
The United States federal government and most state governments impose an income tax. They are determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income, which is the total income less allowable deductions. Income is broadly defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and trusts may be taxable on undistributed income. Partnerships are not taxed (with some exceptions in the case of federal income taxation), but their partners are taxed on their shares of partnership income. Residents and citizens are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on income within the jurisdiction. Several types of credits reduce tax, and some types of credits may exceed tax before credits. Most business expenses are deductible. Individuals may deduct certain personal expenses, including home mortgage interest, state taxes, contributions to charity, and some other items. Some deductions are subject to limits, and an Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) applies at the federal and some state levels.
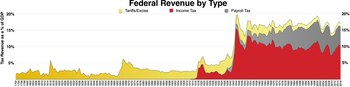
The federal government has imposed an income tax since the ratification of the Sixteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution was ratified in 1913, and 42 US states impose state income taxes. Income taxes are levied on wages as well as on capital gains, and fund federal and state governments. Payroll taxes are levied only on wages, not gross incomes, but contribute to reducing the after-tax income of most Americans. The most common payroll taxes are FICA taxes that fund Social Security and Medicare. Capital gains are currently taxable at a lower rate than wages, and capital losses reduce taxable income to the extent of gains.
Taxpayers generally must determine for themselves the income tax that they owe by filing tax returns. Advance payments of tax are required in the form of tax withholding or estimated tax payments. Due dates and other procedural details vary by jurisdiction, but April 15, Tax Day is the deadline for individuals to file tax returns for federal and many state and local returns. Tax as determined by the taxpayer may be adjusted by the taxing jurisdiction.
For federal individual (not corporate) income tax, the average rate paid in 2020 on adjusted gross income (income after deductions) was 13.6%. However, the tax is progressive, meaning that the tax rate increases with increased income. Over the last 20 years, this has meant that the bottom 50% of taxpayers have always paid less than 5% of the total individual federal income taxes paid, (gradually declining from 5% in 2001 to 2.3% in 2020) with the top 50% of taxpayers consistently paying 95% or more of the tax collected, and the top 1% paying 33% in 2001, increasing to 42% by 2020.
Basics
Sources of U.S. income tax laws
United States income tax law comes from a number of sources. These sources have been divided by one author into three tiers as follows:
- Tier 1
- United States Constitution
- Internal Revenue Code (IRC) (legislative authority, written by the United States Congress through legislation)
- Treasury regulations
- Federal court opinions (judicial authority, written by courts as interpretation of legislation)
- Treaties (executive authority, written in conjunction with other countries, subject to ratification in the United States by advice and consent of the U.S. Senate - other countries have their own ratification procedures)
- Tier 2
- Agency interpretative regulations (executive authority, written by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and Department of the Treasury), including:
- Final, Temporary and Proposed Regulations promulgated under IRC § 7805 or other specific statutory authority;
- Treasury Notices and Announcements;
- Executive agreements with other countries;
- Public Administrative Rulings (IRS Revenue Rulings, which provide informal guidance on specific questions and are binding on all taxpayers)
- Agency interpretative regulations (executive authority, written by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and Department of the Treasury), including:
- Tier 3
- Legislative History
- Private Administrative Rulings (private parties may approach the IRS directly and ask for a Private Letter Ruling on a specific issue – these rulings are binding only on the requesting taxpayer).
Where conflicts exist between various sources of tax authority, an authority in Tier 1 outweighs an authority in Tier 2 or 3. Similarly, an authority in Tier 2 outweighs an authority in Tier 3. Where conflicts exist between two authorities in the same tier, the "last-in-time rule" is applied. As the name implies, the "last-in-time rule" states that the authority that was issued later in time is controlling.
Regulations and case law serve to interpret the statutes. Additionally, various sources of law attempt to do the same thing. Revenue Rulings, for example, serves as an interpretation of how the statutes apply to a very specific set of facts. Treaties serve in an international realm.
Basic concepts
A tax is imposed on net taxable income in the United States by the federal, most state, and some local governments. Income tax is imposed on individuals, corporations, estates, and trusts. The definition of net taxable income for most sub-federal jurisdictions mostly follows the federal definition.
The rate of tax at the federal level is graduated; that is, the tax rates on higher amounts of income are higher than on lower amounts. Federal individual tax rates vary from 10% to 37%. Some states and localities impose an income tax at a graduated rate, and some at a flat rate on all taxable income.
Individuals are eligible for a reduced rate of federal income tax on capital gains and qualifying dividends. The tax rate and some deductions are different for individuals depending on filing status. Married individuals may compute tax as a couple or separately. Single individuals may be eligible for reduced tax rates if they are head of a household in which they live with a dependent.
Taxable income is defined in a comprehensive manner in the Internal Revenue Code and tax regulations issued by the Department of Treasury and the Internal Revenue Service. Taxable income is gross income as adjusted minus deductions. Most states and localities follow these definitions at least in part, though some make adjustments to determine income taxed in that jurisdiction. Taxable income for a company or business may not be the same as its book income.
Gross income includes all income earned or received from whatever source. This includes salaries and wages, tips, pensions, fees earned for services, price of goods sold, other business income, gains on sale of other property, rents received, interest and dividends received, proceeds from selling crops, and many other types of income. Some income, such as municipal bond interest, is exempt from income tax.

Adjustments (usually reductions) to gross income of individuals are made for contributions to many types of retirement or health savings plans, certain student loan interest, half of self-employment tax, and a few other items. The cost of goods sold in a business is a direct reduction of gross income.
Business deductions: Taxable income of all taxpayers is reduced by deductions for expenses related to their business. These include salaries, rent, and other business expenses paid or accrued, as well as allowances for depreciation. The deduction of expenses may result in a loss. Generally, such loss can reduce other taxable income, subject to some limits.
Personal deductions: The former deduction for personal exemptions was repealed for 2018 through 2025.
Standard deduction: Individuals get a deduction from taxable income for certain personal expenses. An individual may claim a standard deduction. For 2021, the basic standard deduction was $12,550 for single individuals or married persons filing separately, $25,100 for a joint return or surviving spouse, and $18,800 for a head of household.
Itemized deductions: Those who choose to claim actual itemized deductions may deduct the following, subject to many conditions and limitations:
- Medical expenses in excess of 10% of adjusted gross income,
- Certain taxes limited to $10,000 or $5,000 in 2018 through 2025,
- Home mortgage interest,
- Contributions to charities,
- Losses on nonbusiness property due to casualty, and
- Deductions for expenses incurred in the production of income in excess of 2% of adjusted gross income.
Capital gains: Capital gains include gains on selling stocks and bonds, real estate, and other capital assets. The gain is the excess of the proceeds over the adjusted tax basis (cost less depreciation deductions allowed) of the property. This lower rate of tax also applies to qualified dividends from U.S. corporations and many foreign corporations. There are limits on how much net capital loss may reduce other taxable income.

Tax credits: All taxpayers are allowed a credit for foreign taxes and for a percentage of certain types of business expenses. Individuals are also allowed credits related to education expenses, retirement savings, and child care expenses. Each of the credits is subject to specific rules and limitations. Some credits are treated as refundable payments.
Alternative minimum tax: All taxpayers are also subject to the Alternative Minimum Tax if their income exceeds certain exclusion amounts. This tax applies only if it exceeds regular income tax and is reduced by some credits.
Additional Medicare tax: High-income earners may also have to pay an additional 0.9% tax on wages, compensation, and self-employment income.
Net investment income tax: Net investment income is subject to an additional 3.8% tax for individuals with income in excess of certain thresholds.
Tax returns: U.S. corporations and most resident individuals must file income tax returns to self assess income tax if any tax is due or to claim a tax refund. Some taxpayers must file an income tax return because they satisfy one of the several other conditions. Tax returns may be filed electronically. Generally, an individual's tax return covers the calendar year. Corporations may elect a different tax year. Most states and localities follow the federal tax year and require separate returns.
Tax payment: Taxpayers must pay income tax due without waiting for an assessment. Many taxpayers are subject to withholding taxes when they receive income. To the extent withholding taxes do not cover all taxes due, all taxpayers must make estimated tax payments or face penalties.
Tax penalties: Failing to make payments on time, or failing to file returns, can result in substantial penalties. Certain intentional failures may result in criminal penalties, including monetary fines and/or imprisonment.
Tax returns may be examined and adjusted by tax authorities. Taxpayers have rights to appeal any change to tax, and these rights vary by jurisdiction. Taxpayers may also go to court to contest tax changes. Tax authorities may not make changes after a certain period of time (generally three or four years from the tax return due date).
Federal income tax rates for individuals


Federal income brackets and tax rates for individuals are adjusted annually for inflation. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) accounts for changes to the CPI and publishes the new rates as "Tax Rate Schedules".
Marginal tax rates


| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2010 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $8,375 | $0 – $16,750 | $0 – $8,375 | $0 – $11,950 |
| 15% | $8,376 – $34,000 | $16,751 – $68,000 | $8,376 – $34,000 | $11,951 – $45,550 |
| 25% | $34,001 – $82,400 | $68,001 – $137,300 | $34,001 – $68,650 | $45,551 – $117,650 |
| 28% | $82,401 – $171,850 | $137,301 – $209,250 | $68,651 – $104,625 | $117,651 – $190,550 |
| 33% | $171,851 – $373,650 | $209,251 – $373,650 | $104,626 – $186,825 | $190,551 – $373,650 |
| 35% | $373,651+ | $373,651+ | $186,826+ | $373,651+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2011 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $8,500 | $0 – $17,000 | $0 – $8,500 | $0 – $12,150 |
| 15% | $8,501 – $34,500 | $17,001 – $69,000 | $8,501 – $34,500 | $12,151 – $46,250 |
| 25% | $34,501 – $83,600 | $69,001 – $139,350 | $34,501 – $69,675 | $46,251 – $119,400 |
| 28% | $83,601 – $174,400 | $139,351 – $212,300 | $69,676 – $106,150 | $119,401 – $193,350 |
| 33% | $174,401 – $379,150 | $212,301 – $379,150 | $106,151 – $189,575 | $193,351 – $379,150 |
| 35% | $379,151+ | $379,151+ | $189,576+ | $379,151+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2012 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $8,700 | $0 – $17,400 | $0 – $8,700 | $0 – $12,400 |
| 15% | $8,701 – $35,350 | $17,401 – $70,700 | $8,701 – $35,350 | $12,401 – $47,350 |
| 25% | $35,351 – $85,650 | $70,701 – $142,700 | $35,351 – $71,350 | $47,351 – $122,300 |
| 28% | $85,651 – $178,650 | $142,701 – $217,450 | $71,351 – $108,725 | $122,301 – $198,050 |
| 33% | $178,651 – $388,350 | $217,451 – $388,350 | $108,726 – $194,175 | $198,051 – $388,350 |
| 35% | $388,351+ | $388,351+ | $194,176+ | $388,351+ |
Beginning in 2013, an additional tax of 3.8% applies to net investment income in excess of certain thresholds.
