| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Concrete" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (July 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |

Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most widely used building material. Its usage worldwide, ton for ton, is twice that of steel, wood, plastics, and aluminium combined.
When aggregate is mixed with dry Portland cement and water, the mixture forms a fluid slurry that is easily poured and molded into shape. The cement reacts with the water through a process called concrete hydration that hardens it over several hours to form a hard matrix that binds the materials together into a durable stone-like material that has many uses. This time allows concrete to not only be cast in forms, but also to have a variety of tooled processes performed. The hydration process is exothermic, which means ambient temperature plays a significant role in how long it takes concrete to set. Often, additives (such as pozzolans or superplasticizers) are included in the mixture to improve the physical properties of the wet mix, delay or accelerate the curing time, or otherwise change the finished material. Most concrete is poured with reinforcing materials (such as steel rebar) embedded to provide tensile strength, yielding reinforced concrete.
In the past, lime-based cement binders, such as lime putty, were often used but sometimes with other hydraulic cements, (water resistant) such as a calcium aluminate cement or with Portland cement to form Portland cement concrete (named for its visual resemblance to Portland stone). Many other non-cementitious types of concrete exist with other methods of binding aggregate together, including asphalt concrete with a bitumen binder, which is frequently used for road surfaces, and polymer concretes that use polymers as a binder. Concrete is distinct from mortar. Whereas concrete is itself a building material, mortar is a bonding agent that typically holds bricks, tiles and other masonry units together. Grout is another material associated with concrete and cement. It does not contain coarse aggregates and is usually either pourable or thixotropic, and is used to fill gaps between masonry components or coarse aggregate which has already been put in place. Some methods of concrete manufacture and repair involve pumping grout into the gaps to make up a solid mass in situ.
Etymology
The word concrete comes from the Latin word "concretus" (meaning compact or condensed), the perfect passive participle of "concrescere", from "con-" (together) and "crescere" (to grow).
History
Ancient times
Concrete floors were found in the royal palace of Tiryns, Greece, which dates roughly to 1400 to 1200 BC. Lime mortars were used in Greece, such as in Crete and Cyprus, in 800 BC. The Assyrian Jerwan Aqueduct (688 BC) made use of waterproof concrete. Concrete was used for construction in many ancient structures.
Mayan concrete at the ruins of Uxmal (AD 850–925) is referenced in Incidents of Travel in the Yucatán by John L. Stephens. "The roof is flat and had been covered with cement". "The floors were cement, in some places hard, but, by long exposure, broken, and now crumbling under the feet." "But throughout the wall was solid, and consisting of large stones imbedded in mortar, almost as hard as rock."
Small-scale production of concrete-like materials was pioneered by the Nabatean traders who occupied and controlled a series of oases and developed a small empire in the regions of southern Syria and northern Jordan from the 4th century BC. They discovered the advantages of hydraulic lime, with some self-cementing properties, by 700 BC. They built kilns to supply mortar for the construction of rubble masonry houses, concrete floors, and underground waterproof cisterns. They kept the cisterns secret as these enabled the Nabataeans to thrive in the desert. Some of these structures survive to this day.
In the Ancient Egyptian and later Roman eras, builders discovered that adding volcanic ash to lime allowed the mix to set underwater. They discovered the pozzolanic reaction.
Classical era



The Romans used concrete extensively from 300 BC to AD 476. During the Roman Empire, Roman concrete (or opus caementicium) was made from quicklime, pozzolana and an aggregate of pumice. Its widespread use in many Roman structures, a key event in the history of architecture termed the Roman architectural revolution, freed Roman construction from the restrictions of stone and brick materials. It enabled revolutionary new designs in terms of both structural complexity and dimension. The Colosseum in Rome was built largely of concrete, and the Pantheon has the world's largest unreinforced concrete dome.
Concrete, as the Romans knew it, was a new and revolutionary material. Laid in the shape of arches, vaults and domes, it quickly hardened into a rigid mass, free from many of the internal thrusts and strains that troubled the builders of similar structures in stone or brick.
Modern tests show that opus caementicium had as much compressive strength as modern Portland-cement concrete (c. 200 kg/cm ). However, due to the absence of reinforcement, its tensile strength was far lower than modern reinforced concrete, and its mode of application also differed:
Modern structural concrete differs from Roman concrete in two important details. First, its mix consistency is fluid and homogeneous, allowing it to be poured into forms rather than requiring hand-layering together with the placement of aggregate, which, in Roman practice, often consisted of rubble. Second, integral reinforcing steel gives modern concrete assemblies great strength in tension, whereas Roman concrete could depend only upon the strength of the concrete bonding to resist tension.
The long-term durability of Roman concrete structures has been found to be due to its use of pyroclastic (volcanic) rock and ash, whereby the crystallization of strätlingite (a specific and complex calcium aluminosilicate hydrate) and the coalescence of this and similar calcium–aluminium-silicate–hydrate cementing binders helped give the concrete a greater degree of fracture resistance even in seismically active environments. Roman concrete is significantly more resistant to erosion by seawater than modern concrete; it used pyroclastic materials which react with seawater to form Al-tobermorite crystals over time. The use of hot mixing and the presence of lime clasts are thought to give the concrete a self-healing ability, where cracks that form become filled with calcite that prevents the crack from spreading.
The widespread use of concrete in many Roman structures ensured that many survive to the present day. The Baths of Caracalla in Rome are just one example. Many Roman aqueducts and bridges, such as the magnificent Pont du Gard in southern France, have masonry cladding on a concrete core, as does the dome of the Pantheon.
Middle Ages
After the Roman Empire, the use of burned lime and pozzolana was greatly reduced. Low kiln temperatures in the burning of lime, lack of pozzolana, and poor mixing all contributed to a decline in the quality of concrete and mortar. From the 11th century, the increased use of stone in church and castle construction led to an increased demand for mortar. Quality began to improve in the 12th century through better grinding and sieving. Medieval lime mortars and concretes were non-hydraulic and were used for binding masonry, "hearting" (binding rubble masonry cores) and foundations. Bartholomaeus Anglicus in his De proprietatibus rerum (1240) describes the making of mortar. In an English translation from 1397, it reads "lyme ... is a stone brent; by medlynge thereof with sonde and water sement is made". From the 14th century, the quality of mortar was again excellent, but only from the 17th century was pozzolana commonly added.
The Canal du Midi was built using concrete in 1670.
Industrial era

Perhaps the greatest step forward in the modern use of concrete was Smeaton's Tower, built by British engineer John Smeaton in Devon, England, between 1756 and 1759. This third Eddystone Lighthouse pioneered the use of hydraulic lime in concrete, using pebbles and powdered brick as aggregate.
A method for producing Portland cement was developed in England and patented by Joseph Aspdin in 1824. Aspdin chose the name for its similarity to Portland stone, which was quarried on the Isle of Portland in Dorset, England. His son William continued developments into the 1840s, earning him recognition for the development of "modern" Portland cement.
Reinforced concrete was invented in 1849 by Joseph Monier. and the first reinforced concrete house was built by François Coignet in 1853. The first concrete reinforced bridge was designed and built by Joseph Monier in 1875.
Prestressed concrete and post-tensioned concrete were pioneered by Eugène Freyssinet, a French structural and civil engineer. Concrete components or structures are compressed by tendon cables during, or after, their fabrication in order to strengthen them against tensile forces developing when put in service. Freyssinet patented the technique on 2 October 1928.
Composition
See also: Slag and Heavy metalsConcrete is an artificial composite material, comprising a matrix of cementitious binder (typically Portland cement paste or asphalt) and a dispersed phase or "filler" of aggregate (typically a rocky material, loose stones, and sand). The binder "glues" the filler together to form a synthetic conglomerate. Many types of concrete are available, determined by the formulations of binders and the types of aggregate used to suit the application of the engineered material. These variables determine strength and density, as well as chemical and thermal resistance of the finished product.

Construction aggregates consist of large chunks of material in a concrete mix, generally a coarse gravel or crushed rocks such as limestone, or granite, along with finer materials such as sand.
Cement paste, most commonly made of Portland cement, is the most prevalent kind of concrete binder. For cementitious binders, water is mixed with the dry cement powder and aggregate, which produces a semi-liquid slurry (paste) that can be shaped, typically by pouring it into a form. The concrete solidifies and hardens through a chemical process called hydration. The water reacts with the cement, which bonds the other components together, creating a robust, stone-like material. Other cementitious materials, such as fly ash and slag cement, are sometimes added—either pre-blended with the cement or directly as a concrete component—and become a part of the binder for the aggregate. Fly ash and slag can enhance some properties of concrete such as fresh properties and durability. Alternatively, other materials can also be used as a concrete binder: the most prevalent substitute is asphalt, which is used as the binder in asphalt concrete.
Admixtures are added to modify the cure rate or properties of the material. Mineral admixtures use recycled materials as concrete ingredients. Conspicuous materials include fly ash, a by-product of coal-fired power plants; ground granulated blast furnace slag, a by-product of steelmaking; and silica fume, a by-product of industrial electric arc furnaces.
Structures employing Portland cement concrete usually include steel reinforcement because this type of concrete can be formulated with high compressive strength, but always has lower tensile strength. Therefore, it is usually reinforced with materials that are strong in tension, typically steel rebar.
The mix design depends on the type of structure being built, how the concrete is mixed and delivered, and how it is placed to form the structure.
Cement
Main article: Cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general usage. It is a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, and many plasters. It consists of a mixture of calcium silicates (alite, belite), aluminates and ferrites—compounds, which will react with water. Portland cement and similar materials are made by heating limestone (a source of calcium) with clay or shale (a source of silicon, aluminium and iron) and grinding this product (called clinker) with a source of sulfate (most commonly gypsum).
Cement kilns are extremely large, complex, and inherently dusty industrial installations. Of the various ingredients used to produce a given quantity of concrete, the cement is the most energetically expensive. Even complex and efficient kilns require 3.3 to 3.6 gigajoules of energy to produce a ton of clinker and then grind it into cement. Many kilns can be fueled with difficult-to-dispose-of wastes, the most common being used tires. The extremely high temperatures and long periods of time at those temperatures allows cement kilns to efficiently and completely burn even difficult-to-use fuels. The five major compounds of calcium silicates and aluminates comprising Portland cement range from 5 to 50% in weight.
Curing
Combining water with a cementitious material forms a cement paste by the process of hydration. The cement paste glues the aggregate together, fills voids within it, and makes it flow more freely.
