| This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. (June 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Vaginal artery | |
|---|---|
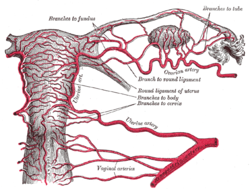 Arteries of the female reproductive tract (posterior view): uterine artery, ovarian artery and vaginal arteries. Arteries of the female reproductive tract (posterior view): uterine artery, ovarian artery and vaginal arteries. | |
 Vessels of the uterus and its appendages, rear view. Vessels of the uterus and its appendages, rear view. | |
| Details | |
| Source | Internal iliac artery Uterine artery |
| Vein | Vaginal venous plexus |
| Supplies | Urinary bladder, ureter, vagina |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria vaginalis |
| TA98 | A12.2.15.035F |
| TA2 | 4336 |
| FMA | 18832 |
| Anatomical terminology[edit on Wikidata] | |
The vaginal artery is an artery in females that supplies blood to the vagina and the base of the bladder.
Structure

The vaginal artery is usually a branch of the internal iliac artery. Some sources say that the vaginal artery can arise from the uterine artery, but the phrase vaginal branches of uterine artery is the term for blood supply to the vagina coming from the uterine artery.
The vaginal artery is frequently represented by two or three branches. These descend to the vagina, supplying its mucous membrane. They anastomose with branches from the uterine artery. It can send branches to the bulb of the vestibule, the fundus of the bladder, and the contiguous part of the rectum.
Function
The vaginal artery supplies oxygenated blood to the muscular wall of the vagina, along with the uterine artery and the internal pudendal artery. It also supplies the cervix, along with the uterine artery.
Other animals
In horses, the vaginal artery may haemorrhage after birth, which can cause death.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 616 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 616 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Kyung Won, PhD. Chung (2005). Gross Anatomy (Board Review). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 290. ISBN 0-7817-5309-0.
- ^ Łaniewski, Paweł; Herbst-Kralovetz, Melissa (2018-01-01), "Vagina", in Skinner, Michael K. (ed.), Encyclopedia of Reproduction (Second Edition), Oxford: Academic Press, pp. 353–359, ISBN 978-0-12-815145-7, retrieved 2021-01-18
- Graziottin, Alessandra; Gambini, Dania (2015-01-01), Vodušek, David B.; Boller, François (eds.), "Chapter 4 - Anatomy and physiology of genital organs – women", Handbook of Clinical Neurology, Neurology of Sexual and Bladder Disorders, 130, Elsevier: 39–60, doi:10.1016/B978-0-444-63247-0.00004-3, ISBN 9780444632470, PMID 26003238, retrieved 2021-01-18
- Mahendroo, Mala; Nallasamy, Shanmugasundaram (2018-01-01), "Cervix", in Skinner, Michael K. (ed.), Encyclopedia of Reproduction (Second Edition), Oxford: Academic Press, pp. 339–346, ISBN 978-0-12-815145-7, retrieved 2021-01-18
- McAuliffe, Siobhan B., ed. (2014-01-01), "Chapter 12 - Reproductive disorders", Knottenbelt and Pascoe's Color Atlas of Diseases and Disorders of the Horse (Second Edition), W.B. Saunders, pp. 443–513, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7234-3660-7.00012-2, ISBN 978-0-7234-3660-7, S2CID 241150397, retrieved 2021-02-06
External links
- Anatomy photo:43:13-0206 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Pelvis: Branches of Internal Iliac Artery"