| Barred owl | |
|---|---|

| |
| Conservation status | |
 Least Concern (IUCN 3.1) | |
| CITES Appendix II (CITES) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Strigiformes |
| Family: | Strigidae |
| Genus: | Strix |
| Species: | S. varia |
| Binomial name | |
| Strix varia Barton, 1799 | |
| Subspecies | |
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Syrnium varium | |
The barred owl (Strix varia), also known as the northern barred owl, striped owl or, more informally, hoot owl or eight-hooter owl, is a North American large species of owl. A member of the true owl family, Strigidae, they belong to the genus Strix, which is also the origin of the family's name under Linnaean taxonomy. Barred owls are largely native to eastern North America, but have expanded their range to the west coast of North America where they are considered invasive. Mature forests are their preferred habitat, but they can also acclimatise to various gradients of open woodlands. Their diet consists mainly of small mammals, but this species is an opportunistic predator and is known to prey upon other small vertebrates such as birds, reptiles, and amphibians, as well as a variety of invertebrates.
Barred owls are brown to gray overall, with dark striping on the underside. Barred owls have typical nesting habits for a true owl, tending to raise a relatively small brood often in a tree hollow or snag (but sometimes also in other nesting sites) in forested areas. As a result of the barred owl's westward expansion, the species has begun to encroach on the range of the related and threatened spotted owl (Strix occidentalis). Evidence shows the assorted threats posed by the invading barred species are only increasing. In response, biologists have recommended culling operations to mitigate the negative effect of the barred on the spotted owl species.
Basics

The barred owl was first described by Philadelphia naturalist Benjamin Smith Barton in 1799. The species was named due to the varied directions the dusky markings take on their underside.
The barred owl is roughly intermediate in size between the larger Ural and the smaller tawny owl, but the structural features of its relatively short and decurved claws more so resemble the tawny species as does their dietary and habitat ecology. The spotted owl has been hypothesized to be within a superspecies with the barred owl. However, genetic testing reveals very early divergence (likely at or near their ancestor's entry to North America) between spotted and barred owls. A fossil species once called Strix brea from the early Pleistocene in California does little to resolve the ancestry of modern species, given its ambiguous relation to any living Strix. The fossil species was larger (more similar in size and slenderness to the spotted owl, albeit with a slightly smaller skull and geographically isolated from that species) and longer-legged than either the spotted and barred owls, and is now considered to be in a separate genus, Oraristrix. Pleistocene era fossils of probable barred owls are known from Florida, Tennessee and Ontario.
Subspecies


The subspecies of the barred owl vary mostly by region, with slight to moderate variation by coloring, size and extent of feathering on the toes. Although several have been described in the past, the barred owl may include only three subspecies, subsequent to the separation of the fulvous and cinereous forms.
- S. v. varia (Barton, 1799): The northern barred owl. This race lives throughout the Northeastern United States and the Upper Midwest, ranging as far south as Oklahoma, the Carolinas and northern Georgia. It is also considered to comprise all western "invader" birds found as far west as California and British Columbia. However, genetic study of westerly birds show a substantial isolation, possibly up to the subspecific level, of the western and eastern populations of the northern owls, with an estimated divergence of around 7,000 years, perhaps indicating an unknown history of the species in remote forests of northern and central Canada (far west of what was considered their original distribution) that radiated more recently to comprise the western populations. This race is generally the typical mid gray-brown variety of barred owl. However, a paler variation with very washed out markings and a more pure whitish base color is known (in eastern Canada such as Quebec), formerly considered a race S. v. albescens, as well as darker and browner variation in northern Minnesota (formerly S. v. brunnescens). This race is fairly large (described as the largest race on average with the probable separation of the cinereous owl). The wing chord and tail length may measure from 312 to 340 mm (12.3 to 13.4 in) and 215 to 230 mm (8.5 to 9.1 in) in males and 320 to 352 mm (12.6 to 13.9 in) and 224 to 257 mm (8.8 to 10.1 in) in females. One nominate bird had a tarsus length of 63.5 mm (2.50 in) and the culmen from the cere may measure 23.5 to 30 mm (0.93 to 1.18 in).
- S. v. georgica (Latham, 1801): The southern barred owl or, alternately, the Florida barred owl. This subspecies is found in southern North Carolina closer to the coast along to broadly through Georgia and all of Florida. This is the smallest of the three subspecies on average. Known wing chord lengths can vary from 315 to 357 mm (12.4 to 14.1 in). Tail length is 205 to 231 mm (8.1 to 9.1 in) and the bill from the cere is 23 to 28 mm (0.91 to 1.10 in). Males in Florida were found to weigh from 681 to 800 g (1.501 to 1.764 lb), with averages in two samples of 718 and 744 g (1.583 and 1.640 lb), while two females weighed 850 and 875 g (1.874 and 1.929 lb), respectively. It therefore appears to show less pronounced sexual dimorphism than the northern barred owl race.
- S. v. helveola (Bangs, 1899): The Texas barred owl. Comprises most barred owls found in Texas. The distributional range is considered to range as far north as Lee County, east to Chambers County, west to Kerr County and south to Nueces County. In this race, the ground coloration tends to pale gingery-cream and the back and head tend to be a pale brown ranging into an almost cinnamon color. The toes can vary from rather bare to slightly bristled. This race is similar to other barred owls in size, perhaps averaging marginally smaller than those in the nominate race, but its bill and feet are larger on average than the preceding two races.
Description

The barred owl is considered somewhat subdued and drab in coloration compared to the sometimes rich coloring of other sympatric owls. Overall, this owl is greyish-brown or brown. The brownish color extends from the head to the back. Barred owls are scalloped with white bars on the mantle and the back, bearing as well some whitish spotting on the wing coverts. The underside has a pale creamy gray-brown base color (ranging into dirty white in the palest individuals) overlaid about the throat and upper chest with horizontal, slightly crescent-shaped barring (hence its common name), while the belly is boldly streaked in a vertical pattern. The streaking is usually blackish, dusky brown, or sometimes rufescent- (reddish-) brown. The head is fairly large (although not especially so for a species in Strix) and rounded with no ear tufts. The facial disc is pale grayish-brown with darker yet subtle concentric lines. The bill is pale straw-yellow (occasionally showing a mild greenish tint) while the cere (a bare structure at the base of the beak) is "horn-colored". Its eyes are a dark brown color; the eyes may appear intensely black in the field and, although large, are fairly closely set.
The barred owl has well-developed eye anatomy. As is typical of owls, their ocular anatomy is quite distinct from diurnal raptors especially in terms of their photoreceptor cells, as they have a very large number of rod cells in their quite sensitive retina. However, their pecten oculi is smaller relative to the size of their large ocular globe (other large owls are known to have similar pecten proportions). The vision in limited or almost no light during a laboratory study of a barred owl was found to be similar to that of other owls, including the long-eared owl (Asio otus) and the barn owl (Tyto alba). The tarsi and toes are feathered up to the dark gray, black-tipped talons. These feathers are more sparse and bristled in the southern races. On individuals with bare sections of their toes, the toes are yellowish-gray in color. The flight feathers are barred with whitish buff and brown while the tail is brown or grayish-brown with 4–5 whitish bars. Young barred owls with their second set of down feathers are fluffy brownish-white, with indistinct darker barring on their head, back and mantle. They quickly become juveniles which resemble adults but have less distinct markings (especially about the head and neck), more buff coloring overall, often some remnant down, pinkish skin and a pale, blue-green cere. Also the tail at this age may have as many as seven bands (though sometimes have four like adults). Full adult plumage is obtained via molt after about a year as well as adult bare part characteristics. A study of tail molt in Washington showed that molt tends to occur relatively quickly, and that young individuals are difficult to age by state of molt alone. Southern barred owls tend to be darker and slightly smaller than northerly ones. Rare captive and wild barred owls with albinism have been described and are pure white but tend to retain their brown eyes.

The barred owl is a large species. The adult measures anywhere from 40 to 63 cm (16 to 25 in) in length while the wingspan may range from 96 to 125 cm (38 to 49 in). The wing area (measured by square centimeter relative to the body mass) is quite intermediate among American owls, with the wing loading being lower than larger, but proportionately small-winged larger owls and even than some smaller owls. The barred has high wing-loading. Wing-loading is related to hunting technique, with higher wing-loading owls typically hunting from a perch, with only a brief flight necessary to obtain food, whilst lower wing-loading owls often hunt their prey from active flight. As is the case in most owls, the various wing feathers of barred owls are uncharacteristically soft and bear a comb-like shape, which in turn renders their flight functionally silent during their hunts. Like most birds of prey, the female is larger than the male barred owl, sometimes described as reverse sexual dimorphism (due to the fact that males average larger than females in most non-raptorial birds).
Among standard measurements, the wing chord of grown males varies from 303 to 340 mm (11.9 to 13.4 in), with an average from three sources of 326.2 mm (12.84 in), the tail may measure from 182 to 250 mm (7.2 to 9.8 in), with an average of 219.6 mm (8.65 in) and the culmen from the cere may measure from 22 to 27 mm (0.87 to 1.06 in), with an average of 24.3 mm (0.96 in). Meanwhile, for the female, the wing chord may range from 318 to 357 mm (12.5 to 14.1 in), averaging 335.8 mm (13.22 in), the tail from 204 to 257 mm (8.0 to 10.1 in), averaging 223.3 mm (8.79 in) and the culmen from the cere 20 to 30.7 mm (0.79 to 1.21 in), averaging 25.1 mm (0.99 in). Sexual dimorphism is particularly pronounced in barred owls by body mass as males within a population are sometimes a third lighter in weight. In the nominate subspecies (S. v. varia), average weights for males have been reported as 621.9 g (1.371 lb) (sample size 12), 632 g (1.393 lb) (sample size 20) and 681 g (1.501 lb) (sample size unknown) in three samples. The weight range for adult males is known to vary from 468 to 812 g (1.032 to 1.790 lb). The considerably larger female of the nominate subspecies has been reported to average 801 g (1.766 lb) (sample size 24), 872.6 g (1.924 lb) (sample size 14) and 909.5 g (2.005 lb) (sample size unknown). Altogether, fully-grown female barred owls may weigh from 610 to 1,150 g (1.34 to 2.54 lb).
Vocalization
The barred owl is a powerful vocalist, with an array of calls that are considered "spectacular, loud and emphatic". Calls probably carry well over 0.8 km (0.50 mi). Its usual call is a series of eight accented hoots ok-ok-ok-ok ok-ok-buhooh, or the "typical two-phrase hoot" with a downward pitch at the end. The most common mnemonic device for remembering the call is "Who cooks for you, who cooks for you all." Due to its best known call, the barred owl is sometimes colloquially referred to as Old Eight-Hooter. At 80% of study posts in Virginia, barred owls responded to playback of this call. A further call is the "ascending type" or the "legato" call, a series of variable notes ending in oo-aw or hoo-aah. At least two other variations on the legato/ascending call are known. 56% of studied owls in Virginia engaged in the ascending type call but 36% uttered only the closing notes. The isolated hoo-aah, sometimes called the "inspection call", was the most common song type in north Florida and the most likely to be heard during daylight. Several other calls, although some are not dissimilar variations on the main calls, are known. Some of these vary into cackles, hoots, caws and gurgles, at times described as "sudden demonic laughter", "cat-like screams" and "prolonged outbursts of cackling" and seem to be, among Strix species, an idiosyncrasy endemic to the barred owl.
Another call type is the "mumble", a grumbling, slurred and subtle err-ERR-err, also an up-and-down "twitter" call at a high pitch. When agitated, this species will make a buzzy, rasping hiss about three times in three seconds, repeating every 10–30 seconds, and will click its beak together forcefully. Females and juveniles beg with high scratching skreeechch notes. The voice of the two sexes is similar, but the female has a higher-pitched voice with longer terminal notes. Of calls, 87 to 94% are identifiable to sex per one study. While calls are most common at night, the birds do call during the day as well, especially when provoked by human playback or imitation. They are more responsive than any hawk in the east to playback of calls of their own species. The barred owl is noisy in most seasons but peak vocalization times for barred owls tend to be between late January (in Florida) and early April (in Canada). Two seasonal peaks in vocalizations, one right before breeding and another after the young have dispersed, was detected in Connecticut, with peak vocalizations on nights with extensive cloud cover. Peak times for vocalizations are between 6:00 pm and 6:00 am, with the least frequent vocalizations around mid-afternoon.
Distribution and habitat

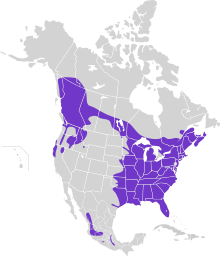
The barred owl is distributed throughout most of the eastern United States, as well as much of southern Canada. They are found as far northeast as much of Nova Scotia (western two-thirds), New Brunswick and Sept-Îles, in much of Quebec, up to Lake Mistassini, and Ontario, up to Moosonee. The barred owl has been recorded as ended up as far north as central Labrador, though the species is not yet confirmed to breed in the province. The barred owl ranges in every part of the eastern United States continuously from northernmost Maine down throughout New England, the Mid-Atlantic states, much of the Midwest, the Southeast United States and all of Florida. They are found to as far west without substantial gaps to the limits of western Minnesota, easternmost South Dakota, the southeastern corner of Nebraska, the eastern half roughly of Kansas, most of Oklahoma and east Texas to as far west as Cisco and Burnet. Arguably and discontinuously from Texas, the species may range into central and southern Mexico but these populations are now often considered a separate species. These initial parts of the range in the eastern and central stretches would be considered as where the species is "native". A wandering barred owl was once seen flying over Lake Michigan 48 km (30 mi) from the nearest land.
Range expansions

The remaining parts of the range are considered where the barred owl introduced itself in the last century or so. The historical lack of trees in the Great Plains presumably acted as a barrier to the range expansion, and recent increases in forests broke down this barrier. Increases in forest distribution along the Missouri River and its tributaries provided barred owls with sufficient foraging habitat, protection from the weather, and concealment from avian predators. This allowed barred owls to move westward, initially solely along other forested river corridors (e.g. the Yellowstone and Musselshell), but increases in forests in the northern Great Plains decades later would allow them to connect their eastern and western distributions across southern Canada. These increases in forests were caused by European-American settlers via wildfire suppression and ceasing the fires historically set by Native Americans, as well as by increased tree-planting.
In Canada, the barred owls with range expansion now range through southern Manitoba (excluding the southwest corner), a broad section of south-central Saskatchewan, and east-central and nearly all of western Alberta, now up to High Level. The barred owl has been present in Manitoba at least since 1886, Alberta since 1932 and Saskatchewan since 1948. However, a study in Alberta has shown that barred owls have likely been present for no less than 100 years. This owl species currently ranges through much of British Columbia, where they have been expanding their range since at least 1943, including Vancouver Island and as far north as Fort St. John. The barred owl has had a further northward expansion in the west to southeastern Alaska (Skagway to Ketchikan) and extreme southwestern Yukon. In the western United States they also range into northwestern Montana and northern Idaho. Barred owls were first verified in southwest Montana in 1909 and in northwest Montana in 1921 (although reports of the species may date back to the 1870s) but not in Idaho until 1968. Of unknown origin, barred owls have been seen in Colorado since around the turn of the 20th century. They range broadly in eastern and western Washington (reached by 1965) and western Oregon (reached by 1972) (mostly along the forested corridors hugging the montane areas of the Cascade, Olympic and Blue ranges), and northern California (reached by 1976), now down to the Redwood National Forest, the Sierra Nevada and outer San Francisco.
Habitat