As stated by Abrams' law, a lower water-to-cement ratio yields a stronger, more durable concrete, whereas more water gives a freer-flowing concrete with a higher slump. The hydration of cement involves many concurrent reactions. The process involves polymerization, the interlinking of the silicates and aluminate components as well as their bonding to sand and gravel particles to form a solid mass. One illustrative conversion is the hydration of tricalcium silicate:
- Cement chemist notation: C3S + H → C-S-H + CH + heat
- Standard notation: Ca3SiO5 + H2O → CaO・SiO2・H2O (gel) + Ca(OH)2 + heat
- Balanced: 2 Ca3SiO5 + 7 H2O → 3 CaO・2 SiO2・4 H2O (gel) + 3 Ca(OH)2 + heat
- (approximately as the exact ratios of CaO, SiO2 and H2O in C-S-H can vary)
The hydration (curing) of cement is irreversible.
Aggregates
Main article: Construction aggregate
Fine and coarse aggregates make up the bulk of a concrete mixture. Sand, natural gravel, and crushed stone are used mainly for this purpose. Recycled aggregates (from construction, demolition, and excavation waste) are increasingly used as partial replacements for natural aggregates, while a number of manufactured aggregates, including air-cooled blast furnace slag and bottom ash are also permitted.
The size distribution of the aggregate determines how much binder is required. Aggregate with a very even size distribution has the biggest gaps whereas adding aggregate with smaller particles tends to fill these gaps. The binder must fill the gaps between the aggregate as well as paste the surfaces of the aggregate together, and is typically the most expensive component. Thus, variation in sizes of the aggregate reduces the cost of concrete. The aggregate is nearly always stronger than the binder, so its use does not negatively affect the strength of the concrete.
Redistribution of aggregates after compaction often creates non-homogeneity due to the influence of vibration. This can lead to strength gradients.
Decorative stones such as quartzite, small river stones or crushed glass are sometimes added to the surface of concrete for a decorative "exposed aggregate" finish, popular among landscape designers.
Admixtures
Admixtures are materials in the form of powder or fluids that are added to the concrete to give it certain characteristics not obtainable with plain concrete mixes. Admixtures are defined as additions "made as the concrete mix is being prepared". The most common admixtures are retarders and accelerators. In normal use, admixture dosages are less than 5% by mass of cement and are added to the concrete at the time of batching/mixing. (See § Production below.) The common types of admixtures are as follows:
- Accelerators speed up the hydration (hardening) of the concrete. Typical materials used are calcium chloride, calcium nitrate and sodium nitrate. However, use of chlorides may cause corrosion in steel reinforcing and is prohibited in some countries, so that nitrates may be favored, even though they are less effective than the chloride salt. Accelerating admixtures are especially useful for modifying the properties of concrete in cold weather.
- Air entraining agents add and entrain tiny air bubbles in the concrete, which reduces damage during freeze-thaw cycles, increasing durability. However, entrained air entails a tradeoff with strength, as each 1% of air may decrease compressive strength by 5%. If too much air becomes trapped in the concrete as a result of the mixing process, defoamers can be used to encourage the air bubble to agglomerate, rise to the surface of the wet concrete and then disperse.
- Bonding agents are used to create a bond between old and new concrete (typically a type of polymer) with wide temperature tolerance and corrosion resistance.
- Corrosion inhibitors are used to minimize the corrosion of steel and steel bars in concrete.
- Crystalline admixtures are typically added during batching of the concrete to lower permeability. The reaction takes place when exposed to water and un-hydrated cement particles to form insoluble needle-shaped crystals, which fill capillary pores and micro-cracks in the concrete to block pathways for water and waterborne contaminates. Concrete with crystalline admixture can expect to self-seal as constant exposure to water will continuously initiate crystallization to ensure permanent waterproof protection.
- Pigments can be used to change the color of concrete, for aesthetics.
- Plasticizers increase the workability of plastic, or "fresh", concrete, allowing it to be placed more easily, with less consolidating effort. A typical plasticizer is lignosulfonate. Plasticizers can be used to reduce the water content of a concrete while maintaining workability and are sometimes called water-reducers due to this use. Such treatment improves its strength and durability characteristics.
- Superplasticizers (also called high-range water-reducers) are a class of plasticizers that have fewer deleterious effects and can be used to increase workability more than is practical with traditional plasticizers. Superplasticizers are used to increase compressive strength. It increases the workability of the concrete and lowers the need for water content by 15–30%.
- Pumping aids improve pumpability, thicken the paste and reduce separation and bleeding.
- Retarders slow the hydration of concrete and are used in large or difficult pours where partial setting is undesirable before completion of the pour. Typical retarders include sugar, sodium gluconate, citric acid, and tartaric acid.
Mineral admixtures and blended cements
| Property | Portland cement |
Siliceous fly ash |
Calcareous fly ash |
Slag cement |
Silica fume | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proportion by mass (%) | SiO2 | 21.9 | 52 | 35 | 35 | 85–97 |
| Al2O3 | 6.9 | 23 | 18 | 12 | — | |
| Fe2O3 | 3 | 11 | 6 | 1 | — | |
| CaO | 63 | 5 | 21 | 40 | < 1 | |
| MgO | 2.5 | — | — | — | — | |
| SO3 | 1.7 | — | — | — | — | |
| Specific surface (m/kg) | 370 | 420 | 420 | 400 | 15,000 – 30,000 | |
| Specific gravity | 3.15 | 2.38 | 2.65 | 2.94 | 2.22 | |
| General purpose | Primary binder | Cement replacement | Cement replacement | Cement replacement | Property enhancer | |
| ||||||
Inorganic materials that have pozzolanic or latent hydraulic properties, these very fine-grained materials are added to the concrete mix to improve the properties of concrete (mineral admixtures), or as a replacement for Portland cement (blended cements). Products which incorporate limestone, fly ash, blast furnace slag, and other useful materials with pozzolanic properties into the mix, are being tested and used. These developments are ever growing in relevance to minimize the impacts caused by cement use, notorious for being one of the largest producers (at about 5 to 10%) of global greenhouse gas emissions. The use of alternative materials also is capable of lowering costs, improving concrete properties, and recycling wastes, the latest being relevant for circular economy aspects of the construction industry, whose demand is ever growing with greater impacts on raw material extraction, waste generation and landfill practices.
- Fly ash: A by-product of coal-fired electric generating plants, it is used to partially replace Portland cement (by up to 60% by mass). The properties of fly ash depend on the type of coal burnt. In general, siliceous fly ash is pozzolanic, while calcareous fly ash has latent hydraulic properties.
- Ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBFS or GGBS): A by-product of steel production is used to partially replace Portland cement (by up to 80% by mass). It has latent hydraulic properties.
- Silica fume: A by-product of the production of silicon and ferrosilicon alloys. Silica fume is similar to fly ash, but has a particle size 100 times smaller. This results in a higher surface-to-volume ratio and a much faster pozzolanic reaction. Silica fume is used to increase strength and durability of concrete, but generally requires the use of superplasticizers for workability.
- High reactivity metakaolin (HRM): Metakaolin produces concrete with strength and durability similar to concrete made with silica fume. While silica fume is usually dark gray or black in color, high-reactivity metakaolin is usually bright white in color, making it the preferred choice for architectural concrete where appearance is important.
- Carbon nanofibers can be added to concrete to enhance compressive strength and gain a higher Young's modulus, and also to improve the electrical properties required for strain monitoring, damage evaluation and self-health monitoring of concrete. Carbon fiber has many advantages in terms of mechanical and electrical properties (e.g., higher strength) and self-monitoring behavior due to the high tensile strength and high electrical conductivity.
- Carbon products have been added to make concrete electrically conductive, for deicing purposes.
- New research from Japan's University of Kitakyushu shows that a washed and dried recycled mix of used diapers can be an environmental solution to producing less landfill and using less sand in concrete production. A model home was built in Indonesia to test the strength and durability of the new diaper-cement composite.
Production


Concrete production is the process of mixing together the various ingredients—water, aggregate, cement, and any additives—to produce concrete. Concrete production is time-sensitive. Once the ingredients are mixed, workers must put the concrete in place before it hardens. In modern usage, most concrete production takes place in a large type of industrial facility called a concrete plant, or often a batch plant. The usual method of placement is casting in formwork, which holds the mix in shape until it has set enough to hold its shape unaided.
Concrete plants come in two main types, ready-mix plants and central mix plants. A ready-mix plant blends all of the solid ingredients, while a central mix does the same but adds water. A central-mix plant offers more precise control of the concrete quality. Central mix plants must be close to the work site where the concrete will be used, since hydration begins at the plant.
A concrete plant consists of large hoppers for storage of various ingredients like cement, storage for bulk ingredients like aggregate and water, mechanisms for the addition of various additives and amendments, machinery to accurately weigh, move, and mix some or all of those ingredients, and facilities to dispense the mixed concrete, often to a concrete mixer truck.
Modern concrete is usually prepared as a viscous fluid, so that it may be poured into forms. The forms are containers that define the desired shape. Concrete formwork can be prepared in several ways, such as slip forming and steel plate construction. Alternatively, concrete can be mixed into dryer, non-fluid forms and used in factory settings to manufacture precast concrete products.
Interruption in pouring the concrete can cause the initially placed material to begin to set before the next batch is added on top. This creates a horizontal plane of weakness called a cold joint between the two batches. Once the mix is where it should be, the curing process must be controlled to ensure that the concrete attains the desired attributes. During concrete preparation, various technical details may affect the quality and nature of the product.
Design mix
Design mix ratios are decided by an engineer after analyzing the properties of the specific ingredients being used. Instead of using a 'nominal mix' of 1 part cement, 2 parts sand, and 4 parts aggregate, a civil engineer will custom-design a concrete mix to exactly meet the requirements of the site and conditions, setting material ratios and often designing an admixture package to fine-tune the properties or increase the performance envelope of the mix. Design-mix concrete can have very broad specifications that cannot be met with more basic nominal mixes, but the involvement of the engineer often increases the cost of the concrete mix.
Concrete mixes are primarily divided into nominal mix, standard mix and design mix.
Nominal mix ratios are given in volume of . Nominal mixes are a simple, fast way of getting a basic idea of the properties of the finished concrete without having to perform testing in advance.
Various governing bodies (such as British Standards) define nominal mix ratios into a number of grades, usually ranging from lower compressive strength to higher compressive strength. The grades usually indicate the 28-day cure strength.
Mixing
See also: Volumetric concrete mixer and Concrete mixerThorough mixing is essential to produce uniform, high-quality concrete.
Separate paste mixing has shown that the mixing of cement and water into a paste before combining these materials with aggregates can increase the compressive strength of the resulting concrete. The paste is generally mixed in a high-speed, shear-type mixer at a w/c (water to cement ratio) of 0.30 to 0.45 by mass. The cement paste premix may include admixtures such as accelerators or retarders, superplasticizers, pigments, or silica fume. The premixed paste is then blended with aggregates and any remaining batch water and final mixing is completed in conventional concrete mixing equipment.
