Dog breed
| Vizsla | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||
| Other names | Hungarian Vizsla Magyar Vizsla Hungarian Pointer | ||||||||||||||||
| Origin | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Dog (domestic dog) | |||||||||||||||||
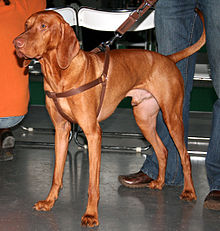
The Vizsla (Hungarian: [ˈviʒlɒ]), also known as Hungarian Vizsla, Magyar Vizsla or Hungarian Pointer, is a dog breed from Hungary and belongs to the Fédération Cynologique Internationale (FCI) group 7 (Pointing Dogs), the Canadian Kennel Club (CKC) group 1 (Sporting group), and the American Kennel Club (Sporting group). The Hungarian or Magyar Vizsla or Smooth-Haired Vizsla are sporting dogs and loyal companions. The Vizsla's medium size is one of the breed's most appealing characteristics. As a hunter of fowl and upland game, the Vizsla has held a prominent position among sporting dogs – that of household companion and family dog.
The Hungarian Vizsla is a versatile hunting dog that was traditionally and is currently used to hunt, point, and retrieve, referring to the dog's natural ability in tracking, pointing, and retrieving game, including in water. Although they are lively, gentle-mannered, demonstrably affectionate and sensitive, they are also fearless and possess a well-developed protective instinct.
Description
Appearance
The Hungarian Vizsla is a short-coated hunting dog of distinguished appearance and bearing. Robust, but rather lightly built, they are lean dogs that have defined muscles.
Various breeds are often mistaken for Vizslas and vice versa. Redbone Coonhounds, Weimaraners and Rhodesian Ridgebacks are most commonly mixed up. The body structure of a Vizsla is very similar in appearance to a Weimaraner and a Redbone Coonhound, though the Vizsla is typically leaner with a more defined musculature. Weimaraners and Rhodesian Ridgebacks are generally larger than Vizslas.
The nose of the Vizsla will usually be a reddish color that blends with the coat color. Black, brown, light pink, or another color nose is an indication of another breed. A Vizsla's eye and nail color usually also blend with the coat color.
Color and coats

The standard coat is French-row yellow in several shadings. The coat could also be described as a yellow, orange, copper-brown color, russet gold, and dark sandy gold. Solid, dark, mahogany red and pale yellow are considered faults and a disqualification in competitions. Small areas of white on the fore-chest, neck, or tail are permissible but not preferred. Some variations in the Vizsla coat color along their back (saddle-type marks) are typical.
The American Kennel Club (AKC) breed standards for the Vizsla states that the coat should be short, smooth, dense, and close-lying, without a woolly undercoat. The Vizsla is not suited to being kept outside since, unlike most other breeds, it does not have an undercoat. They are self-cleaning dogs and rarely need to be bathed, if ever. They have little noticeable "dog smell" detectable by humans. After several forays into lakes and streams they will develop an aroma that is a weaker version of the 'wet dog' smell. A quick bath and this odor will vanish.
Grooming and cleaning
Maintaining a vizsla's coat is relatively simple because of its short hair. When wet, a quick towel pat-down dries the dog fast, and for mud or dirt, letting it dry makes brushing it off easy. Using a velvet brush not only keeps their coat shiny but also helps in removing much of what they shed. Unlike most dogs, vizslas shed during all seasons, so it is important to keep up with brushing. Aside from their fur, keeping their claws trimmed prevents injury due to excessive length and chewing on hard items like raw marrow bones prevents plaque buildup and ensures clean teeth.
Size
The Vizsla is a medium-sized dog, The average height and weight:
- Males
- Height: 23–27 in (58–69 cm)
- Weight: 45–66 lb (20–30 kg)
- Females
- Height: 20.5–24 in (52–61 cm)
- Weight: 40–55 lb (18–25 kg)
Tail

The Vizsla holds its tail horizontal to the ground and wags it vigorously while charging through rough scrub and undergrowth.
