| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Thermoplastic" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (March 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
A thermoplastic, or thermosoftening plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate by intermolecular forces, which weaken rapidly with increased temperature, yielding a viscous liquid. In this state, thermoplastics may be reshaped, and are typically used to produce parts by various polymer processing techniques such as injection molding, compression molding, calendering, and extrusion. Thermoplastics differ from thermosetting polymers (or "thermosets"), which form irreversible chemical bonds during the curing process. Thermosets do not melt when heated, but typically decompose and do not reform upon cooling.
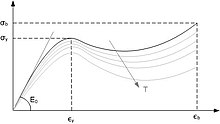
Above its glass transition temperature and below its melting point, the physical properties of a thermoplastic change drastically without an associated phase change. Some thermoplastics do not fully crystallize below the glass transition temperature, retaining some or all of their amorphous characteristics. Amorphous and semi-amorphous plastics are used when high optical clarity is necessary, as light is scattered strongly by crystallites larger than its wavelength. Amorphous and semi-amorphous plastics are less resistant to chemical attack and environmental stress cracking because they lack a crystalline structure.
Brittleness can be decreased with the addition of plasticizers, which increases the mobility of amorphous chain segments to effectively lower the glass transition temperature. Modification of the polymer through copolymerization or through the addition of non-reactive side chains to monomers before polymerization can also lower it. Before these techniques were employed, plastic automobile parts would often crack when exposed to cold temperatures. These are linear or slightly branched long chain molecules capable of repeatedly softening on heating and hardening on cooling.
Acrylic
Today's acrylics industry can be divided into two distinct multibillion-dollar markets: on one hand the polyacrylic acids (PAA) and its ester derivatives (PAc) market, on the other hand, the poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) market. PMMA is also known by trade names such as Lucite, Perspex and Plexiglas. It serves as a sturdy substitute for glass for items such as aquariums, buttons, motorcycle helmet visors, aircraft windows, viewing ports of submersibles, and lenses of exterior lights of automobiles. It is extensively used to make signs, including lettering and logos. In medicine, it is used in bone cement and to replace eye lenses. Acrylic paint consists of PMMA particles suspended in water.
For many decades, PMMA has been the predominant methacrylic ester produced worldwide. Major players in the PMMA market are Mitsubishi Rayon (Japan), Arkema SA (France), LG MMA (South Korea), Chi Mei Corp. (Taiwan), Sumimoto Chemical Company Ltd (Japan), Evonik Industries (Germany), BASF (Germany), Dow Chemical Company (U.S.), AkzoNobel (The Netherlands), Quinn Plastics (UK) and Cytec Industries (U.S.). Regarding the PAA and PAc market, key manufacturers are Nippon Shokubai Company Ltd. (Japan), Arkema SA (France) and Dow Chemical Company (U.S.)
ABS
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is a terpolymer synthesized from styrene and acrylonitrile in the presence of polybutadiene. ABS is a light-weight material that exhibits high impact resistance and mechanical toughness. It poses few risks to human health under normal handling. It is used in many consumer products, such as toys, appliances, and telephones.
Nylon
Nylon belongs to a class of polymers called polyamides. It has served as a substitute mainly for hemp, cotton and silk, in products such as parachutes, cords, sails, flak vests and clothing. Nylon fibres are useful in making fabrics, rope, carpets and musical strings, whereas, in bulk form, nylon is used for mechanical parts including machine screws, gears and power tool casings. In addition, it is used in the manufacture of heat-resistant composite materials.
PLA
Polylactic acid (polylactide) is a compostable thermoplastic aliphatic polyester derived from renewable resources, such as corn starch (in the United States), sugar beet pulp (in Europe), tapioca roots, chips or starch (mostly in Asia), or sugarcane. It is the most common material used for 3D printing with fused deposition modeling (FDM) techniques.
Polybenzimidazole
Polybenzimidazole (PBI, short for Poly-) fiber is a synthetic fiber with a very high melting point. It has exceptional thermal and chemical stability and does not readily ignite. It was first discovered by American polymer chemist Carl Shipp Marvel in the pursuit of new materials with superior stability, retention of stiffness, toughness at elevated temperature. Due to its high stability, polybenzimidazole is used to fabricate high-performance protective apparel such as firefighter's gear, astronaut space suits, high temperature protective gloves, welders' apparel and aircraft wall fabrics. In recent years, polybenzimidazole found its application as membrane in fuel cells.
Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate (PC) thermoplastics are known under trademarks such as Lexan, Makrolon, Makroclear, and arcoPlus. They are easily worked, molded, and thermoformed for many applications, such as electronic components, construction materials, data storage devices, automotive and aircraft parts, check sockets in prosthetics, and security glazing. Polycarbonates do not have a unique resin identification code. Items made from polycarbonate can contain the precursor monomer bisphenol A (BPA). Susceptible to UV light, exposure results in yellowing (degradation is especially visible in headlamps that lost or didn't have proper protective coating).
Polyether sulfone
Polyether sulfone (PES) or polysulfone is a class of specially engineered thermoplastics with high thermal, oxidative, and hydrolytic stability, and good resistance to aqueous mineral acids, alkalis, salt solutions, oils and greases.
Polyoxymethylene
Polyoxymethylene (POM), also known as acetal, polyacetal and polyformaldehyde, is an engineering thermoplastic used in precision parts requiring high stiffness, low friction, and excellent dimensional stability. As with many other synthetic polymers, it is produced by different chemical firms with slightly different formulas and sold variously by such names as Delrin, Celcon, Ramtal, Duracon, Kepital and Hostaform.
Polyether ether ketone
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a colourless organic thermoplastic polymer in the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) family, used in engineering applications. It was originally introduced by Victrex PLC, then ICI (Imperial Chemical Industries) in the early 1980s. It has attractive properties like good abrasion resistance, low flammability and emission of smoke and toxic gases.
Polyetherimide
Polyetherimide (PEI), produced by a novel nitro displacement reaction involving bisphenol A, 4, 4’-methylenedianiline and 3-nitrophthalic anhydride, has high heat distortion temperature, tensile strength and modulus. They are generally used in high performance electrical and electronic parts, microwave appliances, and under-the-hood automotive parts.
Polyethylene
Polyethylene (polyethene, polythene, PE) is a family of similar materials categorized according to their density and molecular structure. It is also known as poly and is obtained by the addition polymerisation of ethylene. It may be of low density or high density depending upon the process used in its manufacturing. It is resistant to moisture and most of the chemicals. It is flexible at room temperature (and low temperature) and can be heat sealed. Since it is an inexpensive plastic it is made in large amounts to cater to the demand. For example:
- ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) is tough and resistant to chemicals. It is used to manufacture moving machine parts, bearings, gears, artificial joints and some bulletproof vests.
- High-density polyethylene (HDPE), recyclable plastic no. 2, is commonly used as milk jugs, liquid laundry detergent bottles, outdoor furniture, margarine tubs, portable gasoline cans, drinking water distribution systems, water drainage pipes, and grocery bags.
- Medium-density polyethylene (MDPE) is used for packaging film, sacks and gas pipes and fittings.
- Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is flexible and is used in the manufacture of squeeze bottles, milk jug caps, retail store bags and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) as stretch wrap in transporting and handling boxes of durable goods, and as the common household food covering.
Polyphenylene oxide
Polyphenylene oxide (PPO), which is obtained from the free-radical, step-growth oxidative coupling polymerization of 2,6-xylenol, has many attractive properties such as high heat distortion and impact strength, chemical stability to mineral and organic acids, and low water absorption. PPO is difficult to process, and hence the commercial resin (Noryl) is made by blending PPO with high-impact polystyrene (HIPS), which serves to reduce the processing temperature.
Polyphenylene sulfide
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) obtained by the condensation polymerization of p-dichlorobenzene and sodium sulfide, has outstanding chemical resistance, good electrical properties, excellent flame retardance, low coefficient of friction and high transparency to microwave radiation. PPS is principally used in coating applications. This is done by spraying an aqueous slurry of PPS particles and heating to temperatures above 370 °C. Particular grades of PPS can be used in injection and compression molding at temperatures (300 to 370 °C) at which PPS particles soften and undergo apparent crosslinking. Principal applications of injection and compression molded PPS include cookware, bearings, and pump parts for service in various corrosive environments.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP) is useful for such diverse products as reusable plastic food containers, microwave- and dishwasher-safe plastic containers, diaper lining, sanitary pad lining and casing, ropes, carpets, plastic moldings, piping systems, car batteries, insulation for electrical cables and filters for gases and liquids. In medicine, it is used in hernia treatment and to make heat-resistant medical equipment. Polypropylene sheets are used for stationery folders and packaging and clear storage bins. Polypropylene is defined by the recyclable plastic number 5. Although relatively inert, it is vulnerable to ultraviolet radiation and can degrade considerably in direct sunlight. Polypropylene is not as impact-resistant as the polyethylenes (HDPE, LDPE). It is also somewhat permeable to highly volatile gases and liquids.
