| United States District Court for the Middle District of Alabama | |
|---|---|
| (M.D. Ala.) | |
 | |
 | |
| Location | Frank M. Johnson Jr. Federal Building and U.S. Courthouse(Montgomery)More locations |
| Appeals to | Eleventh Circuit |
| Established | February 6, 1839 |
| Judges | 3 |
| Chief Judge | Emily C. Marks |
| Officers of the court | |
| U.S. Attorney | Jonathan S. Ross (Acting) |
| U.S. Marshal | Jesse Seroyer Jr. |
| almd.uscourts.gov | |
The United States District Court for the Middle District of Alabama (in case citations, M.D. Ala.) is a United States district court in the Eleventh Circuit (except for patent claims and claims against the U.S. government under the Tucker Act, which are appealed to the Federal Circuit).
The District was established on February 6, 1839.
The United States Attorney's Office for the Middle District of Alabama represents the United States in civil and criminal litigation in the court. As of September 30, 2023 the United States attorney is Jonathan S. Ross.
Organization of the court
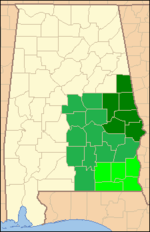
The United States District Court for the Middle District of Alabama is one of three federal judicial districts in Alabama. Court for the District is held at Dothan, Montgomery, and Opelika.
Eastern Division comprises the following counties: Chambers, Lee, Macon, Randolph, Russell, and Tallapoosa.
Northern Division comprises the following counties: Autauga, Barbour, Bullock, Butler, Chilton, Coosa, Covington, Crenshaw, Elmore, Lowndes, Montgomery, and Pike.
Southern Division comprises the following counties: Coffee, Dale, Geneva, Henry, and Houston.
Current judges
As of June 30, 2020:
| # | Title | Judge | Duty station | Born | Term of service | Appointed by | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active | Chief | Senior | ||||||
| 20 | Chief Judge | Emily C. Marks | Montgomery | 1973 | 2018–present | 2019–present | — | Trump |
| 22 | District Judge | R. Austin Huffaker Jr. | Montgomery | 1973 | 2019–present | — | — | Trump |
| 23 | District Judge | vacant | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 14 | Senior Judge | Myron H. Thompson | Montgomery | 1947 | 1980–2013 | 1991–1998 | 2013–present | Carter |
| 16 | Senior Judge | Harold Albritton | Montgomery | 1936 | 1991–2004 | 1998–2004 | 2004–present | G.H.W. Bush |
| 19 | Senior Judge | William Keith Watkins | Montgomery | 1951 | 2005–2019 | 2011–2019 | 2019–present | G.W. Bush |
Vacancies and pending nominations
| Seat | Prior judge's duty station | Seat last held by | Vacancy reason | Date of vacancy | Nominee | Nominated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | Montgomery | Andrew L. Brasher | Elevation | June 30, 2020 | – | – |
Former judges
| # | Judge | State | Born–died | Active service | Chief Judge | Senior status | Appointed by | Reason for termination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | William Crawford | AL | 1784–1849 | 1839–1849 | — | — | J.Q. Adams/Operation of law | death |
| 2 | John Gayle | AL | 1792–1859 | 1849–1859 | — | — | Taylor | death |
| 3 | William Giles Jones | AL | 1808–1883 | 1859–1861 | — | — | Buchanan | resignation |
| 4 | George Washington Lane | AL | 1806–1863 | 1861–1863 | — | — | Lincoln | death |
| 5 | Richard Busteed | AL | 1822–1898 | 1863–1874 | — | — | Lincoln | resignation |
| 6 | John Bruce | AL | 1832–1901 | 1875–1901 | — | — | Grant | death |
| 7 | Thomas G. Jones | AL | 1844–1914 | 1901–1914 | — | — | T. Roosevelt | death |
| 8 | Henry De Lamar Clayton Jr. | AL | 1857–1929 | 1914–1929 | — | — | Wilson | death |
| 9 | Charles Brents Kennamer | AL | 1874–1955 | 1931–1955 | — | — | Hoover | death |
| 10 | Frank Minis Johnson | AL | 1918–1999 | 1955–1979 | 1966–1979 | — | Eisenhower | elevation to 5th Cir. |
| 11 | Thomas Virgil Pittman | AL | 1916–2012 | 1966–1970 | — | — | L. Johnson | seat abolished |
| 12 | Robert Edward Varner | AL | 1921–2006 | 1971–1986 | 1979–1984 | 1986–2006 | Nixon | death |
| 13 | Truman McGill Hobbs | AL | 1921–2015 | 1980–1991 | 1984–1991 | 1991–2015 | Carter | death |
| 15 | Joel Fredrick Dubina | AL | 1947–present | 1986–1990 | — | — | Reagan | elevation to 11th Cir. |
| 17 | Ira De Ment | AL | 1931–2011 | 1992–2002 | — | 2002–2011 | G.H.W. Bush | death |
| 18 | Mark Fuller | AL | 1958–present | 2002–2015 | 2004–2011 | — | G.W. Bush | resignation |
| 21 | Andrew L. Brasher | AL | 1981–present | 2019–2020 | — | — | Trump | elevation to 11th Cir. |
- ^ Jointly appointed to the Middle, Northern, and Southern Districts of Alabama.
- Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 23, 1860, confirmed by the United States Senate on January 30, 1860, and received commission on January 30, 1860.
- Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 5, 1864, confirmed by the Senate on January 20, 1864, and received commission on January 20, 1864.
- ^ Jointly appointed to the Middle and Northern Districts of Alabama.
- From 1875 to 1886, Judge Bruce was jointly appointed to the Southern District of Alabama.
- Recess appointment; formally nominated on December 5, 1901, confirmed by the Senate on December 17, 1901, and received commission the same day.
- From 1931 to 1936, Judge Kennamer was jointly appointed to the Middle and Northern Districts of Alabama.
- Recess appointment; formally nominated on January 12, 1956, confirmed by the Senate on January 31, 1956, and received commission the same day.
- Judge Pittman was jointly appointed to the Middle and Southern Districts of Alabama.
Chief judges
Chief judges have administrative responsibilities with respect to their district court. Unlike the Supreme Court, where one justice is specifically nominated to be chief, the office of chief judge rotates among the district court judges. To be chief, a judge must have been in active service on the court for at least one year, be under the age of 65, and have not previously served as chief judge.
A vacancy is filled by the judge highest in seniority among the group of qualified judges. The chief judge serves for a term of seven years, or until age 70, whichever occurs first. The age restrictions are waived if no members of the court would otherwise be qualified for the position.
When the office was created in 1948, the chief judge was the longest-serving judge who had not elected to retire, on what has since 1958 been known as senior status, or declined to serve as chief judge. After August 6, 1959, judges could not become or remain chief after turning 70 years old. The current rules have been in operation since October 1, 1982.
Succession of seats
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Court decisions
Browder v. Gayle (1956) – Court rules that bus segregation in Montgomery was unconstitutional under the Fourteenth Amendment. Decision upheld by U.S. Supreme Court six months later.
Gomillion v. Lightfoot (1958) – Court dismissed action, which was later affirmed by the Fifth Circuit. In 1960, the U.S. Supreme Court reversed the decision, finding that electoral districts drawn in Tuskegee, with the purpose of disenfranchising black voters, violated the Fifteenth Amendment.
Lee v. Macon County Board of Education (1963) – Court rules segregation in schooling was unconstitutional under the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendment. Decision upheld by U.S. Supreme Court.
United States v. Alabama (1966) – Court rules poll tax violates the Fourteenth and Fifteenth Amendment. U.S. Supreme Court concurred three weeks later in an unrelated case, Harper v. Virginia Board of Elections.
Glassroth v. Moore (2002) – Court rules that a display of the Ten Commandments, erected by Alabama Chief Justice Roy Moore in the Alabama Judicial Building violated the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment.
U.S. attorneys
| Name | Term Started | Term Ended | Presidents served under |
|---|---|---|---|
| John A. Minnis | 1870 | 1874 | Ulysses S. Grant |
| N. S. McAfee | 1874 | 1875 | Ulysses S. Grant |
| Charles B. Mayer | 1876 | 1880 | Ulysses S. Grant Rutherford B. Hayes |
| William Hugh Smith | 1880 | 1885 | Rutherford B. Hayes James A. Garfield Chester A. Arthur Grover Cleveland |
| George H. Craig | 1885 | 1885 | Grover Cleveland |
| William H. Denson | 1885 | 1889 | Grover Cleveland Benjamin Harrison |
| Lewis E. Parsons, Jr. | 1889 | 1893 | Benjamin Harrison Grover Cleveland |
| Henry D. Clayton, Jr. | 1893 | 1896 | Grover Cleveland |
| George F. Moore, Jr. | 1896 | 1897 | Grover Cleveland William McKinley |
| Warren S. Reese, Jr. | 1897 | 1906 | William McKinley Theodore Roosevelt |
| Erastus J. Parsons | 1906 | 1913 | Theodore Roosevelt William H. Taft Woodrow Wilson |
| Thomas D. Samford | 1913 | 1924 | Woodrow Wilson Warren G. Harding Calvin Coolidge |
