| Schizotequatrovirus | |
|---|---|
| |
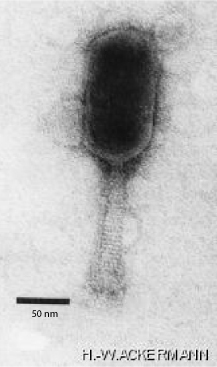
| Electron micrograph of a virion of species Schizotequattrovirus | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Duplodnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Heunggongvirae |
| Phylum: | Uroviricota |
| Class: | Caudoviricetes |
| Family: | Straboviridae |
| Genus: | Schizotequatrovirus |
| Species | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Schizotequatrovirus (formerly Schizot4virus) is a unassigned genus of viruses in the unassigned family Straboviridae, in the class Caudoviricetes,. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus.
Taxonomy
The following list is a map of T4virus species according to ICTV Version 2022
Group: dsDNA
- Class: Caudoviricetes
- Family: Straboviridae
- Genus: Schizotequatrovirus
- Family: Straboviridae
Structure

The virions of Schizotequatrovirus are nonenveloped, with a head and tail. The head is a prolate spheroid approximately 140 nm in length and 70 nm in width. The tail is around 140 nm long, has 6 long terminal fibers, 6 short spikes, and a small base plate. The tail is enclosed in a sheath, which loosens and slides around the tail core upon contraction.
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizotequatrovirus | Head-Tail | T=13 Q=21 | Non-enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
Genome
Genomes are linear. All three species have been fully sequenced. They range between 244k and 248k nucleotides, with 381 to 405 proteins. The complete genomes are available from National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), along with the complete genome for Vibrio phage VH7D, an unclassified virus strain.
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. The virus attaches to the host cell using its terminal fibers, and uses viral exolysin to degrade the cell wall enough to eject the viral DNA into the host cytoplasm via contraction of its tail sheath. DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. Once the viral genes have been replicated, the procapsid is assembled and packed. The tail is then assembled and the mature virions are released via lysis. Bacteria serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are passive diffusion.
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schizotequatrovirus | Bacteria | None | Injection | Lysis | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
History
According to ICTV's 2010–11 report, the genus Schizot4likevirus was first accepted as a new genus, at the same time as its type species Vibrio phage KVP40, as well as its containing subfamily Tevenvirinae. At the same time, Vibrio phage nt-1 was moved into the genus from its previous classification in T4-like viruses (now T4virus). This proposal is available here. In 2015, the genus was renamed to Schizot4virus. In 2019, with Master Species List 34, the genus was renamed again, now to Schizotequatrovirus
References
- ^ "Virus Taxonomy: 2022 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2022. Retrieved 15 September 2023.
- ^ "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 1 July 2015.
- ^ NCBI. "Schizot4virus Complete Genomes". Retrieved 13 February 2015.
External links
| Taxon identifiers | |
|---|---|
| Schizot4likevirus | |
Categories: