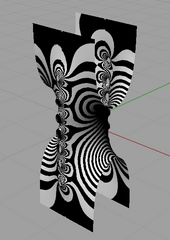
Zebra analysis, or zebra striping, is a diagnostic shading technique used in computer graphics to visualize curvature on smooth surfaces. It is primarily used for computer-aided design (CAD), where it helps checking that surfaces meet smoothly. It is a simulation of the visual effect of placing an object in a tunnel lit by parallel rows of lights, or a perfectly reflecting object in a room with striped walls.
Implementation
Zebra striping has been implemented in a number of CAD and non-CAD products, including (but not limited to) Fusion 360, Autodesk Inventor, AutoCAD, Rhinoceros 3D, and SolidWorks. It can be implemented as an environment map using radiating pie wedges as the source texture.
See also
References
- Kenton Fleming, Computer Aided Engineering: An Undergraduate course in computer aided design and analysis for mechanical engineering technology, Southern Polytechnic State University. http://www.intellectbase.org/e_publications/jagr/JAGR_Volume_2_Issue_2.pdf
- "Zebra Analysis reference". Fusion Help. Retrieved 2024-04-10.
- "To Analyze Smoothness". Autodesk Inventor 2023. Retrieved 2024-04-10.
- "About Analyzing Surface Continuity With Zebra Analysis". Autodesk AutoCAD 2024. Retrieved 2024-04-10.
- "Zebra | Rhino 3-D modeling". docs.mcneel.com. Retrieved 2024-04-10.
- "Zebra Stripes - 2020 - SOLIDWORKS Help". help.solidworks.com. Retrieved 2024-04-10.