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2013 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $8,925 | $0 – $17,850 | $0 – $8,925 | $0 – $12,750 |
| 15% | $8,926 – $36,250 | $17,851 – $72,500 | $8,926 – $36,250 | $12,751 – $48,600 |
| 25% | $36,251 – $87,850 | $72,501 – $146,400 | $36,251 – $73,200 | $48,601 – $125,450 |
| 28% | $87,851 – $183,250 | $146,401 – $223,050 | $73,201 – $111,525 | $125,451 – $203,150 |
| 33% | $183,251 – $398,350 | $223,051 – $398,350 | $111,526 – $199,175 | $203,151 – $398,350 |
| 35% | $398,351 – $400,000 | $398,351 – $450,000 | $199,176 – $225,000 | $398,351 – $425,000 |
| 39.6% | $400,001+ | $450,001+ | $225,001+ | $425,001+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2014 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $9,075 | $0 – $18,150 | $0 – $9,075 | $0 – $12,950 |
| 15% | $9,076 – $36,900 | $18,151 – $73,800 | $9,076 – $36,900 | $12,951 – $49,100 |
| 25% | $36,901 – $89,350 | $73,801 – $148,850 | $36,901 – $74,425 | $49,101 – $127,550 |
| 28% | $89,351 – $186,350 | $148,851 – $226,850 | $74,426 – $113,425 | $127,551 – $206,600 |
| 33% | $186,351 – $405,100 | $226,851 – $405,100 | $113,426 – $202,550 | $206,601 – $405,100 |
| 35% | $405,101 – $406,750 | $405,101 – $457,600 | $202,551 – $228,800 | $405,101 – $432,200 |
| 39.6% | $406,751+ | $457,601+ | $228,801+ | $432,201+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2015 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $9,225 | $0 – $18,450 | $0 – $9,225 | $0 – $13,150 |
| 15% | $9,226 – $37,450 | $18,451 – $74,900 | $9,226 – $37,450 | $13,151 – $50,200 |
| 25% | $37,451 – $90,750 | $74,901 – $151,200 | $37,451 – $75,600 | $50,201 – $129,600 |
| 28% | $90,751 – $189,300 | $151,201 – $230,450 | $75,601 – $115,225 | $129,601 – $209,850 |
| 33% | $189,301 – $411,500 | $230,451 – $411,500 | $115,226 – $205,750 | $209,851 – $411,500 |
| 35% | $411,501 – $413,200 | $411,501 – $464,850 | $205,751 – $232,425 | $411,501 – $439,000 |
| 39.6% | $413,201+ | $464,851+ | $232,426+ | $439,001+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2016 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $9,275 | $0 – $18,550 | $0 – $9,275 | $0 – $13,250 |
| 15% | $9,276 – $37,650 | $18,551 – $75,300 | $9,276 – $37,650 | $13,251 – $50,400 |
| 25% | $37,651 – $91,150 | $75,301 – $151,900 | $37,651 – $75,950 | $50,401 – $130,150 |
| 28% | $91,151 – $190,150 | $151,901 – $231,450 | $75,951 – $115,725 | $130,151 – $210,800 |
| 33% | $190,151 – $413,350 | $231,451 – $413,350 | $115,726 – $206,675 | $210,801 – $413,350 |
| 35% | $413,351 – $415,050 | $413,351 – $466,950 | $206,676 – $233,475 | $413,351 – $441,000 |
| 39.6% | $415,051+ | $466,951+ | $233,476+ | $441,001+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2017 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $9,325 | $0 – $18,650 | $0 – $9,325 | $0 – $13,350 |
| 15% | $9,326 – $37,950 | $18,651 – $75,900 | $9,326 – $37,950 | $13,351 – $50,800 |
| 25% | $37,951 – $91,900 | $75,901 – $153,100 | $37,951 – $76,550 | $50,801 – $131,200 |
| 29% | $91,901 – $191,650 | $153,101 – $233,350 | $76,551 – $116,675 | $131,201 – $212,500 |
| 33% | $191,651 – $416,700 | $233,351 – $416,700 | $116,676 – $208,350 | $212,501 – $416,700 |
| 35% | $416,701 – $418,400 | $416,701 – $470,700 | $208,351 – $235,350 | $416,701 – $444,550 |
| 39.6% | $418,401+ | $470,701+ | $235,351+ | $444,501+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2018 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $9,525 | $0 – $19,050 | $0 – $9,525 | $0 – $13,600 |
| 12% | $9,526 – $38,700 | $19,051 – $77,400 | $9,526 – $38,700 | $13,601 – $51,800 |
| 22% | $38,701 – $82,500 | $77,401 – $165,000 | $38,701 – $82,500 | $51,801 – $82,500 |
| 24% | $82,501 – $157,500 | $165,001 – $315,000 | $82,501 – $157,500 | $82,501 – $157,500 |
| 32% | $157,501 – $200,000 | $315,001 – $400,000 | $157,501 – $200,000 | $157,501 – $200,000 |
| 35% | $200,001 – $500,000 | $400,001 – $600,000 | $200,001 – $300,000 | $200,001 – $500,000 |
| 37% | $500,001+ | $600,001+ | $300,001+ | $500,001+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2019 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $9,700 | $0 – $19,400 | $0 – $9,700 | $0 – $13,850 |
| 12% | $9,701 – $39,475 | $19,401 – $78,950 | $9,701 – $39,475 | $13,851 – $52,850 |
| 22% | $39,476 – $84,200 | $78,951 – $168,400 | $39,476 – $84,200 | $52,851 – $84,200 |
| 24% | $84,201 – $160,725 | $168,401 – $321,450 | $84,201 – $160,725 | $84,201 – $160,700 |
| 32% | $160,726 – $204,100 | $321,451 – $408,200 | $160,726 – $204,100 | $160,701 – $204,100 |
| 35% | $204,101 – $510,300 | $408,201 – $612,350 | $204,101 – $306,175 | $204,101 – $510,300 |
| 37% | $510,301+ | $612,351+ | $306,176+ | $510,301+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2020 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $9,875 | $0 – $19,750 | $0 – $9,875 | $0 – $14,100 |
| 12% | $9,876 – $40,125 | $19,751 – $80,250 | $9,876 – $40,125 | $14,101 – $53,700 |
| 22% | $40,126 – $85,525 | $80,251 – $171,050 | $40,126 – $85,525 | $53,701 – $85,500 |
| 24% | $85,526 – $163,300 | $171,051 – $326,600 | $85,526 – $163,300 | $85,501 – $163,300 |
| 32% | $163,301 – $207,350 | $326,601 – $414,700 | $163,301 – $207,350 | $163,301 – $207,350 |
| 35% | $207,351 – $518,400 | $414,701 – $622,350 | $207,351 – $311,175 | $207,351 – $518,400 |
| 37% | $518,401+ | $622,051+ | $311,176+ | $518,401+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2021 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $9,950 | $0 – $19,900 | $0 – $9,950 | $0 – $14,200 |
| 12% | $9,951 – $40,525 | $19,901 – $81,050 | $9,951 – $40,525 | $14,201 – $54,200 |
| 22% | $40,526 – $86,375 | $81,051 – $172,750 | $40,526 – $86,375 | $54,201 – $86,350 |
| 24% | $86,376 – $164,925 | $172,751 – $329,850 | $85,526 – $164,925 | $86,351 – $164,900 |
| 32% | $164,926 – $209,425 | $329,851 – $418,850 | $163,301 – $209,425 | $164,901 – $209,400 |
| 35% | $209,426 – $523,600 | $418,851 – $628,300 | $209,426 – $314,150 | $209,401 – $523,600 |
| 37% | $523,601+ | $628,301+ | $314,151+ | $523,601+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2022 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $10,275 | $0 – $20,550 | $0 – $10,275 | $0 – $14,650 |
| 12% | $10,276 – $41,775 | $20,551 – $83,550 | $10,276 – $41,775 | $14,651 – $55,900 |
| 22% | $41,776 – $89,075 | $83,551 – $178,150 | $41,776 – $89,075 | $55,901 – $89,050 |
| 24% | $89,076 – $170,050 | $178,151 – $340,100 | $89,076 – $170,050 | $89,051 – $170,050 |
| 32% | $170,051 – $215,950 | $340,101 – $431,900 | $170,051 – $215,950 | $170,051 – $215,950 |
| 35% | $215,951 – $539,900 | $431,901 – $647,850 | $215,951 – $323,925 | $215,951 – $539,900 |
| 37% | $539,901+ | $647,851+ | $323,926+ | $539,901+ |
| Marginal tax rates and income brackets for 2023 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal tax rate | Single taxable income | Married filing jointly or qualified widow(er) taxable income | Married filing separately taxable income | Head of household taxable income |
| 10% | $0 – $11,000 | $0 – $22,000 | $0 – $11,000 | $0 – $15,700 |
| 12% | $11,000 – $44,725 | $22,000 – $89,450 | $11,000 – $44,725 | $15,700 – $59,850 |
| 22% | $44,725 – $95,375 | $89,450 – $190,750 | $41,776 – $95,375 | $59,850 – $95,350 |
| 24% | $95,375 – $182,100 | $190,750 – $364,200 | $95,375 – $182,100 | $95,350 – $182,100 |
| 32% | $182,100 – $231,250 | $364,200 – $462,500 | $182,100 – $231,250 | $182,100 – $231,250 |
| 35% | $231,250 – $578,125 | $462,500 – $693,750 | $231,250 – $346,875 | $231,250 – $578,100 |
| 37% | $578,125+ | $693,750+ | $346,875+ | $578,100+ |
An individual pays tax at a given bracket only for each dollar within that tax bracket's range. The top marginal rate does not apply in certain years to certain types of income. Significantly lower rates apply after 2003 to capital gains and qualifying dividends (see below).
Example of a tax computation
Income tax for year 2017:
Single taxpayer making $40,000 gross income, no children, under 65 and not blind, taking standard deduction;
- $40,000 gross income – $6,350 standard deduction – $4,050 personal exemption = $29,600 taxable income
- amount in the first income bracket = $9,325; taxation of the amount in the first income bracket = $9,325 × 10% = $932.50
- amount in the second income bracket = $29,600 – $9,325 = $20,275.00; taxation of the amount in the second income bracket = $20,275.00 × 15% = $3,041.25
- Total income tax is $932.50 + $3,041.25 = $3,973.75 (~9.93% effective tax)
Note, however, that taxpayers with taxable income of less than $100,000 must use IRS provided tax tables. Under that table for 2016, the income tax in the above example would be $3,980.00.
In addition to income tax, a wage earner would also have to pay Federal Insurance Contributions Act tax (FICA) (and an equal amount of FICA tax must be paid by the employer):
- $40,000 (adjusted gross income)
- $40,000 × 6.2% = $2,480 (Social Security portion)
- $40,000 × 1.45% = $580 (Medicare portion)
- Total FICA tax paid by employee = $3,060 (7.65% of income)
- Total federal tax of individual = $3,973.75 + $3,060.00 = $7,033.75 (~17.58% of income)
Total federal tax including employer's contribution:
- Total FICA tax contributed by employer = $3,060 (7.65% of income)
- Total federal tax of individual including employer's contribution = $3,973.75 + $3,060.00 + $3,060.00 = $10,093.75 (~25.23% of income)
Effective income tax rates
Effective tax rates are typically lower than marginal rates due to various deductions, with some people actually having a negative liability. The individual income tax rates in the following chart include capital gains taxes, which have different marginal rates than regular income. Only the first $118,500 of someone's income is subject to social insurance (Social Security) taxes in 2016. The table below also does not reflect changes, effective with 2013 law, which increased the average tax paid by the top 1% to the highest levels since 1979, at an effective rate of 33%, while most other taxpayers have remained near the lowest levels since 1979.
| Effective federal tax rates and average incomes for 2010 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quintile | Average income before taxes | Effective individual income tax rate | Effective payroll tax rate | Combined effective income and payroll tax rate | Total effective federal tax rate (includes corporate income and excise taxes) |
| Lowest | $24,100 | −9.2% | 8.4% | −0.8% | 1.5% |
| Second | $44,200 | −2.3% | 7.8% | 5.5% | 7.2% |
| Middle | $65,400 | 1.6% | 8.3% | 9.9% | 11.5% |
| Fourth | $95,500 | 5.0% | 9.0% | 14.0% | 15.6% |
| Highest | $239,100 | 13.8% | 6.7% | 20.5% | 24.0% |
| 81st to 90th percentiles | $134,600 | 8.1% | 9.4% | 17.5% | 19.3% |
| 91st to 95th percentiles | $181,600 | 10.7% | 8.9% | 19.6% | 21.6% |
| 96th to 99th percentiles | $286,400 | 15.1% | 7.1% | 22.2% | 24.9% |
| Top 1% | $1,434,900 | 20.1% | 2.2% | 22.3% | 29.4% |
Taxable income
Income tax is imposed as a tax rate times taxable income. Taxable income is defined as gross income less allowable deductions. Taxable income as determined for federal tax purposes may be modified for state tax.