Sample analysis—workability
Main article: Concrete slump test

Workability is the ability of a fresh (plastic) concrete mix to fill the form/mold properly with the desired work (pouring, pumping, spreading, tamping, vibration) and without reducing the concrete's quality. Workability depends on water content, aggregate (shape and size distribution), cementitious content and age (level of hydration) and can be modified by adding chemical admixtures, like superplasticizer. Raising the water content or adding chemical admixtures increases concrete workability. Excessive water leads to increased bleeding or segregation of aggregates (when the cement and aggregates start to separate), with the resulting concrete having reduced quality. Changes in gradation can also affect workability of the concrete, although a wide range of gradation can be used for various applications. An undesirable gradation can mean using a large aggregate that is too large for the size of the formwork, or which has too few smaller aggregate grades to serve to fill the gaps between the larger grades, or using too little or too much sand for the same reason, or using too little water, or too much cement, or even using jagged crushed stone instead of smoother round aggregate such as pebbles. Any combination of these factors and others may result in a mix which is too harsh, i.e., which does not flow or spread out smoothly, is difficult to get into the formwork, and which is difficult to surface finish.
Workability can be measured by the concrete slump test, a simple measure of the plasticity of a fresh batch of concrete following the ASTM C 143 or EN 12350-2 test standards. Slump is normally measured by filling an "Abrams cone" with a sample from a fresh batch of concrete. The cone is placed with the wide end down onto a level, non-absorptive surface. It is then filled in three layers of equal volume, with each layer being tamped with a steel rod to consolidate the layer. When the cone is carefully lifted off, the enclosed material slumps a certain amount, owing to gravity. A relatively dry sample slumps very little, having a slump value of one or two inches (25 or 50 mm) out of one foot (300 mm). A relatively wet concrete sample may slump as much as eight inches. Workability can also be measured by the flow table test.
Slump can be increased by addition of chemical admixtures such as plasticizer or superplasticizer without changing the water-cement ratio. Some other admixtures, especially air-entraining admixture, can increase the slump of a mix.
High-flow concrete, like self-consolidating concrete, is tested by other flow-measuring methods. One of these methods includes placing the cone on the narrow end and observing how the mix flows through the cone while it is gradually lifted.
After mixing, concrete is a fluid and can be pumped to the location where needed.
Curing

Maintaining optimal conditions for cement hydration
Concrete must be kept moist during curing in order to achieve optimal strength and durability. During curing hydration occurs, allowing calcium-silicate hydrate (C-S-H) to form. Over 90% of a mix's final strength is typically reached within four weeks, with the remaining 10% achieved over years or even decades. The conversion of calcium hydroxide in the concrete into calcium carbonate from absorption of CO2 over several decades further strengthens the concrete and makes it more resistant to damage. This carbonation reaction, however, lowers the pH of the cement pore solution and can corrode the reinforcement bars.
Hydration and hardening of concrete during the first three days is critical. Abnormally fast drying and shrinkage due to factors such as evaporation from wind during placement may lead to increased tensile stresses at a time when it has not yet gained sufficient strength, resulting in greater shrinkage cracking. The early strength of the concrete can be increased if it is kept damp during the curing process. Minimizing stress prior to curing minimizes cracking. High-early-strength concrete is designed to hydrate faster, often by increased use of cement that increases shrinkage and cracking. The strength of concrete changes (increases) for up to three years. It depends on cross-section dimension of elements and conditions of structure exploitation. Addition of short-cut polymer fibers can improve (reduce) shrinkage-induced stresses during curing and increase early and ultimate compression strength.
Properly curing concrete leads to increased strength and lower permeability and avoids cracking where the surface dries out prematurely. Care must also be taken to avoid freezing or overheating due to the exothermic setting of cement. Improper curing can cause spalling, reduced strength, poor abrasion resistance and cracking.
Curing techniques avoiding water loss by evaporation
During the curing period, concrete is ideally maintained at controlled temperature and humidity. To ensure full hydration during curing, concrete slabs are often sprayed with "curing compounds" that create a water-retaining film over the concrete. Typical films are made of wax or related hydrophobic compounds. After the concrete is sufficiently cured, the film is allowed to abrade from the concrete through normal use.
Traditional conditions for curing involve spraying or ponding the concrete surface with water. The adjacent picture shows one of many ways to achieve this, ponding—submerging setting concrete in water and wrapping in plastic to prevent dehydration. Additional common curing methods include wet burlap and plastic sheeting covering the fresh concrete.
For higher-strength applications, accelerated curing techniques may be applied to the concrete. A common technique involves heating the poured concrete with steam, which serves to both keep it damp and raise the temperature so that the hydration process proceeds more quickly and more thoroughly.
Alternative types
Main article: Types of concreteAsphalt
Main article: Asphalt concreteAsphalt concrete (commonly called asphalt, blacktop, or pavement in North America, and tarmac, bitumen macadam, or rolled asphalt in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland) is a composite material commonly used to surface roads, parking lots, airports, as well as the core of embankment dams. Asphalt mixtures have been used in pavement construction since the beginning of the twentieth century. It consists of mineral aggregate bound together with asphalt, laid in layers, and compacted. The process was refined and enhanced by Belgian inventor and U.S. immigrant Edward De Smedt.
The terms asphalt (or asphaltic) concrete, bituminous asphalt concrete, and bituminous mixture are typically used only in engineering and construction documents, which define concrete as any composite material composed of mineral aggregate adhered with a binder. The abbreviation, AC, is sometimes used for asphalt concrete but can also denote asphalt content or asphalt cement, referring to the liquid asphalt portion of the composite material.
Graphene enhanced concrete
Graphene enhanced concretes are standard designs of concrete mixes, except that during the cement-mixing or production process, a small amount of chemically engineered graphene (typically < 0.5% by weight) is added. These enhanced graphene concretes are designed around the concrete application.
Microbial
Bacteria such as Bacillus pasteurii, Bacillus pseudofirmus, Bacillus cohnii, Sporosarcina pasteuri, and Arthrobacter crystallopoietes increase the compression strength of concrete through their biomass. However some forms of bacteria can also be concrete-destroying. Bacillus sp. CT-5. can reduce corrosion of reinforcement in reinforced concrete by up to four times. Sporosarcina pasteurii reduces water and chloride permeability. B. pasteurii increases resistance to acid. Bacillus pasteurii and B. sphaericuscan induce calcium carbonate precipitation in the surface of cracks, adding compression strength.
Nanoconcrete

Nanoconcrete (also spelled "nano concrete"' or "nano-concrete") is a class of materials that contains Portland cement particles that are no greater than 100 μm and particles of silica no greater than 500 μm, which fill voids that would otherwise occur in normal concrete, thereby substantially increasing the material's strength. It is widely used in foot and highway bridges where high flexural and compressive strength are indicated.
Pervious
Main article: Pervious concretePervious concrete is a mix of specially graded coarse aggregate, cement, water, and little-to-no fine aggregates. This concrete is also known as "no-fines" or porous concrete. Mixing the ingredients in a carefully controlled process creates a paste that coats and bonds the aggregate particles. The hardened concrete contains interconnected air voids totaling approximately 15 to 25 percent. Water runs through the voids in the pavement to the soil underneath. Air entrainment admixtures are often used in freeze-thaw climates to minimize the possibility of frost damage. Pervious concrete also permits rainwater to filter through roads and parking lots, to recharge aquifers, instead of contributing to runoff and flooding.
Polymer
Main article: Polymer concretePolymer concretes are mixtures of aggregate and any of various polymers and may be reinforced. The cement is costlier than lime-based cements, but polymer concretes nevertheless have advantages; they have significant tensile strength even without reinforcement, and they are largely impervious to water. Polymer concretes are frequently used for the repair and construction of other applications, such as drains.
Plant fibers
Plant fibers and particles can be used in a concrete mix or as a reinforcement. These materials can increase ductility but the lignocellulosic particles hydrolyze during concrete curing as a result of alkaline environment and elevated temperatures Such process, that is difficult to measure, can affect the properties of the resulting concrete.
Sulfur concrete
Main article: Sulfur concreteSulfur concrete is a special concrete that uses sulfur as a binder and does not require cement or water.
Volcanic
Volcanic concrete substitutes volcanic rock for the limestone that is burned to form clinker. It consumes a similar amount of energy, but does not directly emit carbon as a byproduct. Volcanic rock/ash are used as supplementary cementitious materials in concrete to improve the resistance to sulfate, chloride and alkali silica reaction due to pore refinement. Also, they are generally cost effective in comparison to other aggregates, good for semi and light weight concretes, and good for thermal and acoustic insulation.
Pyroclastic materials, such as pumice, scoria, and ashes are formed from cooling magma during explosive volcanic eruptions. They are used as supplementary cementitious materials (SCM) or as aggregates for cements and concretes. They have been extensively used since ancient times to produce materials for building applications. For example, pumice and other volcanic glasses were added as a natural pozzolanic material for mortars and plasters during the construction of the Villa San Marco in the Roman period (89 BC – 79 AD), which remain one of the best-preserved otium villae of the Bay of Naples in Italy.
Waste light
Main article: Waste light concreteWaste light is a form of polymer modified concrete. The specific polymer admixture allows the replacement of all the traditional aggregates (gravel, sand, stone) by any mixture of solid waste materials in the grain size of 3–10 mm to form a low-compressive-strength (3–20 N/mm) product for road and building construction. One cubic meter of waste light concrete contains 1.1–1.3 m of shredded waste and no other aggregates.
Recycled Aggregate Concrete (RAC)
| This section does not cite any sources. Please help improve this section by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (October 2024) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Recycled aggregate concretes are standard concrete mixes with the addition or substitution of natural aggregates with recycled aggregates sourced from construction and demolition wastes, disused pre-cast concretes or masonry. In most cases, recycled aggregate concrete results in higher water absorption levels by capillary action and permeation, which are the prominent determiners of the strength and durability of the resulting concrete. The increase in water absorption levels is mainly caused by the porous adhered mortar that exists in the recycled aggregates. Accordingly, recycled concrete aggregates that have been washed to reduce the quantity of mortar adhered to aggregates show lower water absorption levels compared to untreated recycled aggregates.
The quality of the recycled aggregate concrete is determined by several factors, including the size, the number of replacement cycles, and the moisture levels of the recycled aggregates. When the recycled concrete aggregates are crushed into coarser fractures, the mixed concrete shows better permeability levels, resulting in an overall increase in strength. In contrast, recycled masonry aggregates provide better qualities when crushed in finer fractures. With each generation of recycled concrete, the resulting compressive strength decreases.
Properties
Main article: Properties of concreteConcrete has relatively high compressive strength, but much lower tensile strength. Therefore, it is usually reinforced with materials that are strong in tension (often steel). The elasticity of concrete is relatively constant at low stress levels but starts decreasing at higher stress levels as matrix cracking develops. Concrete has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion and shrinks as it matures. All concrete structures crack to some extent, due to shrinkage and tension. Concrete that is subjected to long-duration forces is prone to creep.
