| Yak-50 | |
|---|---|
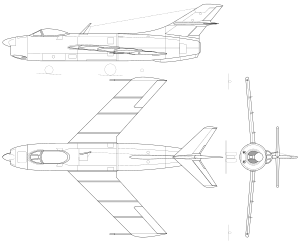 | |
| General information | |
| Type | Fighter/interceptor |
| Manufacturer | Yakovlev |
| Status | Cancelled |
| Primary user | Soviet Air Forces |
| History | |
| First flight | 15 July 1949 |
Yakovlev Yak-50 was an early experimental turbojet interceptor aircraft designed in 1948 by the Yakovlev OKB in the USSR. The aircraft was essentially a stretched version of the Yakovlev Yak-30 (1948), with a more powerful engine and greater wing sweep. The Yak-50 is perhaps most significant as the first Yakovlev aircraft equipped with velosipednoye (bicycle) landing gear, a trademark of later Yakovlev designs. The Yak-50 designation was later reused for a propeller-driven aerobatic and trainer aircraft.
Development and design
On February 21, 1949 a Sovmin order requested the Yakovlev OKB to design a lightweight, radar-equipped, all-weather and night interceptor capable of Mach 0.97 at 4,000 m (13,000 ft). The aircraft was to utilize the Klimov VK-1 engine which first appeared on Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-15 and MiG-17 fighters. This engine was itself a Soviet copy of the British Rolls-Royce Nene centrifugal turbojet initially known as the RD-45. The leading fighter OKBs each created a prototype to meet the requirement, which included the Lavochkin La-200, MiG I-320, Sukhoi Su-15 (unrelated to the later aircraft with the same designation) and the Yak-50 (again, unrelated to the later aircraft). A major difference was that while Yakolev used one engine, the other design bureaus used two.
Testing
The aircraft first flew on 15 July 1949, with test pilot Anokhin achieving supersonic speed (Mach 1.03 at 10,000 m (33,000 ft)) in a shallow dive during one of the test flights.
Ultimately, none of the newly developed aircraft was selected, and an upgraded MiG-17 was eventually employed. Yakolev later used the velosipednoye landing gear in the Yak-140 fighter and the Yak-120, and later in the Yak-25 and Yak-28 where it proved highly successful.
The Yak-50 never received an ASCC name or USAF reporting number.
Operators
Specifications
Data from
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 11.12 m (36 ft 6 in)
- Wingspan: 8.01 m (26 ft 3 in)
- Wing area: 16 m (170 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 3,085 kg (6,801 lb)
- Gross weight: 4,155 kg (9,160 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Klimov VK-1 centrifugal-flow turbojet engine, 26.5 kN (6,000 lbf) thrust
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,120 km/h (700 mph, 600 kn)
- Range: 850 km (530 mi, 460 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 16,050 m (52,660 ft)
- Rate of climb: 68 m/s (13,400 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 260 kg/m (53 lb/sq ft)
- Thrust/weight: 0.65
Armament
- Guns: 2× 23 mm Nudelman-Rikhter NR-23 cannons, 80 rounds/gun
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
References
- Gunston, Bill. Yakovlev Aircraft since 1924. London, UK: Putnam Aeronautical Books, 1997. ISBN 1-55750-978-6.
External links
| Yakovlev aircraft | |
|---|---|
| Early aircraft | |
| Fighters | |
| Bombers | |
| Transports | |
| Reconnaissance | |
| Helicopters | |
| Trainers | |
| Experimental | |