 January 2007). "Sehwag out, Ganguly picked for ODIs". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 24 September 2009. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Vasu, Anand (12 February 2007). "Sehwag and Munaf back for SL series". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- ^ "ESPNcricinfo Statsguru – SC Ganguly – One-Day Internationals". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Vaidyanathan, Siddarth (21 January 2007). "India edge past despite Chanderpaul's masterclass". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 5 July 2009. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Reporter, ESPNcricinfo (17 February 2007). "Ganguly happy with World Cup preparations". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 6 April 2010. Retrieved 24 May 2008.
- Reporter, ESPNcricinfo (7 January 2006). "'I will play in the 2007 World Cup' – Ganguly". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 15 January 2010.
- Vaidyanathan, Siddhartha (17 March 2007). "Brilliant Bangladesh stun India". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 1 June 2008.
- Vasu, Anand (3 April 2007). "BCCI faces its toughest challenge". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 10 August 2010. Retrieved 1 June 2008.
- Reporter, ESPNcricinfo (4 April 2007). "The Greg Chappell Timeline: A controversial reign". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 1 June 2008.
- Premachandran, Dileep (8 December 2007). "Yuvraj and Ganguly put India on top". ESPNcricinfo. ESPN. Archived from the original on 3 July 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- "Most Runs in Test Matches in 2007". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 16 March 2008. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- "Most Runs in One-Day Internationals in 2007". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 2 March 2008. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- "Mainly Aussie". ESPNcricinfo. 3 January 2008.
- Reporter, BBC (20 February 2008). "Dhoni tops Indian auction bidding". BBC. BBC Online. Archived from the original on 15 October 2010. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Chatterjee, Mridula (19 April 2008). "Kolkata Knight Riders Defeat Bangalore Royal Challengers". India-Server.com. Archived from the original on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- "Rajasthan Royals vs Kolkata Knight Riders". Rajasthan Royals. Archived from the original on 27 April 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- "Sourav Ganguly to be BCCI president?". Zee News. 7 July 2008. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Mukherjee, Sumit (8 July 2009). "Ganguly may try to become BCCI chief in 2014". The Times of India. The Times Group. Archived from the original on 10 July 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Reporter, BBC (7 October 2008). "Ganguly to quit after Test series". BBC. BBC Online. Archived from the original on 3 November 2008. Retrieved 14 January 2010.
- "Batting and bowling averages: Border–Gavaskar Trophy, 2008/09 – India". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 21 February 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Chopra, Nikhil (18 October 2008). "Ganguly retiring at the right time". Zee News. Archived from the original on 8 July 2012. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- "Sourav Ganguly | Cricket365 | Stats & Records | International | Cricket365 | Cricket News". Cricket365. Archived from the original on 21 June 2014. Retrieved 11 August 2014.
- Staff, ESPNcricinfo (10 November 2008). "Dhoni carries forward Ganguly's flame". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 18 October 2009. Retrieved 10 December 2008.
- Parker, Ajit (11 November 2008). "Saurav Ganguly retires from test cricket in style by captaining a victorious Indian side against Aussies". India Daily. The Times Group. Archived from the original on 1 February 2010. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Staff, ESPNcricinfo (23 May 2009). "We would have done better under Ganguly – Dinda". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 16 March 2010. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Shukla, Shirish (24 July 2009). "Ganguly's Dadagiri on Bengali TV show". Hindustan Times. HT Media Ltd. Archived from the original on 5 June 2011. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Staff, ESPNcricinfo (22 August 2009). "Ganguly appointed to Bengal administrative post". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 27 August 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Staff, ESPNcricinfo (10 October 2009). "Ganguly mulls Ranji stint with Bengal". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 11 December 2009. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Staff, ESPNcricinfo (15 December 2009). "Ganguly, Saha centuries revive Bengal". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- "Kolkata Knight Riders". Indian Premier League Official Website. Archived from the original on 17 March 2010. Retrieved 22 March 2010.
- "Twenty20 batting and fielding for each team by Sourav Ganguly". CricketArchive. Archived from the original on 7 November 2012. Retrieved 19 May 2011.
- "Twenty20 bowling for each team by Sourav Ganguly". CricketArchive. Archived from the original on 30 November 2011. Retrieved 19 May 2011.
- "Sourav Ganguly to Join Pune Warriors". The Times of India. The Times Group. 25 April 2011. Archived from the original on 9 September 2011. Retrieved 11 May 2011.
- "Twenty20 batting for each team by Sourav Ganguly". CricketArchive. Archived from the original on 7 November 2012. Retrieved 23 May 2011.