Gross income
Main article: Gross incomeThe Internal Revenue Code states that "gross income means all income from whatever source derived," and gives specific examples. Gross income is not limited to cash received, but "includes income realized in any form, whether money, property, or services." Gross income includes wages and tips, fees for performing services, gain from sale of inventory or other property, interest, dividends, rents, royalties, pensions, alimony, and many other types of income. Items must be included in income when received or accrued. The amount included is the amount the taxpayer is entitled to receive. Gains on property are the gross proceeds less amounts returned, cost of goods sold, or tax basis of property sold.
Certain types of income are exempt from income tax. Among the more common types of exempt income are interest on municipal bonds, a portion of Social Security benefits, life insurance proceeds, gifts or inheritances, and the value of many employee benefits.
Gross income is reduced by adjustments and deductions. Among the more common adjustments are reductions for alimony paid and IRA and certain other retirement plan contributions. Adjusted gross income is used in calculations relating to various deductions, credits, phase outs, and penalties.
Business deductions
Main article: Tax deductionMost business deductions are allowed regardless of the form in which the business is conducted. Therefore, an individual small business owner is allowed most of the same business deductions as a publicly traded corporation. A business is an activity conducted regularly to make a profit. Only a few business-related deductions are unique to a particular form of business-doing. The deduction of investment expenses by individuals, however, has several limitations, along with other itemized (personal) deductions.
The amount and timing of deductions for income tax purposes is determined under tax accounting rules, not financial accounting ones. Tax rules are based on principles similar in many ways to accounting rules, but there are significant differences. Federal deductions for most meals and entertainment costs are limited to 50% of the costs (with an exception for tax year 2021, allowing a 100% deduction for meals purchased in a restaurant). Costs of starting a business (sometimes called pre-operating costs) are deductible ratably over 60 months. Deductions for lobbying and political expenses are limited. Some other limitations apply.
Expenses likely to produce future benefits must be capitalized. The capitalized costs are then deductible as depreciation (see MACRS) or amortization over the period future benefits are expected. Examples include costs of machinery and equipment and costs of making or building property. IRS tables specify lives of assets by class of asset or industry in which used. When an asset the cost of which was capitalized is sold, exchanged, or abandoned, the proceeds (if any) are reduced by the remaining unrecovered cost to determine gain or loss. That gain or loss may be ordinary (as in the case of inventory) or capital (as in the case of stocks and bonds), or a combination (for some buildings and equipment).
Most personal, living, and family expenses are not deductible. Business deductions allowed for federal income tax are almost always allowed in determining state income tax. Only some states, however, allow itemized deductions for individuals. Some states also limit deductions by corporations for investment related expenses. Many states allow different amounts for depreciation deductions. State limitations on deductions may differ significantly from federal limitations.
Business deductions in excess of business income result in losses that may offset other income. However, deductions for losses from passive activities may be deferred to the extent they exceed income from other passive activities. Passive activities include most rental activities (except for real estate professionals) and business activities in which the taxpayer does not materially participate. In addition, losses may not, in most cases, be deducted in excess of the taxpayer's amount at risk (generally tax basis in the entity plus share of debt).
Personal deductions
Prior to 2018, individuals were allowed a special deduction called a personal exemption. This was not allowed after 2017 but will be allowed again in 2026. This was a fixed amount allowed each taxpayer, plus an additional fixed amount for each child or other dependents the taxpayer supports. The amount of this deduction was $4,000 for 2015. The amount is indexed annually for inflation. The amount of exemption was phased out at higher incomes through 2009 and after 2012 (no phase out in 2010–2012).
Citizens and individuals with U.S. tax residence may deduct a flat amount as a standard deduction. This was $12,550 for single individuals and $25,100 for married individuals filing a joint return for 2021. Alternatively, individuals may claim itemized deductions for actual amounts incurred for specific categories of nonbusiness expenses. Expenses incurred to produce tax exempt income and several other items are not deductible. Home owners may deduct the amount of interest and property taxes paid on their principal and second homes. Local and state income taxes are deductible through the SALT deduction although this deduction is currently limited to $10,000. Contributions to charitable organizations are deductible by individuals and corporations, but the deduction is limited to 50% and 10% of gross income, respectively. Medical expenses in excess of 10% of adjusted gross income are deductible, as are uninsured casualty losses due to a federally declared disaster. Other income producing expenses in excess of 2% of adjusted gross income are also deductible. Before 2010, the allowance of itemized deductions was phased out at higher incomes. The phase out expired for 2010.
Retirement savings and fringe benefit plans
Employers get a deduction for amounts contributed to a qualified employee retirement plan or benefit plan. The employee does not recognize income with respect to the plan until he or she receives a distribution from the plan. The plan itself is organized as a trust and is considered a separate entity. For the plan to qualify for tax exemption, and for the employer to get a deduction, the plan must meet minimum participation, vesting, funding, and operational standards.
Examples of qualified plans include:
- Pension plans (defined benefit pension plan),
- Profit sharing plans (defined contribution plan),
- Employee Stock Ownership Plan (ESOPs),
- Stock purchase plans,
- Health insurance plans,
- Employee benefit plans,
- Cafeteria plans.
Employees or former employees are generally taxed on distributions from retirement or stock plans. Employees are not taxed on distributions from health insurance plans to pay for medical expenses. Cafeteria plans allow employees to choose among benefits (like choosing food in a cafeteria), and distributions to pay those expenses are not taxable.
In addition, individuals may make contributions to Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs). Those not currently covered by other retirement plans may claim a deduction for contributions to certain types of IRAs. Income earned within an IRA is not taxed until the individual withdraws it.
Capital gains
Main article: Capital gains tax in the United StatesTaxable income includes capital gains. However, individuals are taxed at a lower rate on long term capital gains and qualified dividends (see below). A capital gain is the excess of the sales price over the tax basis (usually, the cost) of capital assets, generally those assets not held for sale to customers in the ordinary course of business. Capital losses (where basis is more than sales price) are deductible, but deduction for long term capital losses is limited to the total capital gains for the year, plus for individuals up to $3,000 of ordinary income ($1,500 if married filing separately). An individual may exclude $250,000 ($500,000 for a married couple filing jointly) of capital gains on the sale of the individual's primary residence, subject to certain conditions and limitations. Gains on depreciable property used in a business are treated as ordinary income to the extent of depreciation previously claimed.
In determining gain, it is necessary to determine which property is sold and the amount of basis of that property. This may require identification conventions, such as first-in-first-out, for identical properties like shares of stock. Further, tax basis must be allocated among properties purchased together unless they are sold together. Original basis, usually cost paid for the asset, is reduced by deductions for depreciation or loss.
Certain capital gains are deferred; that is, they are taxed at a time later than the year of disposition. Gains on property sold for installment payments may be recognized as those payments are received. Gains on real property exchanged for like-kind property are not recognized, and the tax basis of the new property is based on the tax basis of the old property.
Before 1986 and from 2004 onward, individuals were subject to a reduced rate of federal tax on capital gains (called long-term capital gains) on certain property held more than 12 months. The reduced rate of 15% applied for regular tax and the Alternative Minimum Tax through 2011. The reduced rate also applies to dividends from corporations organized in the United States or a country with which the United States has an income tax treaty. This 15% rate was increased to 20% in 2012. Beginning in 2013, capital gains above certain thresholds is included in net investment income subject to an additional 3.8% tax.
| Ordinary income rate | Long-term capital gain rate* | Short-term capital gain rate | Recapture of depreciation on long-term gain of real estate | Long-term gain on collectibles | Long-term gain on certain small business stock |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10% | 0% | 10% | 10% | 10% | 10% |
| 15% | 0% | 15% | 15% | 15% | 15% |
| 25% | 15% | 25% | 25% | 25% | 25% |
| 28% | 15% | 28% | 25% | 28% | 28% |
| 33% | 15% | 33% | 25% | 28% | 28% |
| 35% | 20% | 35% | 25% | 28% | 28% |
| 37% | 20% | 37% | 25% | 28% | 28% |
- * Capital gains up to $250,000 ($500,000 if filed jointly) on real estate used as primary residence are exempt
Accounting periods and methods
The US tax system allows individuals and entities to choose their tax year. Most individuals choose the calendar year. There are restrictions on choice of tax year for some closely held entities. Taxpayers may change their tax year in certain circumstances, and such change may require IRS approval.
Taxpayers must determine their taxable income based on their method of accounting for the particular activity. Most individuals use the cash method for all activities. Under this method, income is recognized when received and deductions taken when paid. Taxpayers may choose or be required to use the accrual method for some activities. Under this method, income is recognized when the right to receive it arises, and deductions are taken when the liability to pay arises and the amount can be reasonably determined. Taxpayers recognizing cost of goods sold on inventory must use the accrual method with respect to sales and costs of the inventory.
Methods of accounting may differ for financial reporting and tax purposes. Specific methods are specified for certain types of income or expenses. Gain on sale of property other than inventory may be recognized at the time of sale or over the period in which installment sale payments are received. Income from long-term contracts must be recognized ratably over the term of the contract, not just at completion. Other special rules also apply.
Other taxable and tax exempt entities
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (August 2020) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
Partnerships and LLCs
Business entities treated as partnerships are not subject to income tax at the entity level. Instead, their members include their share of income, deductions, and credits in computing their own tax. The character of the partner's share of income (such as capital gains) is determined at the partnership level. Many types of business entities, including limited liability companies (LLCs), may elect to be treated as a corporation or as a partnership. Distributions from partnerships are not taxed as dividends.
Corporations
Main article: Corporate tax in the United States
Corporate tax is imposed in the U.S. at the federal, most state, and some local levels on the income of entities treated for tax purposes as corporations. A corporation wholly owned by U.S. citizens and resident individuals may elect for the corporation to be taxed similarly to partnerships as an S Corporation. Corporate income tax is based on taxable income, which is defined similarly to individual taxable income.
Shareholders (including other corporations) of corporations (other than S Corporations) are taxed on dividend distributions from the corporation. They are also subject to tax on capital gains upon sale or exchange of their shares for money or property. However, certain exchanges, such as in reorganizations, are not taxable.
Multiple corporations may file a consolidated return at the federal and some state levels with their common parent.
Corporate tax rates
Federal corporate income tax is imposed at 21% from 2018. Dividend exclusions and certain corporation-only deductions may significantly lower the effective rate.
Deductions for corporations
Most expenses of corporations are deductible, subject to limitations also applicable to other taxpayers. (See relevant deductions for details.) In addition, regular U.S. corporations are allowed a deduction of 100% of dividends received from 10% or more foreign subsidiaries, 50% of amounts included in income under section 951A, and 37.5% of foreign branch income.
Some deductions of corporations are limited at federal or state levels. Limitations apply to items due to related parties, including interest and royalty expenses.
Estates and trusts
Estates and trusts may be subject to income tax at the estate or trust level, or the beneficiaries may be subject to income tax on their share of income. Where income must be distributed, the beneficiaries are taxed similarly to partners in a partnership. Where income may be retained, the estate or trust is taxed. It may get a deduction for later distributions of income. Estates and trusts are allowed only those deductions related to producing income, plus $1,000. They are taxed at graduated rates that increase rapidly to the maximum rate for individuals. The tax rate for trust and estate income in excess of $11,500 was 35% for 2009. Estates and trusts are eligible for the reduced rate of tax on dividends and capital gains through 2011.
Tax-exempt entities
Main article: Tax exemptionU.S. tax law exempts certain types of entities from income and some other taxes. These provisions arose during the late 19th century. Charitable organizations and cooperatives may apply to the IRS for tax exemption. Exempt organizations are still taxed on any business income. An organization which participates in lobbying, political campaigning, or certain other activities may lose its exempt status. Special taxes apply to prohibited transactions and activities of tax-exempt entities.
Social insurance taxes (Social Security tax and Medicare tax, or FICA)
Main article: Federal Insurance Contributions Act taxThe United States social insurance system is funded by a tax similar to an income tax. Social Security tax of 6.2% is imposed on wages paid to employees. The tax is imposed on both the employer and the employee. The maximum amount of wages subject to the tax for 2020 was $137,700. This amount is indexed for inflation. A companion Medicare Tax of 1.45% of wages is imposed on employers and employees with no limitation. A self-employment tax composed of both the employer and employee amounts (totaling 15.3%) is imposed on self-employed persons.