The habitat used by barred owl is largely old deciduous, mixed forests and, occasionally, coniferous forests. Old growth forests are preferred due to more extensive potential nest sites, less lower-branch density to impede hunting (and perhaps superior structural complexity to aid hunting), greater security from mobbing and perhaps greater thermoregulation. They are often found in bottomland hardwood forests in the largest swath of the native breeding range, often (particularly from Virginia south and west) with deep, dark stands of oak, gum and cypress. Secondary habitat, often used during foraging forays in the south, are often oak savanna or cabbage-palm areas. Regardless of area, some variety of water is frequently present, including riparian areas or swampy ground. Closed canopy forests were preferred in a study from Oklahoma (62.8% of habitat used), followed by fallow agricultural fields (10.6%), wetlands (8.1%) and open terrain (6.2%). The latter three were visited during hunting forays, and wetlands and open terrain areas were not used outside of the breeding season. Along the Atlantic coast area from New England to New Jersey, barred owls are often found in mixed swamps areas with cedars, seldom wandering to adjacent wetlands or farmland. The species may be at home in wooded areas in mountainous regions. More upland wooded habitats, often in mixed woods containing hemlock, alder, poplar, pine and oak, are typical in the northern part of the range. A study in northern New Jersey found at least 15 species of both conifer and deciduous trees were routinely used for differing purposes. In Michigan, barred owl habitat usually consists largely of some combination of hemlock and maple trees, with mixed forest usage being use disproportionately to its prevalence in the environment. Large oak stands were preferred in Minnesota, a bit ahead of mixed forest and far ahead of white cedar swamps and other habitat types, which were either too dense, too open or had too few attractive nesting sites.
Barred owls are not confined to extensive forest, also dwelling extensively in semi-open wooded areas, locally in large parks with mature trees, and in forest adjacent regions recently logged. Recent studies show suburban neighborhoods can be ideal habitat for barred owls, and the species may be considered a local synanthrope. Using transmitters, scientists found that some regional populations, such as in Charlotte, North Carolina, increased faster in the suburban settings than in old growth forest. A factor of this suburban success may be easily accessible rodent prey in such settings. However, for breeding and roosting needs, this species needs at least some large trees and can be locally absent in some urban areas for this reason. The increased offspring offset the death rate due to impacts from cars, other types of collisions and disease. Similarly, in Piedmont, South Carolina, productivity of the owls was higher in suburban areas and they comprised 41% of the territories of the local owls but various sorts of anthropogenic mortality were seemingly higher. In suburban areas of Ohio, 41.4% of barred owl range was forested, 29.8% was low-density residential areas and less than 15% was pasture. On the other hand, studies from the Northeastern United States, such as in New Jersey, found barred owls breeding mainly in plots of old-growth woodlands, and rarely successfully breeding in peri-urban areas, in part because of competitive and predatory displacement by great horned owls. Furthermore, a study in North Carolina showed most barred owls appear to favor areas with at least 86 to 370 ha (210 to 910 acres) of woods but did not seem to be affected by the presence of roadways.
In the Pacific Northwest, they can be quite adaptive to secondary forests. On the other hand, in Ontario where the barred owl is native, secondary forest seemed to be largely avoided per a study. In the recent western part of the range, barred owls often dwell in mixed wood areas, often where there are lowland stands of balsam poplar, trembling aspen and white spruce, occasionally but not commonly in pure conifer boreal stands. Barred owls in California preferred stands of red alder. More so confined to inland areas, as in eastern Washington, Idaho, Manitoba and Montana, they prefer Douglas fir, ponderosa pine, paper birch, burr oak and western larch. In north-central Alberta, the use of old growth forest was far more prevalent than its occurrence in the wild. In the Cascades Range of Washington, barred owls usually dwell in areas with more grand firs, taller and more diverse tree heights, more enclosed canopies, higher numbers of trees per acre and less ground cover. In Saskatchewan, barred owls preferred areas with a minimum of 66% forest cover.
Behavior

The barred owl, like most owls, is largely adapted to nocturnality. Between 5:00 am and 8:00 pm, juvenile barred owls were recorded to sleep an average of 28% of each hour. Peak times in Minnesota were found to be right after sunset and just before dawn. Nonetheless, they are not as fully nocturnal as many owls and rank around 6th amongst 19 regular North American owl species for the regularity of their activity outside of nightfall, especially in particular circumstances such as when a rival or a human impersonator is emitting barred owls calls or whilst hunting. Often daytime activity tends to be early in the morning or around dusk but potentially at any time (overcast days being preferred). This species often spends the daytime hidden away in the dense foliage of a tree, often at minimum 5 m (16 ft) above the ground, but sometimes also roosts in a branch close to a broad trunk or in a natural tree hollow. Roost tree heights in Minnesota was typically 8 to 12 m (26 to 39 ft) while, in Illinois, they were up to 9 m (30 ft). Recently fledged owls sometimes roost in tall grass, usually after falling from the nest tree.
Roost site selection may be partially dictated by thermoregulation, as in spotted owls, with shadier roosts likely to mitigate heat stress. They seldom rely on camouflage, instead often flying at the least disturbance and not allowing close approaches, making them potentially difficult to observe. Yet, on the other hand, they can be surprisingly tame and seemingly curious of people in the wild; further they are considered "as mild and engaging" as a predator can be. Barred owls are regularly subject to mobbing by small birds, from several small passerines to corvids and woodpeckers, and mammals when discovered by them during the daytime, and such situations may lead to them being attacked by diurnal birds of prey. There are some records of barred owls engaging in allopreening, presumably between pairs, with each other in the wild. They are skilled and silent fliers and frequently use routine forest flyways with open understory and low branch densities.

Like most species of owl in the Strix genus, the barred owl tends to be highly territorial regardless of the time of year. The territories are claimed by singing from different perches, often near the perimeter of its perceived home range. The boundaries are almost always well-maintained by barred owls and are generally stable from year to year and even generation to generation. Territory sizes have been determined via radio telemetry. The average territory size of 13 in Minnesota was 273 ha (670 acres), of 7 in Michigan it was 282 ha (700 acres) and of 10 in Wisconsin was 337.9 ha (835 acres). Another Minnesota study found pairs to occupy a mean of about 226 ha (560 acres) in mixed hardwood-conifer woods. Pairs in an Oklahoma study were reportedly found every 110 to 165 ha (270 to 410 acres). The mean territory size from 10 studies was estimated from throughout the range. In this study, the breeding season mean area was calculated at 256.7 ha (634 acres) in males and 297.8 ha (736 acres) in females; whereas the means in nonbreeding season were 900.4 ha (2,225 acres) in males and 536.2 ha (1,325 acres) in females. Overall, the annual mean home range for males was 782 ha (1,930 acres) and for females was 538.7 ha (1,331 acres). The breeding range's mean home size in Washington was 321 ha (790 acres), while it was 971 ha (2,400 acres) in the non-breeding season.
The ranges of pairs overlaps in the breeding season, at 87–95% range overlap, but decreases down to 45% after hatching. In a Florida study of barred owls, territorial responses, including several duets, by a pair were found to be provoked by researchers playing calls of both "stranger" owls and recordings of owls that were neighbors to the pair being tested. The aggressive response even to known neighbors in this study is unusual. In tawny owls in a study from Italy, for instance, they responded mildly or not at all to the calls of neighboring tawny owls known to them but with great aggression to the calls of "stranger" owls. Due to its rather stolidly territorial nature, the barred owl is not normally a migratory species. Claims in the past of "rather impressive" flights in New England in the past were lacking in verifiable details. Of 158 banded recoveries in the northern part of the range, movements during winter were found to cover no further than 10 km (6.2 mi), while all those recovered in Saskatchewan and Alberta scarcely moved at all. There is little to no evidence of nomadic behavior as has been recorded in several other owls in the north.
Dietary biology

Barred owls are opportunistic predators of the woodlands. Like the tawny owl, the barred owl usually hunts from a perch. During hunting efforts, they glide briefly from perch to perch until prey is detected. The barred owl has incredibly large eyes that capture as much light as possible, allowing for better night vision. Attacks may be carried out merely 6 to 10 m (20 to 33 ft) away from the prey due to the effectiveness of the silencing wing feathers. The barred owl, especially compared to the predominantly arboreal prey of the spotted owl, usually prefers to target small animals that are terrestrial. However, barred owls will also flush and capture night-roosting birds, and capture bats on the wing as well. Daytime hunting has been reported several times, although peak hunting time is typically shortly after sunset. Although they usually hunt within woodlands, they also occasionally hunt in open terrain, more typical of the hunting areas of a bird like the long-eared owl. Cases of snow-plunging have been verified for barred owls, allowing them to capture prey like voles in subnivean zones that they use as hidden snow tunnels during winter, a hunting method once thought particular to great grey owls. While hunting squirrels in the Foothill Model Forest of Alberta, barred owls were seen to make several passes before succeeding. Hunting on the ground is usually done to obtain foods such as invertebrates or amphibians. These owls may wade into shallow water to capture fish and may do an unusual amount of aquatic foraging, as compared to any Strix species or North American owl.
Due to its relatively modest foot size, it does not usually take particularly large prey. However, owls in general have proportionately larger feet and more powerful grips than similarly sized diurnal raptors, while the physiology of the daytime raptors differs. While the mechanism of the killing feet overlap, owls kill mainly with constriction and sacrifice velocity with their physiology while diurnal raptors have higher velocity and kill mainly by trauma inflicted by their enlarged talons. A majority of prey of barred owls is eaten outright but, with large prey, the barred owl may eat the head first and then return to consume the remainder of the body. Cases of owls of any variety scavenging on carrion are generally rare, but at least three instances of carrion-feeding by barred owls have been observed, more recently eating deer and squirrel roadkills on a remote camera in North Carolina. The pellet of the barred owl averages about 3.5 cm (1.4 in) in diameter and 7.2 cm (2.8 in) in length.

The barred owl has been known to consume a diversity of animals from different taxonomic classes. Primarily, these owls live off of small mammals. Other vertebrates are rarely neglected though, especially birds and amphibians, but also occasionally reptiles and fish. For an owl its size, the barred owl also consumes a large amount of arthropods and other invertebrates. One study from a wide swath of the range found that among 2234 accrued prey items, 76% were mammals, 15.8% were invertebrates, 5.8% were birds and 2.5% were other vertebrates. In four other studies from different parts of the distribution, the mean balance of mammals in diet was around 64.9%, birds at around 13.4%, invertebrates at around 11.4% and different classes of vertebrates (mostly amphibians) at around 10.3%. A compilation study that included a total of 7077 prey items using all methodologies, 71.9% were mammals, 9.5% were birds, 0.6% reptiles, 6% amphibians, 1.89% fish, 1% earthworms, 0.2% gastropods, 6.5% insects and 2.4% crayfish. Barred owls tend to focus on fairly small-sized prey, although are capable of attacking larger than usual prey in infrequent cases. The mean size of prey taken is seldom estimated in the barred owls' eastern range, although one study estimated mean size of prey in the general east was 33.5 g (1.18 oz). Many more studies have estimated mean prey masses in westerly areas of sympatry with spotted owls to understand how their diets may conflict. Different studies from the west (mainly Washington and Oregon) have variously estimated the mean prey sizes for barred owls at 47.7 g (1.68 oz), 56.1 g (1.98 oz), 60.2 g (2.12 oz), 103.5 g (3.65 oz) and 123.6 g (4.36 oz).
Mammals
The predominant small mammals available in forest and woodland edges are generally small rodents, so the barred owl, like other Strix owls, most often relies on rodents as the primary type of food. Preferred rodents to be taken are voles, mice of the genus Peromyscus and assorted rats, including non-native Rattus species as well as unrelated native types like cotton rats, rice rats and woodrats. These all share with barred owls a penchant for nocturnality and crepuscular habits (although many voles are more correctly considered cathemeral) While during other seasons, the diet of barred owls can be fairly diverse, the winter diet may be almost wholly rodents. This was the case in winter in Montana, where 97.6% of 1153 prey items were montane voles or meadow voles, with a possible slight mixture of other voles. The diet of barred owls in a much smaller study near Urbana, Illinois during winter was less homogeneous but still led by rodents, especially the meadow vole (32.3%) and white-footed mouse (23.5%). A winter food study in Essex County, New Jersey found that among 118 prey items, meadow voles comprised a great majority of the prey, at 91.5% of the balance.
An unusual lack of diversity in barred owl pellets was found in several years of possibly an aseasonal study in Ann Arbor, Michigan where of 777 prey items, 83.3% were meadow voles. At Edwin S. George Preserve near the University of Michigan, the summer diet was also heavily rodent based, as among 146 prey items 37.9% were white-footed mice, 22.6% were southern bog lemming and 6.84% were meadow voles. In a somewhat larger Michigan study, the North American deermouse, lead the prey at 34.9% of 321 prey items. In Minnesota, the barred owl was counted as one of the leading causes of mortality of prairie voles. Studies of the barred owl diet in 6 urban metropolitan areas of British Columbia found that the diet was dominated by young rats of the invasive Rattus genus, comprising 52.8% of 688 prey items, well ahead of native Townsend's voles, which were secondary at 19.2% of the diet. The average weight rats taken by owls were clearly juveniles, estimated to average 103 g (3.6 oz), although several could be anywhere from infant rat to adult rat sizes, i.e. about 25 to 300 g (0.88 to 10.58 oz). The mean size of black rats taken in Oregon was 250 g (8.8 oz), indicating that here large adults of this species were selected. Beyond the typical more meadow-dwelling voles and woodland edge-dwelling native mice, larger and more forest dwelling rodents of different varieties can be of variable import. Numerous woodrat species may be taken and may provide a hearty meal to a barred owl, at a mean body mass when taken (in Oregon) of 285 g (10.1 oz) for unidentified species.
In different areas, barred owls may regularly hunt the diverse members of the squirrel family, despite their general penchant for diurnality. Smaller squirrel varieties are usually focused on when hunted as supplement prey, such as chipmunks, averaging about 83 g (2.9 oz) among the different species they prey upon, and pine squirrels, which average about twice as large as chipmunks. Usually juvenile specimens are focused on when taking the larger Sciurus tree squirrels, at least in summer, but presumably a mixture of yearling and adult Sciurus will be taken during winter. The mean weight of western gray squirrels taken during the breeding season in Oregon was 450 g (16 oz), against a mean adult weight of around 770 g (1.70 lb). The issue of temporal activities is less pertinent to the predator of flying squirrels, which are nocturnal. All studies of the diet of barred owls in Pacific Northwest show the importance of the northern flying squirrel to their diet. This flying squirrel was found to comprise from about 10.9% to 20% of the diet of barred owls (either as the most or second most important prey species) and, with a mean weight of 134 g (4.7 oz) when taken, they comprised up to 25.6% of the food biomass for this owl species. In Green Ridge State Forest in Maryland, although not numerically the most important prey family compared to unidentified cricetids and shrews, the southern flying squirrel was the most often identified prey species for barred owls. Beyond the aforementioned rodent prey, more infrequently rodent prey can including various other cricetid rodents, pocket gophers, mountain beavers (average weight when taken of up to 550 g (1.21 lb)) and jumping mice. The largest known rodent prey of barred owls are adult muskrat, which were estimated to weigh 1,169 g (2.577 lb) when taken.
The other primary mammalian prey types are the shrews and the moles. At least a dozen species of shrew and most North American species of mole are known as prey of the barred owl. 12.8% of 7077 total prey items from across the range were shrews or moles. A small sample of prey in Michigan was led by the very small masked shrew, which weighs around 4 g (0.14 oz), at 24% of 34 prey items. A much larger shrew, the northern short-tailed shrew at around 21 g (0.74 oz), was the leading prey in Glenwood, Minnesota at 36% of 81 prey items. This prey species also is taken quite regularly in several other parts of the range, as well as a closely-related species. Assorted other shrew species and the smallest of the world's moles, the American shrew mole are regular supplement prey elsewhere, especially in the Pacific Northwest. The most frequently taken single prey species through the Pacific Northwest, at 11.8% of 4299 total prey items of barred owls, was the 56 g (2.0 oz) coast mole. Usually, moles are secondary if relatively hearty prey elsewhere in the range.
Secondary prey can include several species of cottontail rabbits (Sylvilagus sp.) and snowshoe hares (Lepus americanus). 3.2% of 7077 prey items from across the range for barred owls were rabbits or hares. Among cottontails, small juveniles are largely taken, but rabbits as large as an adult brush rabbits can be taken. The weights of snowshoe hares taken by barred owls in the Pacific Northwest were estimated at ranging from 50 g (0.11 lb) leverets to juveniles and standard-sized adults about 1,200 to 1,400 g (2.6 to 3.1 lb).
Bats are infrequently reported as prey in most of the range but an unusually close association was detected in Valdosta, Georgia, where most of the prey, 65% of pellet contents and 37 total bats, were southeastern myotis (Myotis austroriparius). Barred owls are also known predators of small mammalian carnivorans, mainly mustelids such as stoats (Mustela erminea) and long-tailed weasels (Neogale frenata). Predation on small American mink (Neogale vison) have also been reported. As they are seemingly not affected by strong odor, eastern spotted and western spotted skunks (Spilogale gracilis & S. putorius) of all ages can be taken. Much larger mammals are sometimes recorded in the foods of barred owls, but there are few details known about the age, condition, or circumstances (i.e. they may have been consumed as carrion or, perhaps more likely, young or infirm specimens were taken). Some such prey species recorded have included the Virginia opossum, the North American porcupine, the striped skunk and the domestic cat. Adults of all these species are known to count amongst the prey of great horned owls which are better suited than barred owls to take particularly large prey given its more robust morphology.
Birds