Tests can be performed to ensure that the properties of concrete correspond to specifications for the application.

The ingredients affect the strengths of the material. Concrete strength values are usually specified as the lower-bound compressive strength of either a cylindrical or cubic specimen as determined by standard test procedures.
The strengths of concrete is dictated by its function. Very low-strength—14 MPa (2,000 psi) or less—concrete may be used when the concrete must be lightweight. Lightweight concrete is often achieved by adding air, foams, or lightweight aggregates, with the side effect that the strength is reduced. For most routine uses, 20 to 32 MPa (2,900 to 4,600 psi) concrete is often used. 40 MPa (5,800 psi) concrete is readily commercially available as a more durable, although more expensive, option. Higher-strength concrete is often used for larger civil projects. Strengths above 40 MPa (5,800 psi) are often used for specific building elements. For example, the lower floor columns of high-rise concrete buildings may use concrete of 80 MPa (11,600 psi) or more, to keep the size of the columns small. Bridges may use long beams of high-strength concrete to lower the number of spans required. Occasionally, other structural needs may require high-strength concrete. If a structure must be very rigid, concrete of very high strength may be specified, even much stronger than is required to bear the service loads. Strengths as high as 130 MPa (18,900 psi) have been used commercially for these reasons.
Energy efficiency
The cement produced for making concrete accounts for about 8% of worldwide CO2 emissions per year (compared to, e.g., global aviation at 1.9%). The two largest sources of CO2 are produced by the cement manufacturing process, arising from (1) the decarbonation reaction of limestone in the cement kiln (T ≈ 950 °C), and (2) from the combustion of fossil fuel to reach the sintering temperature (T ≈ 1450 °C) of cement clinker in the kiln. The energy required for extracting, crushing, and mixing the raw materials (construction aggregates used in the concrete production, and also limestone and clay feeding the cement kiln) is lower. Energy requirement for transportation of ready-mix concrete is also lower because it is produced nearby the construction site from local resources, typically manufactured within 100 kilometers of the job site. The overall embodied energy of concrete at roughly 1 to 1.5 megajoules per kilogram is therefore lower than for many structural and construction materials.
Once in place, concrete offers a great energy efficiency over the lifetime of a building. Concrete walls leak air far less than those made of wood frames. Air leakage accounts for a large percentage of energy loss from a home. The thermal mass properties of concrete increase the efficiency of both residential and commercial buildings. By storing and releasing the energy needed for heating or cooling, concrete's thermal mass delivers year-round benefits by reducing temperature swings inside and minimizing heating and cooling costs. While insulation reduces energy loss through the building envelope, thermal mass uses walls to store and release energy. Modern concrete wall systems use both external insulation and thermal mass to create an energy-efficient building. Insulating concrete forms (ICFs) are hollow blocks or panels made of either insulating foam or rastra that are stacked to form the shape of the walls of a building and then filled with reinforced concrete to create the structure.
Fire safety

Concrete buildings are more resistant to fire than those constructed using steel frames, since concrete has lower heat conductivity than steel and can thus last longer under the same fire conditions. Concrete is sometimes used as a fire protection for steel frames, for the same effect as above. Concrete as a fire shield, for example Fondu fyre, can also be used in extreme environments like a missile launch pad.
Options for non-combustible construction include floors, ceilings and roofs made of cast-in-place and hollow-core precast concrete. For walls, concrete masonry technology and Insulating Concrete Forms (ICFs) are additional options. ICFs are hollow blocks or panels made of fireproof insulating foam that are stacked to form the shape of the walls of a building and then filled with reinforced concrete to create the structure.
Concrete also provides good resistance against externally applied forces such as high winds, hurricanes, and tornadoes owing to its lateral stiffness, which results in minimal horizontal movement. However, this stiffness can work against certain types of concrete structures, particularly where a relatively higher flexing structure is required to resist more extreme forces.
Earthquake safety
As discussed above, concrete is very strong in compression, but weak in tension. Larger earthquakes can generate very large shear loads on structures. These shear loads subject the structure to both tensile and compressional loads. Concrete structures without reinforcement, like other unreinforced masonry structures, can fail during severe earthquake shaking. Unreinforced masonry structures constitute one of the largest earthquake risks globally. These risks can be reduced through seismic retrofitting of at-risk buildings, (e.g. school buildings in Istanbul, Turkey).
Construction

Concrete is one of the most durable building materials. It provides superior fire resistance compared with wooden construction and gains strength over time. Structures made of concrete can have a long service life. Concrete is used more than any other artificial material in the world. As of 2006, about 7.5 billion cubic meters of concrete are made each year, more than one cubic meter for every person on Earth.
Reinforced
Main article: Reinforced concrete
The use of reinforcement, in the form of iron was introduced in the 1850s by French industrialist François Coignet, and it was not until the 1880s that German civil engineer G. A. Wayss used steel as reinforcement. Concrete is a relatively brittle material that is strong under compression but less in tension. Plain, unreinforced concrete is unsuitable for many structures as it is relatively poor at withstanding stresses induced by vibrations, wind loading, and so on. Hence, to increase its overall strength, steel rods, wires, mesh or cables can be embedded in concrete before it is set. This reinforcement, often known as rebar, resists tensile forces.
Reinforced concrete (RC) is a versatile composite and one of the most widely used materials in modern construction. It is made up of different constituent materials with very different properties that complement each other. In the case of reinforced concrete, the component materials are almost always concrete and steel. These two materials form a strong bond together and are able to resist a variety of applied forces, effectively acting as a single structural element.
Reinforced concrete can be precast or cast-in-place (in situ) concrete, and is used in a wide range of applications such as; slab, wall, beam, column, foundation, and frame construction. Reinforcement is generally placed in areas of the concrete that are likely to be subject to tension, such as the lower portion of beams. Usually, there is a minimum of 50 mm cover, both above and below the steel reinforcement, to resist spalling and corrosion which can lead to structural instability. Other types of non-steel reinforcement, such as Fibre-reinforced concretes are used for specialized applications, predominately as a means of controlling cracking.
Precast
Main article: Precast concretePrecast concrete is concrete which is cast in one place for use elsewhere and is a mobile material. The largest part of precast production is carried out in the works of specialist suppliers, although in some instances, due to economic and geographical factors, scale of product or difficulty of access, the elements are cast on or adjacent to the construction site. Precasting offers considerable advantages because it is carried out in a controlled environment, protected from the elements, but the downside of this is the contribution to greenhouse gas emission from transportation to the construction site.
Advantages to be achieved by employing precast concrete:
- Preferred dimension schemes exist, with elements of tried and tested designs available from a catalogue.
- Major savings in time result from manufacture of structural elements apart from the series of events which determine overall duration of the construction, known by planning engineers as the 'critical path'.
- Availability of Laboratory facilities capable of the required control tests, many being certified for specific testing in accordance with National Standards.
- Equipment with capability suited to specific types of production such as stressing beds with appropriate capacity, moulds and machinery dedicated to particular products.
- High-quality finishes achieved direct from the mould eliminate the need for interior decoration and ensure low maintenance costs.
Mass structures
Main article: Mass concrete
Due to cement's exothermic chemical reaction while setting up, large concrete structures such as dams, navigation locks, large mat foundations, and large breakwaters generate excessive heat during hydration and associated expansion. To mitigate these effects, post-cooling is commonly applied during construction. An early example at Hoover Dam used a network of pipes between vertical concrete placements to circulate cooling water during the curing process to avoid damaging overheating. Similar systems are still used; depending on volume of the pour, the concrete mix used, and ambient air temperature, the cooling process may last for many months after the concrete is placed. Various methods also are used to pre-cool the concrete mix in mass concrete structures.
Another approach to mass concrete structures that minimizes cement's thermal by-product is the use of roller-compacted concrete, which uses a dry mix which has a much lower cooling requirement than conventional wet placement. It is deposited in thick layers as a semi-dry material then roller compacted into a dense, strong mass.
Surface finishes
Main article: Decorative concrete
Raw concrete surfaces tend to be porous and have a relatively uninteresting appearance. Many finishes can be applied to improve the appearance and preserve the surface against staining, water penetration, and freezing.
Examples of improved appearance include stamped concrete where the wet concrete has a pattern impressed on the surface, to give a paved, cobbled or brick-like effect, and may be accompanied with coloration. Another popular effect for flooring and table tops is polished concrete where the concrete is polished optically flat with diamond abrasives and sealed with polymers or other sealants.
Other finishes can be achieved with chiseling, or more conventional techniques such as painting or covering it with other materials.
The proper treatment of the surface of concrete, and therefore its characteristics, is an important stage in the construction and renovation of architectural structures.
Prestressed
Main article: Prestressed concrete
Prestressed concrete is a form of reinforced concrete that builds in compressive stresses during construction to oppose tensile stresses experienced in use. This can greatly reduce the weight of beams or slabs, by better distributing the stresses in the structure to make optimal use of the reinforcement. For example, a horizontal beam tends to sag. Prestressed reinforcement along the bottom of the beam counteracts this. In pre-tensioned concrete, the prestressing is achieved by using steel or polymer tendons or bars that are subjected to a tensile force prior to casting, or for post-tensioned concrete, after casting.
There are two different systems being used:
- Pretensioned concrete is almost always precast, and contains steel wires (tendons) that are held in tension while the concrete is placed and sets around them.
- Post-tensioned concrete has ducts through it. After the concrete has gained strength, tendons are pulled through the ducts and stressed. The ducts are then filled with grout. Bridges built in this way have experienced considerable corrosion of the tendons, so external post-tensioning may now be used in which the tendons run along the outer surface of the concrete.
More than 55,000 miles (89,000 km) of highways in the United States are paved with this material. Reinforced concrete, prestressed concrete and precast concrete are the most widely used types of concrete functional extensions in modern days. For more information see Brutalist architecture.
Placement
Once mixed, concrete is typically transported to the place where it is intended to become a structural item. Various methods of transportation and placement are used depending on the distances involve, quantity needed, and other details of application. Large amounts are often transported by truck, poured free under gravity or through a tremie, or pumped through a pipe. Smaller amounts may be carried in a skip (a metal container which can be tilted or opened to release the contents, usually transported by crane or hoist), or wheelbarrow, or carried in toggle bags for manual placement underwater.
Cold weather placement

Extreme weather conditions (extreme heat or cold; windy conditions, and humidity variations) can significantly alter the quality of concrete. Many precautions are observed in cold weather placement. Low temperatures significantly slow the chemical reactions involved in hydration of cement, thus affecting the strength development. Preventing freezing is the most important precaution, as formation of ice crystals can cause damage to the crystalline structure of the hydrated cement paste. If the surface of the concrete pour is insulated from the outside temperatures, the heat of hydration will prevent freezing.
