| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Polyetherimide" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (September 2014) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names PEI, Ultem | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.126.800 |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | (C37H24O6N2)n |
| Molar mass | Variable |
| Appearance | Amber-to-transparent solid |
| Density | 1.27 g/cm |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C , 100 kPa).
| |
Polyetherimide (PEI; branded as Ultem) is an amorphous, amber-to-transparent thermoplastic with characteristics similar to the related plastic PEEK. When comparing PEI to PEEK, the former is cheaper but has lower impact strength and a tighter temperature range.
PEI plastics were first introduced into the market by General Electric (GE) in 1982 under the trade name Ultem.
Due to its adhesive properties and chemical stability it became a popular bed material for FFF 3D printers.
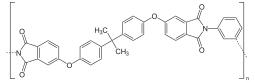
Structure
The molecular formula of the PEI repeating unit is C37H24O6N2 and the molecular weight is 592.61 g/mol. It contains phthalimide and bisphenol A sub-units.
Properties
The glass transition temperature of PEI is 217 °C (422 °F). Its amorphous density at 25 °C is 1.27 g/cm(.046 lb/in³). It is prone to stress cracking in chlorinated solvents. Polyetherimide is able to resist high temperatures while maintaining stable electrical properties over a wide range of frequencies. This high strength material offers excellent chemical resistance and ductile properties suitable for various applications, even those involving steam exposure.
References
- "Ultem". Curbell Plastics. Retrieved 2 November 2023.
- http://www.mcmaster.com/#ultem/=otzvqt Referenced Oct 7, 2013
- "What Is Polyetherimide (PEI)?". Retrieved 2024-10-15.
- Scott, Chris. "polyetherimide information and properties". www.polymerprocessing.com. Retrieved 2018-04-30.
- "Injection Molding Material Selection Guide". www.abtecinc.com. Retrieved 2018-04-30.
This article about polymer science is a stub. You can help Misplaced Pages by expanding it. |