Throughout the barred owl's range, other birds are taken as prey, although avian species make up a much smaller proportion of their diets than mammals. The maximum known representation of bird prey in a barred owl food study was 25.1% in Alberta, meaning that they augment their diet less heavily with bird prey than their near equivalent in Europe, the tawny owl. No specific variety of bird is subject to the most frequent predation by barred owls and birds are the most diverse class in these owl's prey spectrum, with more than 100 species of bird known to be hunted. Conspicuous nesting sites of barn swallow and purple martin on manmade structures and objects were revealed via video-monitoring to suffer heavy predation by barred owls. In the case of the barn swallows, all ages of swallow as well as possibly eggs were eaten. 65 of 95 monitoring barn swallow nests were consumed by owls over a 3-year period. The muddy bank nests of cliff swallows are also vulnerable to barred owls, while other swallow species are known to be opportunistically taken.
In more enclosed wooded areas, radio-tagging and video-monitoring of various passerines nests as well as examinations of owl pellets has shed light on the relationship of barred owls with these potential prey resources. Not only was the barred owl found to be a surprisingly routine predator at woodland passerine nests, but that an unexpected bulk of the acts of predation in studies from Missouri and Illinois were carried out during the daytime. Many different forest bird species (most frequently acadian flycatchers and indigo buntings in Missouri and Illinois) were hunted. These studies indicated that the barred owl may snatch passerines of any age, but recent fledglings are taken preferentially due to their more conspicuous behavior and limited ability to fly away. In Minnesota, about 62% of studied hermit thrush and ovenbird fledglings were taken per one study, with all thrush that nested in the 50 m (160 ft) radius of the barred owl's nests failing to produce any young. A similarly high rate of local determent by barred owls has been found for other woodland thrushes like the veery, wood thrush and varied thrush, with the additional finding that pre-dawn singing by certain thrushes, when their escape abilities are dulled by the dim light, leaves them vulnerable to barred owl ambushes. Forest birds seem to recognize the barred owl as a threat, with mobbing behavior evoked easily by playing recordings of their calls in the daytime.

A wide diversity of bird prey may be occasionally hunted by barred owls in different circumstances. Smaller or mid-sized bird prey species known have including different species, though usually a relatively low species diversity and in low numbers, beyond swallows and thrushes of tyrant flycatchers, vireos, chickadees, wrens, mimids, tanagers, other cardinalids and finches. Somewhat higher diversity of species are known from the sparrow and warbler families. Birds down to the size of the calliope hummingbird, North America's smallest hummingbird at 2.7 g (0.095 oz), may be taken by barred owls. At the opposite end of passerine prey for barred owls, this species will sometimes take all ages of the American crow, from very young nestlings to adults. Numerous non-passerine birds are also taken, though seldom in great numbers and of low known species diversity. One exceptional family is the woodpeckers, which are probably so widely taken because of their generally overlapping habitat preferences with those of barred owls. Several species of woodpecker are preyed upon almost throughout the range, including at least a half dozen in Oregon alone, from the smallest North American species, the downy woodpecker, to the largest, the pileated woodpecker. Other small-to-medium-sized bird species known as prey for barred owls are: mountain quail, grey partridge, rock dove, band-tailed pigeon, mourning dove, purple gallinule, killdeer, American woodcock, least tern, snowy egret, cattle egret and belted kingfisher. Although they take many chicks of gamebirds, adults of these species are vulnerable as well. In many areas, ruffed grouse are not infrequently taken, comprising up to nearly 6% of prey items in Alberta. In Oregon, the weights estimated for ruffed grouse taken by barred owls varied enormously, from small chicks estimated at 25 g (0.88 oz), to adults weighing about 576 g (1.270 lb). Broader study in the Pacific Northwest indicated that adult ruffed grouse were mainly taken. Barred owls are also known to take adult spruce grouse of about the same size as the ruffed grouse, as well as much larger species including the common pheasant and the sooty grouse, the latter estimated to average 1,050 g (2.31 lb) when taken. Barred owls are also known to prey on the young of other, larger birds, such as the American white ibis and wild turkey.
Other prey
Barred owl predation on reptiles is widely reported but they seldom take large numbers in any given area. Most reported instances of such captures are of various small lizards, often of skinks in the genus Plestiodon, most often from the Midwest to the western parts of the range. Several reported instances of barred owls hunting snakes are also known, but they are perhaps even more seldom preyed upon than lizards. More than a half dozen snake species are known to be captured, several of which are colubrids, which are mostly harmless. The estimated body mass of black racer taken in Oregon was only 77 g (2.7 oz), well under their mean mature size. However, consumption or predation on dangerous pit vipers, such as timber rattlesnakes and copperheads, by barred owls has been reported, although it is not known whether these are taken as adults. Rarer still is barred owl predation on turtles. Predation by this species was reported upon a very young river cooter, which had a carapace width of only 31.4 mm (1.24 in), as well as on juvenile gopher tortoise and apparently diamondback terrapin. Much more characteristic than any reptilian prey are amphibians, with various types of frogs, salamanders and similar species reported in this owl's foods. Amphibians were considerably more popular in the diet in western part of range, comprising 10.5% of known studies against 4.4% in the east. In total, well over 20 amphibian species have been identified in the foods of barred owls and amphibians collectively can make up to 24.5% of the local diet (as was reported in Alberta). While salamanders and newts are probably often visually discerned while scanning the forest floor, many frogs are probably hunted down by sound during their crepuscular choruses.
Amphibians are taken almost entirely during the breeding season, as they become unavailable to barred owls during the winter months. Most reported amphibian prey in Oregon were unidentified "medium-sized salamanders". A diversity of frog sizes may be taken, varying potentially in size from spring peepers, which average around 4 g (0.14 oz), to American bullfrogs, which average around in mature bullfrogs 430 g (15 oz). A notable act of successful predation was carried out by a barred owl on a rough-skinned newt, which contains toxins that are often deadly to predators. Apparently, the owl was able to survive after consuming the newt. The rarest variety of vertebrate prey for barred owls is fish. However, there are several accrued accounts of fishing by these owls, including older accounts of barred owls coming to ice holes made by human fishermen and more recent accounts of possibly routine fishing by the owls on the St. Johns River in Florida, in the latter case utilizing a fishing dock as a hunting perch. At least five species of fish have been identified in the foods of barred owls, including fairly large fish like brown bullheads and largemouth bass.

The balance of assorted invertebrates in the diet of barred owls can be quite high. Although many of those found in pellets are unidentified to species, nearly 40 species of invertebrates have been found in their foods. Broad studies indicate arthropods (including millipedes and spiders but predominantly insects) in general comprise up to about 16% of the barred owl's foods. When hunting insects, barred owls most often prefer ground-based beetles. In Oregon, 11.7% of the diet was assorted beetles (14 species were identified), being somewhat more numerous among 3686 prey items than other non-rodent prey orders. However, some insects prey such as luna moth, eastern tiger swallowtail and green darner are presumably hawked on the wing around dawn and dusk. It is known that barred owls will sometimes come hunt near manmade light sources and campfires, flying out from the perch to quickly capture flying insects that were attracted to them. Of 123 prey items found in southern Manitoba, flying Sphinx moths and flightless scarab beetles each comprised 7% (most of the remaining balance being unidentified mammals and birds). Crayfish of at least four identified species are another widely taken type of invertebrate, presumably snatched up by barred owls from shallow waterways. Crayfish seem to be exclusively taken in the east and Midwest, areas where they comprised 3.4% of all known food studies, and none at all were recorded in the western part of the range. In Missouri, annually up to 31.1% (though, in some years, 0%) of the diet was comprised by crayfish. Barred owls occasionally feed on snails and slugs, the latter especially in the Pacific Northwest. Another snail, the Pacific sideband, was surprisingly often present in the foods in Oregon as at least 135 were taken. Beyond slugs, other "soft" invertebrates are sometimes hunted, especially earthworms. Earthworms were most prominent in the foods of barred owls in Nova Scotia, where 27.6% of 186 video-monitored prey deliveries in Nova Scotia were worms, the most regularly delivered of all prey types there.
Interspecies predatory relationships
The barred owl's range overlaps with multiple other predators of similar prey species. Due to the time period barred owls are active, the most interaction occurs with other owl species. Of the owls in North America, about three-quarters are reliant on similar small mammal prey, usually rodents, with a mixture of other prey genera as supplements. Other than its ecology where it today co-exists with spotted owls, however, there is some level of niche differentiation from a majority of sympatric owls. In the eastern forest biome, the barred owl is the only large owl species to dwell mainly in continuous forest areas. While many of the owls sympatric with barred owls over majority of their eastern and Midwestern range share a preference for hole-nesting, smaller hole-nesting owls usually prefer different habitats, such as the open country-dwelling barn owl and the screech owls, which usually in North America dwell at the interface of forest and open habitats. Both North American species in the Aegolius owl genus are forest-dwelling cavity nesters but are much smaller and are at entirely different trophic levels.
A singular diurnal raptor species that mirrors the barred owl at nearly all ecological levels is the red-shouldered hawk. Both species have similar distributions, habitat preferences and somewhat similar dietary habits and trophic level. They may considered as nearly nocturnal and diurnal ecological equivalents. In multiple parts of the range, including southwestern Ohio, North Carolina and northern Michigan, the paralleling habitat usage and nesting behavior of the barred owl and red-shouldered hawk has been noted. One of the few respects in which their habitat usage differs is that the barred owl is more adaptive to nesting in suburban areas if they have old growth trees that provide plentiful tree hollows. In contrast, red-shouldered hawks tend to avoid suburban areas whilst nesting, but may acclimate to these areas during the winter. Barred owls seldom alter their range throughout the year and remain more or less constrained to the stands they used during nesting. The red-shouldered hawk averages somewhat smaller and has a more limited diet than barred owls, but probably goes after dangerous prey such as snakes more regularly. Multiple occasions are recorded where the barred owl and red-shouldered hawk have nested in the same area, often within the same grove of trees, remarkably with little to no conflict. At least one nest was found including eggs from both species. When nesting near other hawks like red-tailed hawks and Cooper's hawks, the relationship tends to be much more contentious between hawk and owl, despite barred owls sometimes sharing space or using the old nests of these hawks. A wing-clapping display by a pair of barred owls was recorded during antagonistic encounters in Manitoba with a pair of broad-winged hawks. Wing-claps were previously not recorded in this species, and when recorded for other owl species were often for the purposes of courtship displays.

One predator that is a major source of conflict for the barred owl is the great horned owl. In every part of their range, barred owls are compelled to share space with the larger owls. There is habitat partitioning between the barred owl and great horned owl that allows them to often co-exist. Great horned owls prefer various more open habitats mixed with trees, often in rather upland areas, which differs from the habitats preferred by the barred owl. If a great horned owl moves into an area, barred owls appear to avoid said areas, based on radio telemetry data. In much of the east, habitat alteration and fragmentation tends to favor the great horned owl at the expense of the barred owl. Where more continuous forest is available, however, the great horned and barred owl can occur surprisingly close to one another. In one case, a barred owl was observed to roost only 400 m (1,300 ft) from a great horned owl. In general the reforestation at the northern sections of the Great Plains have, on the contrary, benefited barred owls (and may have been a part of allowing their westward expansion) and been perhaps slightly detrimental to the great horned owl. However, even where the habitat becomes less ideal, the great horned owl is unlikely to vacate an area, unlike the barred owl which can be entirely displaced if woods become too small and fragmented. Great horned owls and barred owls have similar diets, as both are wide-ranging, large and opportunistic owls. However, the great horned owl is larger in bulk, sometimes averaging nearly twice as heavy, with much heavier, larger feet and talons. The great horned owl has a more powerful grip strength and access to a wider variety of prey than barred owls, which take fewer prey species because they occur in more limited habitats and have a smaller overall distribution. A study utilizing stable isotopes in Alberta appeared to confirm that the great horned owl preys on nearly twice as many prey species as do the barred owls of the area.
The great horned owl is indeed likely to be the greatest natural enemy of the barred owl. There are several accounts of the horned owl species preying on nestlings, fledglings and adults of the barred. Other than horned owls, predation of the barred owl seems to be fairly rare outside of the nestling age, both due to the owl's relatively large size and their nesting habits, most often in secluded tree hollows. One more virulent nest predator is likely to be raccoons (Procyon lotor), which can nearly decimate both tree hollow and stick nest locations of almost any kind of bird, especially in peri-urban areas where they largely exist without controlling predators. Both the American marten and the fisher are known to be nest predators of barred owls, in turn appearing to cause the owls to switch nest sites. Other birds of prey may be an occasional threat to barred owls. Northern goshawks have reportedly killed both young and adult barred owls. One modern account mentions predation by a goshawk on a nestling barred owl (i.e. weight about 392 g (13.8 oz)). A well-known instance of a goshawk attack on an adult barred owl concluded with the owl and goshawk killing one another. There are some very rare, singular cases of predation on barred owls (age unknown) by red-tailed hawks, which nonetheless generally appears to be a less menacing co-inhabitant than the goshawk. More surprisingly, a Cooper's hawk, a smaller species of raptor, was observed to apparently prey upon a full-grown barred owl in British Columbia. An American alligator was reported to have preyed on a barred owl in at least one instance.
On the other hand, the barred owl is a significant predator of smaller raptor species as well. Most smaller owls that co-exist with barred owls are at occasional risk of predation. A particular cause of concern in intraguild predations by the barred has been their encroachment into the areas inhabited by western screech owl (Megascops kennicotti). Several instances of predation have been noted on the screech owls and the recent, unprecedented presence of the barred owls appears to have a correlation with the decline of the western screech owl in British Columbia and in Bainbridge Island, Washington. In one instance, a biologist who called in an eastern screech owl (Megascops asio) in Ohio observed it to be immediately captured and consumed by a barred owl. The barred owl is a serious predator of eastern screech owls, but is less deadly to them in general than the great horned owl. Various additional owl species known to be preyed upon by barred owls including the flammulated owl (Psiloscops flammeolus), northern pygmy owl (Glaucidium gnoma), northern saw-whet owl (Aegolius acadius) and long-eared owl (Asio otus). The interspecific owl trophic chain was perhaps most conspicuous in a case where a barred owl that was shot in New England was found to have a long-eared owl inside its stomach which in turn had an eastern screech-owl in its own stomach. More unexpectedly, barred owls may even prey on other Strix species. As many as four records of circumstantial but likely predation by barred owls on spotted owls have been reported. A likely event of predation by a barred owl on an adult great grey owl was observed. The authors hypothesized that the victim may have been a smaller male great grey owl (which can be about the same body mass as a large female barred) but this is the only known instance to date of a great gray owl being killed by another species of Strix owl. Barred owls have been known to take adults (or full-grown juveniles) of diurnal raptors as well, including snail kites, Cooper's hawks, sharp-shinned hawks and possibly swallow-tailed kites.
Reproduction

The barred owl's preferred nest site is usually the hollow trunk of a large tree or the broken-off snag from a large tree branch. Hollows or snags may be made by any variety of sources, often due to a disease or storm, with hollows and snags large enough to accommodate these birds usually only occurring in an old-growth tree. Typically, nest sites are in rather deep and dark wooded areas, often with a well-developed understory but somewhat sparse lower branches, and may be fairly close to water. Average nest heights are between 6.8 and 13.4 m (22 and 44 ft) above the ground. In 25 studies from throughout the range, mean nest tree height was 18.2 m (60 ft) (lowest mean from Florida where it was 5.9 m (19 ft); the highest from Oregon where it was 28 m (92 ft)), mean nest tree diameter was 65.7 cm (25.9 in) (thinnest mean in Saskatchewan at 47.4 cm (18.7 in); thickest in Washington at 106 cm (42 in)), while the mean height of the tree cavity used from these studies was 9.8 m (32 ft).
A big beech with a rotting core, encompassing a large cavity reached through a deep crevice, is an ideal nest site. The most widely reported nesting trees in breeding cards were elms (21%) and beeches (15%), followed by oaks, hickories, yellow birches, sycamores, aspens, maples and poplars. In Washington, the most often used nest trees were balsam poplar, Douglas fir and grand fir. Balsam poplar comprised 62% of known nest sites in Manitoba as well. It was found in Maryland that snags used were significantly higher than the average height of miscellaneous snags available in environment. The mean size of tree holes the owls used in Maryland was 33 cm (13 in) in inside diameter and 54 cm (21 in) in depth. These were slightly larger than the average from Michigan, which hollow used averaged 25 cm (9.8 in) in mean diameter and 35 cm (14 in) in mean depth. Record depth tree cavities used by barred owls was around 2.4 m (7.9 ft) deep from the opening on the tree. One study of cavity nesting birds in Ontario found that the barred owl preferred to nest in the most massive trees of any cavity-nester in the study area. In continuous bottomland forest, nests are often about every 226 ha (560 acres). Territory lines often remain the same even after the original owls are replaced entirely by a new pair. It was thought in Nova Scotia that some pairs may prospect a potential nest site as much as year before they use it. Despite usually using sickly or dying trees, some nests have found in partially hollow but still living oaks.