Other tax items
Credits
Main article: Tax creditsThe federal and state systems offer numerous tax credits for individuals and businesses. Among the key federal credits for individuals are:
- Child credit: For 2017, a credit up to $1,000 per qualifying child. For 2018 to 2025, the credit rose to $2,000 per qualifying child but made having a Social Security Number (SSN) a condition of eligibility for each child. For 2021, the credit was temporarily raised to $3,000 per child aged 6 to 17 and $3,600 per qualifying child aged 0 to 5 and was made fully refundable.
- Child and dependent care credit: a credit up to $6,000, phased out at incomes above $15,000. For 2021, the credit was raised up to $16,000, phased out at $125,000.
- Earned Income Tax Credit: this refundable credit is granted for a percentage of income earned by a low income individual. The credit is calculated and capped based on the number of qualifying children, if any. This credit is indexed for inflation and phased out for incomes above a certain amount. For 2015, the maximum credit was $6,422.
- Credit for the elderly and disabled: A nonrefundable credit up to $1,125.
- Two mutually exclusive credits for college expenses.
Businesses are also eligible for several credits. These credits are available to individuals and corporations and can be taken by partners in business partnerships. Among the federal credits included in a "general business credit" are:
- Credit for increasing research expenses.
- Work Incentive Credit or credit for hiring people in certain enterprise zones or on welfare.
- A variety of industry specific credits.
In addition, a federal foreign tax credit is allowed for foreign income taxes paid. This credit is limited to the portion of federal income tax arising due to foreign source income. The credit is available to all taxpayers.
Business credits and the foreign tax credit may be offset taxes in other years.
States and some localities offer a variety of credits that vary by jurisdiction. States typically grant a credit to resident individuals for income taxes paid to other states, generally limited in proportion to income taxed in the other state(s).
Alternative minimum tax
Main article: Alternative Minimum TaxTaxpayers must pay the higher of the regular income tax or the alternative minimum tax (AMT). Taxpayers who have paid AMT in prior years may claim a credit against regular tax for the prior AMT. The credit is limited so that regular tax is not reduced below current year AMT.
AMT is imposed at a nearly flat rate (20% for corporations, 26% or 28% for individuals, estates, and trusts) on taxable income as modified for AMT. Key differences between regular taxable income and AMT taxable income include:
- The standard deduction and personal exemptions are replaced by a single deduction, which is phased out at higher income levels,
- No deduction is allowed for individuals for state taxes,
- Most miscellaneous itemized deductions are not allowed for individuals,
- Depreciation deductions are computed differently, and
- Corporations must make a complex adjustment to more closely reflect economic income.
Special taxes
There are many federal tax rules designed to prevent people from abusing the tax system. Provisions related to these taxes are often complex. Such rules include:
- Accumulated earnings tax on corporation accumulations in excess of business needs,
- Personal holding company taxes,
- Passive foreign investment company rules, and
- Controlled foreign corporation provisions.
Special industries
Tax rules recognize that some types of businesses do not earn income in the traditional manner and thus require special provisions. For example, insurance companies must ultimately pay claims to some policy holders from the amounts received as premiums. These claims may happen years after the premium payment. Computing the future amount of claims requires actuarial estimates until claims are actually paid. Thus, recognizing premium income as received and claims expenses as paid would seriously distort an insurance company's income.
Special rules apply to some or all items in the following industries:
- Insurance companies (rules related to recognition of income and expense; different rules apply to life insurance and to property and casualty insurance)
- Shipping (rules related to the revenue recognition cycle)
- Extractive industries (rules related to expenses for exploration and development and for recovery of capitalized costs)
In addition, mutual funds (regulated investment companies) are subject to special rules allowing them to be taxed only at the owner level. The company must report to each owner his/her share of ordinary income, capital gains, and creditable foreign taxes. The owners then include these items in their own tax calculation. The fund itself is not taxed, and distributions are treated as a return of capital to the owners. Similar rules apply to real estate investment trusts and real estate mortgage investment conduits.
State, local and territorial income taxes
Main article: State income tax
Income tax is also levied by most U.S. states and many localities on individuals, corporations, estates, and trusts. These taxes are in addition to federal income tax and are deductible for federal tax purposes. State and local income tax rates vary from zero to 16% of taxable income. Some state and local income tax rates are flat (single rate), and some are graduated. State and local definitions of what income is taxable vary highly. Some states incorporate the federal definitions by reference. Taxable income is defined separately and differently for individuals and corporations in some jurisdictions. Some states impose alternative or additional taxes based on a second measure of income or capital.
States and localities tend to tax all income of residents. States and localities only tax nonresidents on income allocated or apportioned to the jurisdiction. Generally, nonresident individuals are taxed on wages earned in the state based on the portion of days worked in the state. Many states require partnerships to pay tax for nonresident partners.
Tax returns are filed separately for states and localities imposing income tax, and may be due on dates that differ from federal due dates. Some states permit related corporations to file combined or consolidated returns. Most states and localities imposing income tax require estimated payments where tax exceeds certain thresholds and require withholding tax on payment of wages.
Puerto Rico also imposes its own taxation laws; however, unlike in the states, only some residents there pay federal income taxes (though everyone must pay all other federal taxes). The other unincorporated territories of Guam, American Samoa, the Northern Mariana Islands and the Virgin Islands also impose their own income taxation laws, under a "mirror" tax law based on federal income tax law.
International aspects

The United States imposes tax on all citizens of the United States, including those who are residents of other countries, all individuals who are residents for tax purposes, and domestic corporations, defined as corporations created or organized in the United States or under Federal or state law.
Federal income tax is imposed on citizens, residents, and domestic corporations based on their worldwide income. To mitigate double taxation, a credit is allowed for foreign income taxes. This foreign tax credit is limited to that part of current year tax attributable to foreign source income. Determining such part involves determining the source of income and allocating and apportioning deductions to that income. Many, but not all, tax resident individuals and corporations on their worldwide income, but few allow a credit for foreign taxes.
In addition, federal income tax may be imposed on non-resident non-citizens as well as foreign corporations on U.S. source income. Federal tax applies to interest, dividends, royalties, and certain other income of nonresident aliens and foreign corporations not effectively connected with a U.S. trade or business at a flat rate of 30%. This rate is often reduced under tax treaties. Foreign persons are taxed on income effectively connected with a U.S. business and gains on U.S. realty similarly to U.S. persons. Nonresident aliens who are present in the United States for a period of 183 days in a given year are subject to U.S. capital gains tax on certain net capital gains realized during that year from sources within the United States. The states tax non-resident individuals only on income earned within the state (wages, etc.), and tax individuals and corporations on business income apportioned to the state.
The United States has income tax treaties with over 65 countries. These treaties reduce the chance of double taxation by allowing each country to fully tax its citizens and residents and reducing the amount the other country can tax them. Generally the treaties provide for reduced rates of tax on investment income and limits as to which business income can be taxed. The treaties each define which taxpayers can benefit from the treaty. U.S. treaties do not apply to income taxes imposed by the states or political subdivisions, except for the non discrimination provisions that appear in almost every treaty. Also, U.S. treaties generally do not permit U.S. persons from invoking treaty provisions with respect to U.S. taxes, with certain relatively standard exceptions.
Tax collection and examinations
Tax returns
Individuals (with income above a minimum level), corporations, partnerships, estates, and trusts must file annual reports, called tax returns, with federal and appropriate state tax authorities. These returns vary greatly in complexity level depending on the type of filer and complexity of their affairs. On the return, the taxpayer reports income and deductions, calculates the amount of tax owed, reports payments and credits, and calculates the balance due.
Federal individual, estate, and trust income tax returns are due by April 15 for most taxpayers. Corporate and partnership federal returns are due two and one half months following the corporation's year end. Tax exempt entity returns are due four and one half months following the entity's year end. All federal returns may be extended with most extensions available by merely filing a single page form. Due dates and extension provisions for state and local income tax returns vary.
Income tax returns generally consist of the basic form with attached forms and schedules. Several forms are available for individuals and corporations, depending on the complexity and nature of the taxpayer's affairs. Many individuals are able to use the one page Form 1040-EZ, which requires no attachments except wage statements from employers (Forms W-2). Individuals claiming itemized deductions must complete Schedule A. Similar schedules apply for interest (Schedule B), dividends (Schedule B), business income (Schedule C), capital gains (Schedule D), farm income (Schedule F), and self-employment tax (Schedule-SE). All taxpayers must file those forms for credits, depreciation, AMT, and other items that apply to them.
Electronic filing of tax returns may be done for taxpayers by registered tax preparers.
If a taxpayer discovers an error on a return, or determines that tax for a year should be different, the taxpayer should file an amended return. These returns constitute claims for refund if taxes are determined to have been overpaid.

The IRS, state, and local tax authorities may examine a tax return and propose changes. Changes to tax returns may be made with minimal advance involvement by taxpayers, such as changes to wage or dividend income to correct errors. Other examination of returns may require extensive taxpayer involvement, such as an audit by the IRS. These audits often require that taxpayers provide the IRS or other tax authority access to records of income and deductions. Audits of businesses are usually conducted by IRS personnel at the business location.
Changes to returns are subject to appeal by the taxpayer, including going to court. IRS changes are often first issued as proposed adjustments. The taxpayer may agree to the proposal or may advise the IRS why it disagrees. Proposed adjustments are often resolved by the IRS and taxpayer agreeing to what the adjustment should be. For those adjustments to which agreement is not reached, the IRS issues a 30-day letter advising of the adjustment. The taxpayer may appeal this preliminary assessment within 30 days within the IRS.
The Appeals Division reviews the IRS field team determination and taxpayer arguments, and often proposes a solution that the IRS team and the taxpayer find acceptable. When an agreement is still not reached, the IRS issues an assessment as a notice of deficiency or 90-day letter. The taxpayer then has three choices: file suit in United States Tax Court without paying the tax, pay the tax and sue for refund in regular court, or simply pay the tax and be done. Recourse to court can be costly and time-consuming but is often successful.
IRS computers routinely make adjustments to correct mechanical errors in returns. In addition, the IRS conducts an extensive document matching computer program that compares taxpayer amounts of wages, interest, dividends, and other items to amounts reported by taxpayers. These programs automatically issue 30-day letters advising of proposed changes. Only a very small percentage of tax returns are actually examined. These are selected by a combination of computer analysis of return information and random sampling. The IRS has long maintained a program to identify patterns on returns most likely to require adjustment.
Procedures for examination by state and local authorities vary by jurisdiction.
Tax collection
Taxpayers are required to pay all taxes owed based on the self-assessed tax returns, as adjusted. The IRS collection process may provide time payment plans that include interest and a "penalty" that is merely added interest. Where taxpayers do not pay tax owed, the IRS has strong means to enforce collection. These include the ability to levy bank accounts and seize property. Generally, significant advance notice is given before levy or seizure. However, in certain rarely used jeopardy assessments the IRS may immediately seize money and property. The IRS Collection Divisions are responsible for most collection activities.
Withholding of tax
Main article: Tax withholding in the United StatesPersons paying wages or making certain payments to foreign persons are required to withhold income tax from such payments. Income tax withholding on wages is based on declarations by employees and tables provided by the IRS. Persons paying interest, dividends, royalties, and certain other amounts to foreign persons must also withhold income tax at a flat rate of 30%. This rate may be reduced by a tax treaty. These withholding requirements also apply to non-U.S. financial institutions. Additional backup withholding provisions apply to some payments of interest or dividends to U.S. persons. The amount of income tax withheld is treated as a payment of tax by the person receiving the payment on which tax was withheld.
Employers and employees must also pay Social Security tax, the employee portion of which is also to be withheld from wages. Withholding of income and Social Security taxes are often referred to as payroll tax.
Statute of limitations
The IRS is precluded from assessing additional tax after a certain period of time. In the case of federal income tax, this period is generally three years from the later of the due date of the original tax return or the date the original return was filed. The IRS has an additional three more years to make changes if the taxpayer has substantially understated gross income. The period under which the IRS may make changes is unlimited in the case of fraud, or in the case of failure to file a return.
