| Revision as of 11:33, 24 May 2011 view source79.71.110.67 (talk) →Used within and against Communism: North Korea is more relatedable to Nazi Germany than Vietnam← Previous edit | Latest revision as of 07:27, 6 January 2025 view source Zac67 (talk | contribs)Extended confirmed users11,639 editsm Reverted 1 edit by Oct13 (talk) to last revision by RootOfAllLightTags: Twinkle Undo | ||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| {{Short description|Far-right, authoritarian, ultranationalistic political ideology}} | |||
| {{About||the Italian political movement|Italian Fascism}} | |||
| {{Other uses}} | |||
| {{Criticism section|date=April 2011}} | |||
| {{pp-semi-indef}} | |||
| {{Use dmy dates|date=January 2024}} | |||
| ], dictator of ] (left), and ], dictator of ] (right), were fascist leaders.]] | |||
| '''Fascism''' ({{IPAc-en|ˈ|f|æ|ʃ|ɪ|z|əm}} {{respell|FASH|iz|əm}}) is a <!-- DO NOT REMOVE THIS TERM, SEE TALK PAGE -->]<!-- DO NOT REMOVE THIS TERM, SEE TALK PAGE -->, ], and ] political ideology and movement,<ref>{{harvp|Turner|1975|p=162|ps=: "... goals of radical and authoritarian nationalism"}}; {{harvp|Larsen|Hagtvet|Myklebust|1984|p=424|ps=: "... organized form of integrative radical nationalist authoritarianism"}}; {{harvp|Paxton|2004|pp=32, 45, 173|ps=: (32) "... antiliberal values, more aggressive nationalism and racism, and a new aesthetic of instinct and violence", (173) "... overtly violent racism and nationalism. ... its defining elements—unlimited particular sovereignty, a relish for war, and a society based on violent exclusion"}}; {{harvp|Nolte|1965|p=300|ps=: "National fascism, as we have shown, is distinguished from nationalism by, among other things, the fact it demands the destruction of a neighbouring state whose very existence appears to threaten its own position of power and the historic remains of its past dominant status in the area."}}</ref><ref name="Britannica">{{harvp|Encyclopedia Britannica ''Fascism''|ps=: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the rule of elites, and the desire to create a {{lang|de|Volksgemeinschaft}} (German: "people's community"), in which individual interests would be subordinated to the good of the nation"}}</ref><ref name="m-w" /> characterized by a ]ial leader, centralized ], ], forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural ], subordination of ] for the perceived good of the ] or ], and strong regimentation of society and the economy.<ref name="Britannica"/><ref name="m-w">{{cite encyclopedia|title=fascism |url=https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/fascism |dictionary=] |access-date=22 August 2017 |archive-date=22 August 2017 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170822084905/https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/fascism |url-status=live}}</ref> Opposed to ], ], ], ], ], ], and ],{{sfnp|International Encyclopedia of Political Science|loc=Fascism|p=889}}<ref name="USHMM">{{cite web |title=Fascism |url=https://encyclopedia.ushmm.org/content/en/article/fascism-1 |access-date=7 August 2022 |website=] |language=en}}</ref> fascism is at the far right of the traditional ].<ref name="RoutledgeCompanion"/><ref name="USHMM"/><ref name="University-Aristotle-Hartley-Wilhelm-Hawkesworth">{{harvp|Griffin|1995|pp=8, 307}}; {{harvp|Kallis|2003b|p=71}}; {{harvp|Hartley|2004|p=187}}; {{harvp|Reich|1970}}; {{harvp|Hawkesworth|Kogan|1992}}; {{harvp|Copsey|2008}}; {{harvp|Goodwin|2011}}; {{harvp|Woodley|2010}}; {{harvp|Blamires|2006}}; {{harvp|Richardson|2017}}; {{harvp|Eley|2013}}; {{harvp|Wistrich|1976}}; {{harvp|Staudenmaier|2004}}</ref> | |||
| Fascism rose to prominence in early-20th-century Europe.<ref name="RoutledgeCompanion">{{harvp|Davies|Lynch|2002|pp=}}</ref>{{sfnp|International Encyclopedia of Political Science|loc=Fascism|p=887–888}} The first fascist movements ] during ], before ], most notably ].<ref name="RoutledgeCompanion"/> Fascism also had adherents outside of Europe.{{sfnp|Encyclopedia Britannica ''Fascism''}} Fascists saw World War I as a ] that brought massive changes to the nature of war, society, the state, and technology. The advent of ] and the mass mobilization of society erased the distinction between civilians and combatants. A military citizenship arose, in which all citizens were involved with the military in some manner.{{sfnmp|Blamires|2006|1pp=140–141, 670|Mann|2004|2p=65}} The war resulted in the rise of a powerful state capable of mobilizing millions of people to serve on the front lines, providing logistics to support them, and having unprecedented authority to intervene in the lives of citizens.{{sfnmp|Blamires|2006|1pp=140–141, 670|Mann|2004|2p=65}} | |||
| Fascism rejects the view that violence is inherently negative or pointless but rather views ], ], and war as means to national rejuvenation.{{sfnmp|Grčić|2000|1p=120 |2a1=Griffin|2a2=Feldman|2y=2004c|2p=185 |Spielvogel|2012|3p=935 |Payne|1995|4p=106}}{{sfnp|Rietbergen|2000|pp=160–161}} Fascists often advocate for the establishment of a totalitarian ],{{sfnp|Griffin|2013|pp=1–6}}{{sfnp|Mussolini|2002|p=40}} and for a ] economy (a market economy in which the state plays a strong directive role through ] policies), with the principal goal of achieving ] (national economic self-sufficiency).<ref>{{harvnb|Davies|Lynch|2002|p=275|ps=: "Detailed and intrusive state direction of the economy and/or society. Dirigisme was central to both fascism and Communist systems. However, in the case of fascism, there was no requirement for outright state ownership of the means of production, as long as the economy could be harnessed to serve what fascists deemed to be the 'national interest'."}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Berend |first=Iván T. |author-link=Iván T. Berend |title=An Economic History of Twentieth-Century Europe: Economic Regimes from Laissez-Faire to Globalization |publisher=] |year=2016 |pages=93}}</ref> Fascism's extreme authoritarianism and nationalism centres around the own group, but that can manifest as a belief in ], revival of historical greatness (like Mussolini seeking to restore the Roman Empire) or in case of ], ] or a ] which blended with some variant of ] or ] against a demonized "]", such as ], ], ], ], or ]. These ideas have motivated fascist regimes to commit ]s, ], ]s, and ]s.{{sfnmp|1a1=Kallis|1y=2011|2a1=Paxton|2y=1998|3a1=Lancaster|3y=2011}}<ref>{{cite web | url=https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/new-research-reveals-how-the-nazis-targeted-transgender-people-180982931/ | title=New Research Reveals How the Nazis Targeted Transgender People }}</ref> During ], the genocidal and imperialist ambitions of the fascist ] resulted in the murder of millions of people. | |||
| {{pp-move-indef|small=yes}} | |||
| {{Fascism sidebar}} | |||
| {{Nationalism sidebar}} | |||
| {{Forms of government}} | |||
| Since the end of World War II in 1945, fascism has been largely disgraced, and few parties have openly described themselves as ''fascist''; the term is often used ] by political opponents. The descriptions '']'' or '']'' are sometimes applied to contemporary parties with ideologies similar to, or rooted in, 20th-century fascist movements.<ref name="RoutledgeCompanion"/>{{sfnp|Enciclopedia Italiana ''Neofascismo''}} Some opposition groups have adopted the label ] (often shortened to ]) to signify their stance.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Bogel-Burroughs |first1=Nicholas |last2=Garcia |first2=Sandra E. |date=28 September 2020 |title=What Is Antifa, the Movement Trump Wants to Declare a Terror Group? |language=en-US |work=] |url=https://www.nytimes.com/article/what-antifa-trump.html |access-date=7 September 2022 |issn=0362-4331}}</ref> | |||
| '''Fascism''' ({{IPAc-en|icon|ˈ|f|æ|ʃ|ɪ|z|əm}}) is a ], ] ] political ]. <ref>Turner, Henry Ashby. ''Reappraisals of Fascism''. New Viewpoints, 1975. p. 162. States fascism's "goals of radical and authoritarian nationalism".</ref><ref>Larsen, Stein Ugelvik; Hagtvet, Bernt; Myklebust, Jan Petter. ''Who were the Fascists Fascists: social roots of European Fascism''. p. 424."organized form of integrative radical nationalist authoritarianism"</ref> Fascists advocate the creation of a ] ] that seeks the mass mobilization of a nation through ], ], and family policy including ].<ref>Cyprian Blamires. ''World fascism: a historical encyclopedia, Volume 1''. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CLIO, Inc., 2006. Pp. 670.</ref> Fascists seek to purge forces and ideas deemed to be the cause of ] and ] and produce their nation's rebirth based on commitment to the national community based on organic unity where individuals are bound together by suprapersonal connections of ], ], and ].<ref>Cyprian Blamires. ''World fascism: a historical encyclopedia, Volume 1''. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CLIO, Inc., 2006. Pp. 140-141.</ref> Fascists believe that a nation requires strong leadership, singular collective identity, and the will and ability to commit violence and wage war in order to keep the nation strong.<ref name=gj120>Grčić, Joseph. ''Ethics and political theory''. Lanham, Maryland, USA: University of America, Inc, 2000. p. 120</ref> Fascist governments forbid and suppress opposition to the state.<ref>Kent, Allen; Lancour, Harold; Nasri, William Z. ''Encyclopedia of Library and Information Science: Volume 62 – Supplement 25 – Automated Discourse Generation to the User-Centered Revolution: 1970–1995.'' CRC Press, 1998. ISBN 9780824720629. p. 69.</ref> | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| Fascists promote violence and war as actions that create national regeneration, spirit and ].<ref>Griffin, Roger (ed.); Feldman, Matthew (ed.). ''Fascism: Fascism and culture''. London, UK; New York, USA: Routledge, 2004. p. 185.</ref> Fascists exalt ] as providing positive transformation in society, in providing spiritual renovation, education, instilling of a will to dominate in people's character, and creating national comradeship through military service.<ref>Kallis, Aristotle. ''Fascist Ideology: Territory and Expansionism in Italy and Germany, 1922-1945''. New York, USA: Routledge, 2000. Pp. 39-40.</ref> | |||
| ], as displayed on caps and helmets of ]]] | |||
| The Italian term {{lang|it|fascismo}} is derived from {{lang|it|fascio}}, meaning 'bundle of sticks', ultimately from the ] word {{lang|la|]}}.<ref name="m-w"/> This was the name given to political organizations in Italy known as ], groups similar to ]s or ]s. According to Italian fascist dictator ]'s own account, the ] were founded in Italy in 1915.{{sfnp|Mussolini|2006|p=227}} In 1919, Mussolini founded the ] in Milan, which became the ] two years later. The fascists came to associate the term with the ancient Roman fasces or {{lang|it|]}},{{sfnp|Falasca-Zamponi|2000|p=95}} a bundle of rods tied around an axe,<ref>{{cite web |last=Johnston |first=Peter |date=12 April 2013 |title=The Rule of Law: Symbols of Power |url=http://www.okwu.edu/keating-center/2013/04/the-rule-of-law-symbols-of-power/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170330232643/http://www.okwu.edu/keating-center/2013/04/the-rule-of-law-symbols-of-power/ |archive-date=30 March 2017 |access-date=28 April 2013 |publisher=The Keating Center, ] |language=en-US}}</ref> an ] symbol of the authority of the civic ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://intraweb.stockton.edu/eyos/page.cfm?siteID=78&pageID=35 |title=Policing Rome: Maintaining Order in Fact and Fiction |last=Watkins |first=Tom |work=Fictional Rome |publisher=] |location=Stockton, New Jersey |year=2013 |access-date=28 April 2013 |archive-date=16 March 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20140316011914/http://intraweb.stockton.edu/eyos/page.cfm?siteID=78&pageID=35 |url-status=dead}}</ref> carried by his ]s.<ref>{{cite web |url=https://Britannica.com/topic/fasces |author=<!-- not stated --> |title=Fasces |website=Britannica.com |publisher=Britannica |access-date=17 April 2024 |quote=When carried inside Rome, the ax was removed (unless the magistrate was a dictator or general celebrating a triumph) as recognition of the right of a Roman citizen to appeal a magistrate's ruling.}}</ref> The symbolism of the fasces suggested strength through unity: a single rod is easily broken, while the bundle is difficult to break.{{sfn|Brennan|2022|pp=2, 12}} Similar symbols were developed by different fascist movements; for example, the symbol of ] is five arrows joined by a yoke.<ref>{{cite book |first=Wendy |last=Parkins |title=Fashioning the body politic: dress, gender, citizenship |location=Oxford; New York |publisher=Berg |date=2002 |page=178}}</ref> | |||
| ==Definitions== | |||
| Fascism was founded by Italian ] in ] who combined ] and ] political views, but it gravitated to the right in the early 1920s.<ref name="ZeevSternhell">Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 161.</ref><ref>Cristogianni Borsella, Adolph Caso. ''Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative''. Wellesley, Massachusetts, USA: Branden Books, 2007. p. 76</ref> The majority of scholars generally consider fascism to be on the ],<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.publiceye.org/eyes/whatfasc.html |title= What is Fascism? Some General Ideological Features |last=Lyons |first=Matthew N. |work=PublicEye.org |publisher=Political Research Associates |accessdate=2009-10-27}}</ref><ref name="ah.brookes.ac.uk">Griffin, Roger: "The Palingenetic Core of Fascism", ''Che cos'è il fascismo? Interpretazioni e prospettive di ricerche'', Ideazione editrice, Rome, 2003 </ref><ref name=sr3>Stackleberg, Rodney , Routeledge, 1999, p. 3</ref><ref name=er71>Eatwell, Roger: "A 'Spectral-Syncretic Approach to Fascism', ''The Fascism Reader'', Routledge, 2003 pp 71–80 </ref> while others claim it is the extreme form of a centrist ideology. <ref name=ls112>Lipset, Seymour: "Fascism as Extremism of the Middle Class", ''The Political Man'', Johns Hopkins University Press, 1959 pp 127-179</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Definitions of fascism}} | |||
| {{Fascism sidebar}} | |||
| Historian ] once wrote that "trying to define 'fascism' is like trying to nail jelly to the wall."{{sfnp|Kershaw|2016|p=228}} Each group described as "fascist" has at least some unique elements, and frequently definitions of "fascism" have been criticized as either too broad or too narrow.{{sfnmp|Payne|1980|1p=7|2a1=Griffiths|2y=2000}} According to many scholars, fascists—especially when they're in power—have historically attacked communism, conservatism, and parliamentary liberalism, attracting support primarily from the far-right.<ref name="Laqueur 1997 p223">{{harvp|Laqueur|1997|p=223}}; {{harvp|Eatwell|1996|p=39}}; {{harvp|Griffin|1991|pp=185–201}}; {{harvp|Weber|1982|p=8}}</ref> | |||