Usually in areas with few or no natural tree hollows, often within younger secondary forests or overharvested areas, this species will uses other birds' nests and occasionally also the dreys of squirrels. Evidence shows that the preference of barred owls for hollows and snags over bird nests is due to their earlier nest type having a more secure microclimate with better shelter (additionally, owl nests in hollows generally tend to be somewhat less vulnerable to predation than those of owls using old bird nests). Nest built by other birds that are most widely used are probably red-shouldered hawk and Cooper's hawks, while those of red-tailed hawks, usually being in more open areas, are used secondarily outside of a local basis. In the south, nests have been found between fronds of palmetto palm leaves, in holes of broken palm stems and rotten snags of the palms. One unconventional nest was on the ground at the base of a lookout tower in Everglades National Park. Another was on the roof of a shed in Saskatchewan. Yet another was in an earthen bank in Texas. Locally, barred owls can take to nest boxes but, in general, barred owls take to these less readily than their cousin Strix owls in Europe. Suitable nesting hollows may be used quite often in subsequent years, with records of a single hollow seeing up to 25 years of barred owl use (presumably not by the same owls however). Other long-used nests were one reused in New England for 10 years by the same pair until it rotted out and while a nest box in Nova Scotia was reused 10 times over 16 years. Over 6 years in Minnesota, 14 nest boxes were reused; 7 were used once, 6 were twice and one was used three times. Like all owls, barred owls never construct their owl nest but they may press or dig slightly if soil is present or remove the top leaves from a squirrel drey.
In normal circumstances, barred owls tend to pair bond for life. Courting pairs are usually newly mature birds but also possibly widowed owls or those re-establishing existing pair bonds after the winter. During courtship, barred owl males especially may engage in nodding, bowing with half-spread wings and may wobble and twist their head from side to side. Courting pairs will often engage in duets. Copulation between pairs usually occurs in late winter, February to March, and occurs several times, probably to ensure implantation. The female enters a pre-breeding lethargy stage wherein she is fed by the male. In barred owls, egg laying occurs at two to three day intervals. Egg laying typically begins in March and runs throughout April. In more tropical locales like Florida, egg laying may occur as early as late December, though 22 were laid in between early January and early March. At similar latitudes in Texas, 22 first eggs were laid between as early as mid-February to as late as early June (although the latter may have been a replacement clutch). 23 clutches in Iowa and Illinois were initiated in between late February and late April, with roughly corresponding initial egg dates in New Jersey and probably western Maryland as well. 63 initial eggs in New England were laid between mid-March and mid-May. Further north, 38 clutches in Nova Scotia were initiated in between late March and late May, with initial clutches dates about a week later in Ontario. Normally the female lays 2 to 3 eggs, although as many as 5 is possible, directly on the base of the nest site. The mean clutch size in three broad samples from several parts of the range was between 2.22 and 2.46. In Minnesota, the mean clutch size was 2.68. The eggs are pure white, slightly rough and not glossy, and oval in shape. In 157 eggs, the length of the egg could measure from 42.5 to 55.5 mm (1.67 to 2.19 in) while the diameter could range from 37.5 to 45.3 mm (1.48 to 1.78 in), with a mean of 50.6 mm × 43.3 mm (1.99 in × 1.70 in). 25 eggs in Nova Scotia averaged slightly smaller, at 49 mm × 41 mm (1.9 in × 1.6 in). The mean weight of the egg is around 45.5 g (1.60 oz). The female alone incubates, doing so for about 28 days, while the male gathers food for her.
The female tends to closely brood the young for three weeks. Then after, she begins to hunt for the young. Both parents normally continue hunt for the young until they are about 6 weeks old and can fly well. During the first three weeks, the male does all prey deliveries, either bringing prey directly into the nest or leaves for the female at the nest entrance or on a nearby branch. The mean number of prey deliveries when the young are 6–10 days old is 2.4 per night, 1.4 when they are 11–15 days old, 3.6 when they are 16–20 days old and 2.2 when they are 21–25 days old. He will continue hunting until the young disperse. The female's prey deliveries are much more frequent when she resumes hunting, ranging from a mean of 4.8 to 8 deliveries nightly. Male prey deliveries are often sporadically at any point through the night while female deliveries tend to be clustered immediately after sunset or just before sunrise. Barred owls have a variable reaction to human disturbance. Some parent owls remain sitting, while some leave the nest upon a person's approach and some attack people climbing to the nest, as well as those approaching young on or near the ground. There are several accounts of barred owls engaging in fierce nest defense against humans, sometimes reportedly knocking people out of trees. However, their aggression is variable and, based on studies of similar owls like tawny and Ural owls from Europe, attacks tend to only occur when intrusions and disturbance by humans are frequent. A distraction display was recorded by a female barred owl when humans approached. In it, she spread and quivered her wings and engaged in chittering and squealing, somewhat similar to the sounds made by begging young.

The average hatchling weighs about 46 g (1.6 oz). Like most birds, the young are initially altricial. The white down feathers that the barred owls are hatched with is replaced by white-tipped barred-buff second down at two to three weeks of age, correspondingly with growth of the wing primaries. The earlier chicks are bigger and stronger, while the latter ones may not survive if food is scarce. Size differences between barred owl nestlings may be less pronounced if the female does not begin incubation until the laying of the second egg. The larger young may fight with the younger siblings for food. The young barred owls first start moving about the nest at around this 3 week point and may start to perform threat displays if scared. Adult-like feathers begin to appear at six weeks of age, starting at the scapulars, then radiating down across the abdomen and flanks up through the upper breast, with the last wisps of down remaining for up to 4 months. The young often start exploring around the nest tree, often falling to ground, which makes them quite vulnerable to predation despite the parents' continued protection. However, the fledglings can usually clamber back up the tree using their feet and bills, constantly wing-flapping.
Fledging occurs at about 36–39 days. After that, both parents continue to hunt for the young but prey deliveries taper off as the young begin to make their first flights and practice hunting. Short flights are typical when the young barred owls are up to around 10 weeks old with longer flights commencing at about 14 weeks. By the time they are flying and hunting somewhat assuredly in early to mid-autumn, the young move away and gain independence. Dispersal of 5 young from Nova Scotia was 0.8 to 64 km (0.50 to 39.77 mi) away from their nests of origin. Furthermore, a recovered 6 month old was 8 km (5.0 mi) away from its nest of origin, while five encountered as adults were found at a distance of 16 and 43 km (9.9 and 26.7 mi) from the nests where they hatched. An exceptional dispersal distance from Nova Scotia was 1,600 km (990 mi) away to Stoney Creek, Ontario. The post-dispersal stage is one of great mortality among young owls. Usually juvenile owls are considered "floaters", often hovering around the perimeter of fiercely defended territories for some time. In some areas, floaters may make use of nest boxes more readily than mature birds. Yearlings have been known to breed only very rarely, otherwise barred owl usually first breed when they are around two (sometimes three) years old. Therefore, around two years old is considered the age of maturity. The percentages of successful nests (i.e. at least 1 fledgling produced per attempt), per study were found to be: 86% of 22 clutches in Minnesota (with a mean of 2.42 fledglings per successful attempt), 66% of 114 clutches in Michigan (with a mean of 1.97 fledglings per successful attempt), 25% of 6 clutches in Maryland (with a mean of 1 fledgling per all attempts and 1.48 per successful attempts), 69% of 48 clutches in Nova Scotia (with a mean of 0.25 fledgling per all attempts and 2 per successful attempts) and 50% of 12 nests in Washington state. Little is known about the specific factors that dictate breeding success, but are likely to include the quality of the nesting site, the food supply in the area, the levels of disturbance from outside actors (usually humans) and the maturity of the pair.
Longevity and parasitism
The barred owl is a naturally long-living bird. Some record lifespans recorded per banding studies in the wild are 18 years 2 months (initial banding Kentucky, died in Ohio) and 24 years and 1 month in Minnesota. There are several records of breeding barred owls nesting successfully for a decade or more. The record lifespan for a barred owl in captivity, where many animals can live longer without the stresses of surviving in wild conditions, was 34 years and 1 month, with six records of captive barred owls living over 30 years. Known causes of mortality are diverse, some due to predation (largely great horned owls, for nestlings to adults, and probably raccoons, for eggs, nestlings and fledglings). Some mortality is known to occur during hunting accidents. There are cases of barred owls being inadvertently killed in furbearer traps. Sometimes deaths occurs due to the defenses of prey. One barred owl was killed by the bite of an unknown rodent that was likely defending itself. Some cases of cannibalism between adult barred owls have been reported as well. This species, like other forest owls, is vulnerable to the respiratory disease aspergillosis. Spontaneous infections of West Nile fever are also known to kill wild barred owls. Barred owls were the most regularly infected with West Nile Virus of owl species in Georgia, as about 15% of studied barred tested positive (still at a lower rate than some hawks). Cases of Avipoxvirus are also known in barred owls but, as with West Nile virus, the rate of mortality to viral infection is not well-known. A case of follicular thyroid cancer was found in a wild barred owl that was unable to continue to fly. Fatty liver diseases have been recorded for barred owls in captivity. Eye lesions are fairly common in barred owls, but can be survived and possibly surgically corrected.

Parasitism is frequent in barred owls as expected for many different kinds of wild birds. The parasite load of helminths was determined to be higher in larger owls in Florida like the barred and great horned owl and lower in smaller owl species, like eastern screech owl. While parasitic infestations are not typically detected as direct mortality causes, in some severe cases complications or direct death can occur. These cases of mortality are most widely recorded in cases of toxoplasmosis, although generally owls have lower rates of dangerous Toxoplasma parasites than some other species of birds of prey. Of barred owls in one study, 26.7% had Toxoplasma gondii, the cause of toxoplasmosis, upon necropsy study, with adults having it more often than immature birds. Lethal cases of trichomoniasis are also known. The effect of other parasites are more poorly known beyond generally compromising their hosts' condition, but in one case Sarcocystis strixi may have caused paralysis in a barred owl. Other parasites recorded in barred owls include Eimeria varia, Novyella, Neodiplostomum as well as apparently rare species of Centrorhynchus and Tetrameres that were first found within barred owls. Trematode flatworms such as strigeids as well as Tylodelphys and Brachylaima are found in intermediate volume in barred owls relative to other owls. Invertebrates such as hippoboscid flies and Mallophaga are known to infect barred owls as ectoparasites but seldom at severe levels. Concern was expressed that barred owls may compromise spotted owl populations with novel parasites. However, studies of Haemoproteus in barred and spotted owls in northwestern California found that native parasites were finding a new host in barred owls and may have been transmitted from spotted to barred owls but that the barred owl acted as a poor parasite host and may have diluted the parasite levels in owl populations. Furthermore, there was no evidence found that barred owls were spreading parasites to spotted owls.
Status

The barred owl is one of the most common owls in North America. Partners in Flight estimates that the barred owl may number up to 3 million individuals globally, making it, perhaps, the second most numerous North American owl behind the great horned owl and perhaps slightly ahead of other commoner species like barn owls and northern saw-whet owls. It estimated that Canada in total holds about 10,000–50,000 pairs. Canadian Maritimes had highest densities known, with 3600 pairs, being found in 80% of 10 km (3.9 sq mi) blocks totaling 377; this was a conspicuously higher density than that recorded in Ontario, where they were in 28% of 1824 study blocks. Iowa, Tennessee and Maryland had the highest densities of pairs apparently in the United States, being present from 39 to 47% of blocks. Throughout the year, the mean number of sightings per route is 0.12 sightings while during Christmas Bird Counts (CBC), the mean in 0.25 per route.
Barred owl and northern spotted owl

Barred owls are thought to be partly responsible for the recent decline of the northern spotted owl, native to British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and California. The 2011 Revised Recovery Plan for the Northern Spotted Owl states "Based on the best available scientific information, competition from the barred owl (S. varia) poses a significant and complex threat to the spotted owl." Northern spotted owls were thought to be already declining considerably before barred owls moved into their range, mostly in sync with large-scale logging operations and land development carried out by humans, with their problems now further exacerbated by the barred species's presence. There are ecological discrepancies between the species in areas of sympatry. While both species prefer old-growth forest areas, the spotted owls tend to live in significantly higher elevation areas in Washington's Cascade mountains, with nest sites averaging 966.2 m (3,170 ft) meters above sea level against a mean of 54.1 m (177 ft) for barred owls, in areas with more steep slopes. The barred owls of the area additionally prefer wetter, more variable forest areas, down to riparian zones with limited forested land, while the spotted tended to cluster in more homogeneous upland and ancient coniferous forests. However, little is known on the feasibility or benefits of habitat maintenance that favors spotted over barred owls. Habitat management measures are hypothesized to be insufficient to mitigate the negative effect the barred owls are having. In areas where barred owls moved in within 0.8 km (0.50 mi) of a spotted owl nest area, 39% of spotted owls disappeared and were not seen again, while in areas still free of barred owls (so spared from this interspecific pressure), 11% of spotted owls disappeared and were not found again.