Penalties
Main article: IRS penaltiesTaxpayers who fail to file returns, file late, or file returns that are wrong, may be subject to penalties. These penalties vary based on the type of failure. Some penalties are computed as interest, some are fixed amounts, and some are based on other measures. Penalties for filing or paying late are generally based on the amount of tax that should have been paid and the degree of lateness. Penalties for failures related to certain forms are fixed amounts, and vary by form from very small to huge.
Intentional failures, including tax fraud, may result in criminal penalties. These penalties may include jail time or forfeiture of property. Criminal penalties are assessed in coordination with the United States Department of Justice.
History
Constitutional
Main article: United States income tax (legal history) See also: Taxation history of the United States
Article I, Section 8, Clause 1 of the United States Constitution (the "Taxing and Spending Clause"), specifies Congress's power to impose "Taxes, Duties, Imposts and Excises", but Article I, Section 8 requires that, "Duties, Imposts and Excises shall be uniform throughout the United States."
The Constitution specifically stated Congress' method of imposing direct taxes, by requiring Congress to distribute direct taxes in proportion to each state's population "determined by adding to the whole Number of free Persons, including those bound to Service for a Term of Years, and excluding Indians not taxed, three fifths of all other Persons". It had been argued that head taxes and property taxes (slaves could be taxed as either or both) were likely to be abused, and that they bore no relation to the activities in which the federal government had a legitimate interest. The fourth clause of section 9 therefore specifies that, "No Capitation, or other direct, Tax shall be laid, unless in Proportion to the Census or enumeration herein before directed to be taken."
Taxation was also the subject of Federalist No. 33 penned secretly by the Federalist Alexander Hamilton under the pseudonym Publius. In it, he asserts that the wording of the "Necessary and Proper" clause should serve as guidelines for the legislation of laws regarding taxation. The legislative branch is to be the judge, but any abuse of those powers of judging can be overturned by the people, whether as states or as a larger group.
The courts have generally held that direct taxes are limited to taxes on people (variously called "capitation", "poll tax" or "head tax") and property. All other taxes are commonly referred to as "indirect taxes", because they tax an event, rather than a person or property per se. What seemed to be a straightforward limitation on the power of the legislature based on the subject of the tax proved inexact and unclear when applied to an income tax, which can be arguably viewed either as a direct or an indirect tax.
Early federal income taxes
The first income tax suggested in the United States was during the War of 1812. The idea for the tax was based on the British Tax Act of 1798. The British tax law applied progressive rates to income. The British tax rates ranged from 0.833% on income starting at £60 to 10% on income above £200. The tax proposal was developed in 1814. Because the Treaty of Ghent was signed in 1815, ending hostilities and the need for additional revenue, the tax was never imposed in the United States.
In order to help pay for its war effort in the American Civil War, Congress imposed the first federal income tax in U.S. history through passage of the Revenue Act of 1861. The act created a flat tax of three percent on incomes above $800 (which was 5.6 times the 1861 nominal gross domestic product per capita of $144.31; the corresponding income in 2021 is $384K). This taxation of income reflected the increasing amount of wealth held in stocks and bonds rather than property, which the federal government had taxed in the past. The Revenue Act of 1862 established the first national inheritance tax and added a progressive taxation structure to the federal income tax, implementing a tax of five percent on incomes above $10,000. Congress later further raised taxes, and by the end of the war, the income tax constituted about one-fifth of the revenue of the federal government. To collect these taxes, Congress created the Office of the Commissioner of Internal Revenue within the Treasury Department. The federal income tax would remain in effect until its repeal in 1872.
In 1894, Democrats in Congress passed the Wilson-Gorman tariff, which imposed the first peacetime income tax. The rate was 2% on income over $4,000, which meant fewer than 10% of households would pay any. ($4,000 was 19.3 times the 1894 nominal GDP per capita of $207.23; the corresponding income in 2021 is $1.3M.) The purpose of the income tax was to make up for revenue that would be lost by tariff reductions. In 1895 the United States Supreme Court, in its ruling in Pollock v. Farmers' Loan & Trust Co., held a tax based on receipts from the use of property to be unconstitutional. The Court held that taxes on rents from real estate, on interest income from personal property, and other income from personal property (which includes dividend income) were treated as direct taxes on property, and therefore had to be apportioned (divided among the states based on their populations). Since apportionment of income taxes is impractical, this had the effect of prohibiting a federal tax on income from property. However, the Court affirmed that the Constitution did not deny Congress the power to impose a tax on real and personal property, and it affirmed that such would be a direct tax. Due to the political difficulties of taxing individual wages without taxing income from property, a federal income tax was impractical from the time of the Pollock decision until the time of ratification of the Sixteenth Amendment (below).
Progressive Era
For several years, the issue of an income tax lay unaddressed. In 1906, President Theodore Roosevelt revived the idea in his Sixth Annual Message to Congress. He said:
There is every reason why, when next our system of taxation is revised, the National Government should impose a graduated inheritance tax, and, if possible, a graduated income tax.
During the speech he cited the Pollock case without naming it specifically. The income tax became an issue again in Roosevelt's later speeches, including the 1907 State of the Union and during the 1912 election campaign.
Roosevelt's successor, William Howard Taft, also took up the issue of the income tax. Like Roosevelt, Taft cited the Pollock decision and gave a major speech in June 1909 regarding the Income Tax. One month later, Congress passed the resolution that would become the 16th Amendment.
Ratification of the Sixteenth Amendment
Main article: Sixteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution
In response, Congress proposed the Sixteenth Amendment (ratified by the requisite number of states in 1913), which states:
The Congress shall have power to lay and collect taxes on incomes, from whatever source derived, without apportionment among the several States, and without regard to any census or enumeration.
The Supreme Court in Brushaber v. Union Pacific Railroad, 240 U.S. 1 (1916), indicated that the amendment did not expand the federal government's existing power to tax income (meaning profit or gain from any source) but rather removed the possibility of classifying an income tax as a direct tax on the basis of the source of the income. The Amendment removed the need for the income tax to be apportioned among the states on the basis of population. Income taxes are required, however, to abide by the law of geographical uniformity.
Some tax protesters and others opposed to income taxes cite what they contend is evidence that the Sixteenth Amendment was never properly ratified, based in large part on materials sold by William J. Benson. In December 2007, Benson's "Defense Reliance Package" containing his non-ratification argument which he offered for sale on the Internet, was ruled by a federal court to be a "fraud perpetrated by Benson" that had "caused needless confusion and a waste of the customers' and the IRS' time and resources". The court stated: "Benson has failed to point to evidence that would create a genuinely disputed fact regarding whether the Sixteenth Amendment was properly ratified or whether United States Citizens are legally obligated to pay federal taxes." See also Tax protester Sixteenth Amendment arguments.
Modern interpretation of the power to tax incomes
The modern interpretation of the Sixteenth Amendment taxation power can be found in Commissioner v. Glenshaw Glass Co. 348 U.S. 426 (1955). In that case, a taxpayer had received an award of punitive damages from a competitor for antitrust violations and sought to avoid paying taxes on that award. The Court observed that Congress, in imposing the income tax, had defined gross income, under the Internal Revenue Code of 1939, to include:
gains, profits, and income derived from salaries, wages or compensation for personal service ... of whatever kind and in whatever form paid, or from professions, vocations, trades, businesses, commerce, or sales, or dealings in property, whether real or personal, growing out of the ownership or use of or interest in such property; also from interest, rent, dividends, securities, or the transaction of any business carried on for gain or profit, or gains or profits and income derived from any source whatever.
(Note: The Glenshaw Glass case was an interpretation of the definition of "gross income" in section 22 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1939. The successor to section 22 of the 1939 Code is section 61 of the current Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended.)
The Court held that "this language was used by Congress to exert in this field the full measure of its taxing power", id., and that "the Court has given a liberal construction to this broad phraseology in recognition of the intention of Congress to tax all gains except those specifically exempted."
The Court then enunciated what is now understood by Congress and the Courts to be the definition of taxable income, "instances of undeniable accessions to wealth, clearly realized, and over which the taxpayers have complete dominion." Id. at 431. The defendant in that case suggested that a 1954 rewording of the tax code had limited the income that could be taxed, a position which the Court rejected, stating:
The definition of gross income has been simplified, but no effect upon its present broad scope was intended. Certainly punitive damages cannot reasonably be classified as gifts, nor do they come under any other exemption provision in the Code. We would do violence to the plain meaning of the statute and restrict a clear legislative attempt to bring the taxing power to bear upon all receipts constitutionally taxable were we to say that the payments in question here are not gross income.
Tax statutes passed after the ratification of the Sixteenth Amendment in 1913 are sometimes referred to as the "modern" tax statutes. Hundreds of Congressional acts have been passed since 1913, as well as several codifications (i.e., topical reorganizations) of the statutes (see Codification).
In Central Illinois Public Service Co. v. United States, 435 U.S. 21 (1978), the U.S. Supreme Court confirmed that wages and income are not identical as far as taxes on income are concerned, because income not only includes wages, but any other gains as well. The Court in that case noted that in enacting taxation legislation, Congress "chose not to return to the inclusive language of the Tariff Act of 1913, but, specifically, 'in the interest of simplicity and ease of administration,' confined the obligation to withhold to 'salaries, wages, and other forms of compensation for personal services'" and that "committee reports ... stated consistently that 'wages' meant remuneration 'if paid for services performed by an employee for his employer'".
Other courts have noted this distinction in upholding the taxation not only of wages, but also of personal gain derived from other sources, recognizing some limitation to the reach of income taxation. For example, in Conner v. United States, 303 F. Supp. 1187 (S.D. Tex. 1969), aff'd in part and rev'd in part, 439 F.2d 974 (5th Cir. 1971), a couple had lost their home to a fire, and had received compensation for their loss from the insurance company, partly in the form of hotel costs reimbursed. The court acknowledged the authority of the IRS to assess taxes on all forms of payment, but did not permit taxation on the compensation provided by the insurance company, because unlike a wage or a sale of goods at a profit, this was not a gain. As the Court noted, "Congress has taxed income, not compensation".
By contrast, other courts have interpreted the Constitution as providing even broader taxation powers for Congress. In Murphy v. IRS, the United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit upheld the federal income tax imposed on a monetary settlement recovery that the same court had previously indicated was not income, stating: "lthough the 'Congress cannot make a thing income which is not so in fact,'... it can label a thing income and tax it, so long as it acts within its constitutional authority, which includes not only the Sixteenth Amendment but also Article I, Sections 8 and 9."
Similarly, in Penn Mutual Indemnity Co. v. Commissioner, the United States Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit indicated that Congress could properly impose the federal income tax on a receipt of money, regardless of what that receipt of money is called:
It could well be argued that the tax involved here is an "excise tax" based upon the receipt of money by the taxpayer. It certainly is not a tax on property and it certainly is not a capitation tax; therefore, it need not be apportioned. ... Congress has the power to impose taxes generally, and if the particular imposition does not run afoul of any constitutional restrictions then the tax is lawful, call it what you will.
Income tax rates in history
History of top rates
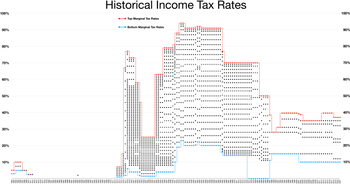



- In 1913, the top tax rate was 7% on incomes above $500,000 (equivalent to $15.4 million in 2023 dollars) and a total of $28.3 million was collected.
- During World War I, the top rate rose to 77% and the income threshold to be in this top bracket increased to $1,000,000 (equivalent to $23.8 million in 2023 dollars).
- Under Treasury Secretary Andrew Mellon, top tax rates were reduced in 1921, 1924, 1926, and 1928. Mellon argued that lower rates would spur economic growth. By 1928, the top rate was scaled down to 24% along with the income threshold for paying this rate lowered to $100,000 (equivalent to $1.77 million in 2023 dollars).
- During the Great Depression and World War II, the top income tax rate rose from pre-war levels. In 1939, the top rate was 75% applied to incomes above $5,000,000 (equivalent to $110 million in 2023 dollars). During 1944 and 1945, the top rate was its all-time high at 94% applied to income above $200,000 (equivalent to $3.46 million in 2023 dollars).