- "Former India cricket captain Sourav Ganguly retires". BBC. 29 October 2012. Archived from the original on 30 October 2012.
- "Sourav Ganguly quits IPL, retires from all levels of cricket". 29 October 2012. Archived from the original on 1 November 2012. Retrieved 29 October 2012.
- "It was like driving a Rolls-Royce one day and sleeping on the pavement the next". ESPN. 27 February 2018. Retrieved 21 May 2022.
- "Sourav Ganguly on teaming up with SRK, Shoaib Akhtar for IPL: Read an excerpt from A Century Is Not Enough". Firstpost. 27 February 2018. Retrieved 21 May 2022.
- Chakrabarty, Shamik (26 March 2019). "IPL 2019: Sourav Ganguly joins Delhi Capitals, says no conflict of interest". The Indian Express. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- Team Sportstar (28 March 2019). "Watch: Sourav Ganguly bats at Delhi Capitals nets". Sportstar. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- "The cricketing god Indians pray will deliver big". BBC News. 23 October 2019.
- "Sourav Ganguly's Security Cover Upgraded to 'Z' Category". NDTV. 17 May 2023.
- Tiwari 2005, p. 104.
- Dubey 2006, p. 120.
- Datta 2007, p. 309.
- Bose 2006, p. 35.
- Dinakar, Sitesh (14 December 2007). "Sourav Ganguly—the comeback man". The Hindu. Chennai, India. Archived from the original on 1 May 2008. Retrieved 19 January 2010.
- Daityari 2003, p. 83.
- Brijnath, Rohit (13 March 2000). "Poor team performance and morale, overbearing officials, but Saurav Ganguly isn't scared". India Today. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ^ Dubey 2006, p. 215.
- Tiwari 2005, p. 89.
- Mandhani 2008, p. 67.
- "India Captains' Playing Record in Test Matches". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 18 September 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "Statsguru home: SC Ganguly Test matches – Batting analysis not as captain". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 17 July 2012. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "Statsguru home: SC Ganguly Test matches – Batting analysis as captain". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 29 July 2012. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "Indian Cricketers: Most Test Matches". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 9 November 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "Indian Cricketers: Most Test Runs". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 5 November 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "Indian Cricketers: Most One-Day Internationals". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 13 October 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "Most Runs in Career: One-Day Internationals". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 5 November 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "ESPNcricinfo – Records – One-Day Internationals – Most runs in career". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 5 November 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- "Opening Pairs with an Aggregate of 1000 Runs or more". Howstat Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 21 July 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2008.
- Corresspondent, Special (5 August 2005). "Ganguly joins 10,000-club". The Hindu. Chennai, India: The Hindu Group. Archived from the original on 23 February 2009. Retrieved 14 January 2010.
- Kavoori 2009, p. 923.
- ^ Bose 2006, p. 280.
- Engel 2006, p. 45.
- Mahajan, Rohit (20 October 2008). "I wanted to go out with dignity, on a winning note". Outlook. 48 (42). Mumbai, India: Vinod Mehta: 18. Retrieved 22 January 2010.
- Petropoulos, Thrasy (12 November 2003). "World Cup 2003 – Team profile – India". BBC. BBC Online. Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2010.
- Sharma, Chetan (12 November 2003). "Sourav Ganguly will have to get the team balance right". The Tribune. Dyal Singh Majithia. Archived from the original on 23 February 2009. Retrieved 14 January 2010.
- Bose 2006, p. 282.
- Engel 2006, p. 32.
- Bhattacharya, Rahul (12 September 2007). "The heart of the matter". ESPNcricinfo Magazine. ESPN. Archived from the original on 18 November 2008. Retrieved 10 February 2010.
- "Sourav Ganguly – Test Matches / Batting Analysis". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 6 January 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- "Sourav Ganguly – ODI Matches / Batting Analysis". ESPNcricinfo. Archived from the original on 10 April 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2015.
- "Man-of-the-Match monopoly". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- "fastest to reach 9000 ODI runs". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- "Highest individual scores for India in World Cups". ESPNcricinfo. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- "A century of centuries on debut". Wisden India. Archived from the original on 17 November 2015. Retrieved 23 March 2017.
- ^ "Team records | One-Day Internationals | ESPNcricinfo Statsguru | ESPNcricinfo". Stats.espncricinfo.com. Archived from the original on 22 June 2013. Retrieved 7 June 2012.
- ^ "Cricket Records | Records | India | ODI matches | Most matches as captain | ESPNcricinfo". Stats.espncricinfo.com. Archived from the original on 1 March 2014. Retrieved 17 December 2012.