Since the 1960s, barred owls have been expanding their range westward from the eastern US and Canada. While some authors have described the expansion of barred owls into the west as "natural", others state that this is a mischaracterization, as there is little to suggest that the barred owls could have reached the spotted's range without the inadvertent aid of humans — increasing temperatures, wildlife suppression, and tree planting likely facilitated the range increase. When spotted owls and barred owls share the same area, the barred owls generally are more aggressive and out-compete the spotted owls, leading to decreased populations of the native owls. The more aggressive response of barred owls to interspecific stimuli has been verified with experiments incorporating vocalization and owl dummies. Additionally, the adult survival rates appear higher for barred owls (an estimated 91%) than for spotted owls (an estimated 82%). Therefore, the barred owl is considered "demographically superior". In December 2023, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service issued a draft of a management plan indicating that hunters in the Pacific Northwest would be encouraged to shoot more than a half million barred owls. The rationale was to cull the numbers of this invasive species, to help protect native species, particularly the spotted owl which had been listed as threatened under the Endangered Species Act.
Another potential threat is that barred owls and spotted owls occasionally interbreed, creating hybrids ("sparred owl" or "botted owl"). Only 47 hybrids with barred owls (all between female barred owls and male spotted owls) were found in an analysis of more than 9,000 banded spotted owls; consequently, hybridization between these two species is considered to be "an interesting biological phenomenon that is probably inconsequential compared with the real threat—direct competition between the two species for food and space". Most hybrids favor their barred owl heritage with similar and more pale overall coloring than spotted owls, though the back tends to be intermediate in color between the two and the beak coloring is variable. However, there has been much variation described. Due to variances in appearance, previously hybrids between the species were overestimated from field identification, only being certainly identified by genetic loci. Moreover, no recent hybrids could be detected in a survey of the Cascade Mountains.
In art
John James Audubon illustrated the barred owl in Birds of America (published in London, 1827–1838) as Plate 46, where it is shown threatening a grey squirrel. The image was engraved and colored by Robert Havell's London workshops. The original aquatint by Audubon is owned by the Brooklyn Museum.
References
- ^ BirdLife International (2016). "Strix varia". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016: e.T22689094A93217844. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22689094A93217844.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- "Appendices | CITES". cites.org. Retrieved 2022-01-14.
- Sclater., P. L. (2008). "Remarks on the Nomenclature of the British Owls, and on the Arrangement of the Order Striges". Ibis. 21 (3): 346–352. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.1879.tb07718.x.
- ^ Konig, Claus; Weick, Friedhelm; Becking, Jan-Hendrick (1999). Owls: A Guide to the Owls of the World. Yale University Press. pp. 327–328.
- Evers, L. (2014). Beyond anyone's control. Northwest Science, 88(1), 65–67.
- ^ Kelly, E. G. (2001). The range expansion of the northern barred owl: an evaluation of the impact on spotted owls. Thesis, Oregon State University.
- ^ Mazur, K. M. & James, P.C. (2020). "Barred Owl (Strix varia)", version 1.0. In Birds of the World (A. F. Poole and F. B. Gill, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
- "Barred Owl". Audubon. 2014-11-13. Retrieved 2017-09-01.
- ^ Voous, Karel H.; Cameron, Ad (illustrator) (1988). Owls of the Northern Hemisphere. London, Collins. pp. 225–230. ISBN 978-0-00-219493-8.
- ^ Buchanan, Joseph B.; Gutiérrez, R. J.; Anthony, Robert G.; Cullinan, Tim; Diller, Lowell V.; Forsman, Eric D.; Franklin, Alan B. (2007). "A synopsis of suggested approaches to address potential competitive interactions between Barred Owls (Strix varia) and Spotted Owls (S. occidentalis)". Biological Invasions. 9 (6): 679–691. Bibcode:2007BiInv...9..679B. doi:10.1007/s10530-006-9068-7. S2CID 20935420.
- Livezey, K. B. (2010). "Killing barred owls to help spotted owls I: a global perspective". Northwestern Naturalist. 91 (2): 107–133. doi:10.1898/NWN09-37.1. JSTOR 40856470. S2CID 11691153.
- Barton, B. S. (1883). Barton's Fragments of the Natural History of Pennsylvania. Willughby Society.
- Mayr, E., & Short, L. L. (1970). Species taxa of North American birds: a contribution to comparative systematics. Nuttall Ornithological Club.
- Hanna, Zachary R.; Henderson, James B.; Wall, Jeffrey D.; Emerling, Christopher A.; Fuchs, Jérôme; Runckel, Charles; Mindell, David P.; Bowie, Rauri C. K.; Derisi, Joseph L.; Dumbacher, John P. (2017). "Northern spotted owl (Strix occidentalis caurina) genome: divergence with the barred owl (Strix varia) and characterization of light-associated genes". Genome Biology and Evolution. 9 (10): 2522–2545. doi:10.1093/gbe/evx158. PMC 5629816. PMID 28992302.
- Campbell Jr, K. E.; Bochenski, Z. M. (2010). "A new genus for the extinct late Pleistocene owl Strix brea Howard (Aves: Strigiformes) from Rancho La Brea, California". Records of the Australian Museum. 62: 123–144. doi:10.3853/j.0067-1975.62.2010.1534.
- Howard, H. (1933). "A New Species of Owl from the Pleistocene of Rancho la Brea, California" (PDF). The Condor. 35 (2): 66–69. doi:10.2307/1363650. JSTOR 1363650.
- Parmalee, P. W.; Klippel, W. E. (1982). "Evidence of a Boreal Avifauna in Middle Tennessee during the Late Pleistocene". The Auk. 99 (2): 365–368. JSTOR 4085986.
- ^ Ridgway, R., & Friedmann, H. (1914). The Birds of North and Middle America: A Descriptive Catalog of the Higher Groups, Genera, Species, and Subspecies of Birds Known to Occur in North America, from the Arctic Lands to the Isthmus of Panama, the West Indies and Other Islands of the Caribbean Sea, and the Galapagos Archipelago (Vol. 50). US Government Printing Office.
- Peters, J. L. (1940). Check-list of birds of the world. Vol. 4. Cambridge: Harvard Univ. Press.
- Fujito, Naoko T.; Hanna, Zachary R.; Levy-Sakin, Michal; Bowie, Rauri C K.; Kwok, Pui-Yan; Dumbacher, John P.; Wall, Jeffrey D. (2021). "Genomic Variation and Recent Population Histories of Spotted (Strix occidentalis) and Barred (Strix varia) Owls". Genome Biology and Evolution. 13 (5). doi:10.1093/gbe/evab066. PMC 8120011. PMID 33764456.
- Bishop, L. B. (1931). "Three apparently undescribed owls". Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington. 44: 93–95.
- Wetmore, Alexander (1930). "The Florida Barred Owl in North Carolina". The Auk. 47 (2): 253. doi:10.2307/4075950. JSTOR 4075950.
- ^ Weidensaul, S. (2015). Owls of North America and the Caribbean. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
- Howell, S. N., & Webb, S. (1995). A guide to the birds of Mexico and northern Central America. Oxford University Press.
- Oberholser, H. C. (1974). The Bird Life of Texas. University of Texas Press, Austin, TX, USA.
- ^ Hume, R. (1991). Owls of the world. Running Press, Philadelphia.
- ^ Owls of the World: A Photographic Guide by Mikkola, H. Firefly Books (2012), ISBN 978-1-77085-136-8
- Holt, D.W., Berkley, R., Deppe, C., E. Rocha, P., Petersen, J.L., Rangel Salazar, J.L., Segars, K.P., Wood, K.L. & Marks, J.S. (2019). "Typical Owls". In: del Hoyo, J., Elliott, A., Sargatal, J., Christie, D.A. & de Juana, E. (eds.). Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Lynx Edicions, Barcelona.
- "Barred Owl Identification, All About Birds, Cornell Lab of Ornithology". www.allaboutbirds.org. Retrieved 2023-12-14.
- ^ Braekevelt, C. R.; Smith, S. A.; Smith, B. J. (1996). "Fine structure of the retinal photoreceptors of the barred owl (Strix varia)". Histology and Histopathology. 11 (1): 79–88. PMID 8720450.
- Dice, Lee R. (1945). "Minimum Intensities of Illumination Under Which Owls Can Find Dead Prey by Sight". The American Naturalist. 79 (784): 385–416. doi:10.1086/281276. JSTOR 2457707. S2CID 86535713.
- Terres, J. K. (1980). The Audubon Society Encyclopedia of North American Birds. New York, NY: Knopf. p. 665. ISBN 0-394-46651-9.
- Kelso, Leon; Kelso, Estelle H. (1936). "The Relation of Feathering of Feet of American Owls to Humidity of Environment and to Life Zones". The Auk. 53 (1): 51–56. doi:10.2307/4077355. JSTOR 4077355.
- Shufeldt, R. W. (1911). "Plumages of the Young of the Barred Owl" (PDF). The Wilson Bulletin. 23 (2): 113–119.
- Acker, J.; Garcia, D. (2010). "Notes on rectrix molt in Barred Owls (Strix varia)" (PDF). North American Bird Bander. 35 (2): 61.
- Karalus, K. E. & Eckert, E.W. (1974). The owls of North America (north of Mexico). Garden City, NY: Doubleday and Co.
- Dean, R. (1976). "Albinism and melanism among North American Birds". Bulletin of the Nuttall Ornithological Club. 2: 20–24.
- Barred Owl (Strix varia) – Information, Pictures, Sounds. The Owl Pages (2015-11-04). Retrieved on 2016-08-01.
- Liu, L. G.; Le Piane, K.; Clark, C. J. (2018). "Barred Owl (Strix varia) Feather Pennulae". Integrative and Comparative Biology. 58: E364. doi:10.1093/icb/icy002.
- ^ Earhart, Caroline M.; Johnson, Ned K. (1970). "Size Dimorphism and Food Habits of North American Owls" (PDF). The Condor. 72 (3): 251–264. doi:10.2307/1366002. JSTOR 1366002.
- ^ Carpenter, Thomas W. (1992). "Utility of Wing Length, Tail Length and Tail Barring in Determining the Sex of Barred Owls Collected in Michigan and Minnesota". The Condor. 94 (3): 794–795. doi:10.2307/1369270. JSTOR 1369270.
- ^ Bent, A. C. (1961). Life Histories of North American Birds of Prey (part 2), Orders Falconiformes and Stringiformes (Vol. 170). US Government Printing Office.
- Bosakowski, T. (1987). "Census of Barred Owls and Spotted Owls". In Biology and Conservation of Northern Forest Owls: Symposium Proceedings: February 3–7, 1987, Winnipeg, Manitoba (Vol. 142, p. 307). Fort Collins, Colo.: Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station.
- ^ Odom, K. (2009). Vocalizations, vocal behaviour, and geographic variation in the calls, duets, and duetting behaviour of a nonpasserine, the Barred Owl (Strix varia). M.S. Thesis, University of Windsor.
- Haas, F. C. & Burrows, R. (2005). Birds of Pennsylvania. Lone Pine.
- ^ McGarigal, Kevin; Fraser, James D. (1985). "Barred Owl Responses to Recorded Vocalizations". The Condor. 87 (4): 552–553. doi:10.2307/1367961. JSTOR 1367961.
- ^ Odom, Karan J.; Mennill, Daniel J. (2010). "A Quantitative Description of the Vocalizations and Vocal Activity of the Barred Owl". The Condor. 112 (3): 549–560. doi:10.1525/cond.2010.090163. S2CID 54987338.
- Brewster, W.; Chapman, F. M. (1891). "Notes on the birds of the lower Suwanee River" (PDF). The Auk. 8 (2): 125–138. doi:10.2307/4068066. JSTOR 4068066.
- Saunders, A. A. (1951). A guide to bird songs. New York: Doubleday.
- Taber, Wendell (1940). "The Scream of the Northern Barred Owl". The Auk. 57 (2): 253. doi:10.2307/4078760. JSTOR 4078760.
- Bird, D. M.; Bird, J.O. (1977). "Apparent distraction display by a Barred Owl". Canadian Field-Naturalist. 91 (2): 176–177. doi:10.5962/p.345368.
- Alderfer, Jonathan (2006). National Geographic: Complete Birds of North America. Washington D.C.: National Geographic Society. pp. 330–331. ISBN 978-1-4262-0135-6.
- ^ Mosher, J. A.; Fuller, M. R.; Kopeny, M. (1990). "Surveying Woodland Raptors by Broadcast of Conspecific Vocalizations" (PDF). Journal of Field Ornithology: 453–461. JSTOR 4513583.
- ^ Dunstan, T. C.; Sample, S. D. (1972). "Biology of barred owls in Minnesota". Loon. 44 (4): 111–115.
- Taylor, P. (1983). Wings along the Winnipeg: birds of the Pinawa-Lac du Bonnet region, Manitoba. Winnipeg, MB: (Eco Series no. 2.) Manitoba Nat. Soc.
- Yannielli, L. C. (1989). Preferred habitat of barred owls (Strix varia) in Litchfield County, Connecticut, with additional comments on distribution and abundance. M.S. thesis, South. Conn. State Univ.
- Erskine, A. J. (1992). Atlas of Breeding Birds of the Maritime Provinces. Nova Scotia Museum, Halifax, NS, Canada.
- Gagnon, C. & Bombardier, M. (1996). "Barred Owl." In The breeding birds of Quebec: atlas of the breeding birds of southern Québec., edited by J. Gauthier and Y. Aubry, 598–601. Québec Region, Montréal: Assoc. québecoise des groupes d'ornithologues, Prov. of Quebec Soc. for the protection of birds, Can. Wildl. Serv., Environ. Canada.
- Eagles, P. F., Cadman, M. D., & Helleiner, F. M. (1987). Atlas of the breeding birds of Ontario. University of Waterloo Press.
- ^ Peck, G. K., & James, R. D. (1993). Breeding Birds of Ontario: Nidiology and Distribution. Volume 1: Nonpasserines (first Revision-part A: loons to ducks). Ontario Birds, 11, 18–22.
- Schmelzer, Isabelle; Phillips, Frank (2004). "First Record of a Barred Owl, Strix varia, in Labrador". The Canadian Field-Naturalist. 118 (2): 273. doi:10.22621/cfn.v118i2.929.
- Janssen, R. B. (1987). Birds in Minnesota. University of Minnesota Press, Minneapolis, MN, USA.
- Peterson, R. A. (1995). The South Dakota Breeding Bird Atlas. South Dakota Ornithologists' Union, Northern Prairie Wildlife Research Center, Jamestown, ND, USA.
- Johnsgard, P. A. (1979). Birds of the Great Plains: Breeding Species and their Distribution. University of Nebraska Press, Lincoln, NE, USA.
- ^ Johnsgard, P. A. (1988). North American owls: biology and natural history. Smithsonian Institution.
- Holt, D. W. (1993). "Presence and distribution of Mexican owls: a review" (PDF). J Raptor Res. 27 (3): 154–160.
- ^ Livezey, Kent B. (2009). "Range Expansion of Barred Owls, Part I: Chronology and Distribution". The American Midland Naturalist. 161: 49–56. doi:10.1674/0003-0031-161.1.49. S2CID 86276981.
- Blake, E. R. (1947). "Barred owl thirty miles from land" (PDF). The Wilson Bulletin. 59 (2): 111.
- ^ Holt, Denver W.; Domenech, Rob; Paulson, Anne (2001). "Status and Distribution of the Barred Owl in Montana". Northwestern Naturalist. 82 (3): 102–110. doi:10.2307/3536484. JSTOR 3536484.