| Fascism is ], ], anti-individualist, ], ], anti-], anti-proletarian and anti-].<ref>Walter Laqueur. ''Fascism - a reader's guide: analyses, interpretations, bibliography''. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California, USA: University of California Press, 1976. Pp. 16.</ref> It entails a distinctive type of anti-] and is typically, with a few exceptions, ].<ref>Walter Laqueur. ''Fascism - a reader's guide: analyses, interpretations, bibliography''. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California, USA: University of California Press, 1976. Pp. 16.</ref> Fascism rejects the concepts of ], ], and ] in favour of action, ], ], ], and ].<ref>Frank Bealey, Allan G. Johnson. The Blackwell dictionary of political science: a user's guide to its terms. 2nd edition. Malden, Massachusetts, USA: Blackwell Publishers, 2000. p. 129.</ref> In economics, fascists oppose ] (as a ] movement) and ] (as a ] movement) for being exclusive economic class-based movements.<ref>Walter Laqueur, Walter. ''Fascism: A Readers' Guide : Analysis, Interpretations, Bibliography''. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California, USA: University of California Press, 1976 (first edition, 1978 (paperback edition). p. 338.</ref> Fascists present their ideology as that of an economically trans-class movement that promotes resolving economic ] to secure national solidarity.<ref>Griffin, Roger. ''The Nature of Fascism''. New York, New York, USA: St. Martins Press, 1991. pp. 222–223.</ref> They support a regulated, multi-class, integrated national economic system.<ref>Stanley G. Payne. ''Fascism: Comparison and Definition''. Madison, Wisconson, USA: University of Wisconsin Press, 1980. Pp. 7. </ref> | |||
| Historian ]'s definition is frequently cited as standard by notable ]s,<ref>{{cite web |title=Works citing Stanley Payne's Fascism: Comparison and Definition |url=https://scholar.google.co.uk/scholar?cites=5701423830518078146&as_sdt=2005&sciodt=0%2C5&hl=en |url-status=live |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220802121023/https://scholar.google.co.uk/scholar?cites=5701423830518078146&as_sdt=2005&sciodt=0%2C5&hl=en |archive-date=2 August 2022 |via=]}}</ref> such as ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Griffin |first=Roger |title=The Nature of Fascism |year=1993 |location=London |publication-date=2013 |language=en |doi=10.4324/9781315003627 |author-link=Roger Griffin |doi-access=free |publisher=] |isbn=9781315003627}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Schweller |first=Randall L. |url=https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9781400837854/html?lang=en |title=Unanswered Threats: Political Constraints on the Balance of Power |publisher=] |year=2006 |isbn=978-1-4008-3785-4 |volume=125 |series=Princeton Studies in International History and Politics |language=en |doi=10.1515/9781400837854 |s2cid=266074243 |author-link=Randall Schweller |url-access=subscription}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Rothstein |first=B |title=A New Handbook of Political Science |publisher=] |year=1996 |isbn=9780191521089 |editor-last=Klingemann |editor-first=Hans-Dieter |pages=135, 164 |language=en |chapter=Political institutions: An Overview (Part II, Chapter 4) |author-link=Bo Rothstein |editor-last2=Goodin |editor-first2=Robert E. |editor-link2=Robert E. Goodin}}</ref> ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Finchelstein |first=Federico |url=https://www.degruyter.com/document/doi/10.1515/9780822391555/html |title=Transatlantic Fascism: Ideology, Violence, and the Sacred in Argentina and Italy, 1919-1945 |publisher=] |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-8223-9155-5 |language=en |doi=10.1515/9780822391555 |author-link=Federico Finchelstein |url-access=subscription}}</ref> and ],<ref>{{cite book |last=Shenfield |first=Stephen |url=https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9781315500058/russian-fascism-stephen-shenfield |title=Russian Fascism: Traditions Tendencies Movements |publisher=] |year=2001 |edition=2nd |location=New York |publication-date=2016 |language=en |doi=10.4324/9781315500058 |isbn=9781315500058 |url-access=subscription}}</ref> {{sfnp|Payne|1980|p=7}} His definition of fascism focuses on three concepts: | |||
| ==Etymology== | |||
| # "Fascist negations" – ], ], and anti-]. | |||
| The term ''fascismo'' is derived from the ] word '']''. The fasces, which consisted of a bundle of rods that were tied around an axe, was an ] symbol of the authority of the civic ]. They were carried by his ]s and could be used for ] and ] at his command.<ref>{{cite book|last = New World|first =Websters|title =Webster's II New College Dictionary| publisher =Houghton Mifflin Reference Books| isbn =0618396012|year = 2005}}</ref><ref name="paynee">{{cite book|last = Payne|first =Stanley|title =A History of Fascism, 1914–45| publisher =]| isbn =0299148742|year = 1995}}</ref> The word ''fascismo'' also relates to political organizations in Italy known as ], groups similar to ]s or ]s. | |||
| # "Fascist goals" – the creation of a nationalist ] to regulate economic structure and to transform social relations within a modern, self-determined culture, and the expansion of the nation into an empire. | |||
| # "Fascist style" – a political aesthetic of romantic symbolism, mass mobilization, a positive view of violence, and promotion of masculinity, youth, and charismatic authoritarian leadership.{{sfnmp|Ramswell|2017|1p=9|2a1=Griffin|2a2=Feldman|2y=2004a|2p=258|Kallis|2003b|3pp=84–5|Renton|1999|4p=21}} | |||
| ] lists fourteen "features that are typical of what would like to call 'Ur-Fascism', or 'Eternal Fascism'. These features cannot be organized into a system; many of them contradict each other, and are also typical of other kinds of ] or fanaticism. But it is enough that one of them be present to allow fascism to coagulate around it."<ref name="Eco1995"/> Historian ] argues that there is no such thing as generic fascism. He claims that ] and ] are essentially manifestations of ], and that states such as Nazi Germany and ] are more different from each other than they are similar.{{sfnp|Lukacs|1998|p=118}} | |||
| The symbolism of the fasces suggested ''strength through unity'': a single rod is easily broken, while the bundle is difficult to break.<ref>{{cite book|last =Doordan|first =Dennis P| title =In the Shadow of the Fasces: Political Design in Fascist Italy| publisher =The MIT Press| isbn =0299148742|year =1995}}</ref> Similar symbols were developed by different fascist movements. For example the ] symbol is a bunch of arrows joined together by a ].<ref>{{cite book|last = Parkins|first =Wendy|title =Fashioning the Body Politic: Dress, Gender, Citizenship| publisher =Berg Publishers| isbn =1859735878|year = 2002}}</ref> | |||
| ]|thumb|upright=0.8]] | |||
| ==Definitions== | |||
| {{Main|Definitions of fascism}} | |||
| Historians, political scientists and other scholars have long debated the exact nature of fascism.<ref name="pheonix">{{cite book |last=Gregor |first=A. James |title=Phoenix: Fascism in Our Time |publisher=Transaction Publishers |isbn=0765808552 |year=2002}}</ref> Each form of fascism is distinct, leaving many definitions too wide or narrow.<ref name="deff">{{cite book |last=Payne |first=Stanley G |title=Fascism, Comparison and Definition |publisher=University of Wisconsin Press |isbn=0299080641 |year=1983}}</ref><ref name="intelligentguide">{{cite book |last=Griffiths |first=Richard |title=An Intelligent Person's Guide to Fascism |publisher=Duckworth |isbn=0715629182}}</ref> Since the 1990s, scholars including ], Roger Eatwell, ] and ] have been gathering a rough consensus on the ideology's core tenets. | |||
| In his book '']'' (2018), ] defined fascism thusly: <blockquote> cult of the leader who promises national restoration in the face of humiliation brought on by supposed communists, Marxists and minorities and immigrants who are supposedly posing a threat to the character and the history of a nation ... The leader proposes that only he can solve it and all of his political opponents are enemies or traitors.</blockquote> Stanley says recent global events {{As of|2020|lc=y}}, including the ] and the ], have substantiated his concern about how fascist rhetoric is showing up in politics and policies around the world.<ref>{{cite news |last1=Silva |first1=Christianna |title=Fascism Scholar Says U.S. Is 'Losing Its Democratic Status' |url=https://www.npr.org/2020/09/06/910320018/fascism-scholar-says-u-s-is-losing-its-democratic-status |publisher=] |access-date=7 September 2020 |archive-date=7 September 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200907010731/https://www.npr.org/2020/09/06/910320018/fascism-scholar-says-u-s-is-losing-its-democratic-status |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| For Griffin, fascism is "a genuinely revolutionary, trans-class form of anti-liberal, and in the last analysis, anti-conservative nationalism" built on a complex range of theoretical and cultural influences. He distinguishes an inter-war period in which it manifested itself in elite-led but populist "armed party" politics opposing socialism and liberalism and promising radical politics to rescue the nation from decadence.<ref>Roger Griffin, '''', Chapter published in Alessandro Campi (ed.), ''Che cos'è il fascismo?'' Interpretazioni e prospettive di ricerche, Ideazione editrice, Roma, 2003, pp. 97–122.</ref> | |||
| ] describes fascism as "a genus of political ideology whose mythic core in its various permutations is a ] form of populist ]."{{sfnp|Griffin|1991|p=26}} Without palingenetic ultranationalism, there is no "genuine fascism" according to Griffin.<ref name="Griffin 1994">{{Cite book |last=Griffin |first=Roger |title=Fascism and theater: comparative studies on the aesthetics and politics of performance in Europe, 1925–1945 |date=1996 |publisher=Berghahn Books |isbn=978-1571819017 |editor-last=Berghaus |editor-first=Günter |location=Providence, RI |chapter=Chapter I: Staging the Nation's Rebirth: The Politics and Aesthetics of Performance in the Context of Fascist Studies |author-link=Roger Griffin |access-date=7 October 2013 |chapter-url=https://www.libraryofsocialscience.com/ideologies/resources/griffin-staging-the-nations/ |via=Library of Social Science}}</ref> Griffin further describes fascism as having three core components: "(i) the rebirth myth, (ii) populist ultra-nationalism, and (iii) the myth of decadence."{{sfnp|Griffin|1991|p=201}} In Griffin's view, fascism is "a genuinely revolutionary, trans-class form of anti-liberal, and in the last analysis, anti-conservative nationalism" built on a complex range of theoretical and cultural influences. He distinguishes an inter-war period in which it manifested itself in elite-led but populist "armed party" politics opposing socialism and liberalism, and promising radical politics to rescue the nation from decadence.{{sfnp|Griffin|2003|p=3}} | |||
| Paxton sees fascism as "obsessive preoccupation with community decline, humiliation or victimhood and by compensatory cults of unity, energy and purity". In Paxton's interpretation, fascists are "committed nationalist militants", working uneasily alongside traditional elites and abandoning democratic liberties in pursuit of "internal cleansing" or territorial expansion.<ref name="anatomnyfascismo"/> | |||
| Kershaw argues that the difference between fascism and other forms of right-wing authoritarianism in the ] is that the latter generally aimed "to conserve the existing social order", whereas fascism was "revolutionary", seeking to change society and obtain "total commitment" from the population.{{sfnp|Kershaw|2016|p=228-9}} In ''Against the Fascist Creep'', ] writes regarding Griffin's view: "Following the ] and shifts in fascist organizing techniques, a number of scholars have moved toward the minimalist 'new consensus' refined by Roger Griffin: 'the mythic core' of fascism is 'a populist form of ].' That means that fascism is an ideology that draws on old, ancient, and even arcane myths of racial, cultural, ethnic, and national origins to develop a plan for the 'new man.{{'"}}{{sfnp|Ross|2017|p=5}} Griffin himself explored this 'mythic' or 'eliminable' core of fascism with his concept of ''post-fascism'' to explore the continuation of Nazism in the modern era.{{sfnp|Griffin|2008|loc=Chapter 8: Fascism's New Faces (and New Facelessness) in the 'Post-Fascist' Epoch}} Additionally, other historians have applied this minimalist core to explore ''proto-fascist'' movements.{{sfnp|Roel Reyes|2019}}<ref>{{cite journal|last=Roel Reyes |first=Stefan |date=24 November 2021 |title='Christian Patriots': The Intersection Between Proto-fascism and Clerical Fascism in the Antebellum South |url=https://brill.com/view/journals/hcm/aop/article-10.1163-22130624-00219121/article-10.1163-22130624-00219121.xml |journal=International Journal for History, Culture and Modernity |volume=-1 |issue=aop |pages=82–110 |doi=10.1163/22130624-00219121 |s2cid=244746966 |issn=2213-0624 |doi-access=free}}</ref> | |||
| One common definition of fascism focuses on three groups of ideas: the ''Fascist Negations'' of anti-liberalism, anti-communism and anti-conservatism; nationalist, authoritarian goals for the creation of a regulated economic structure to transform social relations within a modern, self-determined culture; a political aesthetic using romantic symbolism, mass mobilisation, a positive view of violence, promotion of masculinity and youth and charismatic leadership.<ref>Griffin, Roger and Matthew Feldman p. 420-421, 2004 Taylor and Francis.</ref><ref>Kallis, Aristotle, ed. (2003). ''The Fascism Reader,'' London: Routledge, pages 84–85.</ref><ref>Renton, David. ''Fascism: Theory and Practice'', p. 21, London: Pluto Press, 1999.</ref></blockquote> | |||
| ] and Cristóbal Rovira Kaltwasser argue that although fascism "flirted with populism ... in an attempt to generate mass support", it is better seen as an elitist ideology. They cite in particular its exaltation of the Leader, the race, and the state, rather than the people. They see populism as a "thin-centered ideology" with a "restricted morphology" that necessarily becomes attached to "thick-centered" ideologies such as fascism, liberalism, or socialism. Thus populism can be found as an aspect of many specific ideologies, without necessarily being a defining characteristic of those ideologies. They refer to the combination of populism, authoritarianism and ultranationalism as "a marriage of convenience".{{sfnp|Mudde|Kaltwasser|2017|pp=6, 33–34|ps=: "... thin-centered ideologies have a restricted morphology, which necessarily appears attached to—and sometimes is even assimilated into—other ideologies. In fact, populism almost always appears attached to other ideological elements, which are crucial for the promotion of political projects that are appealing to a broader public. Consequently, by itself populism can offer neither complex nor comprehensive answers to the political questions that modern societies generate. ... is not so much a coherent ideological tradition as a set of ideas that, in the real world, appears in combination with quite different, and sometimes contradictory, ideologies." (p. 6)}} | |||
| ===Position in the political spectrum=== | |||
