| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Find sources: "Warthin's tumor" – news · newspapers · books · scholar · JSTOR (January 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this message) |
| Warthin's tumor | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Warthin tumour, monomorphic adenoma, adenolymphoma |
 | |
| Cytopathology of Warthin's tumor, with typical cellular features (and a relatively uncommon binucleated cell). Pap stain. | |
| Specialty | Oncology |
Warthin's tumor, also known as papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum, is a benign cystic tumor of the salivary glands containing abundant lymphocytes and germinal centers (lymph node-like stroma). It is named for pathologist Aldred Scott Warthin, who described two cases in 1929.
Signs and symptoms
Warthin's tumor primarily affects older individuals (age 60–70 years). There is a slight male predilection according to recent studies. The tumor is slow growing, painless, and usually appears in the tail of the parotid gland near the angle of the mandible. In 5–14% of cases, Warthin's tumor is bilateral, but the two masses usually are at different times. Warthin's tumor is highly unlikely to become malignant.
Locations

The gland most likely affected is the parotid gland. In fact, it is the only tumor virtually restricted to the parotid gland. Warthin's tumor is the second most common benign parotid tumor after pleomorphic adenoma, but its prevalence is steadily increasing.
Cause
Its cause is unknown, but there is a strong association with cigarette smoking. Smokers are at 8 times greater risk of developing Warthin's tumor than the general population.
Diagnosis
The appearance of this tumor under the microscope is unique. There are cystic spaces surrounded by two uniform rows of oncocytes, which are epithelial cells with abundant, granular, eosinophilic cytoplasm. The cystic spaces have epithelium referred to as papillary infoldings that protrude into them. Additionally, the epithelium has lymphoid stroma with germinal center formation.
The differential diagnosis includes sebaceous lymphadenoma and oncocytoma.
-
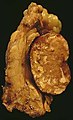 This Warthin's tumor presented as a parotid mass in a middle-aged male, who underwent superficial parotidectomy. The tumor, at the right of the image, is well-demarcated from the adjacent parotid tissue and tends to shell out from it.
This Warthin's tumor presented as a parotid mass in a middle-aged male, who underwent superficial parotidectomy. The tumor, at the right of the image, is well-demarcated from the adjacent parotid tissue and tends to shell out from it.
-
 Low magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor arising from the parotid gland.
Low magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor arising from the parotid gland.
-
 Histopathology of Warthin tumor in the parotid gland. H&E stain.
Histopathology of Warthin tumor in the parotid gland. H&E stain.
-
 Histopathology of Warthin tumor in the parotid gland. Another view of a file "Warthin tumor (1).jpg". H&E stain.
Histopathology of Warthin tumor in the parotid gland. Another view of a file "Warthin tumor (1).jpg". H&E stain.
-
 Histopathology of Warthin tumor in the parotid gland. Higher magnification of a file "Warthin tumor (1).jpg". H&E stain.
Histopathology of Warthin tumor in the parotid gland. Higher magnification of a file "Warthin tumor (1).jpg". H&E stain.
-
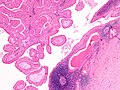 Intermediate magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor.
Intermediate magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor.
-
 High magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor showing the characteristic bilayered epithelium.
High magnification micrograph of a Warthin tumor showing the characteristic bilayered epithelium.
Treatment
Most of these tumors are treated with surgical removal called parotidectomy. Contrary to pleomorphic adenoma, it is non recurrent.
See also
References
- Image by Mikael Häggström, MD. References for entries:
- Köybaşioğlu FF, Önal B, Han Ü, Adabağ A, Şahpaz A (2020). "Cytomorphological findings in diagnosis of Warthin tumor". Turk J Med Sci. 50 (1): 148–154. doi:10.3906/sag-1901-215. PMC 7080357. PMID 31769640.{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Binucleation:
- Dr.S. Malliga (2006-10-18). "A correlative cytological and histopathological study on lesions of salivary gland" (PDF).
- Chan MKM, McGuire LJ: Cytodiagnosis of Lesions Presenting as Salivary Gland Swellings: A Report of Seven Cases. Diagn Cytopathol 8: 439-443, 1992b. - Witt RL, ed. (2005). "Chapter 9 "Benign tumors, cysts, and tumor-like conditions of the salivary glands". Salivary Gland Diseases: Surgical and Medical Management. New York: Thieme Medical Publishers. p. 123. ISBN 1-58890-414-8.
- Limaiem, Faten; Jain, Prachi (2023), "Warthin Tumor", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 32491572, retrieved 2023-11-03
- Steve C Lee (22 December 2022). "Salivary Gland Neoplasms". Medscape. Updated: Jan 13, 2021
Diagrams by Mikael Häggström - Psychogios G, Vlastos I, Thölken R, Zenk J (July 2020). "Warthin's tumour seems to be the most common benign neoplasm of the parotid gland in Germany". European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. 277 (7): 2081–2084. doi:10.1007/s00405-020-05894-z. PMID 32189070. S2CID 212940703.
- Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N (2005). Robbins and Cotran pathologic basis of disease (7th ed.). St. Louis, MO: Elsevier Saunders. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.
- Chakrabarti I, Basu A, Ghosh N (2012). "Oncocytic lesion of parotid gland: A dilemma for cytopathologists". J Cytol. 29 (1): 80–2. doi:10.4103/0970-9371.93236. PMC 3307464. PMID 22438628.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Additional sources
- Kahn, Michael A. Basic Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. Volume 1. 2001.
External links
| Classification | D |
|---|---|
| External resources |
| Glandular and epithelial cancer | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epithelium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Glands |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tumors of lip, oral cavity and pharynx / head and neck cancer | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral cancer |
| ||||||||||||