The American breed standard calls for the tail to be docked to two-thirds of its original length, though docking for cosmetic reasons is opposed by the American Veterinary Medical Association, the American Animal Hospital Association, and the Canadian Veterinary Medical Association. UK's Kennel Club breed standard permits both a docked tail or a natural tail; this accommodates laws in England & Wales and in Scotland which outlaw docking for cosmetic reasons but exempt docking in newborn working dogs.
The docked tail of the Vizsla is significantly longer than that of other dogs with traditionally docked tails such as the Weimaraner, Dobermann, Boxer, and Australian Shepherd. Since the tail is docked when the puppy is less than three days old, this longer dock can result in some variation in tail length among Vizsla dogs from different breeding programs.
Temperament


They are natural hunters with an excellent ability to take training. Not only are they great pointers, but they are excellent retrievers as well. They will retrieve on land and in the water making the most of their natural instincts. However, they must be trained gently and without harsh commands or strong physical correction, as they have sensitive temperaments and can be easily damaged if trained too harshly.
Vizslas thrive on attention, exercise, and interaction. They are intelligent dogs and need a lot of mental stimulation when young. If left alone for long hours, they can be bored and become destructive. With proper socialization and training, Vizslas are very gentle dogs that can be great around children. The Vizsla wants to be close to its owner as much as possible, and it is commonly observed that vizslas insist on sleeping under the covers in their owner's bed at night.
Health

A 2024 UK study found a life expectancy of 13.5 years for the breed compared to an average of 12.7 for purebreeds and 12 for crossbreeds. The Vizsla is considered to be a robust dog but some localized breeding programs using a small number of dogs have led to heritable illnesses in some offspring including:
- Hip dysplasia is very rare but possible.
- Canine epilepsy
- Cancer (mast cell tumors, hemangiosarcoma, lymphoma)
- Sebaceous adenitis
Responsible breeders do not select dogs for breeding if they have such inherent problems. Vizslas can also suffer from hypothyroidism, dwarfism, persistent right aortic arch, tricuspid valve dysplasia, and progressive retinal atrophy. Major risks include epilepsy and lymphosarcoma. Vizslas can also be prone to skin and food allergies.
There is also the possibility of diseases and cancer developing in vizslas that are spayed or neutered. According to the Veterinary Medical DataBases, lymphoma is most likely to occur in gonadectomized vizslas (4.3x) compared to sexually intact vizslas. However, this is due to the fact that there is a 1.1% chance of illness in dogs neutered 12 months after birth compared to the 0.3% chance in dogs neutered before 12 months, and the 0.1% chance in those that are sexually intact.

Vizslas can be prone to various bleeding-related conditions such as hemophilia A and Von Willebrand's disease, leading to significant bleeding even from minor wounds due to a lack of blood clotting. Additionally, they may experience hypothyroidism, necessitating lifelong medication to support their thyroid in producing essential hormones for their survival.
Breeding
A vizsla will begin puberty on average 8–10 months after birth. Though for vizslas and most other breeds, they should not be bred during their first heat; instead, the second or third heat cycle is when they should be bred if desired. But even these measures can vary depending on the dogs mental and physical maturity.
History

The first written reference to the Vizsla dog breed has been recorded in the Illustrated Vienna Chronicle prepared on order of King Louis I of Hungary by the Carmelite Friars in 1357.
The Vizsla has survived the Turkish occupation (1526–1696), the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, World War I, World War II and the Hungarian People's Republic. However, Vizslas faced and survived several near-extinctions in their history, including being overrun by English Pointers and German Shorthaired Pointers in the 1800s (Boggs, 2000:19) and again to near-extinction after World War II. A careful search of Hungary and a poll of Hungarian sportsmen revealed only about a dozen Vizslas of the true type still alive in the country. From that minimum stock, the breed rose to prominence once again. The various "strains" of the Vizsla have become somewhat distinctive as individuals bred stock that suited their hunting style. Outside Hungary, vizslas were commonly bred in Romania, Austria, Slovakia, and Serbia.
The Vizsla started arriving in the United States at the close of World War II. As interest in and devotion to the breed began to increase, owners formed the Vizsla Club of America in order to gain American Kennel Club (AKC) recognition. As a result of registering foundation stock with the AKC, Vizsla owners were able to obtain official recognition on 25 November 1960, as the Vizsla became the 115th breed recognized by the American Kennel Club.
The Vizsla was used in development of other breeds, most notably the Weimaraner, Wirehaired Vizsla and German Shorthaired Pointer breeds. There is much conjecture about those same breeds, along with other pointer breeds, being used to reestablish the Vizsla breed at the end of the 19th century.
Vizsla in the UK
Approximately 4,520 Vizsla puppies are registered with the Kennel Club of Great Britain (KC) each year, making the breed one of the top 50 most popular. The number is steadily rising year after year as more people recognize the breed. There are two breed clubs for the Vizsla in Britain, The Hungarian Vizsla Club and The Hungarian Vizsla Society. The winner of the Best In Show award at Crufts 2010 was a Vizsla named Hungargunn Bear It'n Mind.
Vizsla in the US
About 2,500 vizslas are registered in the U.S. every year. According to the North American Versatile Hunting Dog Association, vizslas are the 7th highest annually registered dog, and this popularity has remained over the past 10 years. Other clubs in the U.S. include the Vizsla Club of America (breeding club) and The American Kennel Club (AKC).
The Vizsla Club of America a club dedicated to the health, betterment, and rescue of the purebred Hungarian vizsla. Established in the year 2000, this club partners with the American Kennel Club Canine Health Foundation to further research in the field of vizsla health, specifically health related issues such as hemangiosarcoma, lymphoma, mast cell cancer, canine epilepsy, brucellosis, diet-related DCM and temperament studies. They also partner with independent rescue organizations in creating a rescue fund for vizslas as well as The Frank Lacko Memorial Cancer Research Fund to research and eventually end cancer in the vizsla breed.
In popular culture
- Kubrick the Dog, a 2011 photography book by British fashion photographer and film maker Sean Ellis as a tribute to his Vizsla dog named Kubrick.
- Comedian Drew Lynch had a Vizsla, Stella, as a service dog, until 2022. They hosted a YouTube series called "Dog Vlog".
See also
- Dogs portal
- List of dog breeds
- National symbols of Hungary
- Wirehaired Vizsla, a breed developed in the 1930s by interbreeding Vizsla and German Wirehaired Pointer
- Hungarian dog breeds
References
- Sources report various pronunciations in English, with some closer approximations of the Hungarian original like /ˈvɪʒlɔː/, /ˈviːʒlə/, or /ˈvɪʒlə/, and others more influenced by the spelling like /ˈviːzlə/ or /ˈviːslə/.
- "Definition of vizsla | Dictionary.com". www.dictionary.com.
- ^ "Definition of VIZSLA". merriam-webster.com. 22 January 2024.
- "Pointing dogs". Federation Cynologique Internationale. 29 October 2020.
- "Sporting dogs". Canadian Kennel Club. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- "Sporting dogs". American Kennel Club. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- "Shooting UK: Hunt, point and retrieve – truly versatile dogs". June 2016. Retrieved 15 October 2023.
- ^ "Vizsla Club of America". Archived from the original on 17 April 2008. Retrieved 16 June 2008.
- ^ "AKC Vizsla Breed Standard". Retrieved 16 June 2008.
- "Colorado Wyoming Vizsla Rescue Group". Retrieved 16 June 2008.
- "Vizsla Dog Breed Information". akc.org. Archived from the original on 4 September 2013. Retrieved 2 April 2005.
- "Managing Your Vizsla". Hungarian Vizsla Club. 15 March 2015. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- "Breed Standards : Vizsla". United Kennel Club.
- "Official Standard for the Vizsla" (PDF). American Kennel Club.
- "Ear cropping and tail docking of dogs". American Veterinary Medical Association.
- "Ear cropping and tail docking". American Animal Hospital Association. June 2021.
- "CVMA | Documents | Cosmetic Alteration – Position Statement". Canadian Veterinary Medical Association. 27 January 2014. Archived from the original on 19 August 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- "Hungarian Vizsla | Breed Standards". The Kennel Club.
- "Kennel Club Welcomes New Scottish Laws To Protect Dog Welfare". The Kennel Club.
- Gottlieb, Gay (2002). The Complete Hungarian Vizsla. Ringpress. ISBN 0-948955-32-5.
- "The VIZSLA". Retrieved 15 September 2015.
- "Hungarian Vizsla: Puppy Facts, Dog Breed Information and More". DogsLife. 31 December 2016. Retrieved 13 October 2020.
- McMillan, Kirsten M.; Bielby, Jon; Williams, Carys L.; Upjohn, Melissa M.; Casey, Rachel A.; Christley, Robert M. (1 February 2024). "Longevity of companion dog breeds: those at risk from early death". Scientific Reports. 14 (1). Springer Science and Business Media LLC. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-50458-w. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 10834484.
- "Orthopedic Foundation for Animals". Archived from the original on 14 June 2008. Retrieved 19 June 2008.
- "Orthopedic Foundation for Animals: Purpose". offa.org. Archived from the original on 31 August 2017. Retrieved 9 May 2013.
- Howe, Lisa M (2015). "Current Perspectives on the Optimal Age to Spay/Castrate Dogs and Cats". Dove Medical Press Limited. 6: 171–180 – via College of Veterinary Medicine and Biomedical Sciences, Texas A&M University.
- Dearth, Kim D R (October 2000). "The Venerable Vizsla". Dog World. 85: 18 – via PJS Publications.
- Pinney, Chris C (1998). Vizslas : Everything about Purchase, Care, Nutrition, Grooming, Behavior, and Training. Hauppauge, New York: Barron’s. p. 64. ISBN 978-0-7641-0321-6.
- ^ Boggs, Bernard C (2000). The Vizsla. Behi Publishing Company. ISBN 0-9700978-0-8.
- KC Registration Statistics Archived 28 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed 28 May 2007.
- "Hungarian Vizsla Club – Kennel Club registered – founded 1968".
- "Hungarian Vizsla Society". Hungarian Vizsla Society.
- "Crufts 2010 won by Hungarian Vizsla called Yogi". BBC News. 14 March 2010. Retrieved 14 March 2010.
- "North American Versatile Hunting Dog Association". North American Versatile Hunting Dog Association.
- ^ "THE VIZSLA CLUB OF AMERICA, INC". The Vizsla Club of America.
- "The American Kennel Club". The American Kennel Club.
- Koshyk, Craig (16 June 2023). "Vizsla: Dog Breed Information, Form, Function, History, and More". Project Upland. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- "The American Kennel Club Canine Health Foundation". The American Kennel Club Canine Health Foundation.
- "Vogue Photog Sean Ellis' Book About His Best Friend: Kubrick the Dog". Racked. 18 October 2010. Retrieved 13 December 2012.
Further reading
- Boggs, B. C. The Vizsla; Glenbrier Publishing Company; Revised Edition, 1972. ISBN 0-9608838-0-0.
- Coffman, Marion I. Versatile Vizsla; Alpine Blue Ribbon Books; 2nd edition (May 2004). ISBN 1-57779-056-1.
- Hart, Ernest H. Vizslas; TFH Publications, 1990. ISBN 0-86622-436-X.
- Pinney, Chris C., D.V.M. Vizslas: A Complete Owner's Guide; Barron's, 1898. ISBN 0-7641-0321-0.
- White, Robert L. Hungarian Vizsla; PetLove Books (Published in UK by Interpret Books). ISBN 1-903098-59-9.
External links
| Dogs originating in Hungary | |
|---|---|