| Fascism is normally described as "]",<ref>Eatwell, Roger: "A Spectral-Syncretic Approach to Fascism", ''The Fascism Reader'', Routledge, 2003, p 79. </ref><ref name=Oxford>{{cite web|title=Fascism|url=http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/fascism?view=uk|work=Oxford English Dictionary|publisher=Oxford Dictionaries Online|accessdate=18 May 2011}}</ref> although writers have found placing fascism on a conventional ]-right ] difficult.<ref>Turner, Stephen P., Käsler, Dirk: ''Sociology Responds to Fascism'', Routledge. 2004, p. 222</ref> There is a scholarly consensus that fascism was influenced by both left and right, conservative and anti-conservative, national and supranational, rational and anti-rational.<ref name="ah.brookes.ac.uk"/> A number of historians have regarded fascism either as a revolutionary centrist doctrine, as a doctrine which mixes philosophies of the left and the right, or as both of those things.<ref name=sr3/><ref name=er71>Eatwell, Roger: "A 'Spectral-Syncretic Approach to Fascism', ''The Fascism Reader'', Routledge, 2003 pp. 71–80 </ref><ref name=ls112/> | |||
| ] says: <blockquote> a form of political behavior marked by obsessive preoccupation with community decline, humiliation, or victimhood and by compensatory cults of unity, energy, and purity, in which a mass-based party of committed nationalist militants, working in uneasy but effective collaboration with traditional elites, abandons democratic liberties and pursues with redemptive violence and without ethical or legal restraints goals of internal cleansing and external expansion.{{sfnp|Paxton|2004|p=216}}</blockquote> | |||
| There were factions within ] on both the left and the right. The accommodation of the political right into Fascism in the early 1920s led to the creation of a number of internal factions in the Italian Fascist movement. The "Fascist left" included ], ], and ], who were committed to advancing ] as a replacement for parliamentary liberalism in order to modernize the economy and advance the interests of workers and the common people.<ref name=sgp112>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2001. p. 112.</ref> The "Fascist right" included members of the Fascist paramilitary "''Squadristi''" and former members of the ] (ANI).<ref name=sgp112/> The ''Squadristi'' wanted to establish of Fascism as a complete dictatorship, while the former ANI members, including ], sought an authoritarian corporatist state to replace the liberal state in Italy, while retaining existing elites.<ref name=sgp112/> There were also smaller factions within the Italian Fascist movement, such as the "clerical Fascists" who sought to shift Italian Fascism from its anti-Catholic roots to accepting Catholicism. There were also "monarchist Fascists" who sought to use Fascism to create an ] under King ].<ref name=sgp112/> | |||
| ] defines fascism as "an ideology that strives to forge social rebirth based on a ]-national radical ]",{{sfnp|Eatwell|1996|p=24}} while ] sees the core tenets of fascism as "self-evident: nationalism; ]; racialism, the need for leadership, a new aristocracy, and obedience; and the negation of the ideals of the Enlightenment and the French Revolution."{{sfnp|Laqueur|1997|p=96}} | |||
| A number of fascist movements described themselves as a "]" outside of the traditional political spectrum.<ref>Mosse, G: "Toward a General Theory of Fascism", ''Fascism'', ed. Griffin, Routeledge, 2003</ref> Mussolini promoted ambiguity about fascism's positions in order to rally as many people to it as possible, saying fascists can be "aristocrats or democrats, revolutionaries and reactionaries, ] and anti-proletarians, pacifists and anti-pacifists".<ref name=nm54>Neocleous, Mark. Fascism. Minneapolis: ], 1997. p. 54.</ref> Mussolini claimed that Italian Fascism's economic system of ] could be identified as either ] or ], which in either case involved "the bureaucratisation of the economic activities of the nation."<ref name=mb158-159>Mussolini, Benito; Schnapp, Jeffery Thompson (ed.); Sears, Olivia E. (ed.); Stampino, Maria G. (ed.). "Address to the National Corporative Council (14 November 1933) and Senate Speech on the Bill Establishing the Corporations (abridged; 13 January 1934)". ''A Primer of Italian Fascism''. University of Nebraska Press, 2000. pp. 158–159.</ref> Mussolini described fascism in any language he found useful.<ref name=nm54/><ref> "a final indicator of the amibiguity between left and right extremes is that many militants switch sides, including the very founder of fascism, Benito Mussolini" Terrorism today, Christopher C. Harmon, Routledge, 2000 ISBN 9780714649986 316 pages</ref> Spanish Falangist leader José Antonio Primo de Rivera was critical of both left-wing and right-wing politics, once saying that "basically the Right stands for the maintenance of an economic structure, albeit an unjust one, while the Left stands for the attempt to subvert that economic structure, even though the subversion thereof would entail the destruction of much that was worthwhile".<ref>Neocleous, Mark. Fascism. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1997. p. 58.</ref> | |||
| Historian ] has defined fascism thusly: | |||
| ===Contemporary international views=== | |||
| <blockquote> modern political phenomenon, ], ], and ], organized in a militia party with a ] conception of politics and the state, an activist and anti-theoretical ideology, with a mythical, virilistic and anti-hedonistic foundation, sacralized as a secular religion, which affirms the absolute primacy of the nation, understood as an ethnically homogeneous organic community, hierarchically organized in a ], with a bellicose vocation to the politics of greatness, power, and conquest aimed at creating a new order and a new civilization.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Gentile |first=Emilio |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=5yWODAAAQBAJ |title=Fascismo: Storia e interpretazione |trans-title=Fascism: History and interpretation |publisher=Editori Laterza |year=2002 |isbn=978-88-581-0916-8 |language=it |via=]}}</ref></blockquote> | |||
| Initially fascism and the Italian Fascists in particular were popular in the world, until ] and the defeat of the ]. ] supported the Italian Fascist regime as late as 1937, claiming that Mussolini had strong qualities that safeguarded Italy from the threat of communism, which was worth the sacrifice of liberties.<ref>Chris Wrigley. ''Winston Churchill: a biographical companion''. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CLIO, 2002. p. 272.</ref> ] ] once claimed that he was the first fascist and declared his respect for the lower-class origins of Mussolini and ].<ref>Robert A. Hill (editor). "The Marcus Garvey and Universal Negro Improvement Association Papers, Vol. X". ''Africa for the Africans, 1923–1945''. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California, USA: University of California Press, 2006. p. 600.</ref> ], prior to the ], said that he was "keeping in touch with the admirable gentleman", referring to Mussolini.<ref>Brice Harris, Jr. ''United States and the Italo-Ethiopian Crisis''. Stanford, California, USA: Stanford California Press p. 43.</ref> ] traveled to Italy to meet Mussolini in December 1931 with the intention of attempting to spread the value of peace.<ref>Stanley Wolpert. ''Gandhi's Passion: The Life and Legacy of Mahatma Gandhi''. New York, New York, USA: Oxford University Press, p. 163.</ref><ref>Mohandas Gandhi, Homer Alexander Jack. New York, New York, USA: Grove, 1956. p. 386.</ref> | |||
| Historian and cultural critic ] has described fascism as "the original phase of authoritarianism, along with early communism, when a population has undergone huge dislocations or they perceive that there's been changes in society that are very rapid, too rapid for their taste".<ref>{{Cite magazine |last= |first= |date=29 March 2023 |title=Who Are You Calling a Fascist? |magazine=] |url=https://newrepublic.com/article/171370/calling-fascist |access-date=13 July 2023 |issn=0028-6583 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230329102010/https://newrepublic.com/article/171370/calling-fascist |archive-date=29 March 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ===''Fascist'' as epithet=== | |||
| {{Main|Fascist (epithet)}} | |||
| Racism was a key feature of German fascism, for which the ] was a high priority. According to ''The Historiography of ]'', "In dealing with the Holocaust, it is the consensus of historians that Nazi Germany targeted Jews as a race, not as a religious group."{{sfnp|Weiss-Wendt|Krieken|Cave|2008|p=73}} Several historians, such as Umberto Eco,<ref name="Eco1995">{{cite news|url=http://www.justicescholars.org/pegc/archive/Articles/eco_ur-fascism.pdf |first=Umberto |last=Eco |author-link=Umberto Eco |title=Eternal Fascism |newspaper=] |publisher=] |location=New York |date=22 June 1995 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051129130630/http://www.justicescholars.org/pegc/archive/Articles/eco_ur-fascism.pdf |archive-date=29 November 2005 |via=justicescholars.org}}</ref> Kevin Passmore,{{sfnp|Passmore|2002|p=31}} and Moyra Grant,{{sfnp|Grant|2003|pp=60–61}} stress ] as a characteristic component of German fascism. Historian ] stated that "Hitler envisioned the ideal German society as a {{lang|de|]}}, a racially unified and hierarchically organized body in which the interests of individuals would be strictly subordinate to those of the nation, or Volk."{{sfnp|Encyclopedia Britannica ''Volksgemeinschaft''}} Kershaw noted that common factors of fascism included "the 'cleansing' of all those deemed not to belong—foreigners, ethnic minorities, 'undesirables{{'"}} and belief in its own nation's superiority, even if it was not biological racism like in Nazism.{{sfnp|Kershaw|2016|p=228-9}} Fascist philosophies vary by application, but remain distinct by one theoretical commonality: all traditionally fall into the far-right sector of any ], catalyzed by afflicted class identities over conventional social inequities.<ref name="RoutledgeCompanion"/> | |||
| Following the defeat of the ] in ], the term ] has been used as a ] word,<ref>Gregor. Mussolini's Intellectuals: Fascist Social and Political Thought, Princeton University Press, 2005 ISBN 0691120099 282 p. 4</ref> often referring to widely varying movements across the political spectrum.<ref>George Orwell, What is Fascism? </ref> In political discourse, the term "fascist" is commonly used to denote authoritarian tendencies, but is often used as a pejorative ] by adherents to both left-wing and right-wing politics to denigrate those with opposing viewpoints. ] wrote in 1944 that "the word 'Fascism' is almost entirely meaningless ... almost any English person would accept 'bully' as a synonym for 'Fascist'".<ref name="orwell1944">{{cite news|url=http://orwell.ru/library/articles/As_I_Please/english/efasc|publisher=Orwell.ru|title=George Orwell: ‘What is Fascism?’|date=8 January 2008}}</ref></blockquote> ] argued in 2005 that "fascism" is the "most misused, and over-used word, of our times".<ref name="intelligentguide">{{cite book |last=Griffiths |first=Richard |title=An Intelligent Person's Guide to Fascism|publisher=Duckworth|url=http://books.google.com/?id=Y668AAAACAAJ&dq=Griffiths,+Richard |isbn=0715629182 |year=2000}}</ref> "Fascist" is sometimes applied to post-war organisations and ways of thinking that academics more commonly term "]".<ref>{{cite book |last=Woolf|first=Stuart |title=Fascism in Europe|publisher=Methuen |year=1981 |url=http://books.google.com/?id=iaMOAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA18 |isbn=9780416302400}}</ref> | |||
| According to the ], many experts see fascism as a mass political movement centered around extreme nationalism, militarism, and the placement of national interests above those of the individual. Fascist regimes often advocate for the overthrow of institutions that they view as "liberal decay" while simultaneously promoting traditional values. They believe in the supremacy of certain peoples and use it to justify the persecution of other groups. Fascist leaders often maintain a cult of personality and seek to generate enthusiasm for the regime by rallying massive crowds. This contrasts with authoritarian governments, which also centralize power and suppress dissent, but want their subjects to remain passive and demobilized.<ref>{{cite web |title=What Is Fascism? |url=https://education.cfr.org/learn/reading/what-fascism |website=CFR Education from the Council on Foreign Relations |language=en |date=14 April 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ===Used within and against Communism=== | |||
| ] ] from the 1970s, commemorating a killed party member. Slogan reads 'Neither Fascism, nor Social fascism. Popular Government']] | |||
| Contrary to the common mainstream academic and popular use of the term, Communist states have sometimes been referred to as "fascist". Marxist interpretations of the term have, for example, been applied in relation to ] under ] and ] under ].<ref name=rg231/> Herbert Matthews, of the '']'' asked "Should we now place Stalinist Russia in the same category as Hitlerite Germany? Should we say that she is Fascist?".<ref>Matthews, Claudio. ''Fascism Is Not Dead...'', ''Nation's Business'', 1946.</ref> ] wrote extensively of "Red Fascism".<ref>Hoover, J. Edgar. '''', 1947.</ref> | |||
| ===Position on the political spectrum=== | |||
| Chinese Marxists used the term to denounce the Soviet Union during the ], and likewise, the Soviets used the term to identify Chinese Marxists.<ref>Quarantotto, Claudio. ''Tutti Fascisti'', 1976.</ref> | |||
| ], ], in 1937. ] was later labeled by some commentators the "last surviving fascist dictator".<ref>{{cite news |title=Franco's dictatorship |url=https://www.britannica.com/biography/Francisco-Franco/Francos-dictatorship |work=Encyclopaedia Britannica}}</ref>]] | |||
| Scholars place fascism on the ] of the ].<ref name="RoutledgeCompanion"/><ref name="USHMM"/><ref name="University-Aristotle-Hartley-Wilhelm-Hawkesworth"/> Such scholarship focuses on its ] and its ] means of opposing ].{{sfnmp|1a1=Davies|1a2=Lynch|1y=2002|1pp=126–127|Zafirovski|2008|2pp=137–138}} Roderick Stackelberg places fascism—including ], which he says is "a radical variant of fascism"—on the political right by explaining: "The more a person deems absolute equality among all people to be a desirable condition, the further left he or she will be on the ideological spectrum. The more a person considers inequality to be unavoidable or even desirable, the further to the right he or she will be."{{sfnp|Stackelberg|1999|pp=4–6}} | |||
| ==Historical causes and development== | |||
| ===Fusion of nationalism and Sorelianism and split in the left (1907–1914)=== | |||
| A key element in the creation of fascism was the fusion of agendas of ] on the political ] with ] ] on the ], around the outbreak of ].<ref name="ZeevSternhell" /> Sorelian syndicalism, unlike other ideologies on the left, held an elitist view that the morality of the working-class needed to be raised.<ref name=zs162>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 162.</ref> The Sorelian concept of the positive nature of social war and its insistence on moral revolution led some syndicalists to believe that war was the ultimate manifestation of social change and moral revolution.<ref name=zs162/> | |||
| Fascism's origins are complex and include many seemingly contradictory viewpoints, ultimately centered on a mythos of national rebirth from decadence.{{sfnp|Griffin|2003|p=5}} Fascism was founded during ] by Italian ] who drew upon both ] organizational tactics and ] political views.{{sfnp|Gregor|2009|p=191}} ] gravitated to the right in the early 1920s.{{sfnmp|1a1=Sternhell|1a2=Sznajder|1a3=Ashéri|1y=1994|1p=161|2a1=Borsella|2a2=Caso|2y=2007|2p=76}} A major element of fascist ideology that has been deemed to be far right is its stated goal to promote the right of a supposedly ] to dominate, while purging society of supposedly inferior elements.{{sfnp|Woshinsky|2008|p=156}} | |||
