| This article relies largely or entirely on a single source. Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Please help improve this article by introducing citations to additional sources. Find sources: "Trinitroethylorthocarbonate" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (May 2017) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name 2,2,2-Trinitroethyl orthocarbonate | |
| Preferred IUPAC name 1,1,1-Trinitro-2-ethane | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem CID | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
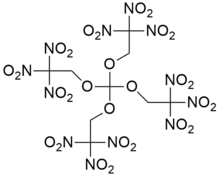
| Chemical formula | C(OCH2C(NO2)3)4 |
| Molar mass | 732.219 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
| Melting point | 161 °C (322 °F; 434 K) |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa). Infobox references | |
Trinitroethylorthocarbonate also known as TNEOC is an organic compound with the chemical formula C(OCH2C(NO2)3)4. It is an oxidizer with excellent chemical stability. Its explosion point is 238 °C, and it begins to be decomposed at 200 °C. Its explosion heat is 5.797 J/g and specific volume is 694 L/kg. Its structure is closely related to that of trinitroethylorthoformate (TNEOF). Both are highly explosive and very shock-sensitive, and may be dissolved in nitroalkanes to reduce their shock-sensitivity.
Synthesis
Trinitroethanol reacts with carbon tetrachloride under a catalyst of FeCl3.
References
- ^ Liu, Jiping (2015). Liquid Explosives. Springer. pp. 5, 6, 8, 136, 309. ISBN 9783662458471. Retrieved 26 March 2016.
This organic chemistry article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
This explosives-related article is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |
