| Zip | |
|---|---|
| Oaks Amusement Park | |
| Location | Oaks Amusement Park |
| Coordinates | 45°28′23″N 122°39′38″W / 45.4730°N 122.66061°W / 45.4730; -122.66061 |
| Status | Removed |
| Opening date | 1927 (1927) |
| Closing date | 1934 (1934) |
| General statistics | |
| Type | Wood |
| Manufacturer | Traver Engineering |
| Designer | Harry G. Traver |
| Height | 60 ft (18 m) |
| Length | 2,500 ft (760 m) |
| Duration | between 1 minute 20 seconds and 1 minute 30 seconds |
| Trains | Single train with 5 cars. Riders are arranged 2 across in a single row for a total of 10 riders per train. |
| Zip at RCDB | |
Zip or Zipp was a steel-framed wooden roller coaster which operated at Oaks Amusement Park in Portland, Oregon. The coaster was a more compact variant of the Giant Cyclone Safety Coasters which were built by Harry Traver of the Traver Engineering Company in the mid to late 1920s.
History and design
One of Harry Traver's more obscure coasters, the Zip was modeled on the larger Giant Cyclone Safety Coasters (the "Terrible Triplets") but was smaller and more compact. The coaster was originally planned to be 3,200 feet (980 m) in length, but this length was reduced so as not to impinge on a nearby trolley right-of-way. The undulating jazz track characteristic of Traver Cyclones was also shortened by 70 feet (21 m). The coaster was also built on a wooden deck to protect it from Willamette River flooding. The coaster was removed in 1934 as a result of high maintenance and insurance costs. The coaster was dismantled and the steel sold to Japan in that same year.
Few photographs were preserved of the Zip. Robert Cartmell, in his book The Incredible Scream Machine: A History of the Roller Coaster, described the stunned reaction of attendees at an American Coaster Enthusiasts meeting when photographic slides of the Zip were first shown. " as if some primeval nightmare had been projected on the screen" Cartmell wrote, and called the coaster "a ride bordering on the macabre".
Ride experience
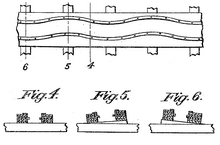
While most Traver Cyclones had 10-car trains, the Zip differed by having shorter 5-car trains. The way these shorter trains zipped along the track is thought to be responsible for the name of the coaster. Like other Traver coasters, the ride had very steep banking. The first curve had an angle of 80 degrees.
It has also been suggested that the shorter trains may have created an even rougher experience than was typical for a Traver Cyclone. It was described as a "rib tickler", where the side-to-side motion of the cars (particularly on the coaster's rapidly undulating "Jazz Track") would slam riders' ribs to either sides of the cars. This led to problems of low ridership (and particularly repeat ridership) that plagued the other Giant Cyclone Safety Coasters. The smaller-than-usual trains, which like the other Cyclones could only run one-at-a-time, also contributed to this problem.
References
- ^ Zigweid, Lisa (March 28, 2011). "Zip, Oaks Park, Portland, OR". Roller Coasters of the Pacific Northwest. Retrieved June 10, 2017.
- Marden, Duane. "Zip (Oaks Amusement Park)". Roller Coaster DataBase.
- ^ Cartmell, Robert (1987). The Incredible Scream Machine: A History of the Roller Coaster. Fairview Park, OH and Bowling Green, OH: Amusement Park Books, Inc. and Bowling Green State University Popular Press. ISBN 0879723416.
- ^ Munch, Richard (1982). Harry G. Traver: Legends of Terror. Mentor, OH: Amusement Park Books, Inc. ISBN 0935408029.
- ^ Heflin, Joe (Fall 1983). "Traver Cyclones: Re-examination". Coaster World. Vol. 4, no. 3. pp. 8–13.
- Removed roller coasters
- Roller coasters introduced in 1927
- Roller coasters that closed in 1934
- Wooden roller coasters
- Roller coasters manufactured by Traver Engineering
- 1927 establishments in Oregon
- History of Portland, Oregon
- Oaks Amusement Park
- Tourist attractions in Portland, Oregon
- Former roller coasters in Oregon