| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (August 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Treaty concerning the accession of the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia and the Slovak Republic to the European Union
Treaty between the Kingdom of Belgium, the Kingdom of Denmark, the Federal Republic of Germany, the Hellenic Republic, the Kingdom of Spain, the French Republic, Ireland, the Italian Republic, the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Kingdom of the Netherlands, the Republic of Austria, the Portuguese Republic, the Republic of Finland, the Kingdom of Sweden, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (Member States of the European Union) and the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia, the Slovak Republic, concerning the accession of the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia and the Slovak Republic to the European Union. | |
|---|---|
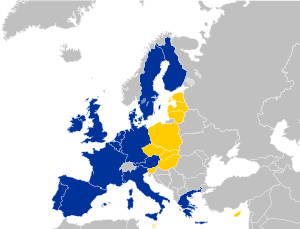 Countries involved in the treaty, with newly joining countries in yellow, and existing EU countries in blue. Countries involved in the treaty, with newly joining countries in yellow, and existing EU countries in blue. | |
| Type | Accession treaty |
| Signed | 16 April 2003 |
| Location | Athens |
| Effective | 1 May 2004 |
| Condition | Ratification by the 10 acceding countries and the 15 member countries of the European Union |
| Signatories | |
| Ratifiers | 25 / 25 |
| Depositary | Government of the Italian Republic |
| Languages | Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, Estonian, Finnish, French, German, Greek, Hungarian, Italian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Maltese, Polish, Portuguese, Slovak, Slovene, Spanish, Swedish |
After amendments made by the Athens Treaty: Consolidated version of TEC (2006) Consolidated version of TEU (2006) Consolidated version of Protocols & Annexes (2006) | |
The Treaty of Accession 2003 was the agreement between the member states of the European Union and ten countries (Czech Republic, Estonia, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Hungary, Malta, Poland, Slovenia, Slovakia), concerning these countries' accession into the EU (see 2004 enlargement of the European Union). At the same time it changed a number of points which were originally laid down in the Treaty of Nice. The treaty was signed on 16 April 2003 in Athens, Greece and it entered into force on 1 May 2004, resulting in enlargement of the European Union with 10 states.
Background


The European Union comprises a large number of overlapping legal structures which is a result of it being defined by successive international treaties.

Member States
As well as other acts which together form the current legal framework (acquis) of the EU, the Treaty of Accession 2003 modifies:
- the Treaty of Rome (establishing the European Economic Community),
- the Euratom Treaty (establishing the European Atomic Energy Community)
- the Maastricht Treaty (establishing the European Union)
All changes to the above treaties are made by article 11-19 in part two of the accession treaty. Beside of revising voting weights and the number of member state representatives at all European institutions, the most notable change outlined how Qualified Majority Voting shall be handled in the Council of the European Union. As from 1 November 2004, whenever the Council vote to adopt a decision by Qualified Majority, this need support both from a majority of member states which at the same time represents minimum 232 out of 321 weighted votes (72,3%), while also as a third requirement those states must represent at least 62% of the total population of the Union. Otherwise the decision in question shall not be adopted.
The Treaty's full name in English is:
- Treaty between the Kingdom of Belgium, the Kingdom of Denmark, the Federal Republic of Germany, the Hellenic Republic, the Kingdom of Spain, the French Republic, Ireland, the Italian Republic, the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, the Kingdom of the Netherlands, the Republic of Austria, the Portuguese Republic, the Republic of Finland, the Kingdom of Sweden, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (Member States of the European Union) and the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia, the Slovak Republic, concerning the accession of the Czech Republic, the Republic of Estonia, the Republic of Cyprus, the Republic of Latvia, the Republic of Lithuania, the Republic of Hungary, the Republic of Malta, the Republic of Poland, the Republic of Slovenia and the Slovak Republic to the European Union.
See also
- The Treaty of Accession was selected as a main motif in numerous collectors' coins. One of sample is the €10 Greece EU Presidency commemorative coin, minted in 2003 to celebrate the event. In the obverse of the coin is written in English and Greek "Hellenic Presidency of E.U." with the official insignia of the Greek presidency of the Council of the European Union in 2003 shown in the center.
- European integration
- European Union law
- 2004 enlargement of the European Union
- Treaty of Accession 2005
- Treaty of Accession 2011
References
- "Article 2 of Treaty of Accession", europarl.europa.eu, retrieved 2024-10-06
- "EUR-Lex - L:2003:236:TOC - EN - EUR-Lex". eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 2022-03-21.
External links
- Treaty of accession 2003
- Consolidated version of the Treaties following the Treaty of Accession
- Summary by Orgalime including voting weights under the Treaty of Accession
- Treaty concerning the accession of 10 new countries to the European Union on CVCE : European integration studies website
| Treaties of Hungary | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9–10th century (age of Magyars) | |||||||||
| 1000–1301 (Árpád dynasty) |
| ||||||||
| 1302–1526 (Middle ages to Tripartition) |
| ||||||||
| Dual reign, Ottoman vassalship, reconquest and Napoleonic Wars (1526–1848) |
| ||||||||
| Austria-Hungary to the end of World War I (1848–1922) |
| ||||||||
| Modern age (1922–) | |||||||||
- Treaties of Accession to the European Union
- Treaties of Estonia
- Treaties of the Czech Republic
- Treaties of Latvia
- Treaties of Cyprus
- Treaties of Lithuania
- Treaties of Malta
- Treaties of Slovenia
- Treaties of Slovakia
- History of Poland (1989–present)
- 2000s in Athens
- Treaties concluded in 2003
- Treaties entered into force in 2004
- 2003 in the European Union
- 2004 in the European Union
- Treaties of Poland
- Treaties of Hungary