The American Concrete Institute (ACI) definition of cold weather placement, ACI 306, is:
- A period when for more than three successive days the average daily air temperature drops below 40 °F (~ 4.5 °C), and
- Temperature stays below 50 °F (10 °C) for more than one-half of any 24-hour period.
In Canada, where temperatures tend to be much lower during the cold season, the following criteria are used by CSA A23.1:
- When the air temperature is ≤ 5 °C, and
- When there is a probability that the temperature may fall below 5 °C within 24 hours of placing the concrete.
The minimum strength before exposing concrete to extreme cold is 500 psi (3.4 MPa). CSA A 23.1 specified a compressive strength of 7.0 MPa to be considered safe for exposure to freezing.
Underwater placement
See also: Underwater construction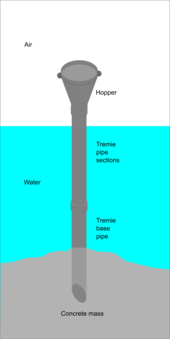
Concrete may be placed and cured underwater. Care must be taken in the placement method to prevent washing out the cement. Underwater placement methods include the tremie, pumping, skip placement, manual placement using toggle bags, and bagwork.
A tremie is a vertical, or near-vertical, pipe with a hopper at the top used to pour concrete underwater in a way that avoids washout of cement from the mix due to turbulent water contact with the concrete while it is flowing. This produces a more reliable strength of the product. The toggle bag method is generally used for placing small quantities and for repairs. Wet concrete is loaded into a reusable canvas bag and squeezed out at the required place by the diver. Care must be taken to avoid washout of the cement and fines.
Underwater bagwork is the manual placement by divers of woven cloth bags containing dry mix, followed by piercing the bags with steel rebar pins to tie the bags together after every two or three layers, and create a path for hydration to induce curing, which can typically take about 6 to 12 hours for initial hardening and full hardening by the next day. Bagwork concrete will generally reach full strength within 28 days. Each bag must be pierced by at least one, and preferably up to four pins. Bagwork is a simple and convenient method of underwater concrete placement which does not require pumps, plant, or formwork, and which can minimise environmental effects from dispersing cement in the water. Prefilled bags are available, which are sealed to prevent premature hydration if stored in suitable dry conditions. The bags may be biodegradable.
Grouted aggregate is an alternative method of forming a concrete mass underwater, where the forms are filled with coarse aggregate and the voids then completely filled from the bottom by displacing the water with pumped grout.
Roads
Concrete roads are more fuel efficient to drive on, more reflective and last significantly longer than other paving surfaces, yet have a much smaller market share than other paving solutions. Modern-paving methods and design practices have changed the economics of concrete paving, so that a well-designed and placed concrete pavement will be less expensive on initial costs and significantly less expensive over the life cycle. Another major benefit is that pervious concrete can be used, which eliminates the need to place storm drains near the road, and reducing the need for slightly sloped roadway to help rainwater to run off. No longer requiring discarding rainwater through use of drains also means that less electricity is needed (more pumping is otherwise needed in the water-distribution system), and no rainwater gets polluted as it no longer mixes with polluted water. Rather, it is immediately absorbed by the ground.
Tube forest
Cement molded into a forest of tubular structures can be 5.6 times more resistant to cracking/failure than standard concrete. The approach mimics mammalian cortical bone that features elliptical, hollow osteons suspended in an organic matrix, connected by relatively weak “cement lines". Cement lines provide a preferable in-plane crack path. This design fails via a “stepwise toughening mechanism". Cracks are contained within the tube, reducing spreading, by dissipating energy at each tube/step.
Environment, health and safety
Main article: Environmental impact of concrete| This section may be unbalanced towards certain viewpoints. Please improve the article or discuss the issue on the talk page. (January 2024) |
The manufacture and use of concrete produce a wide range of environmental, economic and social impacts.
Health and safety
See also: Occupational dust exposure § Construction
Grinding of concrete can produce hazardous dust. Exposure to cement dust can lead to issues such as silicosis, kidney disease, skin irritation and similar effects. The U.S. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health in the United States recommends attaching local exhaust ventilation shrouds to electric concrete grinders to control the spread of this dust. In addition, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has placed more stringent regulations on companies whose workers regularly come into contact with silica dust. An updated silica rule, which OSHA put into effect 23 September 2017 for construction companies, restricted the amount of breathable crystalline silica workers could legally come into contact with to 50 micro grams per cubic meter of air per 8-hour workday. That same rule went into effect 23 June 2018 for general industry, hydraulic fracturing and maritime. That deadline was extended to 23 June 2021 for engineering controls in the hydraulic fracturing industry. Companies which fail to meet the tightened safety regulations can face financial charges and extensive penalties. The presence of some substances in concrete, including useful and unwanted additives, can cause health concerns due to toxicity and radioactivity. Fresh concrete (before curing is complete) is highly alkaline and must be handled with proper protective equipment.
Cement
A major component of concrete is cement, a fine powder used mainly to bind sand and coarser aggregates together in concrete. Although a variety of cement types exist, the most common is "Portland cement", which is produced by mixing clinker with smaller quantities of other additives such as gypsum and ground limestone. The production of clinker, the main constituent of cement, is responsible for the bulk of the sector's greenhouse gas emissions, including both energy intensity and process emissions.
The cement industry is one of the three primary producers of carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas – the other two being energy production and transportation industries. On average, every tonne of cement produced releases one tonne of CO2 into the atmosphere. Pioneer cement manufacturers have claimed to reach lower carbon intensities, with 590 kg of CO2eq per tonne of cement produced. The emissions are due to combustion and calcination processes, which roughly account for 40% and 60% of the greenhouse gases, respectively. Considering that cement is only a fraction of the constituents of concrete, it is estimated that a tonne of concrete is responsible for emitting about 100–200 kg of CO2. Every year more than 10 billion tonnes of concrete are used worldwide. In the coming years, large quantities of concrete will continue to be used, and the mitigation of CO2 emissions from the sector will be even more critical.
Concrete is used to create hard surfaces that contribute to surface runoff, which can cause heavy soil erosion, water pollution, and flooding, but conversely can be used to divert, dam, and control flooding. Concrete dust released by building demolition and natural disasters can be a major source of dangerous air pollution. Concrete is a contributor to the urban heat island effect, though less so than asphalt.
Climate change mitigation
Reducing the cement clinker content might have positive effects on the environmental life-cycle assessment of concrete. Some research work on reducing the cement clinker content in concrete has already been carried out. However, there exist different research strategies. Often replacement of some clinker for large amounts of slag or fly ash was investigated based on conventional concrete technology. This could lead to a waste of scarce raw materials such as slag and fly ash. The aim of other research activities is the efficient use of cement and reactive materials like slag and fly ash in concrete based on a modified mix design approach.
The embodied carbon of a precast concrete facade can be reduced by 50% when using the presented fiber reinforced high performance concrete in place of typical reinforced concrete cladding. Studies have been conducted about commercialization of low-carbon concretes. Life cycle assessment (LCA) of low-carbon concrete was investigated according to the ground granulated blast-furnace slag (GGBS) and fly ash (FA) replacement ratios. Global warming potential (GWP) of GGBS decreased by 1.1 kg CO2 eq/m, while FA decreased by 17.3 kg CO2 eq/m when the mineral admixture replacement ratio was increased by 10%. This study also compared the compressive strength properties of binary blended low-carbon concrete according to the replacement ratios, and the applicable range of mixing proportions was derived.
Climate change adaptation
High-performance building materials will be particularly important for enhancing resilience, including for flood defenses and critical-infrastructure protection. Risks to infrastructure and cities posed by extreme weather events are especially serious for those places exposed to flood and hurricane damage, but also where residents need protection from extreme summer temperatures. Traditional concrete can come under strain when exposed to humidity and higher concentrations of atmospheric CO2. While concrete is likely to remain important in applications where the environment is challenging, novel, smarter and more adaptable materials are also needed.
End-of-life: degradation and waste

Recycling
This paragraph is an excerpt from Concrete recycling. Concrete recycling is the use of rubble from demolished concrete structures. Recycling is cheaper and more ecological than trucking rubble to a landfill. Crushed rubble can be used for road gravel, revetments, retaining walls, landscaping gravel, or raw material for new concrete. Large pieces can be used as bricks or slabs, or incorporated with new concrete into structures, a material called urbanite.There have been concerns about the recycling of painted concrete due to possible lead content. Studies have indicated that recycled concrete exhibits lower strength and durability compared to concrete produced using natural aggregates. This deficiency can be addressed by incorporating supplementary materials such as fly ash into the mixture.
World records
The world record for the largest concrete pour in a single project is the Three Gorges Dam in Hubei Province, China by the Three Gorges Corporation. The amount of concrete used in the construction of the dam is estimated at 16 million cubic meters over 17 years. The previous record was 12.3 million cubic meters held by Itaipu hydropower station in Brazil.
The world record for concrete pumping was set on 7 August 2009 during the construction of the Parbati Hydroelectric Project, near the village of Suind, Himachal Pradesh, India, when the concrete mix was pumped through a vertical height of 715 m (2,346 ft).
The Polavaram dam works in Andhra Pradesh on 6 January 2019 entered the Guinness World Records by pouring 32,100 cubic metres of concrete in 24 hours. The world record for the largest continuously poured concrete raft was achieved in August 2007 in Abu Dhabi by contracting firm Al Habtoor-CCC Joint Venture and the concrete supplier is Unibeton Ready Mix. The pour (a part of the foundation for the Abu Dhabi's Landmark Tower) was 16,000 cubic meters of concrete poured within a two-day period. The previous record, 13,200 cubic meters poured in 54 hours despite a severe tropical storm requiring the site to be covered with tarpaulins to allow work to continue, was achieved in 1992 by joint Japanese and South Korean consortiums Hazama Corporation and the Samsung C&T Corporation for the construction of the Petronas Towers in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
The world record for largest continuously poured concrete floor was completed 8 November 1997, in Louisville, Kentucky by design-build firm EXXCEL Project Management. The monolithic placement consisted of 225,000 square feet (20,900 m) of concrete placed in 30 hours, finished to a flatness tolerance of FF 54.60 and a levelness tolerance of FL 43.83. This surpassed the previous record by 50% in total volume and 7.5% in total area.
The record for the largest continuously placed underwater concrete pour was completed 18 October 2010, in New Orleans, Louisiana by contractor C. J. Mahan Construction Company, LLC of Grove City, Ohio. The placement consisted of 10,251 cubic yards of concrete placed in 58.5 hours using two concrete pumps and two dedicated concrete batch plants. Upon curing, this placement allows the 50,180-square-foot (4,662 m) cofferdam to be dewatered approximately 26 feet (7.9 m) below sea level to allow the construction of the Inner Harbor Navigation Canal Sill & Monolith Project to be completed in the dry.