References
- Bose, Mihir (2006). "The magic of Indian cricket: cricket and society in India". Routledge. ISBN 0-415-35691-1.
- Daityari, Amrita (2003). "Sourav Ganguly: the fire within". Rupa & Company Publishers. ISBN 81-291-0143-2.
- Datta, Debashish (2007). "Sourav Ganguly, the maharaja of cricket". Niyogi Books. ISBN 978-81-89738-20-4.
- Dubey, Abhishek (2006). "Dressing Room". Diamond Pocket Books (P) Ltd. ISBN 81-8419-191-X.
- Engel, Matthew (2006). "Wisden Cricketers' Almanack". John Wisden & Co Ltd. ISBN 978-0-947766-98-6.
- Gilchrist, Adam (2008). "True Colours". Pan Macmillan Australia. ISBN 978-1-4050-3922-2.
- Kavoori, Anandam P. (2009). "The logics of globalization: studies in international communication". Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-0-7391-2184-9.
- Mandhani, Pradeep (2008). "Cricket World Cup '99 frozen". University of Michigan. ISBN 978-1-84353-197-5.
- Tiwari, Vinod (2005). "Sourav Ganguly". Manoj Publications. ISBN 81-8133-985-1.
- Waugh, Steve (2001). "Ashes Diary 2001". HarperCollinsPublishers. ISBN 0-7322-6444-8.
- "Chronology of Important Sports Events — West Bengal". wbsportsandyouth.gov.in. Kolkata: Government of West Bengal – Department of youth services and sports. 2017. Archived from the original on 13 October 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
External links
| Sporting positions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded bySachin Tendulkar | Indian Test captain 2000–2005 |
Succeeded byRahul Dravid |
| Preceded bySachin Tendulkar | Indian One-Day captain 2000–2005 |
Succeeded byRahul Dravid |
| Preceded byPosition started | Kolkata Knight Riders captain 2008 |
Succeeded byBrendon McCullum |
| Preceded byBrendon McCullum | Kolkata Knight Riders captain 2010–2011 |
Succeeded byGautam Gambhir |
| Preceded byYuvraj Singh | Pune Warriors India captain 2012 |
Succeeded byAngelo Mathews |
| Preceded byJagmohan Dalmiya | President of the CAB 2015–present |
Succeeded byIncumbent |
| Preceded byC K Khanna | President of the BCCI 2019–present |
Succeeded byIncumbent |
| India Test cricket captains | |
|---|---|
| |
| Italics denote deputised captaincy |
| India ODI cricket captains | |
|---|---|
| |
| Italics denote deputised captaincy |
| Indian cricketers who have played 100 or more Test matches | |
|---|---|
| |
| ^Dravid and Sehwag played one Test match for ICC World Test XI, which is not included above. |
| Batsmen with 10,000 or more runs in ODI cricket | |
|---|---|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Current players are listed in italics. | |
| ICC Champions Trophy winning captains | |
|---|---|
| ATK | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kolkata, West Bengal | |||||
| The Club | |||||
| Stadiums | |||||
| Owner | Kolkata Games and Sports (Ganguly, Goenka, Neotia, Parekh) | ||||
| |||||
| |||||
| Presidents of CAB | |
|---|---|
| 1928–1949 |
|
| 1950–1991 |
|
| 1992–present |
|
| Note. Associated link | |
| Presidents of the BCCI | |
|---|---|
| 1928–1950 |
|
| 1951–1975 |
|
| 1976–2000 |
|
| 2001–present |
|
Categories:
- 1972 births
- ACC Asian XI One Day International cricketers
- Bengali cricketers
- Bengali Hindus
- Indian sports executives and administrators
- Cricketers at the 1999 Cricket World Cup
- Cricketers at the 2003 Cricket World Cup
- Cricketers at the 2007 Cricket World Cup
- Cricketers who made a century on Test debut
- Bengal cricketers
- East Zone cricketers
- Glamorgan cricketers
- Indian cricketers
- Indian cricket commentators
- Indian cricket administrators
- India Test cricket captains
- India Green cricketers
- India One Day International cricketers
- India Test cricketers
- Kolkata Knight Riders cricketers
- Lancashire cricketers
- Living people
- Northamptonshire cricketers
- Indian expatriate cricketers in England
- Marylebone Cricket Club cricketers
- Cricketers from Kolkata
- Pune Warriors India cricketers
- Recipients of the Arjuna Award
- Recipients of the Padma Shri in sports
- University of Calcutta alumni
- ATK (football club) owners