- The highest marginal tax rate for individuals for U.S. federal income tax purposes for tax years 1952 and 1953 was 92%.
- From 1964 to 2013, the threshold for paying top income tax rate has generally been between $200,000 and $400,000 (unadjusted for inflation). The one exception is the period from 1982 to 1992 when the topmost income tax brackets were removed. From 1981 until 1986 the top marginal rate was lowered to 50% on $86,000 and up (equivalent to $288,220 in 2023 dollars). From 1988 to 1990, the threshold for paying the top rate was even lower, with incomes above $29,750 (equivalent to $76,644 in 2023 dollars) paying the top rate of 28% in those years.
- Top tax rates were increased in 1992 and 1994, culminating in a 39.6% top individual rate applicable to all classes of income.
- Top individual tax rates were lowered in 2004 to 35% and tax rates on dividends and capital gains lowered to 15%, though these changes were enacted to expire with the end of the year 2010 to avoid the Byrd Rule for maintaining fiscal responsibility.
- Based on the summary of federal tax income data in 2009, with a tax rate of 35%, the highest earning 1% of people paid 36.7% of the United States' income tax revenue.
- In 2012, the 2004 cuts were extended to be permanent for individuals earning less than $400K and couples earning less than $450K, but the 2004 cuts were allowed to expire for higher incomes and the two top tax rates changed from 35% to 39.6% and from 33% to 36%.
| Year | Number of brackets | First bracket | Top bracket | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rate | Rate | Income | Adj. 2023 | |||
| 1913 | 7 | 1% | 7% | $500,000 | $15.4 million | First permanent income tax |
| 1916 | 14 | 2% | 15% | $2,000,000 | $56 million | — |
| 1917 | 21 | 2% | 67% | $2,000,000 | $47.6 million | World War I financing |
| 1918 | 56 | 6% | 77% | $1,000,000 | $20.3 million | — |
| 1919 | 56 | 4% | 73% | $1,000,000 | $17.6 million | — |
| 1922 | 50 | 4% | 58% | $200,000 | $3.64 million | — |
| 1923 | 50 | 3% | 43.5% | $200,000 | $3.58 million | — |
| 1924 | 43 | 1.5% | 46% | $500,000 | $8.89 million | — |
| 1925 | 23 | 1.125% | 25% | $100,000 | $1.74 million | Post war reductions |
| 1929 | 23 | 0.375% | 24% | $100,000 | $1.77 million | — |
| 1930 | 23 | 1.125% | 25% | $100,000 | $1.82 million | — |
| 1932 | 55 | 4% | 63% | $1,000,000 | $22.3 million | Depression era |
| 1936 | 31 | 4% | 79% | $5,000,000 | $110 million | — |
| 1940 | 31 | 4.4% | 81.1% | $5,000,000 | $109 million | — |
| 1941 | 32 | 10% | 81% | $5,000,000 | $104 million | World War II |
| 1942 | 24 | 19% | 88% | $200,000 | $3.73 million | Revenue Act of 1942 |
| 1944 | 24 | 23% | 94% | $200,000 | $3.46 million | Individual Income Tax Act of 1944 |
| 1946 | 24 | 19% | 86.45% | $200,000 | $3.12 million | — |
| 1948 | 24 | 16.6% | 82.13% | $400,000 | $5.07 million | — |
| 1950 | 24 | 17.4% | 84.36% | $400,000 | $5.07 million | — |
| 1951 | 24 | 20.4% | 91% | $400,000 | $4.7 million | — |
| 1952 | 26 | 22.2% | 92% | $400,000 | $4.59 million | — |
| 1954 | 26 | 20% | 91% | $400,000 | $4.54 million | — |
| 1964 | 26 | 16% | 77% | $400,000 | $3.93 million | Tax reduction during Vietnam war |
| 1965 | 25 | 14% | 70% | $200,000 | $1.93 million | — |
| 1968 | 33 | 14% | 75.25% | $200,000 | $1.75 million | — |
| 1969 | 33 | 14% | 77% | $200,000 | $1.66 million | — |
| 1970 | 33 | 14% | 71.75% | $200,000 | $1.57 million | — |
| 1971 | 33 | 14% | 70% | $200,000 | $1.5 million | — |
| 1981 | 17 | 13.825% | 69.125% | $215,400 | $721,890 | Reagan era tax cuts |
| 1982 | 14 | 12% | 50% | $85,600 | $270,260 | Reagan era tax cuts |
| 1983 | 14 | 11% | 50% | $109,400 | $334,670 | — |
| 1987 | 5 | 11% | 38.5% | $90,000 | $241,371 | Reagan era tax cuts |
| 1988 | 2 | 15% | 28% | $29,750 | $76,644 | Reagan era tax cuts |
| 1991 | 3 | 15% | 31% | $82,150 | $183,769 | Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1990 |
| 1993 | 5 | 15% | 39.6% | $89,150 | $188,034 | Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act of 1993 |
| 2001 | 5 | 10% | 39.1% | $297,350 | $511,659 | Bush tax cuts |
| 2002 | 6 | 10% | 38.6% | $307,050 | $520,139 | Bush tax cuts |
| 2003 | 6 | 10% | 35% | $311,950 | $516,681 | Bush tax cuts |
| 2013 | 7 | 10% | 39.6% | $400,000 | $523,200 | American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 |
| 2018 | 7 | 10% | 37% | $500,000 | $606,679 | Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 |
Federal income tax rates
Federal and state income tax rates have varied widely since 1913. For example, in 1954, the federal income tax was based on layers of 24 income brackets at tax rates ranging from 20% to 91% (for a chart, see Internal Revenue Code of 1954).
Below is a table of historical marginal income tax rates for married filing jointly tax payers at stated income levels. These income numbers are not the amounts used in the tax laws at the time.
| Historical income tax rates not adjusted for inflation (1913–2020) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | $10,001 | $20,001 | $60,001 | $100,001 | $250,001 |
| 1913 | 1% | 2% | 3% | 5% | 6% |
| 1914 | 1% | 2% | 3% | 5% | 6% |
| 1916 | 2% | 3% | 5% | 7% | 10% |
| 1918 | 16% | 21% | 41% | 64% | 72% |
| 1920 | 12% | 17% | 37% | 60% | 68% |
| 1922 | 10% | 16% | 36% | 56% | 58% |
| 1924 | 7% | 11% | 27% | 43% | 44% |
| 1926 | 6% | 10% | 21% | 25% | 25% |
| 1928 | 6% | 10% | 21% | 25% | 25% |
| 1930 | 6% | 10% | 21% | 25% | 25% |
| 1932 | 10% | 16% | 36% | 56% | 58% |
| 1934 | 11% | 19% | 37% | 56% | 58% |
| 1936 | 11% | 19% | 39% | 62% | 68% |
| 1938 | 11% | 19% | 39% | 62% | 68% |
| 1940 | 14% | 28% | 51% | 62% | 68% |
| 1942 | 38% | 55% | 75% | 85% | 88% |
| 1944 | 41% | 59% | 81% | 92% | 94% |
| 1946 | 38% | 56% | 78% | 89% | 91% |
| 1948 | 38% | 56% | 78% | 89% | 91% |
| 1950 | 38% | 56% | 78% | 89% | 91% |
| 1952 | 42% | 62% | 80% | 90% | 92% |
| 1954 | 38% | 56% | 78% | 89% | 91% |
| 1956 | 26% | 38% | 62% | 75% | 89% |
| 1958 | 26% | 38% | 62% | 75% | 89% |
| 1960 | 26% | 38% | 62% | 75% | 89% |
| 1962 | 26% | 38% | 62% | 75% | 89% |
| 1964 | 23% | 34% | 56% | 66% | 76% |
| 1966–76 | 22% | 32% | 53% | 62% | 70% |
| 1980 | 18% | 24% | 54% | 59% | 70% |
| 1982 | 16% | 22% | 49% | 50% | 50% |
| 1984 | 14% | 18% | 42% | 45% | 50% |
| 1986 | 14% | 18% | 38% | 45% | 50% |
| 1988 | 15% | 15% | 28% | 28% | 28% |
| 1990 | 15% | 15% | 28% | 28% | 28% |
| 1992 | 15% | 15% | 28% | 28% | 31% |
| 1994 | 15% | 15% | 28% | 31% | 39.6% |
| 1996 | 15% | 15% | 28% | 31% | 36% |
| 1998 | 15% | 15% | 28% | 28% | 36% |
| 2000 | 15% | 15% | 28% | 28% | 36% |
| 2002 | 10% | 15% | 27% | 27% | 35% |
| 2004 | 10% | 15% | 25% | 25% | 33% |
| 2006 | 10% | 15% | 15% | 25% | 33% |
| 2008 | 10% | 15% | 15% | 25% | 33% |
| 2010 | 10% | 15% | 15% | 25% | 33% |
| 2012 | 10% | 15% | 15% | 25% | 33% |
| 2014 | 10% | 15% | 15% | 25% | 33% |
| 2016 | 10% | 15% | 15% | 25% | 33% |
| 2018 | 10% | 12% | 12% | 22% | 24% |
| 2020 | 10% | 12% | 12% | 22% | 24% |
Controversies
The complexity of the U.S. income tax laws
United States tax law attempts to define a comprehensive system of measuring income in a complex economy. Many provisions defining income or granting or removing benefits require significant definition of terms. Further, many state income tax laws do not conform with federal tax law in material respects. These factors and others have resulted in substantial complexity. Even venerable legal scholars like Judge Learned Hand have expressed amazement and frustration with the complexity of the U.S. income tax laws. In the article, Thomas Walter Swan, 57 Yale Law Journal No. 2, 167, 169 (December 1947), Judge Hand wrote:
In my own case the words of such an act as the Income Tax ... merely dance before my eyes in a meaningless procession: cross-reference to cross-reference, exception upon exception—couched in abstract terms that offer no handle to seize hold of leave in my mind only a confused sense of some vitally important, but successfully concealed, purport, which it is my duty to extract, but which is within my power, if at all, only after the most inordinate expenditure of time. I know that these monsters are the result of fabulous industry and ingenuity, plugging up this hole and casting out that net, against all possible evasion; yet at times I cannot help recalling a saying of William James about certain passages of Hegel: that they were no doubt written with a passion of rationality; but that one cannot help wondering whether to the reader they have any significance save that the words are strung together with syntactical correctness.
Complexity is a separate issue from flatness of rate structures. Also, in the United States, income tax laws are often used by legislatures as policy instruments for encouraging numerous undertakings deemed socially useful — including the buying of life insurance, the funding of employee health care and pensions, the raising of children, home ownership, and the development of alternative energy sources and increased investment in conventional energy. Special tax provisions granted for any purpose increase complexity, irrespective of the system's flatness or lack thereof.
Proposals for changes of income taxation
Proposals have been made frequently to change tax laws, often with the backing of specific interest groups. Organizations making such proposals include Citizens for Tax Justice, Americans for Tax Reform, Americans for Tax Fairness, Citizens for an Alternative Tax System, Americans For Fair Taxation, and FreedomWorks. Various proposals have been put forth for tax simplification in Congress including the Fair Tax Act and various Flat tax plans.
Alternatives
Proponents of a consumption tax argue that the income tax system creates perverse incentives by encouraging taxpayers to spend rather than save: a taxpayer is only taxed once on income spent immediately, while any interest earned on saved income is itself taxed. To the extent that this is considered unjust, it may be remedied in a variety of ways, e.g. excluding investment income from taxable income, making investments deductible and therefore only taxing them when gains are realized, or replacing the income tax by other forms of tax, such as a sales tax.
Taxation vs. the states
Some economists believe income taxation offers the federal government a technique to diminish the power of the states, because the federal government is then able to distribute funding to states with conditions attached, often giving the states no choice but to submit to federal demands.
Tax protestors
Numerous tax protester arguments have been raised asserting that the federal income tax is unconstitutional, including discredited claims that the Sixteenth Amendment was not properly ratified. All such claims have been repeatedly rejected by the federal courts as frivolous.
