| WHEP-TRS | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
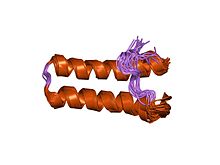 Solution structure of multi-functional peptide motif-1 present in human glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase (eprs). Solution structure of multi-functional peptide motif-1 present in human glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase (eprs). | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | WHEP-TRS | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF00458 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000738 | ||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00614 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1gtr / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
In molecular biology, the protein domain WHEP-TRS refers to helix-turn-helix domains. They are found in variable numbers in glutamyl-prolyl tRNA synthetase (EPRS). This protein domain has an important function in protein–protein interactions between synthetases. WHEP domains exhibit high-affinity interactions with tRNA, indicating a putative evolutionary relationship to facilitate tRNA binding to fused synthetases, thereby enhancing catalytic efficiency.
Protein interactions
EPRS is a component of the interferon-gamma-activated inhibitor of translation (GAIT) complex, which interacts with stem-loop elements (GAIT elements) in mRNAs encoding proinflammatory proteins, for example, vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGFA). WHEP domains interact with the GAIT element in the 3′UTR of target mRNAs and with the regulatory protein NS1-associated protein-1 (NSAP1).
Structure
A conserved domain of 46 amino acids, called WHEP-TRS has been shown to exist in a number of higher eukaryote aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetases. This domain is present one to six times in several enzymes. There are three copies in mammalian aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase in a region that separates the N-terminal glutamyl-tRNA synthetase domain from the C-terminal prolyl-tRNA synthetase domain, and six copies in the intercatalytic region of the Drosophila enzyme. The domain is found at the N-terminal extremity of the mammalian tryptophanyl- tRNA synthetase and histidyl-tRNA synthetase, and the mammalian, insect, nematode and plant glycyl- tRNA synthetases.
References
- ^ Ray PS, Sullivan JC, Jia J, Francis J, Finnerty JR, Fox PL (2011). "Evolution of function of a fused metazoan tRNA synthetase". Mol Biol Evol. 28 (1): 437–47. doi:10.1093/molbev/msq246. PMC 3002251. PMID 20829344.
- Cerini C, Kerjan P, Astier M, Gratecos D, Mirande M, Sémériva M (December 1991). "A component of the multisynthetase complex is a multifunctional aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase". EMBO J. 10 (13): 4267–77. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05005.x. PMC 453179. PMID 1756734.
- Nada S, Chang PK, Dignam JD (April 1993). "Primary structure of the gene for glycyl-tRNA synthetase from Bombyx mori". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (11): 7660–7. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)53008-8. PMID 8463296.