| Nationalist and militarist influences that had begun to combine with syndicalism since 1907 created a split in the political left.<ref name="ZeevSternhell"/> This split was strong in Italy, where nationalists and syndicalists increasingly influenced each other.<ref name="ZeevSternhell"/> ] nationalism, close to Sorelism, influenced radical Italian nationalist ].<ref name=zs163>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 163.</ref> Corradini spoke of the need for a ] movement, led by elitist aristocrats and anti-democrats who shared a revolutionary syndicalist commitment to direct action and a willingness to fight.<ref name=zs163/> Corradini spoke of Italy as being a "proletarian nation" that needed to pursue ] in order to challenge the "]" French and British.<ref name=mb9>Martin Blinkhorn. ''Mussolini and fascist Italy''. Second edition. New York, New York, USA: Routledge, 2003 p. 9.</ref> Corradini's views were part of a wider set of perceptions within the right-wing ] (ANI), which claimed that Italy's economic backwardness was caused by corruption within its political class, liberalism, and division caused by "ignoble socialism".<ref name=mb9/> The ANI held ties and influence among ], Catholics, and the business community.<ref name=mb9/> | |||
| In the 1920s, Mussolini and ] described their ideology as right-wing in the political essay '']'', stating: "We are free to believe that this is the century of authority, a century tending to the 'right,' a fascist century."{{sfnmp|1a1=Schnapp|1a2=Sears|1a3=Stampino|1y=2000|1p=57|Mussolini|1935|2p=26}} Mussolini stated that fascism's position on the political spectrum was not a serious issue for fascists: "ascism, sitting on the right, could also have sat on the mountain of the center. ... These words in any case do not have a fixed and unchanged meaning: they do have a variable subject to location, time and spirit. We don't give a damn about these empty terminologies and we despise those who are terrorized by these words."<ref>Mussolini quoted in {{harvp|Gentile|2005|p=205}}</ref> | |||
| Italian national syndicalists held a common set of principles: the rejection of ] values, ], ], ], ], and ] and the promotion of ], ], and violence.<ref>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 32.</ref> | |||
| Major Italian groups politically on the right, especially rich landowners and big business, feared an uprising by groups on the left, such as sharecroppers and labour unions.{{sfnp|Baranski|West|2001|pp=50–51}} They welcomed fascism and supported its violent suppression of opponents on the left.{{sfnp|Encyclopedia Britannica ''The fascist era''}} The accommodation of the political right into the Italian Fascist movement in the early 1920s created internal factions within the movement. The "fascist left" included ], ], ], ], and ], who were committed to advancing national syndicalism as a replacement for parliamentary liberalism in order to modernize the economy and advance the interests of workers and the common people.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=112}} The "fascist right" included members of the paramilitary ] and former members of the ] (ANI).{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=112}} The Blackshirts wanted to establish fascism as a complete dictatorship, while the former ANI members, including ], sought to institute an authoritarian corporatist state to replace the liberal state in Italy while retaining the existing elites.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=112}} Upon accommodating the political right, there arose a group of monarchist fascists who sought to use fascism to create an ] under King ].{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=112}} | |||
| Radical nationalism in Italy – support for expansionism and cultural revolution to create a "New Man" and a "New State" – began to grow in 1912 during the Italian conquest of ] and was supported by Italian ] and members of the ANI.<ref>Emilio Gentile. The struggle for modernity: nationalism, futurism, and fascism. Westport, Connecticut, USA: Praeger Publishers, 2003. p. 5.</ref> The ANI claimed that liberal democracy was no longer compatible with the modern world and advocated a strong state and ], claiming that humans are naturally predatory and that nations were in a constant struggle where only the strongest could survive.<ref>Emilio Gentile. The struggle for modernity: nationalism, futurism, and fascism. Westport, Connecticut, USA: Praeger Publishers, 2003. p. 6.</ref> | |||
| A number of post-World War II fascist movements described themselves as a ] outside the traditional political spectrum. ] leader ] said: "asically the Right stands for the maintenance of an economic structure, albeit an unjust one, while the Left stands for the attempt to subvert that economic structure, even though the subversion thereof would entail the destruction of much that was worthwhile."{{sfnp|Neocleous|1997|p=54}} | |||
| However, until 1914, Italian nationalists and revolutionary syndicalists with nationalist leanings remained apart. Such syndicalists opposed the ] of 1911 as an affair of financial interests and not the nation.<ref name=zs170>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 170.</ref> World War I was seen by both Italian nationalists and syndicalists as a national affair.<ref>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 173.</ref> | |||
| ===''Fascist'' as a pejorative=== | |||
| ===World War I and the founding of Fascism (1914–1920)=== | |||
| {{Main|Fascist (insult)}} | |||
| {{Missing information|the formation of the Italian Fascist Party|date=January 2011}} | |||
| The term ''fascist'' has been used as a ],{{sfnp|Gregor|2005|p=4}} regarding varying movements across the far right of the political spectrum. ] noted in 1944 that the term had been used to denigrate diverse positions "in internal politics". Orwell said that while fascism is "a political and economic system" that was inconvenient to define, "''as used'', the word 'Fascism' is almost entirely meaningless. ... almost any English person would accept 'bully' as a synonym for 'Fascist{{'"}},{{sfnp|Orwell|2019}} and in 1946 wrote that {{"'}}Fascism' has now no meaning except in so far as it signifies something not desirable."{{sfnp|Orwell|1946}} Richard Griffiths of the ] wrote in 2000 that "fascism" is the "most misused, and over-used word, of our times".{{sfnp|Griffiths|2000}}{{rp|1}} ''Fascist'' is sometimes applied to post-World War II organizations and ways of thinking that academics more commonly term '']''.{{sfnp|Woolf|1981|p=18}} | |||
| At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, the Italian political left became severely split over its position on the war.<ref name=zs170/> The ] opposed the war on the grounds of ], but a number of Italian revolutionary syndicalists supported intervention against Germany and Austria-Hungary on the grounds that their ] regimes needed to be defeated to ensure the success of socialism.<ref name=zs175>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 175.</ref> Corradini presented the same need for Italy as a "proletarian nation" to defeat a reactionary Germany from a nationalist perspective.<ref>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. pp. 173, 175.</ref> The beginning of fascism resulted from this split, with ] forming the Revolutionary Fascio for International Action in October 1914.<ref name=zs175/> At the same time, Benito Mussolini joined the interventionist cause.<ref>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 214.</ref> The Fascists supported nationalism and claimed that ] was a failure.<ref name=zs175/> | |||
| Despite fascist movements' history of ], ]s have sometimes been referred to as ''fascist'', typically as an insult. It has been applied to ] regimes in ] under ] and ] under ].{{sfnp|Griffin|Feldman|2004a|p=231}} Chinese Marxists used the term to denounce the ] during the ], and the Soviets used the term to denounce Chinese Marxists,{{sfnp|Quarantotto|1976}} in addition to ], coining a new term in '']''. In the United States, Herbert Matthews of '']'' asked in 1946: "Should we now place Stalinist Russia in the same category as Hitlerite Germany? Should we say that she is Fascist?"{{sfnp|Matthews|1946}} ], longtime ] director and ardent anti-communist, wrote extensively of ].{{sfnp|Hoover|1947}} The ] in the 1920s was sometimes called ''fascist''. Historian Peter Amann states that, "Undeniably, the Klan had some traits in common with European fascism—chauvinism, racism, a mystique of violence, an affirmation of a certain kind of archaic traditionalism—yet their differences were fundamental ... never envisioned a change of political or economic system."{{sfnp|Amann|1986|p=562}} | |||
| At this time, the Fascists did not have an integrated set of policies and the movement was very small. Its attempts to hold mass meetings were ineffective and it was regularly harassed by government authorities and orthodox socialists.<ref>Anthony James Gregor. ''Young Mussolini and the intellectual origins of fascism''. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California, USA; London, England, UK: University of California Press, 1979. p. 195–196.</ref> Antagonism between interventionists, including Fascists, and anti-interventionist orthodox socialists resulted in violence.<ref name=ajg196>Anthony James Gregor. ''Young Mussolini and the intellectual origins of fascism''. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California, USA; London, England, UK: University of California Press, 1979. p. 196.</ref> Attacks on interventionists were so violent that even democratic socialists who opposed the war, such as ], said that the Italian Socialist Party had gone too far in its campaign to silence supporters of the war.<ref name=ajg196/> | |||
| ==History== | |||
| Italy's use of daredevil elite ] known as the '']'', beginning in 1917, was an important influence on Fascism.<ref name=rg207>Roger Griffin, Matthew Feldman. Fascism: Fascism and culture. London, England, UK; New York, New York, USA: Routledge, 2004. p. 207.</ref> The ''Arditi'' were soldiers who were specifically trained for a life of violence and wore unique blackshirt uniforms and fezzes.<ref name=rg207/> The ''Arditi'' formed a national organization in November 1918, the ''Associazione fra gli Arditi d'Italia'', which by mid-1919 had about twenty thousand young men within it.<ref name=rg207/> Mussolini appealed to the ''Arditi'', and the Fascists' '']'', developed after the war, were based upon the ''Arditi''.<ref name=rg207/> | |||
| {{Further|Fascism and ideology}} | |||
| ===Background and 19th-century roots=== | |||
| With the split between anti-interventionist Marxists and pro-interventionist Fascists complete by the end of the war, the two sides became irreconcilable. The Fascists presented themselves as ] and as opposed to Soviet communism.<ref>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 178.</ref> Benito Mussolini consolidated control over the Fascist movement in 1919 with the founding of the '']'', whose opposition to orthodox socialism he declared: | |||
| ] has been considered an inspiration for fascist and quasi-fascist movements, such as ] and quasi-fascist ]]] | |||
| Early influences that shaped the ideology of fascism have been dated back to ]. The political culture of ancient Greece and specifically the ancient Greek city state of ] under ], with its emphasis on militarism and racial purity, were admired by the Nazis.<ref name="ReferenceB">{{cite journal |date=2013 |title=To what extent was Hitler's rule of Nazi Germany similar to life in Sparta? |url=https://www.academia.edu/4761037 |access-date=15 April 2016 |website=Academia |last1=Whiffen |first1=Timothy}}</ref><ref>Anthony Grafton, Glenn W. Most, Salvatore Settis. ''The Classical Tradition''. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2010. pp. 353. {{ISBN?}}</ref> Nazi '']'' ] emphasized that Germany should adhere to Hellenic values and culture – particularly that of ancient Sparta.<ref name="ReferenceB"/> | |||
| {{quote|We declare war against socialism, not because it is socialism, but because it has opposed nationalism. Although we can discuss the question of what socialism is, what is its program, and what are its tactics, one thing is obvious: the official Italian Socialist Party has been reactionary and absolutely conservative. If its views had prevailed, our survival in the world of today would be impossible.<ref>Stanislao G. Pugliese. ''Fascism, anti-fascism, and the resistance in Italy: 1919 to the present''. Oxford, England, UK: Rowman & Littlefield Publishers, Inc., 2004. 43–44.</ref>}} | |||
| ], founder of the first non-Italian fascist party ],{{sfnp|Sternhell|1976}} claimed the roots of fascism stemmed from the late 18th century ] movement, seeing in its totalitarian nature a foreshadowing of the fascist state.{{sfnp|Camus|Lebourg|2017|p=20}} Historian ] similarly analyzed fascism as an inheritor of the ] and ] of the ], as well as a result of the brutalization of societies in 1914–1918.{{sfnp|Camus|Lebourg|2017|p=20}} | |||
| In 1919, ] and ] movement leader ] created '']'' (a.k.a. the ''Fascist Manifesto'').<ref>Dahlia S. Elazar. The making of fascism: class, state, and counter-revolution, Italy 1919–1922. Westport, Connecticut, USA: Praeger Publishers, 2001. p. 73</ref> The Manifesto was presented on June 6, 1919 in the Fascist newspaper ''Il Popolo d'Italia''. The Manifesto supported the creation of ] for both men ] (the latter being realized only partly in late 1925, with all opposition parties banned or disbanded<ref>Kevin Passmore, Women, Gender and Fascism in Europe, p. 116</ref>); ] on a regional basis; government representation through a ] system of "National Councils" of experts, selected from professionals and tradespeople, elected to represent and hold legislative power over their respective areas, including labour, industry, transportation, public health, communications, etc.; and the abolition of the ].<ref>Cristogianni Borsella, Adolph Caso. ''Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative''. Wellesley, Massachusetts, USA: Branden Books, 2007. p. 69.</ref> The Manifesto supported the creation of an ] for all workers, a ], worker representation in industrial management, equal confidence in labour unions as in industrial executives and public servants, reorganization of the transportation sector, revision of the draft law on invalidity insurance, reduction of the retirement age from 65 to 55, a strong ] on capital, confiscation of the property of religious institutions and abolishment of bishoprics, and revision of military contracts to allow the government to seize 85% of their{{Who|date=January 2011}} profits.<ref>Cristogianni Borsella, Adolph Caso. ''Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative''. Wellesley, Massachusetts, USA: Branden Books, 2007. pp. 69–70.</ref> It also called for the creation of a short-service national militia to serve defensive duties, ] of the armaments industry, and a foreign policy designed to be peaceful but also competitive.<ref>Cristogianni Borsella, Adolph Caso. ''Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative''. Wellesley, Massachusetts, USA: Branden Books, 2007. p. 70.</ref> | |||