See also
- Concrete leveling – Process to level concrete by levelling its underlying foundation
- Concrete mixer – Device that combines cement, aggregate, and water to form concrete
- Concrete masonry unit – Standard-sized block used in constructionPages displaying short descriptions of redirect targets
- Concrete plant – Equipment that combines various ingredients to form concrete
- Heavy metals – Loosely defined subset of elements that exhibit metallic properties
- Hempcrete – Biocomposite material used for construction and insulation
- Particulates – Microscopic solid or liquid matter suspended in the Earth's atmosphere
- Syncrete – Synthetic form of concrete
References
- Gagg, Colin R. (May 2014). "Cement and concrete as an engineering material: An historic appraisal and case study analysis". Engineering Failure Analysis. 40: 114–140. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2014.02.004.
- Crow, James Mitchell (March 2008). "The concrete conundrum" (PDF). Chemistry World: 62–66. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Manager, Samsung C&T Global PR (27 June 2018). "Concrete Matters: A Primer on the Most Popular Man-Made Material". Samsung C&T Newsroom. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- "Scientific Principles". matse1.matse.illinois.edu. Retrieved 24 May 2023.
- Li, Zongjin (2011). Advanced concrete technology. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-90243-1.
- Industrial Resources Council (2008). "Portland Cement Concrete". www.industrialresourcescouncil.org. Retrieved 15 June 2018.
- National Highway Institute. "Portland Cement Concrete Materials" (PDF). Federal Highway Administration. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Limbachiya, Mukesh C.; Kew, Hsein Y. (3 September 2008). Excellence in Concrete Construction through Innovation: Proceedings of the conference held at the Kingston University, United Kingdom, 9 - 10 September 2008. CRC Press. p. 115. ISBN 978-0-203-88344-0.
- Allen, Edward; Iano, Joseph (2013). Fundamentals of building construction: materials and methods (Sixth ed.). Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. p. 314. ISBN 978-1-118-42086-7. OCLC 835621943.
- "concretus". Latin Lookup. Archived from the original on 12 May 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- Heinrich Schliemann; Wilhelm Dörpfeld; Felix Adler (1885). Tiryns: The Prehistoric Palace of the Kings of Tiryns, the Results of the Latest Excavations. New York: Charles Scribner's Sons. pp. 190, 203–204, 215.
- Sparavigna, Amelia Carolina (2011). "Ancient concrete works". arXiv:1110.5230 .
- Jacobsen T and Lloyd S, (1935) "Sennacherib's Aqueduct at Jerwan," Oriental Institute Publications 24, Chicago University Press
- Stella L. Marusin (1 January 1996). "Ancient Concrete Structures". Concrete International. 18 (1): 56–58.
- ^ Gromicko, Nick; Shepard, Kenton (2016). "The History of Concrete". International Association of Certified Home Inspectors, Inc. Retrieved 27 December 2018.
- "Riddle solved: Why was Roman concrete so durable?". MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 6 January 2023. Retrieved 25 October 2024.
- Moore, David (6 October 2014). "Roman Concrete Research". Romanconcrete.com. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- "The History of Concrete". Dept. of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. Archived from the original on 27 November 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- Chiu, Y. C. (2010). An Introduction to the History of Project Management: From the Earliest Times to A.D. 1900. Eburon Uitgeverij B.V. p. 50. ISBN 978-90-5972-437-2.
- Lancaster, Lynne (2005). Concrete Vaulted Construction in Imperial Rome. Innovations in Context. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-511-16068-4.
- Moore, David (1999). "The Pantheon". romanconcrete.com. Archived from the original on 1 October 2011. Retrieved 26 September 2011.
- D.S. Robertson (1969). Greek and Roman Architecture, Cambridge, p. 233
- Cowan, Henry J. (1977). The master builders: a history of structural and environmental design from ancient Egypt to the nineteenth century. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-02740-5. OCLC 2896326.
- "CIVL 1101". www.ce.memphis.edu. Archived from the original on 27 February 2017.
- Robert Mark, Paul Hutchinson: "On the Structure of the Roman Pantheon", Art Bulletin, Vol. 68, No. 1 (1986), p. 26, fn. 5
- Kwan, Stephen; Larosa, Judith; Grutzeck, Michael W. (1995). "29Si and27Al MASNMR Study of Stratlingite". Journal of the American Ceramic Society. 78 (7): 1921–1926. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1995.tb08910.x.
- Jackson, Marie D.; Landis, Eric N.; Brune, Philip F.; Vitti, Massimo; Chen, Heng; Li, Qinfei; Kunz, Martin; Wenk, Hans-Rudolf; Monteiro, Paulo J. M.; Ingraffea, Anthony R. (30 December 2014). "Mechanical resilience and cementitious processes in Imperial Roman architectural mortar". PNAS. 111 (52): 18484–18489. Bibcode:2014PNAS..11118484J. doi:10.1073/pnas.1417456111. PMC 4284584. PMID 25512521.
- Marie D. Jackson; Sean R. Mulcahy; Heng Chen; Yao Li; Qinfei Li; Piergiulio Cappelletti; Hans-Rudolf Wenk (3 July 2017). "Phillipsite and Al-tobermorite mineral cements produced through low-temperature water-rock reactions in Roman marine concrete". American Mineralogist. 102 (7): 1435–1450. Bibcode:2017AmMin.102.1435J. doi:10.2138/am-2017-5993CCBY. S2CID 53452767.
- Knapton, Sarah (3 July 2017). "Secret of how Roman concrete survived tidal battering for 2,000 years revealed". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 4 July 2017.
- Seymour, Linda M.; Maragh, Janille; Sabatini, Paolo; Di Tommaso, Michel; Weaver, James C.; Masic, Admir (6 January 2023). "Hot mixing: Mechanistic insights into the durability of ancient Roman concrete". Science Advances. 9 (1): eadd1602. Bibcode:2023SciA....9D1602S. doi:10.1126/sciadv.add1602. PMC 9821858. PMID 36608117.
- Starr, Michelle (1 February 2024). "We Finally Know How Ancient Roman Concrete Was Able to Last Thousands of Years". ScienceAlert. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- Peter Hewlett and Martin Liska (eds.), Lea's Chemistry of Cement and Concrete, 5th ed. (Butterworth-Heinemann, 2019), pp. 3–4.
- Rassia, Stamatina Th; Pardalos, Panos M. (15 August 2013). Cities for Smart Environmental and Energy Futures: Impacts on Architecture and Technology. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 58. ISBN 978-3-642-37661-0.
- Nick Gromicko & Kenton Shepard. "the History of Concrete". The International Association of Certified Home Inspectors (InterNACHI). Archived from the original on 15 January 2013. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- Herring, Benjamin. "The Secrets of Roman Concrete" (PDF). Romanconcrete.com. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 September 2012. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- Courland, Robert (2011). Concrete planet: the strange and fascinating story of the world's most common man-made material. Amherst, NY: Prometheus Books. ISBN 978-1-61614-481-4. Archived from the original on 4 November 2015. Retrieved 28 August 2015.
- "The History of Concrete and Cement". ThoughtCo. 9 April 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- "Francois Coignet – French house builder". Retrieved 23 December 2016.
- « Château de Chazelet » , notice no PA00097319, base Mérimée, ministère français de la Culture.
- Billington, David (1985). The Tower and the Bridge. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-691-02393-X.
- "Concrete: Scientific Principles". matse1.matse.illinois.edu. Retrieved 6 October 2021.
- ^ Askarian, Mahya; Fakhretaha Aval, Siavash; Joshaghani, Alireza (22 January 2019). "A comprehensive experimental study on the performance of pumice powder in self-compacting concrete (SCC)". Journal of Sustainable Cement-Based Materials. 7 (6): 340–356. doi:10.1080/21650373.2018.1511486. S2CID 139554392.
- Melander, John M.; Farny, James A.; Isberner, Albert W. Jr. (2003). "Portland Cement Plaster/Stucco Manual" (PDF). Portland Cement Association. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 April 2021. Retrieved 13 July 2021.
- Evelien Cochez; Wouter Nijs; Giorgio Simbolotti & Giancarlo Tosato. "Cement Production" (PDF). IEA ETSAP – Energy Technology Systems Analysis Programme. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 January 2013. Retrieved 9 January 2013.
- Gibbons, Jack. "Measuring Water in Concrete". Concrete Construction. Archived from the original on 11 May 2013. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- "Chapter 9: Designing and Proportioning Normal Concrete Mixtures" (PDF). PCA manual. Portland Concrete Association. Archived (PDF) from the original on 26 May 2012. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- ^ "Cement hydration". Understanding Cement. Archived from the original on 17 October 2012. Retrieved 1 October 2012.
- Beaudoin, James; Odler, Ivan (2019). "Hydration, Setting and Hardening of Portland Cement". Lea's Chemistry of Cement and Concrete. pp. 157–250. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-100773-0.00005-8. ISBN 978-0-08-100773-0.
- "The Effect of Aggregate Properties on Concrete". www.engr.psu.edu. Engr.psu.edu. 25 December 2012. Archived from the original on 25 December 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- ^ Veretennykov, Vitaliy I.; Yugov, Anatoliy M.; Dolmatov, Andriy O.; Bulavytskyi, Maksym S.; Kukharev, Dmytro I.; Bulavytskyi, Artem S. (2008). "Concrete Inhomogeneity of Vertical Cast-in-Place Elements in Skeleton-Type Buildings". AEI 2008. pp. 1–10. doi:10.1061/41002(328)17. ISBN 978-0-7844-1002-8.
- Gerry Bye; Paul Livesey; Leslie Struble (2011). "Admixtures and Special Cements". Portland Cement: Third edition. doi:10.1680/pc.36116.185 (inactive 1 November 2024). ISBN 978-0-7277-3611-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of November 2024 (link) - ^ U.S. Federal Highway Administration (14 June 1999). "Admixtures". Archived from the original on 27 January 2007. Retrieved 25 January 2007.
- Cement Admixture Association. "Admixture Types". Archived from the original on 3 September 2011. Retrieved 25 December 2010.
- Hamakareem, Madeh Izat (14 November 2013). "Effect of Air Entrainment on Concrete Strength". The Constructor. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- Bensted, John (1 January 1998), Hewlett, Peter C. (ed.), "14 - Special Cements", Lea's Chemistry of Cement and Concrete (Fourth Edition), Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann, pp. 783–840, doi:10.1016/b978-075066256-7/50026-6, ISBN 978-0-7506-6256-7, retrieved 3 November 2024
- Holland, Terence C. (2005). "Silica Fume User's Manual" (PDF). Silica Fume Association and United States Department of Transportation Federal Highway Administration Technical Report FHWA-IF-05-016. Retrieved 31 October 2014.