- ^ Duncan, J. R., & Duncan, P. A. (1997). Duncan, James R.; Johnson, David H.; Nicholls, Thomas H. (eds.). "Increase in distribution records of owl species in Manitoba based on a volunteer nocturnal survey using Boreal Owl (Aegolius funereus) and Great Gray Owl (Strix nebulosa) playback". Biology and Conservation of Owls of the Northern Hemisphere: 2nd International Symposium. 190. Gen. Tech. Rep. NC-190. St. Paul, MN: US Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service, North Central Forest Experiment Station: 519–524.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Seton, E. E. T. (1886). "The birds of western Manitoba". Auk. 3 (3): 145–156, 320–329. doi:10.2307/4625404. JSTOR 4625404.
- Preble, E. A. (1941). "Barred Owl on Athabaska River, Alberta". The Auk. 58 (3): 407–408. doi:10.2307/4078969. JSTOR 4078969.
- Houston, Stuart (1961). "First Saskatchewan Nest Record of Barred Owl". Blue Jay. 19 (3). doi:10.29173/bluejay2494.
- Priestley, Lisa Takats (2004). "The Barred Owl, Strix varia in Alberta: distribution and status". The Canadian Field-Naturalist. 118 (2): 215. doi:10.22621/cfn.v118i2.916.
- ^ Campbell, W., Dawe, N. K., McTaggart-Cowan, I., Cooper, J. M., Kaiser, G. W., & McNall, M. C. (2011). Birds of British Columbia, Volume 2: Nonpasserines-Diurnal Birds of Prey through Woodpeckers. UBC Press.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Grant, James (1966). "The Barred Owl in British Columbia". The Murrelet. 47 (2): 39–45. doi:10.2307/3536439. JSTOR 3536439.
- Montana Bird Distribution Records Committee (1992). P. D. Skaar's Montana Bird Distribution (4th ed.). Helena, MT, USA: Montana Natural History Program.
- Stephens, D. A., & Sturts, S. H. (1997). "Idaho bird distribution: mapping by latilong". Idaho Mus. Nat. Hist, Spec. Publ (13).
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Nehrling, H. (1900). "Bird Notes from Sao Paulo, Brazil". The Auk. 17 (3): 298–299. doi:10.2307/4069130. JSTOR 4069130.
- Cooke, Wells W. (1909). "The Birds of Colorado: Third Supplement". The Auk. 26 (4): 400–422. doi:10.2307/4071272. JSTOR 4071272.
- Smith, M. R., Mattocks Jr., P.W. & Cassidy, K.M. (1997). K. M. Cassidy; C. E. Grue; M. R. Smith; K. M. Dvornich (eds.). "Breeding birds of Washington State". Washington State Gap Analysis – Final Report. Seattle, WA, USA: Seattle Audubon Society Publications in Zoology no. 1.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Nicholls, Thomas H.; Warner, Dwain W. (1972). "Barred Owl Habitat Use as Determined by Radiotelemetry". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 36 (2): 213–224. doi:10.2307/3799054. JSTOR 3799054.
- ^ McGarigal, Kevin; Fraser, James D. (1984). "The Effect of Forest Stand Age on Owl Distribution in Southwestern Virginia". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 48 (4): 1393–1398. doi:10.2307/3801804. JSTOR 3801804.
- Dickson, J. G. (1988). "Bird communities in oak-gum-cypress forests". Bird Conservation. 3: 51–62.
- ^ Laidig, K. J.; Dobkin, D. S. (1995). "Spatial overlap and habitat associations of barred owls and great horned owls in southern New Jersey". Journal of Raptor Research. 29 (3): 151–157.
- ^ Winton, B. R.; Leslie, D. M. (2004). "Density and habitat associations of barred owls at the edge of their range in Oklahoma". Southeastern Naturalist. 3 (3): 475–482. doi:10.1656/1528-7092(2004)003[0475:DAHAOB]2.0.CO;2. JSTOR 3878075. S2CID 85726566.
- Sutton, C. C.; Sutton, P. T. (1986). "The status and distribution of Barred Owl and Red-shouldered Hawk in southern New Jersey" (PDF). Cassinia. 61: 20–29.
- Smith, C. F. (1978). Distributional ecology of Barred and Great Horned owls in relation to human distribution. Master's Thesis, Univ. of Connecticut, Hartford.
- Rothauser, B. (2003). Barred Owl, Strix varia. NJ Fish and Wildlife.
- Elody, B. I.; Sloan, N. F. (1985). "Movements and habitat use of Barred Owls in the Huron Mountains of Marquette County, Michigan, as determined by radiotelemetry". Jack-Pine Warbler. 63 (1): 3–8.
- ^ Fuller, M. R. (1979). Spatiotemporal ecology of four sympatric raptor species. Phd Thesis, Univ. of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
- Bierregaard, R. O. (2018). "Barred Owls: a nocturnal generalist thrives in wooded, suburban habitats", pp. 138–151 in Urban Raptors. Island Press, Washington, DC. ISBN 9781610918398
- Bryner, Jeanna (2007). "Owls Get Wise to Better Life in Cities". LiveScience.
- Clement, Marion A.; Barrett, Kyle; Baldwin, Robert F. (2019). "Key habitat features facilitate the presence of Barred Owls in developed landscapes". Avian Conservation and Ecology. 14 (2). doi:10.5751/ACE-01427-140212. S2CID 202860589.
- ^ Dykstra, Cheryl R.; Simon, Melinda M.; Daniel, F. Bernard; Hays, Jeffrey L. (2012). "Habitats of Suburban Barred Owls (Strix varia) and Red-Shouldered Hawks (Buteo lineatus) in Southwestern Ohio". Journal of Raptor Research. 46 (2): 190–200. doi:10.3356/JRR-11-05.1. S2CID 86775451.
- ^ Bosakowski, T., Speiser, R., & Benzinger, J. (1987). Distribution, density, and habitat relationships of the Barred Owl in northern New Jersey. Biology and Conservation of Northern Owls. Gen. Tech. Re, RM-142. US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station, Fort Collins, 135–143.
- Rubino, M. J. (2001). Identifying barred owl habitat in the North Carolina Piedmont: using GIS in focal species conservation planning (Master's thesis, North Carolina State University.).
- Van Ael, S. M. (1996). Modelling Barred Owl habitat in northwestern Ontario. Master's Thesis, Lakehead Univ., Thunder Bay, ON.
- Mazur, K. M., James, P. C., Fitzsimmons, M. J., Langen, G., & Espie, R. H. M. (1997). Habitat associations of the Barred Owl in the boreal forest of Saskatchewan, Canada. Journal of Raptor Research, 31(3), 253–259.
- ^ Takats, D. L. (1998). Barred Owl habitat use and distribution in the Foothills Model Forest. Master's Thesis, Univ. of Alberta, Edmonton.
- Dunbar, D. L. (1991). "Status of the spotted owl, Strix occidentalis, and barred owl, Strix varia, in southwestern British Columbia". Canadian Field-Naturalist. 105 (4): 464–468. doi:10.5962/p.358095.
- ^ Olsen, B. (1999). Breeding habitat ecology of the barred owl (Strix varia) at three spatial scales in the boreal mixedwood forest of north-central Alberta. UNM. doi:10.7939/R3280575V
- Singleton, P. H. (2015). "Forest structure within barred owl (Strix varia) home ranges in the Eastern Cascade Range, Washington". Journal of Raptor Research. 49 (2): 129–140. doi:10.3356/rapt-49-02-129-140.1. S2CID 83958216.
- ^ Grossman, S. R.; Hannon, S. J.; Sánchez-Azofeifa, A. (2008). "Responses of Great Horned Owls (Bubo virginianus), Barred Owls (Strix varia), and Northern Saw-whet Owls (Aegolius acadicus) to forest cover and configuration in an agricultural landscape in Alberta, Canada". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 86 (10): 1165–1172. doi:10.1139/Z08-095.
- Hamerstrom, F.; Janick, K. (1973). "Diurnal sleep rhythm of a young barred owl". The Auk. 90 (4): 899–900. doi:10.2307/4084377. JSTOR 4084377.
- Tester, J. R. (1987). "Changes in daily activity rhythms of some free-ranging animals in Minnesota" (PDF). Canadian Field-Naturalist. 101 (1): 13–21. doi:10.5962/p.355849.
- ^ Caldwell, L. D. (1972). "Diurnal hunting by a Barred Owl". Jack Pine Warbler. 50: 93–94.
- ^ Jackson, J. A.; White, R. (1995). "Diurnal roadside hunting by Barred Owls". Journal of Louisiana Ornithology. 3: 13–15.
- Campbell, J. M. (1969). "The owls of the central Brooks Range, Alaska". The Auk. 86 (3): 565–568. doi:10.2307/4083428. JSTOR 4083428.
- ^ Blakemore, L. A. (1940). "Barred Owl food habits in Glenwood Park, Minneapolis, Minnesota". Flicker. 12: 21–23.
- ^ Applegate, R. D. (1975). "Co-roosting of Barred Owls and Common Grackles". Bird-Banding. 46 (2): 169–170. doi:10.2307/4512120. JSTOR 4512120.
- Barrows, C. W. (1981). "Roost selection by Spotted Owls: an adaptation to heat stress". Condor. 83 (4): 302–309. doi:10.2307/1367496. JSTOR 1367496.
- Carter, J. D. (1925). "Behavior of the Barred Owl". The Auk. 42 (3): 443–444. doi:10.2307/4074397. JSTOR 4074397.
- Fitzpatrick, J. W. (1975). "A record of allopreening in the Barred Owl". The Auk. 92 (3): 598–599. doi:10.2307/4084622. JSTOR 4084622.
- Scott, D. (1980). "Owls allopreening in the wild". British Birds. 73: 436–39.
- ^ Livezey, K.B. (2007). "Barred Owl habitat and prey: a review and synthesis of the literature". Journal of Raptor Research. 41 (3): 177–201. doi:10.3356/0892-1016(2007)41[177:BOHAPA]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 86266928.
- ^ Mennill, Daniel; Odom, Karan (2010). "Vocal duets in a nonpasserine: An examination of territory defence and neighbour–stranger discrimination in a neighbourhood of barred owls". Behaviour. 147 (5–6): 619–639. doi:10.1163/000579510X12632972452424.
- Galeotti, Paolo; Pavan, Gianni (2008). "Differential responses of territorial Tawny Owls Strix aluco to the hooting of neighbours and strangers". Ibis. 135 (3): 300–304. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.1993.tb02847.x.
- Mazur, K. M. (1997). Spatial habitat selection by Barred Owls in the boreal forest of Saskatchewan, Canada. Master's Thesis, Univ. of Regina, Regina, SK.
- Nicholls, T. H. & Fuller, M. R. (1987). Territorial Aspects of Barred Owl Home Range and Behavior in Minnesota. In Biology and Conservation of Northern Forest Owls: Symposium Proceedings. February 3–7, 1987, Winnipeg, Manitoba (Vol. 142, p. 121). Fort Collins, Colo.: Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station.
- Elody, B. I. (1983). Techniques for capturing, marking, monitoring, and habitat analysis for the Barred Owl in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan. Master's Thesis, Michigan Technological Univ., Houghton.
- Lilley, G. (1998). A study of the silent flight of the owl. In 4th AIAA/CEAS aeroacoustics conference (p. 2340).
- ^ Wiens, J. David; Anthony, Robert G.; Forsman, Eric D. (2014). "Competitive interactions and resource partitioning between northern spotted owls and barred owls in western Oregon". Wildlife Monographs. 185 (1): 1–50. Bibcode:2014WildM.185....1W. doi:10.1002/wmon.1009.
- ^ Sutherland, D. A.; Jones, I. L. (2010). "Successful Diurnal Foraging by a Barred Owl". Ontario Birds. 28 (3): 152–155.
- Nero, Robert W. (1993). "Evidence of Snow-Plunging by Boreal and Barred Owls". Blue Jay. 51 (3). doi:10.29173/bluejay5428. S2CID 221969147.
- Takats, D. L. (1996). "Foraging observations of a Barred Owl in the Foothills Model Forest". Alberta Naturalist. 26: 29–30.
- ^ Elderkin, M. F. (1987). The breeding and feeding ecology of a Barred Owl Strix varia Barton population in Kings County, Nova Scotia. Master's Thesis, Acadia Univ., Wolfville, NS.
- ^ Ward, Andrea B.; Weigl, Peter D.; Conroy, Rachael M. (2002). "Functional Morphology of Raptor Hindlimbs: Implications for Resource Partitioning". The Auk. 119 (4): 1052–1063. doi:10.1093/auk/119.4.1052.
- Kapfer, Joshua M.; Gammon, David E.; Groves, John D. (2011). "Carrion-feeding by Barred Owls (Strix varia)". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 123 (3): 646–649. doi:10.1676/11-015.1. JSTOR 23033577. S2CID 85768266.
- Forbush, E. H. (1925). Birds of Massachusetts and other New England states. Volume 2. Massachusetts Department of Agriculture, Boston, US.
- ^ Livezey, K.B.; Elderkin, M.F.; Cott, P.A.; Hobbs, J.; Hudson, J.P. (2008). "Barred owls eating worms and slugs: the advantage in not being picky eaters". Northwestern Naturalist. 89 (3): 185–190. doi:10.1898/NWN08-04.1. JSTOR 30135134. S2CID 86062164.
- Barred Owl Archived 2017-10-27 at the Wayback Machine. Fcps.edu. Retrieved on 2016-08-01.
- ^ Snyder, N. F., & Wiley, J. W. (1976). Sexual size dimorphism in hawks and owls of North America (No. 20). American Ornithologists' Union.
- ^ Marks, Jeffrey S.; Hendricks, D. Paul; Marks, Victoria S. (1984). "Winter Food Habits of Barred Owls in Western Montana". The Murrelet. 65 (1): 27–28. doi:10.2307/3534209. JSTOR 3534209.
- Bosakowski, Thomas; Smith, Dwight G. (1992). "Comparative diets of sympatric nesting raptors in the eastern deciduous forest biome". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 70 (5): 984–992. doi:10.1139/z92-140.
- ^ Marti, Carl D.; Korpimäki, Erkki; Jaksić, Fabian M. (1993). "Trophic Structure of Raptor Communities: A Three-Continent Comparison and Synthesis". Current Ornithology. pp. 47–137. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-9582-3_2. ISBN 978-1-4615-9582-3.
- ^ Graham, S. A. (2012). Diet composition, niche and geographic characteristics, and prey size preference of Barred Owls (Strix varia) in the Pacific Northwest. Masters Thesis, Oregon State University.
- ^ Hamer, T.E.; Hays, D.L.; Senger, C.M.; Forsman, E.D. (2001). "Diets of northern barred owls and northern spotted owls in an area of sympatry". Journal of Raptor Research. 35: 221–227.
- Holt, Denver W.; Bitter, Colleen (2007). "Barred Owl Winter Diet and Pellet Dimensions in Western Montana". Northwestern Naturalist. 88: 7. doi:10.1898/1051-1733(2007)88[7:BOWDAP]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1051-1733. S2CID 86350479.
- Cahn, Alvin R.; Kemp, Jack T. (1930). "On the Food of Certain Owls in East-Central Illinois". The Auk. 47 (3): 323–328. doi:10.2307/4075480. JSTOR 4075480.
- Rusling, W. J. (1951). "Food habits of New Jersey owls". Proc. Linnaean Soc. New York. 58–62: 38–45.
- Wilson, Kenneth A. (1938). "Owl Studies at Ann Arbor, Michigan". The Auk. 55 (2): 187–197. doi:10.2307/4078196. JSTOR 4078196.
- Hamerstrom Jr, F. N.; Hamerstrom, F. (1951). "Food of young raptors on the Edwin S. George Reserve". The Wilson Bulletin: 16–25.
- ^ Errington, Paul L. (1932). "Food Habits of Southern Wisconsin Raptors. Part I. Owls". The Condor. 34 (4): 176–186. doi:10.2307/1363563. JSTOR 1363563.
- Allan, P. F. (1936). "Microtus ochrogaster in Minnesota". Journal of Mammalogy. 17 (3): 291. doi:10.1093/jmammal/17.3.291.
- Hindmarch, Sofi; Elliott, John E. (2015). "When Owls go to Town: The Diet of Urban Barred Owls". Journal of Raptor Research. 49: 66–74. doi:10.3356/jrr-14-00012.1. S2CID 59379580.
- Powers, Karen E.; Dimas, Miranda S.; Leon, Angie I.; Vanmeter, Logan M. (2020). "Observed Predation of Neotoma magister (Allegheny Woodrat) by Strix varia (Barred Owl) in Virginia". Northeastern Naturalist. 27. doi:10.1656/045.027.0103. S2CID 213605365.
- HaySmith, L. (1995). "Neotoma floridana floridana: natural history, populations, and movements in northcentral Florida" (PDF). Bulletin of the Florida Museum of Natural History. 38: 211–243. doi:10.58782/flmnh.gdie1905.
- ^ Meritt, D. A. Jr.; Eul, R. (2013). "Barred Owl pellet contents in Michigan" (PDF). Illinois State Academy of Science. Transactions. 106: 55.
- Hayssen, Virginia (15 August 2008). "Patterns of Body and Tail Length and Body Mass in Sciuridae". Journal of Mammalogy. 89 (4): 852–873. doi:10.1644/07-MAMM-A-217.1. S2CID 29249283.