| Historians such as ] and Howard C Payne see ], who ran a 'police state' and suppressed the media, as a forerunner of fascism.{{sfnp|Williams|2015|p=28}} According to ],{{sfnp|Thomson|1966|p=293}} the Italian ] of 1871 led to the 'nemesis of fascism'. ]{{sfnp|Shirer|1960|p=97}} sees a continuity from the views of ] and ], through ], to Hitler; ] speaks of a 'direct line' from Bismarck to Hitler.{{sfnp|Gerwarth|2005|p=166}} Julian Dierkes sees fascism as a 'particularly violent form of ]'.{{sfnp|Dierkes|2010|p=54}} | |||
| The next events that influenced the Fascists were the raid of ] by Italian nationalist ] and the founding of the ] in 1920.<ref>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 186.</ref> D'Annunzio and De Ambris designed the Charter, which advocated national-syndicalist ] ] alongside D'Annunzio's political views.<ref>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 187.</ref> Many Fascists saw the Charter of Carnaro as an ideal constitution for a Fascist Italy.<ref name=zs189>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 189.</ref> | |||
| ], founder and leader of the ], insisted that he and his organisation "were the first fascists".<ref>{{cite book |last1=Gregor |first1=A. James |chapter=5 - Black Nationalism and Neofascism: Marcus Garvey and the Universal Negro Improvement Association |title=The Search for Neofascism: The Use and Abuse of Social Science |date=27 March 2006 |pages=111–136 |doi=10.1017/cbo9780511617225.006 |publisher=] |isbn=9780521859202}}</ref> In 1938, ] wrote "all the things that Hitler was to do so well later, Marcus Garvey was doing in 1920 and 1921".<ref>{{cite journal |last1=Gilroy |first1=Paul |title=Black Fascism |journal=Transition |date=2000 |issue=81/82 |pages=70–91 |jstor=3137450 |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/3137450 |issn=0041-1191}}</ref> | |||
| ===Shift to the right and consolidation of political strength (1920–1922)=== | |||
| ==={{lang|fr|Fin de siècle}} era and fusion of Maurrasism with Sorelianism (1880–1914)=== | |||
| Beginning in 1920, Fascism began to make a shift towards the political right.<ref name=zs189/> This occurred as militant strike activity by industrial workers reached its peak in Italy, where 1919 and 1920 were known as the "Red Years".<ref>Cristogianni Borsella, Adolph Caso. ''Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative''. Wellesley, Massachusetts, USA: Branden Books, 2007. p. 73.</ref> Mussolini and the Fascists took advantage of the situation by allying with industrial businesses and attacking workers and peasants in the name of preserving order and internal peace in Italy.<ref>Cristogianni Borsella, Adolph Caso. ''Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative''. Wellesley, Massachusetts, USA: Branden Books, 2007. p. 75.</ref> | |||
| {{See also|National syndicalism}} | |||
| The historian ] has traced the ideological roots of fascism back to the 1880s and in particular to the {{lang|fr|]}} theme of that time.{{sfnmp|Sternhell|1998|1p=169|Payne|1995|2pp=23–24}} The theme was based on a revolt against ], ], ], ] society, and ].{{sfnp|Sternhell|1998|p=170}} The {{lang|fr|fin-de-siècle}} generation supported ], ], ], and ].{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=24}} They regarded civilization as being in crisis, requiring a massive and total solution.{{sfnp|Sternhell|1998|p=170}} Their intellectual school considered the individual as only one part of the larger collectivity, which should not be viewed as a numerical sum of atomized individuals.{{sfnp|Sternhell|1998|p=170}} They condemned the rationalistic, ] of society and the dissolution of social links in bourgeois society.{{sfnp|Sternhell|1998|p=170}} | |||
| The {{lang|fr|fin-de-siècle}} outlook was influenced by various intellectual developments, including ] biology, {{lang|de|]}}, ]'s racialism, ]'s ], and the philosophies of ], ], and ].{{sfnp|Sternhell|1998|p=171}} ], which gained widespread acceptance, made no distinction between physical and social life, and viewed the human condition as being an unceasing struggle to achieve the ].{{sfnp|Sternhell|1998|p=171}} It challenged positivism's claim of deliberate and rational choice as the determining behaviour of humans, with social Darwinism focusing on heredity, race, and environment.{{sfnp|Sternhell|1998|p=171}} Its emphasis on biogroup identity and the role of organic relations within societies fostered the legitimacy and appeal of nationalism.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=29}} New theories of social and political psychology also rejected the notion of human behaviour being governed by rational choice and instead claimed that emotion was more influential in political issues than reason.{{sfnp|Sternhell|1998|p=171}} Nietzsche's argument that "God is dead" coincided with his attack on the "]" of ], ], and modern ], his concept of the {{lang|de|]}}, and his advocacy of the ] as a primordial instinct, were major influences upon many of the {{lang|fr|fin-de-siècle}} generation.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|pp=24–25}} Bergson's claim of the existence of an {{lang|fr|élan vital}}, or vital instinct, centred upon free choice and rejected the processes of materialism and determinism; this challenged Marxism.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=25}} | |||
| Fascists identified their primary opponents as the majority of socialists on the left who had opposed intervention in World War I.<ref name=zs189/> The Fascists and the Italian political right held common ground: both held Marxism in contempt, discounted class consciousness and believed in the rule of elites.<ref name=zs193>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 193.</ref> The Fascists assisted the anti-socialist campaign of the political right by allying with the right in a mutual effort to destroy the Italian Socialist Party and labour organizations committed to class identity above national identity.<ref name=zs193/> | |||
| {{multiple image | |||
| Fascism sought to accommodate Italian ] by making major alterations to its political agenda – abandoning its previous ], ], and ], adopting policies in support of ], and accepting the ] and the monarchy as institutions in Italy.<ref name=ga145>De Grand, Alexander. ''Italian fascism: its origins and development''. 3rd ed. University of Nebraska Press, 2000. p. 145.</ref> To appeal to Italian conservatives, Fascism adopted policies such as promoting family values, including promotion of a woman's role as a mother.<ref>Fascists and conservatives: the radical right and the establishment in twentieth-century Europe. Routdlege, 1990. p. 14.</ref> Though Fascism adopted a number of positions designed to appeal to ], the Fascists sought to maintain Fascism's revolutionary character, with Angelo Oliviero Olivetti saying "Fascism would like to be conservative, but it will by being revolutionary."<ref>Zeev Sternhell, Mario Sznajder, Maia Ashéri. ''The birth of fascist ideology: from cultural rebellion to political revolution''. Princeton University Press, 1994. p. 190.</ref> The Fascists supported revolutionary action and committed to secure law and order to appeal to both conservatives and syndicalists.<ref>Martin Blinkhorn. ''Fascists and Conservatives''. 2nd edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2001 p. 22.</ref> | |||
| | align = right | |||
| | direction = horizontal | |||
| | width = | |||
| | image1 = Charles Maurras - avant 1922.jpg | |||
| | width1 = 120 | |||
| | caption1 = ] | |||
| | image2 = Georges Sorel.jpg | |||
| | width2 = 113 | |||
| | caption2 = ] | |||
| }} | |||
| In his work ''The Ruling Class'' (1896), ] developed the theory that claims that in all societies an "organized minority" would dominate and rule over an "disorganized majority",{{sfnmp|Outhwaite|2006|1p=442|Koon|1985|2p=6}} stating that there are only two classes in society, "the governing" (the organized minority) and "the governed" (the disorganized majority).{{sfnp|Caforio|2006|p=12}} He claims that the organized nature of the organized minority makes it irresistible to any individual of the disorganized majority.{{sfnp|Caforio|2006|p=12}} | |||
| Prior to its shift to the right, Fascism was a small, urban, northern Italian movement that had about a thousand members.<ref>Cristogianni Borsella, Adolph Caso. ''Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative''. Wellesley, Massachusetts, USA: Branden Books, 2007. p. 72.</ref> Afterward, the Fascist movement's membership soared to approximately 250,000 by 1921.<ref>Cristogianni Borsella, Adolph Caso. ''Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative''. Wellesley, Massachusetts, USA: Branden Books, 2007. p. 76.</ref> | |||
| ] and ] monarchist ] influenced fascism.{{sfnp|Carroll|1998|p=92}} Maurras promoted what he called ], which called for the organic unity of a nation, and insisted that a powerful monarch was an ideal leader of a nation. Maurras distrusted what he considered the democratic mystification of the popular will that created an impersonal collective subject.{{sfnp|Carroll|1998|p=92}} He claimed that a powerful monarch was a personified sovereign who could exercise authority to unite a nation's people.{{sfnp|Carroll|1998|p=92}} Maurras' integral nationalism was idealized by fascists, but modified into a modernized revolutionary form that was devoid of Maurras' monarchism.{{sfnp|Carroll|1998|p=92}} | |||
| ===Rise to power and initial international spread of fascism (1922–1929)=== | |||
| Beginning in 1922, Fascist paramilitaries escalated their strategy from one of attacking socialist offices and homes of socialist leadership figures to one of violent occupation of cities. The Fascists met little serious resistance from authorities and proceeded to take over multiple cities, including ], ], ], ], ], and ].<ref name=rop87>Robert O. Paxton. ''The Anatomy of Fascism''. New York, New York, USA; Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Random House, Inc., 2005 p. 87.</ref> The Fascists attacked the headquarters of socialist and ] unions in Cremona and imposed forced Italianization upon the German-speaking population of Trent and Bolzano.<ref name=rop87/> After seizing these cities, the Fascists made plans to take ].<ref name=rop87/> | |||
| ====Fascist syndicalism==== | |||
| On 24 October 1922, the Fascist party held its annual congress in ], where Mussolini ordered Blackshirts to take control of public buildings and trains and to converge on three points around Rome.<ref name=rop87/> The march would be led by four prominent Fascist leaders representing its different factions: ], a Blackshirt leader; General ]; ], an ex-syndicalist; and ], a monarchist Fascist.<ref name=rop87/> Mussolini himself remained in Milan to await the results of the actions.<ref name=rop87/> The Fascists managed to seize control of multiple post offices and trains in northern Italy while the Italian government, led by a left-wing coalition, was internally divided and unable to respond to the Fascist advances.<ref name=rop88>Robert O. Paxton. ''The Anatomy of Fascism''. New York, New York, USA; Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Random House, Inc., 2005 p. 88.</ref> The Italian government had been in a steady state of turmoil, with multiple governments being created and then being defeated.<ref name=rop88/> The Italian government initially took action to prevent the Fascists from entering Rome, but King ] perceived the risk of bloodshed in Rome in response to attempting to disperse the Fascists to be too high.<ref name=rop90>Robert O. Paxton. ''The Anatomy of Fascism''. New York, New York, USA; Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Random House, Inc., 2005 p. 90.</ref> Victor Emmanuel III decided to appoint Mussolini as ], and Mussolini arrived in Rome on 30 October to accept the appointment.<ref name=rop90/> Fascist propaganda aggrandized this event, known as "]", as a "seizure" of power due to Fascists' heroic exploits.<ref name=rop87/> | |||
| {{Main|Fascist syndicalism}} | |||
| French revolutionary ] ] promoted the legitimacy of ] in his work '']'' (1908) and other works in which he advocated radical syndicalist action to achieve a revolution to overthrow capitalism and the bourgeoisie through a ].{{sfnp|Antliff|2007|pp=75–81}} In ''Reflections on Violence'', Sorel emphasized need for a revolutionary ].{{sfnp|Antliff|2007|p=81}} Also in his work ''The Illusions of Progress'', Sorel denounced democracy as reactionary, saying "nothing is more aristocratic than democracy."{{sfnp|Antliff|2007|p=77}} By 1909, after the failure of a syndicalist general strike in France, Sorel and his supporters left the radical left and went to the radical right, where they sought to merge militant Catholicism and French patriotism with their views—advocating anti-republican Christian French patriots as ideal revolutionaries.{{sfnp|Antliff|2007|p=82}} Initially, Sorel had officially been a ] of Marxism, but by 1910 announced his abandonment of socialist literature and claimed in 1914, using an aphorism of ] that "socialism is dead" because of the "decomposition of Marxism".{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=78}} Sorel became a supporter of reactionary Maurrassian nationalism beginning in 1909 that influenced his works.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=78}} Maurras held interest in merging his nationalist ideals with Sorelian ], known as ], as a means to confront democracy.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=82}} Maurras stated that "a socialism liberated from the democratic and cosmopolitan element fits nationalism well as a well made glove fits a beautiful hand."{{sfnp|Holmes|2000|p=60}} | |||
| The fusion of Maurrassian nationalism and Sorelian syndicalism influenced radical Italian nationalist ].{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=163}} Corradini spoke of the need for a nationalist-syndicalist movement, led by elitist aristocrats and anti-democrats who shared a revolutionary syndicalist commitment to direct action and a willingness to fight.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=163}} Corradini spoke of Italy as being a "proletarian nation" that needed to pursue imperialism in order to challenge the "]" French and British.{{sfnp|Blinkhorn|2006|p=12}} Corradini's views were part of a wider set of perceptions within the right-wing Italian Nationalist Association (ANI), which claimed that Italy's economic backwardness was caused by corruption in its political class, liberalism, and division caused by "ignoble socialism".{{sfnp|Blinkhorn|2006|p=12}} | |||