Polystyrene
Polystyrene is manufactured in various forms that have different applications and can have medium to very low density. Extruded polystyrene (PS or xPS, sometimes colored pink/blue) is used in the manufacture of disposable cutlery, rigid ground contact rated insulating foam board, CD and DVD cases, plastic models of cars and boats, and smoke detector housings. Expanded polystyrene foam (EPS or "styrofoam", white) is used in making insulation and packaging materials, such as the "peanuts" and molded foam used to cushion fragile products. Polystyrene copolymers are used in the manufacture of toys and product casings.
Polyvinyl chloride
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a tough, lightweight material that is durable, fairly rigid and versatile, and is resistant to acids and bases. Much of it is used by the construction industry, such as for vinyl siding, drainpipes, gutters and roofing sheets. It is also converted to flexible forms with the addition of plasticizers, thereby making it useful for items such as hoses, tubing, electrical insulation, coats, jackets and upholstery. Flexible PVC is also used in inflatable products, such as water beds and pool toys. PVC is also a common material in vinyl action figures, especially in countries such as Japan, where the material is used extensively in so-called Sofubi figures (Soft vinyl toys). As PVC bends easily and has a tendency to be bent during transit, a method to mitigate this deformation is to heat the plastic until it becomes mobile, then reform the material into the desired shape.
PVC is produced in many specific modifications to affect its chemical and physical properties. In plasticized polyvinyl chloride (pPVC), plasticizers are added to the raw material before molding to make it more flexible or pliable. Early on, the health and environmental aspects of this were poorly understood and replacements and product bans resulted after studies. The original form is often referred to as unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (uPVC), which is the more commonly used type for installations such as water, waste, and sewer conveyance plumbing.
Chemical modification often produces more drastic changes in properties. Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) is produced through exposing PVC to the continued free-radical chlorination reaction that originally formulates the PVC polymer. The chlorination reaction continues to add chlorine atoms to the polymer hydrocarbon backbone until most commercial applications reach a percent range between 56 and 74% total chlorine. This increase in elemental chlorine content contributes to CPVC's increased expression of chlorine-based characteristics, such as chemical durability, resistance to acids, bases, and salts; susceptibility to ammonia-based compounds, aromatics, esters, ketones; chemical stability; heat energy transfer resistance. CPVC is commonly used in water, chemical, hot and cold, delivery systems for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Polyvinylidene fluoride
Polyvinylidene fluoride, PVDF, belongs to the fluoropolymer class of thermoplastics and is known for its high chemical inertness and resistance. PVDF is obtained through the polymerization of the vinylidene fluoride monomer. PVDF thermoplastic is fabricated into sheets and pipes for engineering uses as well as powders and coatings that can be dissolved in solvents and applied across a product surface. PVDF is widely used in the chemical industry as piping for aggressive chemicals and high purity liquids. The PVDF material is used in construction, transportation, chemical processes, electricity, batteries, waste water and treatment.
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene is commonly recognized under the brand name Teflon. PTFE is hydrophobic: aqueous liquids do not wet the material, as fluorocarbons demonstrate mitigated London dispersion forces due to the high electronegativity of fluorine. This also supports its use in coatings of cooking ware. The polymer has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid and is therefore commonly used for bearings and support of moving mechanical parts.
See also
References
- "Thermosoftening plastics and Thermosetting plastics" (PDF). lgschemistry.org.uk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 September 2008. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- Baeurle SA, Hotta A, Gusev AA (2006). "On the glassy state of multiphase and pure polymer materials". Polymer. 47 (17): 6243–6253. doi:10.1016/j.polymer.2006.05.076.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - A. V. Shenoy and D. R. Saini (1996), Thermoplastic Melt Rheology and Processing, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York. Archived 2015-04-14 at the Wayback Machine
- Charles P. MacDermott and Aroon V. Shenoy (1997), Selecting Thermoplastics for Engineering Applications, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York. Archived 2015-04-14 at the Wayback Machine
- Handbook of Thermoplastics, Second Edition, O. Olabisi & K. Adewale (Ed.) CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, Florida, U. S. A. ISBN 978-1-4665-7722-0, 2016
- Saini D.R., Shenoy A.V. (1985). "Melt Rheology of Some Specialty Polymers". Journal of Elastomers & Plastics. 17 (3): 189–217. doi:10.1177/009524438501700305. S2CID 136747839.
- j.lerouge (2020-12-26). "What the Heck Is Sofubi?! 10 Things You Didn't Know About Soft Vinyl". Invasion Toys News. Retrieved 2022-07-08.
- "How does CPVC piping compare to metal piping?". Corzan Industrial Systems.
- "Chemical Resistance of Thermoplastics Piping Materials TR-19/2007" (PDF). Plastic Pipe Institute, Inc. (PPI).
- "PVDF Performance Characteristics & Data" (PDF). Arkema.
External links
 Media related to Thermoplastic at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Thermoplastic at Wikimedia Commons