- ^ Devereux, J. G.; Mosher, J. A. (1984). "Breeding ecology of Barred Owls in the central Appalachians". Raptor Research. 18 (2): 49–58.
- ^ Whiklo, T. (2012). Nest structure and breeding habitat characteristics of Barred Owls (Strix varia) in Manitoba, Canada. hdl:1993/5218 doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.32357.19682
- Korschgen, Leroy J.; Stuart, Henry B. (1972). "Twenty Years of Avian Predator-Small Mammal Relationships in Missouri". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 36 (2): 269–282. doi:10.2307/3799058. JSTOR 3799058.
- Bergstrom, Bradley J.; Smith, Marvin T. (2017). "Bats as Predominant Food Items of Nesting Barred Owls". Southeastern Naturalist. 16: N1 – N4. doi:10.1656/058.016.0110. S2CID 89723777.
- Linnell, Mark A.; Epps, Clinton W.; Forsman, Eric D.; Zielinski, William J. (2017). "Survival and predation of weasels (Mustela erminea, Mustela frenata) in North America". Northwest Science. 91: 15–26. doi:10.3955/046.091.0104. S2CID 89860715.
- Lesmeister, Damon B.; Millspaugh, Joshua J.; Gompper, Matthew E.; Mong, Tony W. (2010). "Eastern spotted skunk (Spilogale putorius) survival and cause-specific mortality in the Ouachita Mountains, Arkansas". The American Midland Naturalist. 164: 52–60. doi:10.1674/0003-0031-164.1.52. S2CID 83621716.
- Hassler, Kendyl N.; Kessinger, Brin E.; Harms, Caroline E.; Price, Lucas E.; Barton, Ethan P.; Oxenrider, Kevin J.; Rogers, Rich E.; Pearce, Kelly J.; Serfass, Thomas L.; Welsh, Amy B. (2021). "Genetic Confirmation of Predation of an Adult Female Eastern Spotted Skunk by a Barred Owl". Southeastern Naturalist. 20. doi:10.1656/058.020.0sp1111. S2CID 236999938.
- Tosa, Marie I.; Lesmeister, Damon B.; Levi, Taal (2022). "Barred Owl Predation of Western Spotted Skunks". Northwestern Naturalist. 103 (3). doi:10.1898/1051-1733-103.3.250. S2CID 253667556.
- Smith, Dwight G. (2002). Great Horned Owl (1st ed.). Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books. pp. 33, 80–81. ISBN 978-0-8117-2689-4.
- Glue, D. E. (1972). Bird prey taken by British owls. Bird Study, 19(2), 91–96.
- Comay, Orr; Dayan, Tamar (2018). "What determines prey selection in owls? Roles of prey traits, prey class, environmental variables, and taxonomic specialization". Ecology and Evolution. 8 (6): 3382–3392. Bibcode:2018EcoEv...8.3382C. doi:10.1002/ece3.3899. PMC 5869362. PMID 29607033.
- Mahony, Nancy A. (2017). "Evidence of Barred Owls (Strix varia) Depredating Nests of Barn Swallows (Hirundo rustica)". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 129 (3): 641–644. doi:10.1676/16-054.1. JSTOR 26456083. S2CID 89785198.
- Ray, J. D. (2014). "Avian predation on Purple Martins nesting in artificial housing". Bull. Texas Ornith. Soc. 47: 1–2.
- Hamilton, Gary D.; Martin, Robert F. (January 1985). "Investigator Perturbation and Reproduction of the Cliff Swallow". The Auk. 102 (1): 167–170. doi:10.2307/4086836. JSTOR 4086836.
- ^ Gill, Ryan A.; Cox, W. Andrew; Thompson, Frank R. (March 2016). "Timing of Songbird Nest Predation as Revealed by Video Surveillance". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 128 (1): 200–203. doi:10.1676/1559-4491-128.1.200. S2CID 86980126.
- Streby, Henry M.; Refsnider, Jeanine M.; Peterson, Sean M.; Andersen, David E. (December 2008). "Barred Owl Predation on Hermit Thrush and Ovenbird Fledglings". Journal of Raptor Research. 42 (4): 296–298. doi:10.3356/JRR-08-10.1. S2CID 83697804.
- Schmidt, Kenneth A.; Rush, Scott A.; Ostfeld, Richard S. (July 2008). "Wood thrush nest success and post-fledging survival across a temporal pulse of small mammal abundance in an oak forest". Journal of Animal Ecology. 77 (4): 830–837. Bibcode:2008JAnEc..77..830S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2656.2008.01378.x. PMID 18355240.
- Anich, N. M., T. J. Benson, J. D. Brown, C. Roa, J. C. Bednarz, R. E. Brown, and J. G. Dickson (2020). "Swainson's Warbler (Limnothlypis swainsonii)", version 1.0. In Birds of the World (P. G. Rodewald, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
- Sherry, T. W., R. T. Holmes, P. Pyle, and M. A. Patten (2020). American Redstart (Setophaga ruticilla), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (P. G. Rodewald, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
- ^ Fisher, A. K. (1893). The hawks and owls of the United States in their relation to agriculture (No. 3). US Department of Agriculture, Division of Ornithology and Mammalogy.
- Parsons, K. C. and T. L. Master (2020). "Snowy Egret (Egretta thula)", version 1.0. In Birds of the World (A. F. Poole and F. B. Gill, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
- Telfair II, R. C. (2020). "Cattle Egret (Bubulcus ibis), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (S. M. Billerman, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
- Mangelinckx, Joelle M.; Brown, Samantha R.; Allen, R. Bradford; Sullivan, Kelsey; Blomberg, Erik J. (14 February 2020). "Effects of forest characteristics on ruffed grouse nesting ecology in central Maine, USA". Wildlife Biology. 2020 (1). doi:10.2981/wlb.00598. S2CID 211567501.
- Schroeder, M. A., E. J. Blomberg, D. A. Boag, P. Pyle, and M. A. Patten (2020). "Spruce Grouse (Falcipennis canadensis)", version 1.0. In Birds of the World (P. G. Rodewald, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
- Hingtgen, T. M., Mulholland, R., & Repenning, R. W. (1985). Habitat suitability index models: white ibis. Fish and Wildlife Service.
- Yeldell, Nathan A.; Cohen, Bradley S.; Little, Andrew R.; Collier, Bret A.; Chamberlain, Michael J. (2017). "Nest site selection and nest survival of eastern wild turkeys in a pyric landscape". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 81 (6): 1073–1083. Bibcode:2017JWMan..81.1073Y. doi:10.1002/jwmg.21267.
- Conant, R. (1975). A Field Guide to Reptiles and Amphibians of Eastern and Central North America, Second Edition. Boston: Houghton Mifflin.
- Meshaka, W. E. Jr.; Layne, J. N. (2015). "The herpetology of southern Florida" (PDF). Herpetological Conservation and Biology. 10 (5): 1–353.
- Platt, D.R. (1969). Natural history of the hognose snakes Heterodon platyrhinos and Heterodon nasicus. Univ. Kansas Publ. Mus.
- Ernst, C. H., & Ernst, E. M. (2011). Venomous Reptiles of the United States, Canada, and Northern Mexico: Crotalus (Vol. 2). JHU Press.
- Peterson, S.W. (1989). "Barred owl eats hatchling Turtle". Mississippi Kite. 19 (2): 4–5.
- Wilson, Dawn S. (1991). "Estimates of survival for juvenile gopher tortoises, Gopherus polyphemus". Journal of Herpetology. 25 (3): 376–379. doi:10.2307/1564605. JSTOR 1564605.
- "Spring Peeper Profile". National Geographic Society. Archived from the original on June 14, 2007. Retrieved 2020-04-21.
- Frost, D.R.; Grant, T.; Faivovich, J.; Bain, R.H.; Haas, A.; Haddad, C.F.B.; De Sá, R.O.; Channing, A.; Wilkinson, M.; Donnellan, S.C.; Raxworthy, C.J.; Campbell, J.A.; Blotto, B.L.; Moler, P.; Drewes, R.C.; Nussbaum, R.A.; Lynch, J.D.; Green, D.M.; Ward, C.; Wheeler, W.C. (2006). "The Amphibian Tree of Life". Bulletin of the American Museum of Natural History. 297: 1–291. doi:10.1206/0003-0090(2006)297[0001:TATOL]2.0.CO;2. hdl:2246/5781. S2CID 86140137.
- Medina, Shelby L.; Higley, Mark; Dumbacher, John P. (2018). "Rough-skinned newt (Taricha granulosa) predation by Barred Owls (Strix varia)". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 130 (3): 780–783. doi:10.1676/17-052.1. S2CID 91731949.
- Smith, D. G.; Devine, A.; Devine, D. (1983). "Observations of fishing by a Barred Owl" (PDF). Journal of Field Ornithology: 88–89.
- ' VanArman, P. G. (2011). "Role of native crayfish, Procambarus alleni (Faxon) and Procambarus fallax (Hagen), in everglades food webs: a literature review and conceptual model". Florida Scientist. 74 (2): 100–125. JSTOR 24321812.
- Portnoy, J. W., & Dodge, W. E. (1979). Red-shouldered Hawk nesting ecology and behavior. The Wilson Bulletin, 104–117.
- Mason, J.S. (2004). The reproductive success, survival, and natal dispersal of Barred Owls (Strix varia) in rural versus urban habitats in and around Charlotte, North Carolina. M.S. thesis, University of NC.
- ^ Postupalsky, S., Paap, J. M. & Scheller, L. (1997). "Nest sites and reproductive success of Barred Owls (Strix varia) in Michigan". Pages 325–337 in Biology and Conservation of Owls in the Northern Hemisphere: Second International Symposium. J. R. Duncan, D. H. Johnson, and T. H. Nicholls (eds). USDA Forest Service General Technical Report NC-190.
- Roble, S. M. (2013). "Ophiophagy in Red-shouldered Hawks (Buteo lineatus), with the First Record of Eastern Wormsnakes (Carphophis amoenus) as Prey". Banisteria. 41: 80–84.
- Whiklo, Todd M.; Duncan, James R. (2012). "Occurrences of wing clapping behavior in Barred Owls (Strix varia)". Journal of Raptor Research. 46 (4): 413–416. doi:10.3356/JRR-12-18.1. S2CID 86567181.
- Baumgartner, Frederick M. (1939). "Territory and Population in the Great Horned Owl". The Auk. 56 (3): 274–282. doi:10.2307/4079048. JSTOR 4079048.
- Marti, C. D. (1974). "Feeding ecology of four sympatric owls" (PDF). The Condor. 76 (1): 45–61. doi:10.2307/1365983. JSTOR 1365983.
- Duxbury, J. M., & Holroyd, G. L. (1997). "You are what you eat: stable isotope ecology of owl diets in Alberta, Canada". In: Duncan, James R.; Johnson, David H.; Nicholls, Thomas H., eds. Biology and conservation of owls of the Northern Hemisphere: 2nd International symposium. Gen. Tech. Rep. NC-190. St. Paul, MN: US Dept. of Agriculture, Forest Service, North Central Forest Experiment Station. 148–154. (Vol. 190).
- Van Damme, L. M. (2005). "Diet of the great horned owl in the Creston Valley, British Columbia, 1998–2005" (PDF). Wildlife Afield. 2 (2): 73–78.
- Haskell, D. G., Knupp, A. M., & Schneider, M. C. (2001). "Nest predator abundance and urbanization", pp. 243–258 in Avian ecology and conservation in an urbanizing world. Springer, Boston, MA. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-1531-9_11 ISBN 978-1-4615-1531-9
- Mazur, K. M., James, P. C., & Frith, S. D. (1997). "Barred Owl (Strix varia) nest site characteristics in the boreal forest of Saskatchewan, Canada". US DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE FOREST SERVICE GENERAL TECHNICAL REPORT NC, 267–271.
- Smithers, B. L.; Boal, C. W.; Andersen, D. A. (2005). "Northern Goshawk diet in Minnesota: an analysis using video recording systems". Journal of Raptor Research. 39 (3): 264.
- Eifrig, G. (1907). "American Goshawk (Accipiter atricapillus) versus Man and Barred Owl". The Auk: 437–438.
- ^ Shupe, S. (1985). "Observations of the Barred Owl in southeastern Nebraska". Nebraska Bird Review: 37–38.
- Stirling, D. (2011). "Cooper's Hawk Feeding on Barred Owl and Norway Rat in Victoria, British Columbia" (PDF). Wildlife Afield. 8 (1): 120–122.
- Neill, W. T. (1971). The Last of the Ruling Reptiles. Columbia University Press, New York, NY, USA.
- Elliott, K. (2006). "Declining numbers of Western Screech-Owl in the lower mainland of British Columbia" (PDF). British Columbia Birds. 14: 2–11.
- Acker, Jamie (2012). "Recent Trends in Western Screech-Owl and Barred Owl Abundances on Bainbridge Island, Washington". Northwestern Naturalist. 93 (2): 133–137. doi:10.1898/nwn11-21.1. S2CID 85889087.
- Ritchison, G., F. R. Gehlbach, P. Pyle, and M. A. Patten (2020). "Eastern Screech-Owl (Megascops asio)", version 1.0. In Birds of the World. P. G. Rodewald (Ed.). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
- Linkhart, B. D. and D. A. McCallum (2020). "Flammulated Owl (Psiloscops flammeolus)", version 1.0. In Birds of the World (A. F. Poole, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA.
- Graves, Gary R.; Niemi, Gerald J. (2006). "Possible Predation of Great Gray Owl by a Barred Owl". Journal of Raptor Research. 40 (2): 175. doi:10.3356/0892-1016(2006)40[175:PPOGGO]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0892-1016. S2CID 86070731.
- Sykes, P.W. Jr. (1987). "Some aspects of the breeding biology of the Snail Kite in Florida" (PDF). J. Field Ornithol. 58: 171–189. JSTOR 4513216.
- Hertzel, A.X. (2003). "Barred Owl takes Cooper's Hawk?". Loon. 75: 58.
- Coulson, Jennifer O.; Coulson, Thomas D.; Defrancesch, Sherry A.; Sherry, Thomas W. (2008). "Predators of the Swallow-Tailed Kite in Southern Louisiana and Mississippi". Journal of Raptor Research. 42: 1–12. doi:10.3356/JRR-07-08.1. S2CID 84286796.
- ^ Apfelbaum, S. I.; Seelbach, P. (1983). "Nest Tree, Habitat Selection and Productivity of Seven North American Raptor Species Based on the Cornell University Nest Record Card Program". Raptor Research. 17 (4): 97–113.
- James, R. D. (1984). Habitat management guidelines for cavity-nesting birds in Ontario. Ontario ministry of natural resources.
- Bell, R. E. (1964). "A sound-triangulation method for counting Barred Owls". The Wilson Bulletin. 76 (3): 292–294. JSTOR 4159308.
- McComb, W. C.; Noble, R. E. (1981). "Microclimates of nest boxes and natural cavities in bottomland hardwoods". The Journal of Wildlife Management. 45 (1): 284–289. doi:10.2307/3807906. JSTOR 3807906.
- Sattler, Helen Roney (1995). The Book of North American Owls. Clarion Books. p. 41. ISBN 0-395-60524-5.
- ^ Robertson, W. B. (1959). "Barred Owl nesting on the ground". The Auk. 76 (2): 227–230. doi:10.2307/4081780. JSTOR 4081780.
- Houston, C. S. (1999). "Barred Owl nest in attic of shed". Wilson Bulletin. 111 (2): 272–273.
- Shackelford, C. E. (1996). "Barred Owl nest in a natural hole in an earthen bank in eastern Texas". J. Raptor Res. 30 (1): 41.
- Johnson, D. H.; Follen, D. G. (1984). "Barred Owls and nest boxes" (PDF). Raptor Res. 18 (1): 34–35.
- ^ Johnson, D. H. (1987). "Barred Owls and Nest Boxes-Results of a Five-Year Study In Minnesota". In Biology and Conservation of Northern Forest Owls: Symposium Proceedings: February 3–7, 1987, Winnipeg, Manitoba (Vol. 142, No. 3, p. 128). Fort Collins, Colo.: Rocky Mountain Forest and Range Experiment Station.
- "Barred Owl | Audubon Field Guide". www.audubon.org. Retrieved 2023-12-14.
- Robinson, C. (2004). "Barred Owl Mating Behaviour" (PDF). Ontario Birds. 22 (3): 154–156.
- Murray, G. A. (1976). "Geographic variation in the clutch size of seven owl species". Auk. 93 (3): 602–613. JSTOR 4084960.
- ^ Henderson, G. (1933). "Boldness of Barred Owls when danger threatens young" (PDF). Wilson Bulletin. 45: 143.
- Bird, D.M.; Wright, J.O. (1977). "Apparent distraction display by a Barred Owl". Canadian Field-Naturalist. 91 (2): 176–177. doi:10.5962/p.345368.