| Upon being appointed Prime Minister of Italy, Mussolini had to form a coalition government, because the Fascists did not have control over the Italian parliament.<ref name=sgp110>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. p. 110.</ref> The coalition government included a cabinet led by Mussolini and thirteen other ministers, only three of whom were Fascists; others included representatives from the army and the navy, two Catholic Popolari members, two ], one ], one ], one Nationalist member, and the pro-Fascist philosopher ].<ref name=sgp110/> Mussolini's coalition government initially pursued ] policies under the direction of liberal finance minister ], including balancing the budget through deep cuts to the civil service.<ref name=sgp110/> Initially, little drastic change in government policy had occurred and repressive police actions against communist and ] rebels were limited.<ref name=sgp110/> At the same time, however, Mussolini consolidated his control over the ] by creating a governing executive for the party, the ], whose agenda he controlled.<ref name=sgp110/> In addition, the ''Squadristi'' blackshirt militia was transformed into the state-run ], led by regular army officers.<ref name=sgp110/> Militant ''Squadristi'' were initially highly dissatisfied with Mussolini's government and demanded a "Fascist revolution".<ref name=sgp110/> | |||
| The ANI held ties and influence among ], Catholics, and the business community.{{sfnp|Blinkhorn|2006|p=12–13}} Italian national syndicalists held a common set of principles: the rejection of ] values, democracy, liberalism, ], ], and ], and the promotion of ], vitalism, and violence.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=32}} The ANI claimed that liberal democracy was no longer compatible with the modern world, and advocated a strong state and imperialism. They believed that humans are naturally predatory, and that nations are in a constant struggle in which only the strongest would survive.{{sfnp|Gentile|2003|p=6}} | |||
| In this period, to appease the King of Italy, Mussolini formed a close political alliance between the Italian Fascists and Italy's conservative faction in Parliament, which was led by ], a conservative ] and nationalist who was a member of the Italian Nationalist Association (ANI).<ref>De Grand, Alexander. ''Italian fascism: its origins and development''. 3rd ed. University of Nebraska Press, 2000. pp. 45 and 54.</ref> The ANI joined the National Fascist Party in 1923.<ref>De Grand, Alexander. ''Italian fascism: its origins and development''. 3rd ed. University of Nebraska Press, 2000. p. 45.</ref> Because of the merger of the Nationalists with the Fascists, tensions existed between the conservative nationalist and revolutionary syndicalist factions of the movement.<ref name=rs21>Roland Sarti. "Italian fascism: radical politics and conservative goals". ''Fascists and Conservatives''. Ed. Martin Blinkhorn. 2nd edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2001 p. 21.</ref> The conservative and syndicalist factions of the Fascist movement sought to reconcile their differences, secure unity, and promote fascism by taking on the views of each other.<ref name=rs22>Roland Sarti. "Italian fascism: radical politics and conservative goals". ''Fascists and Conservatives''. Ed. Martin Blinkhorn. 2nd edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2001 p. 22.</ref> Conservative nationalist Fascists promoted fascism as a revolutionary movement to appease the revolutionary syndicalists while, to appease conservative nationalist fascists, revolutionary syndicalist Fascists declared they wanted to secure social stability and insure economic productivity.<ref name=rs22/> | |||
| ], Italian modernist author of the ] (1909) and later the co-author of the ] (1919)]] | |||
| The Fascists began their attempt to entrench Fascism in Italy with the ], which guaranteed a plurality of the seats in parliament to any party or coalition list in an election that received 25% or more of the vote.<ref name=sgp113>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. p. 113.</ref> The Acerbo Law was passed in spite of numerous abstentions from the vote.<ref name=sgp113/> In the 1924 election, the Fascists, along with moderates and conservatives, formed a coalition candidate list, and through considerable Fascist violence and intimidation, the list won with 66% of the vote, allowing it to receive 403 seats, most of which went to the Fascists.<ref name=sgp113/> In the aftermath of the election, a crisis and political scandal erupted after Socialist Party deputy ] was kidnapped and murdered by a Fascist.<ref name=sgp113/> The liberals and the leftist minority in parliament walked out in protest in what became known as the ].<ref name=sgp114>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. p. 114.</ref> On 3 January 1925, Mussolini addressed the Fascist-dominated Italian parliament and declared that he was personally responsible for what happened, but he insisted that he had done nothing wrong. He proclaimed himself dictator of Italy, assuming full responsibility over the government and announcing the dismissal of parliament.<ref name=sgp114/> From 1925 to 1929, Fascism steadily became entrenched in power: opposition deputies were denied access to parliament, censorship was introduced, and a December 1925 decree made Mussolini solely responsible to the King. Efforts to Fascistize Italian society accelerated beginning in 1926, with Fascists taking positions in local administration and 30% of all prefects being administered by appointed Fascists by 1929.<ref>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. p. 115.</ref> In 1929, the Fascist regime gained the political support and blessing of the Roman Catholic Church after the regime signed a concordat with the Church, known as the ], which gave the papacy state sovereignty and financial compensation for the seizure of Church lands by the liberal state in the nineteenth century.<ref>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. pp. 119–120.</ref> Though Fascist propaganda had begun to speak of the new regime as an all-encompassing "]" state beginning in 1925, the Fascist party and regime never gained total control over Italy's institutions; King Victor Emmanuel III remained head of state, the armed forces and the judicial system retained considerable autonomy from the Fascist state, Fascist militias were under military control, and initially the economy had relative autonomy as well.<ref>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. p. 122.</ref> | |||
| ] was both an artistic-cultural movement and initially a political movement in Italy led by ] who founded the ] (1908), that championed the causes of modernism, action, and political violence as necessary elements of politics while denouncing liberalism and parliamentary politics. Marinetti rejected conventional democracy based on majority rule and egalitarianism, for a new form of democracy, promoting what he described in his work "The Futurist Conception of Democracy" as the following: "We are therefore able to give the directions to create and to dismantle to numbers, to quantity, to the mass, for with us number, quantity and mass will never be—as they are in Germany and Russia—the number, quantity and mass of mediocre men, incapable and indecisive."{{sfnp|Hewitt|1993|p=153}} | |||
| The Fascist regime began to create a corporatist economic system in 1925 with creation of the ], in which the Italian employers' association ] and Fascist trade unions agreed to recognize each other as the sole representatives of Italy's employers and employees, excluding non-Fascist trade unions.<ref name=cb150>Cyprian Blamires, Paul Jackson. ''World fascism: a historical encyclopedia, Volume 1''. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CLIO, 2006. p. 150.</ref> The Fascist regime first created a Ministry of Corporations that organized the Italian economy into 22 sectoral corporations, banned workers' strikes and lock-outs, and in 1927 created the ], which established workers' rights and duties and created labour tribunals to arbitrate employer-employee disputes.<ref name=cb150/> In practice, the sectoral corporations exercised little independence and were largely controlled by the regime, and employee organizations were rarely led by employees themselves but instead by appointed Fascist party members.<ref name=cb150/> | |||
| Futurism influenced fascism in its emphasis on recognizing the virile nature of violent action and war as being necessities of modern civilization.{{sfnp|Gori|2004|p=14}} Marinetti promoted the need of physical training of young men saying that, in male education, gymnastics should take precedence over books. He advocated segregation of the genders because womanly sensibility must not enter men's education, which he claimed must be "lively, bellicose, muscular and violently dynamic."{{sfnp|Gori|2004|pp=20–21}} | |||
| In the 1920s, Fascist Italy pursued an aggressive foreign policy that included an attack on the Greek island of ], aims to expand Italian territory in the ], plans to wage war against ] and ], attempts to bring Yugoslavia into civil war by supporting Croat and Macedonian separatists to legitimize Italian intervention, and making ] a '']'' ] of Italy, which was achieved through diplomatic means by 1927.<ref>Aristotle A. Kallis. Fascist ideology: territory and expansionism in Italy and Germany, 1922–1945. London, England, UK: Routledge, 2000. p. 132.</ref> In response to revolt in the Italian colony of ], Fascist Italy abandoned previous liberal-era colonial policy of cooperation with local leaders. Instead, claiming that Italians were a superior race to African races and thereby had the right to colonize the "inferior" Africans, it sought to settle 10 to 15 million Italians in Libya.<ref name=aaa134>Ali Abdullatif Ahmida. ''The making of modern Libya: state formation, colonization, and resistance, 1830–1922''. Albany, New York, USA: State University of New York Press, 1994. pp. 134–135.</ref> This resulted in an aggressive military campaign against natives in Libya, including mass killings, the use of ]s, and the forced starvation of thousands of people.<ref name=aaa134/> | |||
| ===World War I and its aftermath (1914–1929)=== | |||
| The March on Rome brought Fascism international attention. One early admirer of the Italian Fascists was ], who, less than a month after the March, had begun to model himself and the ] upon Mussolini and the Fascists.<ref>Ian Kershaw. Hitler, 1889–1936: hubris. New York, New York, USA; London, England, UK: W. W. Norton & Company, 2000. p. 182.</ref> The Nazis, led by Hitler and the German war hero ], attempted a "March on Berlin" modeled upon the March on Rome, which resulted in the failed ] in ] in November 1923, where the Nazis briefly captured ]n Minister President ] and announced the creation of a new German government to be led by a ] of von Kahr, Hitler, and Ludendorff.<ref>David Jablonsky. ''The Nazi Party in dissolution: Hitler and the Verbotzeit, 1923–1925''. London, England, UK; Totowa, New Jersey, USA: Frank Cass and Company Ltd., 1989. pp. 20–26, 30</ref> The Beer Hall Putsch was crushed by Bavarian police, and Hitler and other leading Nazis were arrested and detained until 1925. Another early admirer of Italian Fascism was ], leader of the ] (known by its acronym MOVE) and a self-defined "national socialist" who in 1919 spoke of the need for major changes in property and in 1923 stated the need of a "march on Budapest".<ref name=sgp132>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital Printing Edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. p. 132</ref> Amid a political crisis in Spain involving increased strike activity and rising support for ], Spanish army commander ] engaged in a successful coup against the Spanish government in 1923 and installed himself as a dictator as head of a conservative military ] that dismantled the established party system of government.<ref>Dylan J. Riley. ''The Civic Foundations of Fascism in Europe: Italy, Spain, and Romania, 1870–1945''. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2010. p. 87</ref> Upon achieving power, Primo de Rivera sought to resolve the economic crisis by presenting himself as a compromise arbitrator figure between workers and bosses, and his regime created a corporatist economic system based on the Italian Fascist model.<ref>Dylan J. Riley. ''The Civic Foundations of Fascism in Europe: Italy, Spain, and Romania, 1870–1945''. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2010. pp. 87, 90</ref> | |||
| ] (here in 1917 as a soldier in ]), who in 1914 founded and led the {{lang|it|]}} to promote the Italian intervention in the war as a ] action to liberate Italian-claimed lands from Austria-Hungary]] | |||
| At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, the Italian political left became severely split over its position on the war. The ] (PSI) opposed the war but a number of Italian revolutionary syndicalists supported war against Germany and Austria-Hungary on the grounds that their reactionary regimes had to be defeated to ensure the success of socialism.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=175}} Angelo Oliviero Olivetti formed a pro-interventionist '']'' called the ] in October 1914.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=175}} Benito Mussolini upon being expelled from his position as chief editor of the PSI's newspaper {{lang|it|]}} for his anti-German stance, joined the interventionist cause in a separate ''fascio''.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=214}} The term "fascism" was first used in 1915 by members of Mussolini's movement, the Fasces of Revolutionary Action.{{sfnp|O'Brien|2014|p=52}} | |||
| The first meeting of the Fasces of Revolutionary Action was held on 24 January 1915{{sfnp|O'Brien|2014|p=41}} when Mussolini declared that it was necessary for Europe to resolve its national problems—including national borders—of Italy and elsewhere "for the ideals of justice and liberty for which oppressed peoples must acquire the right to belong to those national communities from which they descended."{{sfnp|O'Brien|2014|p=41}} Attempts to hold mass meetings were ineffective and the organization was regularly harassed by government authorities and socialists.{{sfnp|Gregor|1979|pp=195–196}} | |||
| ===International surge of fascism and World War II (1929–1945)=== | |||
| The events of the ] resulted in an international surge of fascism and the creation of multiple fascist regimes and regimes that adopted fascist policies. The most important new fascist regime was ], under the leadership of Adolf Hitler. With the rise of Hitler and the Nazis to power in 1933, ] was dissolved in Germany, and the Nazis mobilized the country for war, with expansionist territorial aims against multiple countries. In the 1930s the Nazis implemented racial laws that deliberately discriminated against, disenfranchised, and persecuted Jews, homosexuals and other racial and minority groups. Hungarian fascist ] rose to power as Prime Minister of Hungary in 1932 and visited Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany to consolidate good relations with the two regimes. He attempted to entrench his ] throughout the country; created an eight-hour work day, a forty-eight hour work week in industry, and sought to entrench a corporatist economy; and pursued irredentist claims on Hungary's neighbors.<ref>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital Printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. p. 270.</ref> The fascist ] movement in ] soared in political support after 1933, gaining representation in the Romanian government, and an Iron Guard member assassinated Romanian prime minister ].<ref>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital Printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. pp. 282–288.</ref> A variety of para-fascist governments that borrowed elements from fascism were formed during the Great Depression, including those of ], ], ], and ].<ref>Stanley G. Payne. ''A history of fascism, 1914–1945''. Digital Printing edition. Oxon, England, UK: Routledge, 2005. p. 145.</ref> | |||