Distribution
Further information: Progressivity in United States income tax

In the United States, a progressive tax system is employed which equates to higher income earners paying a larger percentage of their income in taxes. According to the IRS, the top 1% of income earners for 2008 paid 38% of income tax revenue, while earning 20% of the income reported. The top 5% of income earners paid 59% of the total income tax revenue, while earning 35% of the income reported. The top 10% paid 70%, earning 46% and the top 25% paid 86%, earning 67%. The top 50% paid 97%, earning 87% and leaving the bottom 50% paying 3% of the taxes collected and earning 13% of the income reported.
From 1979 to 2007 the average federal income tax rate fell 110% for the second lowest quintile, 56% for the middle quintile, 39% for the fourth quintile, 8% for the highest quintile, and 15% for the top 1%, with the bottom quintile moving from a tax rate of zero to negative liability. Despite this, individual income tax revenue only dropped from 8.7 to 8.5% of GDP over that time, and total federal revenue was 18.5% of GDP in both 1979 and 2007, above the postwar average of 18%. Tax code changes have dropped millions of lower earning people from the federal income tax rolls in recent decades. Those with zero or negative liability who were not claimed as dependents by a payer increased from 14.8% of the population in 1984 to 49.5% in 2009.
While there is consensus that overall federal taxation is progressive, there is dispute over whether progressivity has increased or decreased in recent decades, and by how much. The total effective federal tax rate for the top 0.01% of income earners declined from around 75% to around 35% between 1960 and 2005. Total effective federal tax rates fell from 19.1% to 12.5% for the three middle quintiles between 1979 and 2010, from 27.1% to 24% for the top quintile, from 7.5% to 1.5% for the bottom quintile, and from 35.1% to 29.4% for the top 1%.
A 2008 OECD study ranked 24 OECD nations by progressiveness of taxes and separately by progressiveness of cash transfers, which include pensions, unemployment and other benefits. The United States had the highest concentration coefficient in income tax, a measure of progressiveness, before adjusting for income inequality. The United States was not at the top of either measure for cash transfers. Adjusting for income inequality, Ireland had the highest concentration coefficient for income taxes. In 2008, overall income tax rates for the US were below the OECD average.
Effects on income inequality
Further information: Income inequality in the United StatesAccording to the CBO, U.S. federal tax policies substantially reduce income inequality measured after taxes. Taxes became less progressive (i.e., they reduced income inequality relatively less) measured from 1979 to 2011. The tax policies of the mid-1980s were the least progressive period since 1979. Government transfer payments contributed more to reducing inequality than taxes.
See also
- History of taxation in the United States
- Internal Revenue Code § 212 – tax deductibility of investment expenses.
- Payroll taxes in the United States
- Tax Day
- Tax preparation
- Taxation of illegal income in the United States
Other federal taxation:
US State taxes:
Politics:
General:
Explanatory notes
- Contrary to common misconception, residents of Puerto Rico do pay U.S. federal taxes: customs taxes (which are subsequently returned to the Puerto Rico Treasury) (See Dept of the Interior, Office of Insular Affairs. DOI.gov) Archived 2012-06-10 at the Wayback Machine, import/export taxes (See Stanford.wellsphere.com) Archived 2010-04-01 at the Wayback Machine, federal commodity taxes (See Stanford.wellsphere.com) Archived April 1, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, social security taxes (See IRS.gov), etc. Residents pay federal payroll taxes, such as Social Security (See IRS.gov) and Medicare (See Reuters.com), as well as Commonwealth of Puerto Rico income taxes (See Puertorico-herald.org and HTRCPA.com Archived April 29, 2011, at the Wayback Machine). All federal employees (See Heritage.org) Archived 2010-02-10 at the Wayback Machine, those who do business with the federal government (See MCVPR.com) Archived May 15, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, Puerto Rico-based corporations that intend to send funds to the U.S. (See p. 9, line 1.) Archived September 3, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, and some others (For example, Puerto Rican residents that are members of the U.S. military, See Heritage.org Archived February 10, 2010, at the Wayback Machine ; and Puerto Rico residents who earned income from sources outside Puerto Rico, See pp 14–15.) also pay federal income taxes. In addition, because the cutoff point for income taxation is lower than that of the U.S. IRS code, and because the per-capita income in Puerto Rico is much lower than the average per-capita income on the mainland, more Puerto Rico residents pay income taxes to the local taxation authority than if the IRS code were applied to the island. This occurs because "the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico government has a wider set of responsibilities than do U.S. State and local governments" (See GAO.gov). As residents of Puerto Rico pay into Social Security, Puerto Ricans are eligible for Social Security benefits upon retirement, but are excluded from the Supplemental Security Income (SSI) (Commonwealth of Puerto Rico residents, unlike residents of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands and residents of the 50 States, do not receive the SSI. See Socialsecurity.gov), and the island actually receives less than 15% of the Medicaid funding it would normally receive if it were a U.S. state. However, Medicare providers receive less-than-full state-like reimbursements for services rendered to beneficiaries in Puerto Rico, even though the latter paid fully into the system (See p 252). Archived 2011-05-11 at the Wayback Machine In general, "many federal social welfare programs have been extended to Puerto Rican (sic) residents, although usually with caps inferior to those allocated to the states." (The Louisiana Purchase and American Expansion: 1803–1898. By Sanford Levinson and Bartholomew H. Sparrow. New York: Rowman and Littlefield Publishers. 2005. Page 167. For a comprehensive coverage of federal programs made extensive to Puerto Rico see Richard Cappalli's Federal Aid to Puerto Rico (1970)). It has also been estimated (See Egleforum.org) that, because the population of the Island is greater than that of 50% of the States, if it were a state, Puerto Rico would have six to eight seats in the House, in addition to the two seats in the Senate.(See Eagleforum.org, CRF-USA.org Archived 2009-06-10 at the Wayback Machine and Thomas.gov Archived February 1, 2016, at the Wayback Machine [For the later, the official U.S. Congress database website, you will need to resubmit a query. The document in question is called "House Report 110-597 - Puerto Rico Democracy Act of 2007." These are the steps to follow: THOMAS.gov Archived September 29, 2006, at the Wayback Machine > Committee Reports > 110 > drop down "Word/Phrase" and pick "Report Number" > type "597" next to Report Number. This will provide the document "House Report 110-597 - 2007", then from the Table of Contents choose "Background and need for legislation".). Another misconception is that the import/export taxes collected by the U.S. on products manufactured in Puerto Rico are all returned to the Puerto Rico Treasury. This is not the case. Such import/export taxes are returned only for rum products, and even then the US Treasury keeps a portion of those taxes (See the "House Report 110-597 - Puerto Rico Democracy Act of 2007" mentioned above.)
References
- Erica York (January 26, 2023), Summary of the Latest Federal Income Tax Data, 2023 Update, Tax Foundation, Wikidata Q118189145
- Erica York (January 26, 2023), Summary of the Latest Federal Income Tax Data, 2023 Update, Tax Foundation, Wikidata Q118189145
- Samuel A. Donaldson, Federal Income Taxation of Individuals: Cases, Problems and Materials, 4 (2nd Ed. 2007).
- ^ Id.
- See below for additional reading. The U.S. Internal Revenue Service offers many free publications which are available online, including one for individuals and one for corporations, in both .pdf and web formats. An incomplete index is available by topic. Many states offer similar publications.
- "Iowa Tax/Fee Descriptions and Rates". Iowa Department of Revenue. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- ^ CCH State Tax Handbook 2018, page 617, et seq.
- Durante, Alex (October 18, 2022). "2023 Tax Brackets". Tax Foundation. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- CCH State Tax Handbook 2018, page 254, et seq.
- "eCFR :: Title 26 of the CFR -- Internal Revenue". Code of Federal Regulations. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- IRS instructions for Form 1120 Schedule M-3.
- "Overview of the Federal Tax System as in Effect for 2022". Joint Committee on Taxation. Retrieved May 5, 2023.
- "IRS Pub. 502" (PDF). IRS. Note: limit is 7.5% for those over age 65.
- "Questions and Answers for the Additional Medicare Tax". Internal Revenue Service. Retrieved July 6, 2018.
- "Chart C—Other Situations When You Must File" (PDF). IRS. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
- "Income inequality: Top 1 percent took record share of 2012 U.S. income, Associated Press, Sept. 10, 2013.
- ^ "The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2010". The US Congressional Budget Office (CBO). December 4, 2013. Retrieved January 6, 2014.
- Picchi, Aimee (October 17, 2019). "America's richest 400 families now pay a lower tax rate than the middle class". CBS News. Archived from the original on May 11, 2024. (Chart labeled "Effective tax rates by income".) Analysis by economists Emmanuel Saez and Gabriel Zucman.
- "It matters how tax brackets are adjusted". Tax Foundation. October 10, 2014. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- "IRS.gov" (PDF). irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- "Publication 505 (2018), Tax Withholding and Estimated Tax - Internal Revenue Service". www.irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- "IRS.gov – 2012 Tax Rate Tables" (PDF). irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- 26 USC 1411.
- "IRS Pub 17, 2013" (PDF). irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- "IRS Pub. 17, 2014" (PDF). irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- "IRS Pub. 17, 2015" (PDF). irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- "IRS Rev Proc 15-53" (PDF). irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- "IRS Rev Proc 2016-55" (PDF). irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- Individual Tax Reform.
- "What are the 2019 tax brackets for federal income taxes?". June 26, 2019.
- "2020 Tax Brackets". November 14, 2019.
- "2021 Tax Brackets". October 27, 2020.
- "2022 Tax Brackets". November 10, 2021.
- "2023 Tax Brackets". October 18, 2022.
- "2022-2023 Tax Brackets & Federal Income Tax Rates". Forbes Advisor. May 8, 2023. Retrieved May 24, 2023.
- IRS 1040 Instructions for 2016: Tax Tables, page 81.
- "Payroll Tax Cut to Boost Take-Home Pay for Most Workers". irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- "Effective Income Tax Rates". The New York Times. January 17, 2012.
- "The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2011". Congressional Budget Office. November 12, 2014. Retrieved January 20, 2015.
- ^ 26 USC 61.
- 26 CFR 1.61-1(a).
- 26 USC 162, et seq.
- IRS Publication 535, Business Expenses; Fox chapter 22, Hoffman chapters 6 and 7, Pratt chapters 7 and 10.
- 26 USC 263.
- 26 USC 168, et seq, IRS Publication 946, How to Depreciate Property; Fox chapter 24, Hoffman chapter 8, Pratt chapter 9.
- 26 USC 1011, et seq., IRS Topic 409, Capital Gains and Losses, Fox chapters 13–14, Hoffman chapters 13–14, Pratt chapters 14–17.
- 26 USC 269, IRS Publication 925, Passive Activities. Losses from an activity are deductible against other income on disposal of the activity.
- "26 USC 151: Allowance of deductions for personal exemptions". United States Code. Archived from the original on January 3, 2023.
- 26 USC 262, 163, 164, 170; IRS Form 1040, Schedule A; Fox chapter 21, Hoffman chapter 10, Pratt chapter 11.
- "26 USC 265: Expenses and interest relating to tax-exempt income". United States Code. Archived from the original on December 25, 2022, et seq.
- "With new SALT limit, IRS explains tax treatment of state and local tax refunds". Internal Revenue Service. March 29, 2019. Retrieved February 8, 2022.
- "Publication 547 (2023), Casualties, Disasters, and Thefts | Internal Revenue Service". www.irs.gov. Retrieved August 2, 2024.
- "26 USC 165: Losses". uscode.house.gov. Retrieved August 2, 2024.
- 26 USC 68.
- 26 USC 121.
- See generally 26 USC 1045, IRS Topic 409, Capital Gains and Losses and Publication 535, above; Fox chapters 13-14, Hoffman chapters 13–14, Pratt chapters 16–17.
- Lowrey, Annie (January 4, 2013). "Tax Code May Be the Most Progressive Since 1979". The New York Times. Retrieved January 6, 2014.
- Fox, chapter 32; Hoffman, chapter 16; Pratt, chapter 5.
