Vertical pressure variation is the variation in pressure as a function of elevation. Depending on the fluid in question and the context being referred to, it may also vary significantly in dimensions perpendicular to elevation as well, and these variations have relevance in the context of pressure gradient force and its effects. However, the vertical variation is especially significant, as it results from the pull of gravity on the fluid; namely, for the same given fluid, a decrease in elevation within it corresponds to a taller column of fluid weighing down on that point.
Basic formula
A relatively simple version of the vertical fluid pressure variation is simply that the pressure difference between two elevations is the product of elevation change, gravity, and density. The equation is as follows: where
- P is pressure,
- ρ is density,
- g is acceleration of gravity, and
- h is height.
The delta symbol indicates a change in a given variable. Since g is negative, an increase in height will correspond to a decrease in pressure, which fits with the previously mentioned reasoning about the weight of a column of fluid.
When density and gravity are approximately constant (that is, for relatively small changes in height), simply multiplying height difference, gravity, and density will yield a good approximation of pressure difference. If the pressure at one point in a liquid with uniform density ρ is known to be P0, then the pressure at another point is P1:
where h1 - h0 is the vertical distance between the two points.
Where different fluids are layered on top of one another, the total pressure difference would be obtained by adding the two pressure differences; the first being from point 1 to the boundary, the second being from the boundary to point 2; which would just involve substituting the ρ and Δh values for each fluid and taking the sum of the results. If the density of the fluid varies with height, mathematical integration would be required.
Whether or not density and gravity can be reasonably approximated as constant depends on the level of accuracy needed, but also on the length scale of height difference, as gravity and density also decrease with higher elevation. For density in particular, the fluid in question is also relevant; seawater, for example, is considered an incompressible fluid; its density can vary with height, but much less significantly than that of air. Thus water's density can be more reasonably approximated as constant than that of air, and given the same height difference, the pressure differences in water are approximately equal at any height.
Hydrostatic paradox
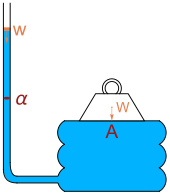
The barometric formula depends only on the height of the fluid chamber, and not on its width or length. Given a large enough height, any pressure may be attained. This feature of hydrostatics has been called the hydrostatic paradox. As expressed by W. H. Besant,
- Any quantity of liquid, however small, may be made to support any weight, however large.
The Flemish scientist Simon Stevin was the first to explain the paradox mathematically. In 1916 Richard Glazebrook mentioned the hydrostatic paradox as he described an arrangement he attributed to Pascal: a heavy weight W rests on a board with area A resting on a fluid bladder connected to a vertical tube with cross-sectional area α. Pouring water of weight w down the tube will eventually raise the heavy weight. Balance of forces leads to the equation
Glazebrook says, "By making the area of the board considerable and that of the tube small, a large weight W can be supported by a small weight w of water. This fact is sometimes described as the hydrostatic paradox."
Hydraulic machinery employs this phenomenon to multiply force or torque. Demonstrations of the hydrostatic paradox are used in teaching the phenomenon.
In the context of Earth's atmosphere
Main article: Barometric formulaIf one is to analyze the vertical pressure variation of the atmosphere of Earth, the length scale is very significant (troposphere alone being several kilometres tall; thermosphere being several hundred kilometres) and the involved fluid (air) is compressible. Gravity can still be reasonably approximated as constant, because length scales on the order of kilometres are still small in comparison to Earth's radius, which is on average about 6371 km, and gravity is a function of distance from Earth's core.
Density, on the other hand, varies more significantly with height. It follows from the ideal gas law that where
- m is average mass per air molecule,
- P is pressure at a given point,
- k is the Boltzmann constant,
- T is the temperature in kelvins.
Put more simply, air density depends on air pressure. Given that air pressure also depends on air density, it would be easy to get the impression that this was circular definition, but it is simply interdependency of different variables. This then yields a more accurate formula, of the form where
- Ph is the pressure at height h,
- P0 is the pressure at reference point 0 (typically referring to sea level),
- m is the mass per air molecule,
- g is the acceleration due to gravity,
- h is height from reference point 0,
- k is the Boltzmann constant,
- T is the temperature in kelvins.
Therefore, instead of pressure being a linear function of height as one might expect from the more simple formula given in the "basic formula" section, it is more accurately represented as an exponential function of height.
Note that in this simplification, the temperature is treated as constant, even though temperature also varies with height. However, the temperature variation within the lower layers of the atmosphere (troposphere, stratosphere) is only in the dozens of degrees, as opposed to their thermodynamic temperature, which is in the hundreds, so the temperature variation is reasonably small and is thus ignored. For smaller height differences, including those from top to bottom of even the tallest of buildings, (like the CN Tower) or for mountains of comparable size, the temperature variation will easily be within the single-digits. (See also lapse rate.)
An alternative derivation, shown by the Portland State Aerospace Society, is used to give height as a function of pressure instead. This may seem counter-intuitive, as pressure results from height rather than vice versa, but such a formula can be useful in finding height based on pressure difference when one knows the latter and not the former. Different formulas are presented for different kinds of approximations; for comparison with the previous formula, the first referenced from the article will be the one applying the same constant-temperature approximation; in which case: where (with values used in the article)
- z is the elevation in meters,
- R is the specific gas constant = 287.053 J/(kg K)
- T is the absolute temperature in kelvins = 288.15 K at sea level,
- g is the acceleration due to gravity = 9.80665 m/s at sea level,
- P is the pressure at a given point at elevation z in Pascals, and
- P0 is pressure at the reference point = 101,325 Pa at sea level.
A more general formula derived in the same article accounts for a linear change in temperature as a function of height (lapse rate), and reduces to above when the temperature is constant: where
- L is the atmospheric lapse rate (change in temperature divided by distance) = −6.5×10 K/m, and
- T0 is the temperature at the same reference point for which P = P0
and the other quantities are the same as those above. This is the recommended formula to use.
See also
References
- "The Barometric Formula".
- Streeter, Victor L. (1966). Fluid Mechanics, 4th edition p.28, McGraw-Hill
- Besant, W. H. (1900). Elementary Hydrostatics. George Bell & Sons. p. 11 – via Internet Archive.
- Roux, Sophie (25 Sep 2012). The Mechanization of Natural Philosophy. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 160. ISBN 978-9400743458.
Stevin provides an original mathematical demonstration of the so-called hydrostatic paradox
- Glazebrook, Richard (1916). Hydrostatics: An elementary textbook, theoretical and practical. Cambridge University Press. p. 42 – via Internet Archive.
- Greenslade, Jr., Thomas B. "Hydrostatic paradox". Kenyon College.
- Explanation on YouTube
- "Radius of the Earth". 2 March 2009.
- "Newton's Law of Gravity". www.splung.com. Retrieved June 23, 2023.
- "A Quick Derivation relating altitude to air pressure" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-28. Retrieved 2011-11-30.
- Merlino, Robert L. (2003). "Statics – Fluids at rest". Retrieved 2014-11-20.
External links
![]() Media related to Hydrostatic paradox at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Hydrostatic paradox at Wikimedia Commons
 where
where


 where
where
 where
where
 where (with values used in the article)
where (with values used in the article)
 where
where