Transport in Slovakia is possible by rail, road, air, or rivers. Slovakia is a developed Central European country with a well-developed rail network (3,662 km) and a highway system (854 km). The main international airport is the M. R. Štefánik Airport in the capital, Bratislava. The most important waterway is the river Danube, which is used by passenger, cargo, and freight ships. The two most important harbours in Slovakia are Komarno harbour and Bratislava harbour.
Railways
Main article: Rail transport in Slovakia Further information: Železnice Slovenskej republiky

- Total: 3,662 km (2008)
- Broad gauge: 99 km of 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) gauge - used for freight transport only, see Uzhhorod - Košice broad gauge track
- Standard gauge: 3,473 km of 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) gauge (1,588 km electrified; 1,011 km double track)
- Narrow gauge: 50 km (45 km of 1,000 mm (3 ft 3+3⁄8 in) gauge; 5 km of 760 mm (2 ft 5+15⁄16 in) gauge)
Slovakia has a range of railway connections that provide access to all of Slovakia in the country and from the rest of Europe. There are many railway operators that control railways across the country, with the main railway operator being ZSSK. The railway network is very dense in the western and eastern parts of Slovakia but is less accessible in central Slovakia. The singular high-speed rail line in Slovakia is the Rychlik between Bratislava and Kosice (Via Zillina). The top speed of the line is 200 km/h (120 mph). The Rychlik was established in 2002 after ZSSK took over ZSR. Most of the country's railways run on Tas REX (Regional Express) which operates at speeds between 140 and 160 km/h (87 and 99 mph).
Train operators

- Passenger
- ZSSK Rychlik - High-speed rail passenger trains
- ZSSK REX - Regional express trains
- Leo Express - Intercity railway
- Regio jet - Intercity trains
- Railjet - High-speed rail passenger trains operated by the OBB
- Cargo
The main cargo train operator for the cargo freight rail in Slovakia is ZSSK cargo.
Roads
See also: List of first class roads in Slovakia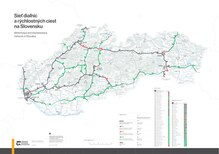
- Total: 43,761 km
- Paved: 38,085 km (including 384 km of express-ways)
- Unpaved: 5,676 km
Slovakia has a total of 43,761 km of roads in the country with 3,336.6 km being main or national roads, 13,958.7 km being secondary and regional roads, and 861.2 km (535.1 mi) being highways, with the rest being other types of roads.
Highways
Main article: Highways in Slovakia

 Motorways in Slovakia
543 km (337 mi) (2022)
Motorways in Slovakia
543 km (337 mi) (2022)
- D1: Bratislava - Trnava - Trenčín - Považská Bystrica - Žilina, Liptovský Mikuláš - Jánovce, Prešov - Košice - Záhor(SK/UA border)
- D2: Kúty (CZ/SK border) - Malacky - Bratislava - Jarovce (SK/H border)
- D3: Dolný Hričov - Žilina - Čadca - Skalité(SK/PL border)
- D4: Jarovce - (SK/A border)
 Expressways in Slovakia 311 km (193 mi)
Expressways in Slovakia 311 km (193 mi)
- R1: Trnava - Nitra - Zvolen - Banská Bystrica
- R2: (SK/CZ border) - Trenčín - Prievidza - Zvolen - Rimavská Sobota - Košice
- R3: (SK/H border) - Zvolen - Martin - (SK/PL border)
- R4: (SK/H border) - Košice - Prešov - Svidník - (SK/PL border)
- R5: Svrčinovec - (SK/CZ border)
- R6: Beluša - Púchov - (SK/CZ border)
- R7: Bratislava - Nové Zámky - Krupina - Lučenec
- R8: Nitra - Topoľčany - Bánovce nad Bebravou
Airports
Main article: List of airports in Slovakia

Slovakia has three international airports. Bratislava Airport is the main and largest international airport. It is located nine kilometres (5+1⁄2 miles) northeast of the city centre. It serves civil and governmental, scheduled and unscheduled domestic and international flights. The current runways support the landing of all common types of aircraft currently used. The airport has enjoyed rapidly growing passenger traffic in recent years; it served 279,028 passengers in 2000 and 2,292,712 in 2018.
Košice International Airport is an airport serving Košice. It is the second-largest international airport in Slovakia.
The Poprad–Tatry Airport is the third busiest airport, the airport is located 5 km west-northwest of Poprad. It is an airport with one of the highest elevations in Central Europe, at 718 m, which is 150 m higher than Innsbruck Airport in Austria.
Ports and harbours

Waterways
- The Danube waterway is 172 km and is used by passenger, cargo, and freight ships of nearly all sizes.
Pipelines
- Petroleum products 416 km; natural gas 6,769 km (2010)
- Gas pipelines 162 km Poland Slovakia interconnector
- Crude oil 19 km Druzhba pipeline
Public transport
Buses and trolleybuses

Most towns and cities in Slovakia have well-developed bus networks. Most of the buses are operated by the city or town council but most regional buses are operated by private operators with the permission of local authorities and/or the county council. There is also a trolleybus system which only operates in large cities and is operated by the town council. They are more of an ecological system of transport than a standard bus.
Tram


Trams are only found in Bratislava and Košice. The first tram to arrive in Slovakia was in 1895 in Bratislava and then later on in 1913 trams arrived in Košice. Today the tram network is expanding rapidly in both cities.
See also
References
- "Regionálny expres (REX)". Rail.cc. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- "Train Categories". ZSSK. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- "ROAD NETWORK - SLOVAK REPUBLIC". cdb.sk. Slovenská správa ciest (Slovak Road Administration). Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- "Letisko Bratislava – O letisku – Štatistické údaje (Airport Bratislava – About airport – Statistical data)". Letisko M.R. Štefánika – Airport Bratislava. 2008. Archived from the original on 3 September 2011. Retrieved 19 January 2008.
- "SLOVAKIA". icpdr.org. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- "Danube Facts and Figures" (PDF). icpdr.org. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
This article incorporates public domain material from The World Factbook. CIA.
External links
| Transport in Europe | |
|---|---|
| Sovereign states |
|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
| Other entities | |