- Kosmatka, S.; Kerkhoff, B.; Panerese, W. (2002). Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures (14 ed.). Portland Cement Association, Skokie, Illinois.
- Gamble, William. "Cement, Mortar, and Concrete". In Baumeister; Avallone; Baumeister (eds.). Mark's Handbook for Mechanical Engineers (Eighth ed.). McGraw Hill. Section 6, page 177.
- Kosmatka, S.H.; Panarese, W.C. (1988). Design and Control of Concrete Mixtures. Skokie, IL: Portland Cement Association. pp. 17, 42, 70, 184. ISBN 978-0-89312-087-0.
- "Paving the way to greenhouse gas reductions". MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology. 28 August 2011. Archived from the original on 31 October 2012. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- U.S. Federal Highway Administration (14 June 1999). "Fly Ash". Archived from the original on 21 June 2007. Retrieved 24 January 2007.
- U.S. Federal Highway Administration. "Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag". Archived from the original on 22 January 2007. Retrieved 24 January 2007.
- U.S. Federal Highway Administration. "Silica Fume". Archived from the original on 22 January 2007. Retrieved 24 January 2007.
- Mullapudi, Taraka Ravi Shankar; Gao, Di; Ayoub, Ashraf (September 2013). "Non-destructive evaluation of carbon nanofibre concrete". Magazine of Concrete Research. 65 (18): 1081–1091. doi:10.1680/macr.12.00187.
- Tuan, Christopher; Yehia, Sherif (1 July 2004). "Evaluation of Electrically Conductive Concrete Containing Carbon Products for Deicing". ACI Materials Journal. 101 (4): 287–293.
- Kloosterman, Karin (23 May 2023). "Tiny house built from diapers and concrete". Green Prophet. Retrieved 6 October 2024.
- "Cold Joints". www.concrete.org.uk. The Concrete Society. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 30 December 2015.
- "Grades of Concrete with Proportion (Mix Ratio)". 26 March 2018.
- "Concrete International". concrete.org. 1 November 1989. Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- "ACI 304R-00: Guide for Measuring, Mixing, Transporting, and Placing Concrete (Reapproved 2009)".
- Sarviel, Ed (1993). Construction Estimating Reference Data. Craftsman Book Company. p. 74. ISBN 978-0-934041-84-3.
- Cook, Marllon Daniel; Ghaeezadah, Ashkan; Ley, M. Tyler (1 February 2018). "Impacts of Coarse-Aggregate Gradation on the Workability of Slip-Formed Concrete". Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering. 30 (2). doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002126.
- "Aggregate in Concrete – the Concrete Network". Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 15 January 2017.
- Ferrari, L.; Kaufmann, J.; Winnefeld, F.; Plank, J. (October 2011). "Multi-method approach to study influence of superplasticizers on cement suspensions". Cement and Concrete Research. 41 (10): 1058–1066. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.06.010.
- "Curing Concrete" Peter C. Taylor CRC Press 2013. ISBN 978-0-415-77952-4. eBook ISBN 978-0-203-86613-9
- "Concrete Testing". Archived from the original on 24 October 2008. Retrieved 10 November 2008.
- ""Admixtures for Cementitious Applications."" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 October 2016.
- "Home" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 12 November 2015.
- The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 2011. p. 106. ISBN 978-0-547-04101-8.
- "Asphalt concrete cores for embankment dams". International Water Power and Dam Construction. Archived from the original on 7 July 2012. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- Polaczyk, Pawel; Huang, Baoshan; Shu, Xiang; Gong, Hongren (September 2019). "Investigation into Locking Point of Asphalt Mixtures Utilizing Superpave and Marshall Compactors". Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering. 31 (9). doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002839. S2CID 197635732.
- Reid, Carlton (2015). Roads Were Not Built for Cars: How Cyclists Were the First to Push for Good Roads & Became the Pioneers of Motoring. Island Press. p. 120. ISBN 978-1-61091-689-9.
- Dalal, Sejal P.; Dalal, Purvang (March 2021). "Experimental Investigation on Strength and Durability of Graphene Nanoengineered Concrete". Construction and Building Materials. 276: 122236. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.122236. S2CID 233663658.
- Dalal, Sejal P.; Desai, Kandarp; Shah, Dhairya; Prajapati, Sanjay; Dalal, Purvang; Gandhi, Vimal; Shukla, Atindra; Vithlani, Ravi (January 2022). "Strength and feasibility aspects of concrete mixes induced with low-cost surfactant functionalized graphene powder". Asian Journal of Civil Engineering. 23 (1): 39–52. doi:10.1007/s42107-021-00407-7. S2CID 257110774.
- Falkow, Stanley; Rosenberg, Eugene; Schleifer, Karl-Heinz; Stackebrandt, Erko (13 July 2006). The Prokaryotes: Vol. 2: Ecophysiology and Biochemistry. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 1005. ISBN 978-0-387-25492-0.
- Metwally, Gehad A. M.; Mahdy, Mohamed; Abd El-Raheem, Ahmed El-Raheem H. (August 2020). "Performance of Bio Concrete by Using Bacillus Pasteurii Bacteria". Civil Engineering Journal. 6 (8): 1443–1456. doi:10.28991/cej-2020-03091559.
- ^ Raju, N. Krishna (2018). Prestressed Concrete, 6e. McGraw-Hill Education. p. 1131. ISBN 978-93-87886-25-4.
- Tiwari, AK; Chowdhury, Subrato (2013). "An over view of the application of nanotechnology in construction materials". Proceedings of the International Symposium on Engineering under Uncertainty: Safety Assessment and Management (ISEUSAM-2012). Cakrabartī, Subrata; Bhattacharya, Gautam. New Delhi: Springer India. p. 485. ISBN 978-81-322-0757-3. OCLC 831413888.
- Thanmanaselvi, M; Ramasamy, V (2023). "A study on durability characteristics of nano-concrete". Materials Today: Proceedings. 80: 2360–2365. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.06.349. ISSN 2214-7853.
- "Ground Water Recharging Through Pervious Concrete Pavement". ResearchGate. Retrieved 26 January 2021.
- Onuaguluchi, Obinna; Banthia, Nemkumar (1 April 2016). "Plant-based natural fibre reinforced cement composites: A review". Cement and Concrete Composites. 68: 96–108. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.02.014. ISSN 0958-9465.
- Wu, Hansong; Shen, Aiqin; Cheng, Qianqian; Cai, Yanxia; Ren, Guiping; Pan, Hongmei; Deng, Shiyi (20 September 2023). "A review of recent developments in application of plant fibers as reinforcements in concrete". Journal of Cleaner Production. 419: 138265. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.138265. ISSN 0959-6526.
- Yan, Libo; Kasal, Bohumil; Huang, Liang (1 May 2016). "A review of recent research on the use of cellulosic fibres, their fibre fabric reinforced cementitious, geo-polymer and polymer composites in civil engineering". Composites Part B: Engineering. 92: 94–132. doi:10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.02.002. ISSN 1359-8368.
- Li, Juan; Kasal, Bohumil (July 2023). "Degradation Mechanism of the Wood-Cell Wall Surface in a Cement Environment Measured by Atomic Force Microscopy". Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering. 35 (7). doi:10.1061/JMCEE7.MTENG-14910. ISSN 0899-1561.
- Li, Juan; Kasal, Bohumil (10 August 2022). "The immediate and short-term degradation of the wood surface in a cement environment measured by AFM". Materials and Structures. 55 (7): 179. doi:10.1617/s11527-022-01988-8. ISSN 1871-6873.
- Li, Juan; Kasal, Bohumil (11 April 2022). "Effects of Thermal Aging on the Adhesion Forces of Biopolymers of Wood Cell Walls". Biomacromolecules. 23 (4): 1601–1609. doi:10.1021/acs.biomac.1c01397. ISSN 1525-7797. PMC 9006222. PMID 35303409.
- Li, Juan; Bohumil, Kasal (5 February 2021). "Repeatability of Adhesion Force Measurement on Wood Longitudinal Cut Cell Wall Using Atomic Force Microscopy". Wood and Fiber Science. 53 (1): 3–16. doi:10.22382/wfs-2021-02. ISSN 0735-6161.
- Lavars, Nick (10 June 2021). "Stanford's low-carbon cement swaps limestone for volcanic rock". New Atlas. Archived from the original on 10 June 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2021.
- Celik, K.; Jackson, M.D.; Mancio, M.; Meral, C.; Emwas, A.-H.; Mehta, P.K.; Monteiro, P.J.M. (January 2014). "High-volume natural volcanic pozzolan and limestone powder as partial replacements for portland cement in self-compacting and sustainable concrete". Cement and Concrete Composites. 45: 136–147. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2013.09.003. hdl:11511/37244. S2CID 138740924.
- ^ Lemougna, Patrick N.; Wang, Kai-tuo; Tang, Qing; Nzeukou, A.N.; Billong, N.; Melo, U. Chinje; Cui, Xue-min (October 2018). "Review on the use of volcanic ashes for engineering applications". Resources, Conservation and Recycling. 137: 177–190. Bibcode:2018RCR...137..177L. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.05.031. S2CID 117442866.
- Brown, R.J.; Calder, E.S. (2005). "Pyroclastics". Encyclopedia of Geology. pp. 386–397. doi:10.1016/b0-12-369396-9/00153-2. ISBN 978-0-12-369396-9.
- Izzo, Francesco; Arizzi, Anna; Cappelletti, Piergiulio; Cultrone, Giuseppe; De Bonis, Alberto; Germinario, Chiara; Graziano, Sossio Fabio; Grifa, Celestino; Guarino, Vincenza; Mercurio, Mariano; Morra, Vincenzo; Langella, Alessio (August 2016). "The art of building in the Roman period (89 B.C. – 79 A.D.): Mortars, plasters and mosaic floors from ancient Stabiae (Naples, Italy)". Construction and Building Materials. 117: 129–143. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.04.101.
- "MASUKO light concrete". Archived from the original on 15 November 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- "Relation Between Compressive and Tensile Strength of Concrete". Archived from the original on 6 January 2019. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
- "Structural lightweight concrete" (PDF). Concrete Construction. The Aberdeen Group. March 1981. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 May 2013.
- "Ordering Concrete by PSI". American Concrete. Archived from the original on 11 May 2013. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- ^ Henry G. Russel, PE. "Why Use High Performance Concrete?" (PDF). Technical Talk. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 May 2013. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- "Concrete in Practice: What, Why, and How?" (PDF). NRMCA-National Ready Mixed Concrete Association. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 August 2012. Retrieved 10 January 2013.
- Ritchie, Hannah; Roser, Max; Rosado, Pablo (11 May 2020). "CO₂ and Greenhouse Gas Emissions". Our World in Data – via ourworldindata.org.