- ^ Varchmin, T. E. M. (1977). The Behavioral and Physical Development of Barred Owl (Strix Varia) Nestlings in Illinois (Doctoral dissertation, Western Illinois University).
- Barred Owl Factsheet Archived 2015-04-28 at the Wayback Machine, Lee and Rose Warner Nature Center, 2008
- ^ Hamer, Thomas E.; Forsman, Eric D. (April 1994). "Hybridization Between Barred and Spotted Owls" (PDF). The Auk. 111 (2): 487–492. doi:10.2307/4088616. JSTOR 4088616.
- Klimkiewicz, M. K.; Futcher, A. G. (1987). "Longevity Records of North American Birds: Coerebinae through Estrildidae" (PDF). Journal of Field Ornithology. 58 (3): 318–333. JSTOR 4513247.
- ^ Orfinger, Alexander B.; Helsel, Debbie; Breeding, Shawnlei F. (2018). "Longevity of the Barred Owl (Strix varia Barton, 1799) from captivity". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 130 (4): 1009. doi:10.1676/1559-4491.130.4.1009. S2CID 196672746.
- Stocek, R. F.; Cartwright, D. J. (1985). "Birds as nontarget catches in the New Brunswick furbearer harvest". Wildlife Society Bulletin. 13 (3): 314–317. JSTOR 3782498.
- Gibson, M. J.; Gibson, D. C.; Bardelmeier, D. G. (1998). "Prey conquers predator: A case study-Barred owl dies from rodent-inflicted wound". Journal of Wildlife Rehabilitation. 21 (3–4): 19–21.
- Lloyd, J. (2016). Cannibalism by a Barred Owl. Open.
- Hunter, D. B., McKeever, K., McKeever, L., & Crawshaw, G. (1987). "Disease susceptibility in owls". In: Biology and conservation of northern forest owls. RW Nero, RJ Clark, RJ Knapton, and RH Hamre (Eds). USDA, Forest Service General Technical Report RM-142. Fort Collins, Colorado, USA, 67–70.
- Lopes, Hugo; Redig, Pat; Glaser, Amy; Armien, Anibal; Wünschmann, Arno (2007). "Clinical findings, lesions, and viral antigen distribution in great gray owls (Strix nebulosa) and barred owls (Strix varia) with spontaneous West Nile virus infection". Avian Diseases. 51 (1): 140–145. doi:10.1637/0005-2086(2007)051[0140:CFLAVA]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 0005-2086. PMID 17461282. S2CID 34386856.
- Ellis, Angela E.; Mead, Daniel G.; Allison, Andrew B.; Stallknecht, David E.; Howerth, Elizabeth W. (2007). "Pathology and Epidemiology of Natural West Nile Viral Infection of Raptors in Georgia". Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 43 (2): 214–223. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-43.2.214. PMID 17495305. S2CID 10160266.
- Deem, Sharon L.; Heard, Darryl J.; Fox, Jonathan H. (1997). "Avian Pox in Eastern Screech Owls and Barred Owls from Florida". Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 33 (2): 323–327. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-33.2.323. PMID 9131568. S2CID 27579503.
- Brandão, João; Manickam, Bala; Blas-Machado, Uriel; Cohen, Eli; Mejia-Fava, Johanna; Divers, Stephen; Mayer, Jörg (2012). "Productive thyroid follicular carcinoma in a wild barred owl (Strix varia)". Journal of Veterinary Diagnostic Investigation. 24 (6): 1145–1150. doi:10.1177/1040638712463562. PMID 23051831. S2CID 24254967.
- James, Stephanie B.; Raphael, Bonnie L.; Clippinger, Tracy (2000). "Diagnosis and treatment of hepatic lipidosis in a barred owl (Strix varia)". Journal of Avian Medicine and Surgery. 14 (4): 268. doi:10.1647/1082-6742(2000)014[0268:DATOHL]2.0.CO;2. ISSN 1082-6742. S2CID 86350310.
- Brooks, D. E.; Murphy, C. J.; Quesenberry, K. E.; Walsh, M. T. (1983). "Surgical correction of a luxated cataractous lens in a barred owl". Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association. 183 (11): 1298–1299. PMID 6605960.
- Herman, C. M. (1944). "The blood protozoa of North American birds". Bird-banding. 15 (3): 89–112. doi:10.2307/4509831. JSTOR 4509831.
- Kinsella, J. M. (2001). "Parasitic helminths of five species of owls from Florida, USA". Comparative Parasitology. 68 (1): 130–133.
- Mikaelian, I.; Dubey, J. P.; Martineau, D. (1997). "Severe hepatitis resulting from toxoplasmosis in a barred owl (Strix varia) from Québec, Canada". Avian Diseases. 41 (3): 738–740. doi:10.2307/1592169. JSTOR 1592169. PMID 9356724.
- Niedringhaus, K. D. (2019). "Trichomonosis due to Trichomonas gallinae infection in barn owls (Tyto alba) and barred owls (Strix varia) from the eastern United States". Veterinary Parasitology: Regional Studies and Reports. 16: 100281. doi:10.1016/j.vprsr.2019.100281. PMID 31027606. S2CID 92499182.
- Lindsay, D. S. (1993). "Prevalence of encysted Toxoplasma gondii in raptors from Alabama". The Journal of Parasitology. 79 (6): 870–873. doi:10.2307/3283724. JSTOR 3283724. PMID 8277379.
- Pokras, M. A. (1993). "Trichomoniasis in owls: report on a number of clinical cases and a survey of the literature". Raptor Biomedicine: 88–91.
- Verma SK, Von Dohlen AR, Mowery JD, Scott D, Cerqueira-Cézar CK, Rosenthal BM, Dubey JP, Lindsay DS (2017). "Sarcocystis strixi n. sp. from a Barred Owl (Strix varia) Definitive Host and Interferon Gamma Gene Knockout Mice as Experimental Intermediate Host". Journal of Parasitology. 103 (6): 768–777. doi:10.1645/16-173. hdl:10919/97335. PMID 28783438. S2CID 20742726.
- Upton SJ, Campbell TW, Weigel M, McKown RD (1990). "The Eimeriidae (Apicomplexa) of raptors: review of the literature and description of new species of the genera Caryospora and Eimeria". Canadian Journal of Zoology. 68 (6): 1256–1265. doi:10.1139/z90-187.
- Telford SR Jr, Forrester DJ (1992). "Morphological comparisons of the Plasmodium (Novyella) species reported from North American birds, with comments on a species from the barred owl Strix varia Barton". Systematic Parasitology. 22 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1007/BF00009632. S2CID 22795312.
- Little, J. W.; Hopkins, S. H. (1939). "Trematodes from the barred owl, Strix varia. Texas: Brachylaima mcintoshi". Harkema: 154–156.
- Van Cleave, H. J.; Pratt, E. M. (1940). "A new species of the genus Centrorhynchus (Acanthocephala) from the barred owl". The Journal of Parasitology. 26 (4): 297–300. doi:10.2307/3272102. JSTOR 3272102.
- Pence, D. B.; Mollhagen, T.; Forrester, D. J. (1975). "Tetrameres (Gynaecophila) strigiphila sp. n. from the Florida barred owl, Strix varia georgica, with notes on the status of the subgenus Gynaecophila (Nematoda: Tetrameridae)". The Journal of Parasitology. 61 (3): 494–498. doi:10.2307/3279331. JSTOR 3279331.
- Chandler, A. C.; Rausch, R. (1947). "A study of strigeids from owls in north central United States". Transactions of the American Microscopical Society. 66 (3): 283–292. doi:10.2307/3223396. JSTOR 3223396.
- Little, J. W. (1975). "Trematodes from the Barred Owl, Strix varia in Texas: Brachylaima mcintoshi Harkema, 1939, and Neodiplostomum reflexum Chandler and Rausch, 1947". In Proceedings of the Oklahoma Academy of Science (Vol. 55, pp. 154–156).
- Shoop, W. L.; Corkum, K. C. (1980). "Tylodelphys immer Dubois 1961 (Trematoda: Diplostomidae) from the barred owl, Strix varia in Louisiana". Journal of Parasitology. 66 (4): 701–702. doi:10.2307/3280545. JSTOR 3280545. PMID 7420256.
- Holt, J. A. (2005). "New host records of chewing lice (Mallophaga) on birds in Florida III". Insecta Mundi. 19 (3): 186.
- Lewicki, K. E. (2013). Haemosporidian parasites of barred owls (Strix varia) and northern spotted owls (S. occidentalis caurina): Investigating the effects of an invasive species on parasite transmission and community dynamics. Doctoral dissertation, Colorado State University.
- Lewicki, Krista E.; Huyvaert, Kathryn P.; Piaggio, Antoinette J.; Diller, Lowell V.; Franklin, Alan B. (2015). "Effects of barred owl (Strix varia) range expansion on Haemoproteus parasite assemblage dynamics and transmission in barred and northern spotted owls (Strix occidentalis caurina)". Biological Invasions. 17 (6): 1713–1727. Bibcode:2015BiInv..17.1713L. doi:10.1007/s10530-014-0828-5. S2CID 254283674.
- The Cornell Lab of Ornithology. "Barred Owl, Life History". allaboutbirds.
- Kirk, David A.; Hyslop, Colleen (1998). "Population status and recent trends in Canadian raptors: A review". Biological Conservation. 83 (1): 91–118. Bibcode:1998BCons..83...91K. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(97)00051-7.
- ^ Sauer, John R.; Link, William A.; Fallon, Jane E.; Pardieck, Keith L.; Ziolkowski, David J. (2013). "The North American Breeding Bird Survey 1966–2011: Summary Analysis and Species Accounts". North American Fauna. 79: 1–32. doi:10.3996/nafa.79.0001.
- Sauer, J. R., Schwartz S., & Hoover, B. (1996). The Christmas Bird Count homepage. Version 95.1. Patuxent Wildlife Research Center, Laurel, MD.
- Livezey, K.B. (2005). "Iverson (2004) on Spotted Owls and Barred Owls: comments on methods and conclusion". Journal of Raptor Research. 39: 102–103.
- Kelly, E.G.; Forsman, E.D.; Anthony, R.G. (2003). "Are Barred Owls displacing Spotted Owls?" (PDF). The Condor. 105: 45. doi:10.1650/0010-5422(2003)105[45:ABODSO]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 86547489.
- Revised Recovery Plan for the Northern Spotted Owl (Strix occidentalis caurina). U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Portland, Oregon. (2011) p. vi
- Pearson, R. R.; Livezey, K. B. (2003). "Distribution, numbers, and site characteristics of spotted owls and barred owls in the Cascade Mountains of Washington". Journal of Raptor Research. 37 (4): 265–276.
- Buchanan, J.; Fleming, T.; Irwin, L. (2004). "A comparison of Barred and Spotted Owl nest-site characteristics in the Eastern Cascade Mountains, Washington". Journal of Raptor Research. 38: 231–237.
- ^ Herter, D. R.; Hicks, L. L. (2000). "Barred owl and spotted owl populations and habitat in the central Cascade Range of Washington". Journal of Raptor Research. 34 (4): 279–286.
- Livezey, K.B.; Fleming, T.L. (2009). "Effects of Barred Owls on Spotted Owls: The need for more than incidental detections and correlational analysis". Journal of Raptor Research. 41 (4): 319–325. doi:10.3356/0892-1016(2007)41[319:EOBOOS]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 86757049.
- Long, L.; Wolfe, J. (2019). "Review of the effects of barred owls on spotted owls" (PDF). Journal of Wildlife Management. 83 (6): 1281–1296. Bibcode:2019JWMan..83.1281L. doi:10.1002/jwmg.21715. S2CID 201192768. S2CID 221379957.. This review cites Mangan, A. O. (2018) Effects of habitat characteristics, weather and presence of Barred Owls (Strix varia) on occupancy dynamics and breeding propensity of Northern Spotted Owls (S. occidentalis caurina) in Mount Rainier National Park. Master's thesis. Oregon State University S2CID 199893769
- Gremel, S. Barred Owl Displaces Northern Spotted Owl at Olympic. Natural Resources Year in Review, U.S. National Park System.
- Monahan, W. B., & Hijmans, R. J. (2007). Distributional dynamics of invasion and hybridization by Strix spp. in western North America. Ornithological Monographs, 55–66.
- Livezey, Kent B.; Root, Terry L.; Gremel, Scott A.; Johnson, Craig (2008). "Natural range expansion of Barred Owls? A critique of Monahan and Hijmans (2007)". The Auk. 125: 230–232. doi:10.1525/auk.2008.125.1.230. S2CID 86273621.
- Peterson, A. Townsend & Robins, C. Richard (2003). "Using Ecological-Niche Modeling to Predict Barred Owl Invasions with Implications for Spotted Owl Conservation" (PDF). Conservation Biology. 17 (4): 1161–1165. Bibcode:2003ConBi..17.1161P. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1739.2003.02206.x. S2CID 86528384. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-06-27.
- Van Lanen, N. J. (2010). Out with the old and in with the new?: investigating competition between Barred Owls (Strix varia) and Northern Spotted Owls (Strix occidentalis caurina) in northwestern California with a playback experiment. Doctoral dissertation, Colorado State University. hdl:10217/38187
- Van Lanen, Nicholas J.; Franklin, Alan B.; Huyvaert, Kathryn P.; Reiser, Raoul F.; Carlson, Peter C. (2011). "Who hits and hoots at whom? Potential for interference competition between barred and northern spotted owls". Biological Conservation. 144 (9): 2194–2201. Bibcode:2011BCons.144.2194V. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2011.05.011. S2CID 53326444.
- "US Government Wants Hunters to Shoot 500,000 Owls". Newsweek. December 7, 2023. Retrieved December 10, 2023.
Barred owls are an invasive species in the Pacific Northwest, originating on the U.S. East Coast, and they pose a huge threat to native protected species, including northern spotted owls.
- Interbreeding Threatens Rare Species, Experts Claim, Guynup, Sharon, National Geographic
- Kelly EG, Forsman ED (2004). "Recent records of hybridization between barred owls (Strix varia) and northern spotted owls (S. occidentalis caurina)". Auk. 121 (3): 806–810. doi:10.1642/0004-8038(2004)121[0806:RROHBB]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 86769738.
- Seamans, M. E.; Corcoran, J.; Rex, A. (2004). "Southernmost record of a spotted owl × barred owl hybrid in the Sierra Nevada". Western Birds. 35: 173–174.
- Funk, W. Chris; Mullins, Thomas D.; Forsman, Eric D.; Haig, Susan M. (2007). "Microsatellite loci for distinguishing spotted owls (Strix occidentalis), barred owls (Strix varia), and their hybrids". Molecular Ecology Notes. 7 (2): 284–286. doi:10.1111/j.1471-8286.2006.01581.x.
- Haig, Susan M.; Mullins, Thomas D.; Forsman, Eric D.; Trail, Pepper W.; Wennerberg, LIV (2004). "Genetic Identification of Spotted Owls, Barred Owls, and Their Hybrids: Legal Implications of Hybrid Identity". Conservation Biology. 18 (5): 1347–1357. Bibcode:2004ConBi..18.1347H. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1739.2004.00206.x. S2CID 43989899.
- Hanna, Zachary R.; Dumbacher, John P.; Bowie, Rauri C K.; Henderson, James B.; Wall, Jeffrey D. (2018). "Whole-Genome Analysis of Introgression Between the Spotted Owl and Barred Owl (Strix occidentalis and Strix varia, Respectively; Aves: Strigidae) in Western North America". G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics. 8 (12): 3945–3952. doi:10.1534/g3.118.200754. PMC 6288836. PMID 30355766.
- Hanna, Z. R. (2017). Genomics of the Spotted Owl (Strix occidentalis) and Barred Owl (Strix varia) in Western North America. Doctoral dissertation, UC Berkeley.
- "Brooklyn Museum". Collections: American Art: Barred Owl.
- "Do Owls Eat Raccoons? The Surprising Truth! | Learn Bird Watching". 7 May 2023.
External links
- Barred Owl – Strix varia. USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- Barred Owl Species Account. Cornell Lab of Ornithology
- "Barred Owl media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Barred Owl photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)