| ]'s concept of the "]" identified the outbreak of war as a moment that forged nationalistic German solidarity.]] | |||
| Fascism also expanded influence outside of Europe, especially in East Asia, the Middle East, and South America. In ], ]'s ''Kai-tsu p'ai'' (Reorganization) faction of the ] (Nationalist Party of China) supported ] in the late 1930s.<ref>Dongyoun Hwang. ''Wang Jingwei, The National Government, and the Problem of Collaboration.'' Ph.D. Dissertation, Duke University. UMI Dissertation Services, Ann Arbor Michigain. 2000, 118.</ref><ref>Larsen, Stein Ugelvik (ed.). ''Fascism Outside of Europe''. New York: Columbia University Press, 2001. ISBN 0880339888. P. 255.</ref> In ], the ], a Nazi movement was formed by ]. The ] led by ], claimed as many as 200,000 members although following coup attempts it faced a crackdown from the ] of ] in 1937.<ref>Griffin, ''The Nature of Fascism'', pp. 150-2</ref> The ] of ] was a ] movement that supported Nazism and exercised influence in Iraqi government through cabinet minister ] who formed a youth paramilitary movement.<ref>I. Gershoni, James P. Jankowski. ''Confronting fascism in Egypt: dictatorship versus democracy in the 1930s''. Stanford, California, USA: Stanford University Press, 2010. Pp. 273.</ref> in the 1930s The ] gained seats in Chile's parliament and attempted a coup d'état that resulted in the ] of 1938.<ref>Stanley G. Payne, ''A History of Fascism: 1914-1945'', London: Routledge, 2001, p. 341-342.</ref> Peruvian president ] founded the ] in 1931 as the state party for his dictatorship. Upon the Revolutionary Union being taken over by ] who sought to mobilise mass support for the group's ] in a manner akin to fascism. He even started a Blackshirts paramilitary arm as a copy of the ], although the Union lost heavily in the 1936 elections and faded into obscurity.<ref>], ''A History of Fascism'', 2001, p. 343</ref> | |||
| Similar political ideas arose in Germany after the outbreak of the war. German sociologist ] spoke of the rise of a "National Socialism" in Germany within what he termed the "ideas of 1914" that were a declaration of war against the "ideas of 1789" (the French Revolution).{{sfnp|Kitchen|2006|p=205}} According to Plenge, the "ideas of 1789"—such as the rights of man, democracy, individualism and liberalism—were being rejected in favor of "the ideas of 1914" that included "German values" of duty, discipline, law and order.{{sfnp|Kitchen|2006|p=205}} Plenge believed that racial solidarity ({{lang|de|Volksgemeinschaft}}) would replace class division and that "racial comrades" would unite to create a socialist society in the struggle of "proletarian" Germany against "capitalist" Britain.{{sfnp|Kitchen|2006|p=205}} He believed that the ] manifested itself in the concept of the People's League of National Socialism.{{sfnp|Hüppauf|1997|p=92}} This National Socialism was a form of state socialism that rejected the "idea of boundless freedom" and promoted an economy that would serve the whole of Germany under the leadership of the state.{{sfnp|Hüppauf|1997|p=92}} This National Socialism was opposed to capitalism because of the components that were against "the national interest" of Germany but insisted that National Socialism would strive for greater efficiency in the economy.{{sfnp|Hüppauf|1997|p=92}} Plenge advocated an authoritarian rational ruling elite to develop National Socialism through a hierarchical ] state.{{sfnp|Rohkrämer|2007|p=130}} | |||
| ====Impact of World War I==== | |||
| During the Great Depression, Mussolini promoted active state intervention in the economy. He denounced the contemporary "]" that he claimed began in 1914 as a failure due to its alleged ], support for unlimited ] and intention to create the "standardization of humankind".<ref name=gb2000>Günter Berghaus. ''Fascism and theatre: comparative studies on the aesthetics and politics of performance''. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California, USA: University of California Press, 2000. 136–137</ref> However, Mussolini claimed that the industrial developments of earlier "]" were valuable and continued to support private property as long as it was productive.<ref name=gb2000/> With the onset of the Great Depression, Fascist Italy began large-scale state intervention into the economy, establishing the ] (''Istituto per la Ricostruzione Industriale'', IRI), a giant state-owned firm and holding company that provided state funding to failing private enterprises.<ref name=cb189>Cyprian Blamires, Paul Jackson. ''World fascism: a historical encyclopedia, Volume 1''. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CLIO, 2006. p. 189.</ref> The IRI was made a permanent institution in Fascist Italy in 1937, pursued Fascist policies to create national ], and had the power to take over private firms to maximize war production.<ref name=cb189/> Nazi Germany similarly pursued an economic agenda with the aims of autarky and rearmament and imposed ] policies, including forcing the German steel industry to use lower-quality German iron ore rather than superior-quality imported iron.<ref>Cyprian Blamires, Paul Jackson. ''World fascism: a historical encyclopedia, Volume 1''. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CLIO, 2006. p. 190.</ref> | |||
| ]}} corps, shown here in 1918 holding daggers, a symbol of their group. They were formed in 1917 as groups of soldiers trained for dangerous missions, characterized by a refusal to surrender and a willingness to fight to the death. Their black uniforms inspired those of the Italian Fascist movement.]] | |||
| Fascists viewed World War I as bringing revolutionary changes in the nature of war, society, the state and technology, as the advent of ] and mass mobilization had broken down the distinction between civilian and combatant, as civilians had become a critical part in economic production for the war effort and thus arose a "military citizenship" in which all citizens were involved to the military in some manner during the war.{{sfnmp|Blamires|2006|1pp=140–141, 670|Mann|2004|2p=65}} World War I had resulted in the rise of a powerful state capable of mobilizing millions of people to serve on the front lines or provide economic production and logistics to support those on the front lines, as well as having unprecedented authority to intervene in the lives of citizens.{{sfnmp|Blamires|2006|1pp=140–141, 670|Mann|2004|2p=65}} Fascists viewed technological developments of weaponry and the state's total mobilization of its population in the war as symbolizing the beginning of a new era fusing state power with ], technology and particularly the mobilizing myth that they contended had triumphed over the myth of progress and the era of liberalism.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|pp=140–141, 670}} | |||
| ==Ideological origins== | |||
| {{main|Ideological origins of Fascism}} | |||
| Although fascism is considered to have first emerged in France in the 1880s, its influences have been considered to go back as far as ]. ], ], and ] have also been considered as influential, as well as contemporary ideas such as the ] of ], the ] of | |||
| ], the nationalist and authoritarian philosophy of ] and the conservatism and social Darwinism of ]. | |||
| ====Impact of the Bolshevik Revolution==== | |||
| ==Core tenets== | |||
| {{see also|The Struggle Against Fascism in Germany}} | |||
| ===Nationalism=== | |||
| ] during his final years in exile<ref>{{cite book |last1=Carr |first1=Edward Hallett |title=The twilight of Comintern 1930–1935 |date=1986 |publisher=Macmillan |isbn=978-0-333-40455-3 |page=433 |quote=Trotsky...maintained during the period of Hitler's rise to power so persistent and, for the most part, so prescient a commentary on the course of events in Germany as to deserve record.}}</ref> and advocated for the tactic of a ] against fascist parties.<ref>{{cite book |last1=Ticktin |first1=Hillel |title=Trotsky's political economy of capitalism |editor1-last=Brotherstone |editor1-first=Terence |editor2-last=Dukes |editor2-first=Paul |date=1992 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7486-0317-6 |page=227}}</ref>]] | |||
| Fascists saw the struggle of nation and race as fundamental in society, in opposition to communism's perception of class struggle.<ref>Ebenstein, William. 1964. ''Today's Isms: Communism, Fascism, Capitalism, and Socialism.'' Prentice Hall (original from the University of Michigan). p. 178. </ref> The fascist view of a nation is of a single organic entity which binds people together by their ancestry and is a natural unifying force of people.<ref>Oliver Zimmer, Nationalism in Europe, 1890–1940 (London, Palgrave, 2003), chapter 4, pp. 80–107.</ref> Fascism seeks to solve economic, political, and social problems by achieving a ] national rebirth, exalting the ] or ] above all else, and promoting cults of unity, strength and purity.<ref name="anatomnyfascismo">{{cite book |last=Paxton |first=Robert |title=The Anatomy of Fascism |publisher=Vintage Books |isbn=1400040949}}</ref><ref name="natureoffascismo">{{cite book |last=Griffin |first=Roger |title=The Nature of Fascism |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |isbn=0312071329 |year=1991}}</ref><ref name="walterlaq">{{cite book |last=Laqueuer |first=Walter |title=Fascism: Past, Present, Future |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=019511793X |year=1997|page=223}}</ref><ref name="britannicafasc">{{cite news |url=http://search.eb.com/eb/article-9117286 |publisher=] |title=Fascism |date=8 January 2008}}</ref><ref name="Passmore">{{cite book |last=Passmore |first=Kevin |title=Fascism: A Very Short Introduction |publisher=Oxford University Press |url=http://books.google.com/?id=EQG0AAAACAAJ&dq=A+Very |isbn=0192801554 |year=2002}}</ref> Benito Mussolini stated in 1922, "For us the nation is not just territory but something spiritual... A nation is great when it translates into reality the force of its spirit."<ref>Griffen, Roger (ed). ''Fascism''. Oxford University Press, 1995. ISBN 0192892495. p. 44.</ref> | |||
| The ] of 1917, in which ] communists led by ] seized power in Russia, greatly influenced the development of fascism.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|pp=95–96}} ] would later formulate a theory of fascism based on a dialectical interpretation of events to analyze the manifestation of ] and the early emergence of Nazi Germany from 1930 to 1933.{{sfn|Wistrich|1976}} In 1917, Mussolini, as leader of the ], praised the October Revolution, but later he became unimpressed with Lenin, regarding him as merely a new version of ].{{sfnp|Neville|2004|p=36}} After World War I, fascists commonly campaigned on ] agendas.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|pp=95–96}} | |||
| Liberal opponents of both fascism and the Bolsheviks argue that there are various similarities between the two, including that they believed in the necessity of a vanguard leadership, showed contempt for bourgeois values, and had totalitarian ambitions.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|pp=95–96}} In practice, both have commonly emphasized revolutionary action, proletarian nation theories, one-party states, and party-armies;{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|pp=95–96}} however, both draw clear distinctions from each other both in aims and tactics, with the Bolsheviks emphasizing the need for an organized ] (]) and an ], internationalist vision for society based on ], while fascists emphasized ] and open hostility towards democracy, envisioning a hierarchical ] as essential to their aims. With the antagonism between ] Marxists and pro-] fascists complete by the end of the war, the two sides became irreconcilable. The fascists presented themselves as ] and as especially opposed to the ].{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=178}} In 1919, Mussolini consolidated control over the fascist movement, known as {{lang|it|]}}, with the founding of the '']''.{{sfnp|Encyclopedia Britannica ''The fascist era''}} | |||
| According to ], an Irish national ], "before everything we must give a national lead to our people...The first essential is national unity. We can only have that when the Corporative system is accepted".<ref>Griffen, Roger (ed). ''Fascism''. Oxford University Press, 1995. ISBN 0192892495. p. 183.</ref> | |||
| ====Fascist Manifesto and Charter of Carnaro==== | |||
| ] described the Nazis as being affiliated with authoritarian nationalism: | |||
| [[File:Promised Borders of the Tready of London.png|thumb|Territories promised to Italy by the | |||
| ], i.e. ], the ] and ] (tan), and the ] area (green). Dalmatia, after the WWI, however, was not assigned to Italy but to ]]] | |||
| In 1919, ] and ] movement leader ] created "]".{{sfnp|Elazar|2001|p=73}} The Fascist Manifesto was presented on 6 June 1919 in the fascist newspaper {{lang|it|]}} and supported the creation of ], including ] (the latter being realized only partly in late 1925, with all opposition parties banned or disbanded);{{sfnp|Passmore|2003|p=116}} ] on a regional basis; government representation through a ] system of "National Councils" of experts, selected from professionals and tradespeople, elected to represent and hold legislative power over their respective areas, including labour, industry, transportation, public health, and communications, among others; and abolition of the ].{{sfnp|Borsella|Caso|2007|p=69}} The Fascist Manifesto supported the creation of an ] for all workers, a ], worker representation in industrial management, equal confidence in labour unions as in industrial executives and public servants, reorganization of the transportation sector, revision of the draft law on invalidity insurance, reduction of the retirement age from 65 to 55, a strong ] on capital, confiscation of the property of religious institutions and abolishment of bishoprics, and revision of military contracts to allow the government to seize 85% of profits.{{sfnp|Borsella|Caso|2007|pp=69–70}} It also called for the fulfillment of expansionist aims in the Balkans and other parts of the Mediterranean, the creation of a short-service national militia to serve defensive duties, ] of the armaments industry, and a foreign policy designed to be peaceful but also competitive.{{sfnp|Borsella|Caso|2007|p=70}} | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| It enables us to see at once why democracy and Bolshevism, which in the eyes of the world are irrevocably opposed to one another, meet again and again on common ground in their joint hatred of and attacks on authoritarian nationalist concepts of State and State systems. For the authoritarian nationalist conception of the State represents something essentially new. In it the French Revolution is superseded.<ref>"Goebbels on National-Socialism, Bolshevism and Democracy, ''Documents on International Affairs'', vol. II, 1938, pp. 17–19. Accessed from the Jewish Virtual Library on February 5, 2009. Joseph Goebbels describes the Nazis as being allied with countries which had "authoritarian nationalist" ideology and conception of the state.</ref> | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| ] cheer the arrival of ] and his blackshirt-wearing nationalist raiders, as D'Annunzio and fascist ] developed the quasi-fascist ] (a city-state in Fiume) from 1919 to 1920 and whose actions inspired the Italian fascist movement. In September 1919 Fiume had 22,488 (62% of the population) Italians in a total population of 35,839 inhabitants]] | |||