- "Making Concrete Change: Innovation in Low-carbon Cement and Concrete". Chatham House. 13 June 2018. Archived from the original on 19 December 2018. Retrieved 17 December 2018.
- Rubenstein, Madeleine (9 May 2012). "Emissions from the Cement Industry". State of the Planet. Earth Institute, Columbia University. Archived from the original on 22 December 2016. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
- "Concrete and Embodied Energy – Can using concrete be carbon neutral". 22 February 2013. Archived from the original on 16 January 2017. Retrieved 15 January 2017.
- Gajda, John (2001). "Energy Use of Single-Family Houses with Various Exterior Walls" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Green Building with Concrete. Taylor & Francis Group. 2015. ISBN 978-1-4987-0411-3.
- "Features and Usage of Foam Concrete". Archived from the original on 29 November 2012.
- "Unreinforced Masonry Buildings and Earthquakes: Developing Successful Risk Reduction Programs FEMA P-774". Archived from the original on 12 September 2011.
- Simsir, C.C.; Jain, A.; Hart, G.C.; Levy, M.P. (12–17 October 2008). Seismic Retrofit Design Of Historic Century-Old School Buildings In Istanbul, Turkey (PDF). 14th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering. Archived from the original (PDF) on 11 January 2012.
- Nawy, Edward G. (2008). Concrete Construction Engineering Handbook. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-0765-7.
- Lomborg, Bjørn (2001). The Skeptical Environmentalist: Measuring the Real State of the World. Cambridge University Press. p. 138. ISBN 978-0-521-80447-9.
- "Minerals commodity summary – cement – 2007". US United States Geological Survey. 1 June 2007. Archived from the original on 13 December 2007. Retrieved 16 January 2008.
- Murray, Lorraine. "Christ the Redeemer (last updated 13 January 2014)". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 5 November 2022.
- ^ "Reinforced concrete". www.designingbuildings.co.uk.
- ^ Claisse, Peter A. (2016), "Composites", Civil Engineering Materials, Elsevier, pp. 431–435, doi:10.1016/b978-0-08-100275-9.00038-3, ISBN 978-0-08-100275-9, retrieved 5 October 2021
- ^ Richardson, John (2003). "Precast concrete structural elements". Advanced Concrete Technology. pp. 3–46. doi:10.1016/B978-075065686-3/50307-4. ISBN 978-0-7506-5686-3.
- ^ "Mass Concret" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 September 2011.
- Sadowski, Łukasz; Mathia, Thomas (2016). "Multi-scale Metrology of Concrete Surface Morphology: Fundamentals and specificity". Construction and Building Materials. 113: 613–621. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.03.099.
- "Winter is Coming! Precautions for Cold Weather Concreting". FPrimeC Solutions. 14 November 2016. Archived from the original on 13 January 2017. Retrieved 11 January 2017.
- "306R-16 Guide to Cold Weather Concreting". Archived from the original on 15 September 2017.
- ^ Larn, Richard; Whistler, Rex (1993). "17 – Underwater concreting". Commercial Diving Manual (3rd ed.). Newton Abbott, UK: David and Charles. pp. 297–308. ISBN 0-7153-0100-4.
- Prefilled lined underwater hand-placed bagwork product datasheet (PDF). www.soluform.co.uk (Report). Soluform. Retrieved 8 September 2024.
- "Mapping of Excess Fuel Consumption". Archived from the original on 2 January 2015.
- Paul, Andrew (17 September 2024). "Bone-like, hollow concrete design makes it 5.6 times stronger". Popular Science. Retrieved 11 October 2024.
- Akerman, Patrick; Cazzola, Pierpaolo; Christiansen, Emma Skov; Heusden, Renée Van; Iperen, Joanna Kolomanska-van; Christensen, Johannah; Crone, Kilian; Dawe, Keith; Smedt, Guillaume De; Keynes, Alex; Laporte, Anaïs; Gonsolin, Florie; Mensink, Marko; Hebebrand, Charlotte; Hoenig, Volker; Malins, Chris; Neuenhahn, Thomas; Pyc, Ireneusz; Purvis, Andrew; Saygin, Deger; Xiao, Carol; Yang, Yufeng (1 September 2020). "Reaching Zero with Renewables".
- "Leading the way to carbon neutrality" (PDF). HeidelbergCement. 24 September 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- "Cement Clinker Calcination in Cement Production Process". AGICO Cement Plant Supplier. 4 April 2019.
- "Carbon footprint" (PDF). Portland Cement Association. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- ^ Lehne, Johanna; Preston, Felix (13 June 2018). "Making Concrete Change: Innovation in Low-carbon Cement and Concrete".
- Proske, Tilo; Hainer, Stefan; Rezvani, Moien; Graubner, Carl-Alexander (September 2013). "Eco-friendly concretes with reduced water and cement contents – Mix design principles and laboratory tests". Cement and Concrete Research. 51: 38–46. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2013.04.011.
- O'Hegarty, Richard; Kinnane, Oliver; Newell, John; West, Roger (November 2021). "High performance, low carbon concrete for building cladding applications". Journal of Building Engineering. 43: 102566. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102566.
- Lee, Jaehyun; Lee, Taegyu; Jeong, Jaewook; Jeong, Jaemin (January 2021). "Sustainability and performance assessment of binary blended low-carbon concrete using supplementary cementitious materials". Journal of Cleaner Production. 280: 124373. Bibcode:2021JCPro.28024373L. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124373. S2CID 224849505.
- Sabry, Fouad (17 January 2022). Translucent Concrete: How-to see-through walls? Using nano optics and mixing fine concrete and optical fibers for illumination during day and night time. One Billion Knowledgeable.
- Mehta, P. Kumar (1 February 2009). "Global Concrete Industry Sustainability". Concrete International. 31 (2): 45–48.
- Luis Emilio Rendon Diaz Miron; Dessi A. Koleva (2017). Concrete Durability: Cementitious Materials and Reinforced Concrete Properties, Behavior and Corrosion Resistance. Springer. pp. 2–. ISBN 978-3319554631.
- "Home". ConcreteRecycling.org. Archived from the original on 12 April 2010. Retrieved 5 April 2010.
- "Urbanite - Reusing Old Concrete - The Concrete Network". ConcreteNetwork.com. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- "Urbanite Construction". www.ecodesignarchitects.co.za. Archived from the original on 7 May 2021. Retrieved 24 May 2020.
- Abdo, Ayman; El-Zohairy, Ayman; Alashker, Yasser; Badran, Mohamed Abd El-Aziz; Ahmed, Sayed (1 January 2024). "Effect of Treated/Untreated Recycled Aggregate Concrete: Structural Behavior of RC Beams". Sustainability. 16 (10): 4039. doi:10.3390/su16104039. ISSN 2071-1050.
- "Khoan Cắt Bê Tông". Retrieved 25 October 2024.
- Abdelfatah, Akmal S.; Tabsh, Sami W. (2011). "Review of Research on and Implementation of Recycled Concrete Aggregate in the GCC". Advances in Civil Engineering. 2011: 1–6. doi:10.1155/2011/567924. ISSN 1687-8086.
- Lu, Linfeng (July 2024). "Optimal Replacement Ratio of Recycled Concrete Aggregate Balancing Mechanical Performance with Sustainability: A Review". Buildings. 14 (7): 2204. doi:10.3390/buildings14072204. ISSN 2075-5309.
- Rao, Akash; Jha, Kumar N.; Misra, Sudhir (1 March 2007). "Use of aggregates from recycled construction and demolition waste in concrete". Resources, Conservation and Recycling. 50 (1): 71–81. Bibcode:2007RCR....50...71R. doi:10.1016/j.resconrec.2006.05.010. ISSN 0921-3449.
- "Itaipu Web-site". 2 January 2012. Archived from the original on 9 February 2012. Retrieved 2 January 2012.
- Sources, Other News (14 July 2009). "China's Three Gorges Dam, by the Numbers". Probe International. Archived from the original on 29 March 2017. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
- "Concrete Pouring of Three Gorges Project Sets World Record". People's Daily. 4 January 2001. Archived from the original on 27 May 2010. Retrieved 24 August 2009.
- "Concrete Pumping to 715 m Vertical – A New World Record Parbati Hydroelectric Project Inclined Pressure Shaft Himachal Pradesh – A case Study". The Masterbuilder. Archived from the original on 21 July 2011. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- "SCHWING Stetter Launches New Truck mounted Concrete Pump S-36". NBM&CW (New Building Materials and Construction World). October 2009. Archived from the original on 14 July 2011. Retrieved 21 October 2010.
- Janyala, Sreenivas (7 January 2019). "Andhra Pradesh: Polavaram project enters Guinness Book of World Record for concrete pouring". The India Express. Retrieved 7 January 2020.
- "Concrete Supplier for Landmark Tower". Construction Week Online. 19 April 2011. Archived from the original on 15 May 2013.
- "The world record Concrete Supplier for Landmark Tower Unibeton Ready Mix". Archived from the original on 24 November 2012.
- "Abu Dhabi – Landmark Tower has a record-breaking pour" (PDF). Al Habtoor Engineering. September–October 2007. p. 7. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 March 2011.
- National Geographic Channel International / Caroline Anstey (2005), Megastructures: Petronas Twin Towers
- "Continuous cast: Exxcel Contract Management oversees record concrete pour". concreteproducts.com. 1 March 1998. Archived from the original on 26 May 2010. Retrieved 25 August 2009.
- Exxcel Project Management – Design Build, General Contractors Archived 28 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Exxcel.com. Retrieved 19 February 2013.
- "Contractors Prepare to Set Gates to Close New Orleans Storm Surge Barrier". www.construction.com. 12 May 2011. Archived from the original on 13 January 2013. Retrieved 13 August 2022.
Further reading
- "The world's growing problem with concrete, the world's most destructive material" (Video). BBC Reel. 6 March 2023.
External links
- Advantage and Disadvantage of Concrete
- Dunning, Brian (4 January 2022). "Skeptoid #813: Why You Need to Care About Concrete". Skeptoid. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
- Getting Buried in Concrete to Explain How It Works on YouTube
- Release of ultrafine particles from three simulated building processes
- Concrete: The Quest for Greener Alternatives
| Stonemasonry | |
|---|---|
| Types | |
| Materials | |
| Tools | |
| Techniques | |
| Products | |
| Organizations | |
| Concrete | |
|---|---|
| History | |
| Composition | |
| Production | |
| Construction | |
| Science | |
| Types | |
| Applications | |
| Organizations | |
| Standards | |
| See also | |
 . Nominal mixes are a simple, fast way of getting a basic idea of the properties of the finished concrete without having to perform testing in advance.
. Nominal mixes are a simple, fast way of getting a basic idea of the properties of the finished concrete without having to perform testing in advance.