| Grady Reynolds | 1924 | 1931 | Calvin Coolidge Herbert Hoover |
| Arthur B. Chilton | 1931 | 1934 | Herbert Hoover Franklin D. Roosevelt |
| Thomas D. Samford | 1934 | 1942 | Franklin D. Roosevelt |
| Edward B. Parker | 1942 | 1953 | Franklin D. Roosevelt Harry S. Truman Dwight D. Eisenhower |
| Hartwell Davis | 1953 | 1962 | Dwight D. Eisenhower John F. Kennedy |
| Ben Hardeman | 1962 | 1969 | John F. Kennedy Lyndon B. Johnson Richard Nixon |
| Leon J. Hopper | 1969 | 1969 | Richard Nixon |
| Ira De Ment | 1969 | 1977 | Richard Nixon Gerald Ford Jimmy Carter |
| Barry E. Teague | 1977 | 1981 | Jimmy Carter Ronald Reagan |
| John C. Bell | 1981 | 1987 | Ronald Reagan |
| James E. Wilson | 1987 | 1994 | Ronald Reagan George H. W. Bush Bill Clinton |
| Charles R. Pitt | 1994 | 2001 | Bill Clinton George W. Bush |
| Leura G. Canary | 2001 | 2011 | George W. Bush Barack Obama |
| George L. Beck Jr. | 2011 | 2017 | Barack Obama Donald Trump |
| A. Clark Morris | 2017 | 2017 | Donald Trump |
| Louis V. Franklin Sr. | 2017 | 2021 | Donald Trump |
| Sandra J. Stewart | 2021 | 2023 | Joe Biden |
| Jonathan S. Ross (Acting) | 2023 | present | Joe Biden |
See also
- Courts of Alabama
- List of current United States district judges
- List of United States federal courthouses in Alabama
References
- U.S. District Courts of Alabama, Legislative history, Federal Judicial Center
- "Middle District of Alabama | Meet The Acting U.S. Attorney". www.justice.gov. March 12, 2015. Retrieved October 18, 2023.
- 28 U.S.C. § 81
- "LEE v. MACON COUNTY BOARD | 231 F.Supp. 743 (1964) | supp7431831 | Leagle.com". Leagle.
- Annual Report of the Attorney General of the United States (1906)
- ^ "Redding Pitt Dies". February 9, 2016.
- ^ "LinkedIn Profile".
- ^ Office (USAO), U. S. Attorney's. "U.S. Attorney's Office - U.S. Department of Justice". www.justice.gov.
- ^ Office (USAO), U. S. Attorney's. "U.S. Attorney's Office - U.S. Department of Justice". www.justice.gov.
- "Alabama U.S. Attorney George Beck Resigns After Six Years of Service". March 13, 2017.
- "Florida Woman Sentenced to Prison for Stolen Identity Refund Fraud". www.justice.gov. September 12, 2017.
- "Social Security Administration Employee and Husband Indicted in Public Benefit Fraud Scheme". www.justice.gov. March 23, 2017.
- ^ "Louis V. Franklin, Sr. Sworn in as United States Attorney for the Middle District Of Alabama". www.justice.gov. October 5, 2017.
- "Middle District of Alabama | Acting U.S. Attorney Sandra J. Stewart Recognizes Law Enforcement During Police Week | United States Department of Justice". www.justice.gov. May 10, 2021. Retrieved March 26, 2024.
- "Middle District of Alabama | Meet the Acting U.S. Attorney". www.justice.gov. March 12, 2015. Retrieved March 26, 2024.
External links
- United States District Court for the Middle District of Alabama
- United States Attorney for the Middle District of Alabama
- Restoring checks and balances in the confirmation process of United States attorneys: hearing before the Subcommittee on Commercial and Administrative Law of the Committee on the Judiciary, House of Representatives, One Hundred Tenth Congress, first session, on H.R. 580, March 6, 2007 (includes list of past U.S. attorneys up to about 1996)
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
| Active district judges of the Eleventh Circuit Court of Appeals | |
|---|---|
| M. Alabama | |
| N. Alabama | |
| S. Alabama | |
| M. Florida | |
| N. Florida | |
| S. Florida | |
| M. Georgia | |
| N. Georgia | |
| S. Georgia | |
| Senior district judges of the Eleventh Circuit Court of Appeals | |
|---|---|
| M. Alabama | |
| N. Alabama | |
| S. Alabama | |
| M. Florida | |
| N. Florida | |
| S. Florida | |
| M. Georgia | |
| N. Georgia | |
| S. Georgia | |
| United States federal courts | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Courts of appeals | |
| District courts |
|
| Specialty courts | |
| Territorial courts | |
| Extinct courts | |
| Note | American Samoa does not have a district court or federal territorial court; federal matters there go to the District of Columbia, Hawaii, or its own Supreme Court. |
| Chief judges of the United States District Court for the Middle District of Alabama | |
|---|---|