- "Partnerships | Internal Revenue Service". www.irs.gov. Retrieved February 8, 2022.
- "Forming a Corporation | Internal Revenue Service". www.irs.gov. Retrieved February 8, 2022.
- "Contribution and Benefit Base". www.ssa.gov. Retrieved July 23, 2020.
- "26 U.S. Code § 21 - Expenses for household and dependent care services necessary for gainful employment". LII / Legal Information Institute. Retrieved February 8, 2022.
- "EITC Income Limits Maximum Credit Amounts - Internal Revenue Service". www.irs.gov. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- See, e.g., CCH 2013 State Tax Handbook, ISBN 978-0-8080-3227-4, Fox Income Tax in the USA, appendix, ISBN 978-0-9851823-3-5, ASIN B00BCSNOGG.
- All residents of PR pay federal taxes, with the exception of federal income taxes which only some residents of Puerto Rico must still pay.
- 26 USC 871 and .
- 26 USC 871(b), 26 USC 881, and 26 USC 897.
- 26 USC 6012.
- Publication 509: Tax Calendars for use in 2017, U.S. Internal Revenue Service, Cat. No. 15013X
- "IRS Can Audit for Three Years, Six, or Forever: Here's How to Tell". www.americanbar.org. Retrieved February 8, 2022.
- "U.S. Constitution - Article 1 Section 8 - The U.S. Constitution Online - USConstitution.net". usconstitution.net. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- Hylton v. United States, 3 U.S. 171 (1796). Penn Mutual Indemnity Co. v. Commissioner, 227 F.2d 16, 19–20 (3rd Cir. 1960).
- Steward Machine Co. v. Davis, 301 U.S. 548 (1937), 581–582.
- "A History of Taxation". Taxworld. Archived from the original on January 20, 2019. Retrieved December 7, 2013.
- Joseph A. Hill, "The Civil War Income Tax", Quarterly Journal of Economics Vol. 8, No. 4 (July 1894), pp. 416–452. JSTOR 1885003; appendix: JSTOR 1885007.
- Weisman (2002), pp. 30–35.
- Weisman (2002), pp. 40–42.
- Pollack, Sheldon D. (2014). "The First National Income Tax, 1861–1872" (PDF). Tax Lawyer. 67 (2).
- Weisman (2002), pp. 99–101.
- Charles F. Dunbar, "The New Income Tax", Quarterly Journal of Economics, Vol. 9, No. 1 (Oct. 1894), pp. 26–46. JSTOR 1883633.
- Chief Justice Fuller's opinion, 158 U.S. 601, 634 Archived December 6, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Origins of the Modern Income Tax, 1894–1913, p. 18, University of Delaware.
- December 3, 1906: Sixth Annual Message.
- Munsey's Magazine, Volume 46.
- Roosevelt said: The first purely income-tax law was past by the Congress in 1861, but the most important law dealing with the subject was that of 1894. This the court held to be unconstitutional. The question is undoubtedly very intricate, delicate, and troublesome. The decision of the court was only reached by one majority. It is the law of the land, and of course is accepted as such and loyally obeyed by all good citizens.
- December 3, 1907: Seventh Annual Message.
- Theodore Roosevelt's Confession of Faith Before the Progressive National Convention.
- William Howard Taft, Jeffrey Rosen.
- ^ June 16, 1909: Message Regarding Income Tax, William Howard Taft.
- The 16th Amendment and 100 years of Federal income taxes, Library of Congress.
- United States Government Printing Office, at Amendments to the Constitution of the United States of America Archived 2008-02-05 at the Wayback Machine; see generally United States v. Thomas, 788 F.2d 1250 (7th Cir. 1986), cert. denied, 107 S.Ct. 187 (1986); Ficalora v. Commissioner, 751 F.2d 85, 85-1 U.S. Tax Cas. (CCH) ¶ 9103 (2d Cir. 1984); Sisk v. Commissioner, 791 F.2d 58, 86-1 U.S. Tax Cas. (CCH) ¶ 9433 (6th Cir. 1986); United States v. Sitka, 845 F.2d 43, 88-1 U.S. Tax Cas. (CCH) ¶ 9308 (2d Cir.), cert. denied, 488 U.S. 827 (1988); United States v. Stahl, 792 F.2d 1438, 86-2 U.S. Tax Cas. (CCH) ¶ 9518 (9th Cir. 1986), cert. denied, 107 S. Ct. 888 (1987); Brown v. Commissioner, 53 T.C.M. (CCH) 94, T.C. Memo 1987–78, CCH Dec. 43,696(M) (1987); Lysiak v. Commissioner, 816 F.2d 311, 87-1 U.S. Tax Cas. (CCH) ¶ 9296 (7th Cir. 1987); Miller v. United States, 868 F.2d 236, 89-1 U.S. Tax Cas. (CCH) ¶ 9184 (7th Cir. 1989); also, see generally Boris I. Bittker, Constitutional Limits on the Taxing Power of the Federal Government, The Tax Lawyer, Fall 1987, Vol. 41, No. 1, p. 3 (American Bar Ass'n).
- Memorandum Opinion, p. 14, Dec. 17, 2007, docket entry 106, United States v. Benson, case no. 1:04-cv-07403, United States District Court for the Northern District of Illinois, Eastern Division.
- Memorandum Opinion, p. 9, Dec. 17, 2007, docket entry 106, United States v. Benson, case no. 1:04-cv-07403, United States District Court for the Northern District of Illinois, Eastern Division.
- ^ 348 U.S.
- Opinion on rehearing, July 3, 2007, p. 16, Murphy v. Internal Revenue Service and United States, case no. 05-5139, United States Court of Appeals for the District of Columbia Circuit, 2007-2 U.S. Tax Cas. (CCH) ¶ 50,531 (D.C. Cir. 2007).
- Penn Mutual Indemnity Co. v. Commissioner, 277 F.2d 16, 60-1 U.S. Tax Cas. (CCH) ¶ 9389 (3d Cir. 1960) (footnotes omitted).
- ^ 1634–1699: McCusker, J. J. (1997). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States: Addenda et Corrigenda (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1700–1799: McCusker, J. J. (1992). How Much Is That in Real Money? A Historical Price Index for Use as a Deflator of Money Values in the Economy of the United States (PDF). American Antiquarian Society. 1800–present: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis. "Consumer Price Index (estimate) 1800–". Retrieved February 29, 2024.
- "Distribution of the Income Tax". The Independent. July 20, 1914. Retrieved August 23, 2012.
- Tax History Project, under year 1920.
- Page 12 of Instructions for 1952 Form 1040, Internal Revenue Service, U.S. Department of the Treasury; page 12 of Instructions for 1953 Form 1040, Internal Revenue Service, U.S. Department of the Treasury.
- History of Federal Individual Income Bottom and Top Bracket Rates. Retrieved 2010-02-04.
- Guenther, Gary (February 12, 2018). Individual Income Tax Rates and Other Key Elements of the Federal Individual Income Tax: 1988 to 2017 (PDF). Washington, D.C.: Congressional Research Service. Retrieved February 25, 2018.
- Logan, D. S. (24 October 2011). "Summary of latest federal individual income tax data". Tax Foundation.
- "Outline of Major Tax Law Provisions in 2013 under Multiple Scenarios" (12 April 2012). Tax Foundation.
- Personal Exemptions and Individual Income Tax Rates: 1913–2002, Internal Revenue Service
- U.S. Federal Individual Marginal Income Tax Rates History, 1913–2009 Archived 2013-01-16 at the Wayback Machine, The Tax Foundation.
- CPI Inflation Calculator.
- Historical U.S. Federal Individual Income Tax Rates and Brackets Tax Foundation. Accessed: 10 August 2024.
- John Stuart Mill's argument, reported by Marvin A. Chirelstein, Federal Income Taxation, p. 433 (Foundation Press, 10th Ed., 2005)
- Chirelstein, loc.cit.
- "Cato Institute publication" (PDF). cato.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 27, 2012. Retrieved August 19, 2018.
- "The Truth About Frivolous Tax Arguments". March 4, 2013. Retrieved July 30, 2013.
- ^ "The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes 2011". Congressional Budget Office, US Government. November 2014.
- ^ McCormally, Kevin (December 18, 2010). "Where Do You Rank as a Taxpayer?". Kiplinger. Retrieved June 18, 2010.
- Reynolds, Alan (May 3, 2011). "The Increasing Progressivity of U.S. Taxes: And the Shrinking Tax Base". Cato Institute. Retrieved January 18, 2014.
- Bluey, Rob (February 19, 2012). "Chart of the Week: Nearly Half of All Americans Don't Pay Income Taxes". Heritage Foundation. Retrieved October 28, 2013.
- Will Freeland; Scott A. Hodge (July 20, 2012). "Tax Equity and the Growth in Nonpayers". Tax Foundation. Archived from the original on December 9, 2016. Retrieved October 28, 2013.
- ^ Thomas Piketty; Emmanuel Saez (2007). "How Progressive is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective" (PDF). Journal of Economic Perspectives. 21 (1): 23–24. doi:10.1257/jep.21.1.3. S2CID 5160267. Retrieved January 25, 2014.
- Michael D. Stroup; Keith Hubbard (August 2013). "An improved index and estimation method for assessing tax progressivity" (PDF). Mercatus Center, George Mason University. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 5, 2015. Retrieved January 18, 2014.
- "The Distribution of Household Income and Federal Taxes, 2010". Congressional Budget Office. December 4, 2013. Retrieved January 21, 2014.
- Growing Unequal?: Income Distribution and Poverty in OECD Countries, OECD Publishing, ISBN 978-92-64-04418-0, 2008, pgs. 103, 104.
Further reading
Government sources:
- IRS Publication 17, Your Federal Income Tax
- IRS Publication 334, Tax Guide for Small Business
- IRS Publication 509, Tax Calendar
- IRS Publication 541, Partnerships
- IRS Publication 542, Corporations
- IRS Publication 544, Sales and Other Dispositions of Assets
- IRS Publication 556 Examination of Returns, Appeal Rights, and Claims for Refund
- IRS Tax Topics
- IRS videos on tax topics
- IRS links to state websites
Law & regulations:
Texts:
- Fox, Stephen C, Income Tax in the USA. 2013 edition ISBN 978-0-9851823-3-5, ASIN B00BCSNOGG.
- Hoffman, William H. Jr.; Willis, Eugene; et al., South-Western Federal Taxation. 2013 edition ISBN 978-1-133-18955-8, ASIN B00B6F3AWI.
- Pratt, James W.; Kulsrud, William N.; et al., Federal Taxation". 2013 edition ISBN 978-1-133-49623-6.
- Whittenberg, Gerald; Altus-Buller, Martha; Gill, Stephen, Income Tax Fundamentals 2010. 2013 edition ISBN 978-1-111-97251-6, ASIN B00B6FBDHW.
History:
- Buenker, John D. The Income Tax and the Progressive Era (Routledge, 2018) excerpt.
- Ellis, Elmer. "Public Opinion and the Income Tax, 1860-1900." Mississippi Valley Historical Review 27.2 (1940): 225-242 online.
- Ratner, Sidney. American Taxation: Its History as a Social Force in Democracy (1942) online
- Thorndike, Joseph J. Their Fair Share: Taxing the Rich in the Age of FDR. Washington, DC: Urban Institute, 2013.
- Weisman, Steven R. (2002). The Great Tax Wars: Lincoln to Wilson-The Fierce Battles over Money That Transformed the Nation. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 0-684-85068-0.
Reference works (annual):
- CCH U.S. Master Tax Guide, 2013 ISBN 978-0-8080-2980-9
- RIA Federal Tax Handbook 2013 ISBN 978-0-7811-0472-2
- Dauchy, E. P., & Balding, C. (2013). Federal Income Tax Revenue Volatility Since 1966. Working Papers w0198, Center for Economic and Financial Research (CEFIR). Available at SSRN 2351376.
Consumer publications (annual):
- J.K. Lasser's Your Income Tax for 2013 ISBN 978-0-470-44711-6, ASIN B009WU0U2C
- Ernst & Young Tax Guide 2013 ISBN 978-1-118-46667-4, ASIN B00A6WOSUK