| ], leader of the Brazilian ] party, emphasized the role of the nation: | |||
| The next events that influenced the fascists in Italy were the raid of ] by Italian nationalist ] and the founding of the ] in 1920.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=186}} D'Annunzio and De Ambris designed the Charter, which advocated national-syndicalist corporatist ] alongside D'Annunzio's political views.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=187}} Many fascists saw the Charter of Carnaro as an ideal constitution for a fascist Italy.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=189}} This behaviour of aggression towards Yugoslavia and ] was pursued by Italian fascists with their persecution of South Slavs—especially Slovenes and Croats. | |||
| ====From populism to conservative accommodations==== | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| In 1920, militant strike activity by industrial workers reached its peak in Italy and 1919 and 1920 were known as the "Red Year" ({{lang|it|]}}).{{sfnp|Borsella|Caso|2007|p=73}} Mussolini and the fascists took advantage of the situation by allying with industrial businesses and attacking workers and peasants in the name of preserving order and internal peace in Italy.{{sfnp|Borsella|Caso|2007|p=75}} | |||
| The best governments in the world cannot succeed in pulling a country out of the quagmire, out of apathy, if they do not express themselves as national energies...Strong governments cannot result either from conspiracies or from military coups, just as they cannot come out of the machinations of parties or the Machiavellian game of political lobbying. They can only be born from the actual roots of the Nation.<ref>Griffen, Roger (ed). ''Fascism''. Oxford University Press, 1995. ISBN 0192892495. p. 236.</ref> | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| Fascists identified their primary opponents as the majority of socialists on the left who had opposed intervention in World War I.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=189}} The fascists and the Italian political right held common ground: both held Marxism in contempt, discounted class consciousness and believed in the rule of elites.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=193}} The fascists assisted the anti-socialist campaign by allying with the other parties and the conservative right in a mutual effort to destroy the Italian Socialist Party and labour organizations committed to class identity above national identity.{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=193}} | |||
| ====Foreign policy==== | |||
| Italian fascists described expansionist ] as a necessity. The 1932 ''Italian Encyclopedia'' stated: "For Fascism, the growth of empire, that is to say the expansion of the nation, is an essential manifestation of vitality, and its opposite a sign of decadence."<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.fordham.edu/halsall/mod/mussolini-fascism.html |title=Fordham.edu |publisher=Fordham.edu |accessdate=2010-06-04}}</ref> Similarly, the Nazis promoted territorial expansionism to provide "living space" to the German nation.<ref>Kershaw, Ian. 2000. Hitler, 1889–1936: Hubris. W. W. Norton & Company. p. 442. </ref> Fascists opposed ] and believed that a nation must have a warrior mentality.<ref name=psg485>Payne, Stanley G. ''A History of Fascism, 1914–1945.'' Routledge, 1996. pp. 485–486.</ref> Benito Mussolini spoke of war idealistically as a source of masculine pride, and spoke negatively of pacifism: | |||
| Fascism sought to accommodate Italian conservatives by making major alterations to its political agenda—abandoning its previous populism, ] and ], adopting policies in support of ] and accepting the ] and the monarchy as institutions in Italy.{{sfnp|De Grand|2000|p=145}} To appeal to Italian conservatives, fascism adopted policies such as promoting family values, including policies designed to reduce the number of women in the workforce—limiting the woman's role to that of a mother. The fascists banned literature on birth control and increased penalties for abortion in 1926, declaring both crimes against the state.{{sfnp|Blinkhorn|2003|p=14}} | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| War alone brings up to their highest tension all human energies and puts the stamp of nobility upon the peoples who have the courage to meet it. Fascism carries this anti-pacifist struggle into the lives of individuals. It is education for combat... war is to man what maternity is to the woman. I do not believe in perpetual peace; not only do I not believe in it but I find it depressing and a negation of all the fundamental virtues of a man.<ref>Bollas, Christopher. 1993. Being a Character: Psychoanalysis and Self-Experience. Routledge. ISBN 9780415088152. p. 205. Speaks of Italian Fascism supporting war and opposing pacifism.</ref></blockquote> | |||
| Although fascism adopted a number of anti-modern positions designed to appeal to people upset with the new trends in sexuality and women's rights—especially those with a ] point of view—the fascists sought to maintain fascism's revolutionary character, with Angelo Oliviero Olivetti saying: "Fascism would like to be conservative, but it will by being revolutionary."{{sfnp|Sternhell|Sznajder|Ashéri|1994|p=190}} The Fascists supported revolutionary action and committed to secure law and order to appeal to both conservatives and syndicalists.{{sfnp|Blinkhorn|2003|p=22}} | |||
| ===Authoritarianism=== | |||
| Many fascist movements support the creation of a ] state. Mussolini's '']'' states, "The Fascist conception of the State is all-embracing; outside of it no human or spiritual values can exist, much less have value. Thus understood, Fascism is totalitarian, and the Fascist State—a synthesis and a unit inclusive of all values—interprets, develops, and potentiates the whole life of a people."<ref>Mussolini, Benito. 1935. Fascism: Doctrine and Institutions. Rome: Ardita Publishers. p 14.</ref> Some have argued that, in spite of Italian Fascism's attempt at totalitarianism, it became an authoritarian cult of personality around Mussolini.<ref>Linz, Juan José. 2000. ''Totalitarian and Authoritarian Regimes: with a major new introduction''. Lynne Rienner Publishers. p. 7. </ref> | |||
| Prior to fascism's accommodations to the political right, fascism was a small, urban, northern Italian movement that had about a thousand members.{{sfnp|Borsella|Caso|2007|p=72}} After Fascism's accommodation of the political right, the fascist movement's membership soared to approximately 250,000 by 1921.{{sfnp|Borsella|Caso|2007|p=76}} A 2020 article by ], Giuseppe De Feo, Giacomo De Luca, and Gianluca Russo in the ], exploring the link between the threat of ] and Mussolini's rise to power, found "a strong association between the Red Scare in Italy and the subsequent local support for the Fascist Party in the early 1920s." According to the authors, it was local elites and large landowners who played an important role in boosting Fascist Party activity and support, which did not come from socialists' core supporters but from ] voters, as they viewed traditional centre-right parties as ineffective in stopping socialism and turned to the Fascists. In 2003, historian Adrian Lyttelton wrote: "The expansion of Fascism in the rural areas was stimulated and directed by the reaction of the farmers and landowners against the peasant leagues of both Socialists and Catholics."{{sfnp|Acemoğlu|De Feo|De Luca|Russo|2020}} | |||
| In ''The Legal Basis of the Total State'', Nazi political theorist ] described the Nazi intention to form a "strong state which guarantees a totality of political unity transcending all diversity" in order to avoid a "disastrous pluralism tearing the German people apart"<ref>Griffen, Roger (ed). 1995. "The Legal Basis of the Total State" – by Carl Schmitt. ''Fascism''. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 72.</ref> | |||
| ====Fascist violence==== | |||
| Japanese fascist ] advocated that Japan follow the Italian and German models, which were "a form of more democratic government going beyond democracy" which itself had "lost its spirit and decayed into a mechanism which insists only on numerical superiority without considering the essence of human beings."<ref>Griffen, Roger (ed). 1995. "The Need for a Totalitarian Japan" – by Nakano Seigo. ''Fascism''. New York: Oxford University Press. p. 239.</ref> | |||
| Beginning in 1922, fascist paramilitaries escalated their strategy from one of attacking socialist offices and the homes of socialist leadership figures, to one of violent occupation of cities. The fascists met little serious resistance from authorities and proceeded to take over several northern Italian cities.{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=87}} The fascists attacked the headquarters of socialist and Catholic labour unions in Cremona and imposed forced Italianization upon the German-speaking population of ].{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=87}}{{sfnp|Ferrandi|Obermair|2023|p=127–167}} After seizing these cities, the fascists made plans to take ].{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=87}} | |||
| ] with three of the four ] during the ] (from left to right: unknown, ], Mussolini, ] and ])]] | |||
| A key authoritarian element of fascism is its endorsement of a prime national leader, who is often known simply as the "Leader" or a similar title, such as '']'' in Italian, '']'' in German, '']'' in Spanish, '']'' in Croatia, or '']'' in Romanian. Fascist leaders who ruled countries were not always heads of state, but were heads of government, such as Benito Mussolini, who held power under the King of Italy, ]. | |||
| On 24 October 1922, the Fascist Party held its annual congress in ], where Mussolini ordered Blackshirts to take control of public buildings and trains and to converge on three points around Rome.{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=87}} The Fascists managed to seize control of several post offices and trains in northern Italy while the Italian government, led by a left-wing coalition, was internally divided and unable to respond to the Fascist advances.{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=88}} King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy perceived the risk of bloodshed in Rome in response to attempting to disperse the Fascists to be too high.{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=90}} Victor Emmanuel III decided to appoint Mussolini as ] and Mussolini arrived in Rome on 30 October to accept the appointment.{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=90}} Fascist propaganda aggrandized this event, known as "]", as a "seizure" of power because of Fascists' heroic exploits.{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=87}} | |||
| ===Social Darwinism=== | |||
| Fascist movements have commonly held ] views of nations, races, and societies.<ref name=psg485/> They argue that nations and races must purge themselves of socially and biologically weak or ] people, while simultaneously promoting the creation of strong people, in order to survive in a world defined by perpetual national and racial conflict.<ref>Griffen, Roger (ed.). Fascism. Oxford University Press, 1995. p. 59.</ref> | |||
| ===Fascist Italy=== | |||
| Italian Fascist philosopher ] in '']'' promoted the concept of conflict as an act of progress, stating that "mankind only progresses through division, and progress is achieved through the clash and victory of one side over another".<ref name=hm285>Hawkins, Mike. ''Social Darwinism in European and American Thought, 1860–1945: Nature as Model and Nature as Threat''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997. p. 285.</ref> Italian Fascist ] claimed that conflict was inevitable: | |||
| Historian Stanley G. Payne says: | |||
| <blockquote> primarily political dictatorship. ... The Fascist Party itself had become almost completely bureaucratized and subservient to, not dominant over, the state itself. Big business, industry, and finance retained extensive autonomy, particularly in the early years. The armed forces also enjoyed considerable autonomy. ... The Fascist militia was placed under military control. ... The judicial system was left largely intact and relatively autonomous as well. The police continued to be directed by state officials and were not taken over by party leaders ... nor was a major new police elite created. ... There was never any question of bringing the Church under overall subservience. ... Sizable sectors of Italian cultural life retained extensive autonomy, and no major state propaganda-and-culture ministry existed. ... The Mussolini regime was neither especially sanguinary nor particularly repressive.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=122}}</blockquote> | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| Conflict is in fact the basic law of life in all social organisms, as it is of all biological ones; societies are formed, gain strength, and move forwards through conflict; the healthiest and most vital of them assert themselves against the weakest and less well adapted through conflict; the natural evolution of nations and races takes place through conflict.<ref name=hm285/></blockquote> | |||
| ====Mussolini in power==== | |||
| In Germany, the Nazis used social Darwinism to promote their ] concept of the German nation as part of the ] and the need for the Aryan race to be victorious in what the Nazis believed was a ] — an ongoing competition and conflict between races.<ref>Hawkins, Mike. ''Social Darwinism in European and American Thought, 1860–1945: Nature as Model and Nature as Threat''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997. pp. 282, 284.</ref> They attempted to strengthen the Aryan race in Germany by killing those they regarded as weak. To this end, ] was introduced in the late 1930s and organized the killing of roughly 275,000 handicapped and elderly German and non-German civilians using carbon monoxide gas.<ref>Hunt, Lynn, Thomas R. Martin, Barbara H. Rosenwein, R. Po-chia Hsia, and Bonnie G. Smith. The Making of the West: Peoples and Cultures. 2nd ed. Vol. C. Boston: Bedford St. Martins, 2005. p. 1064.</ref> | |||
| ] and ] were later claimed. | |||
| {{legend|#01ec95|], ] and ]}} | |||
| ===Social interventionism=== | |||
| {{legend|#f41820|]}} | |||
| Generally, fascist movements endorsed ] dedicated to influencing society to promote the state's interests.{{Citation needed|date=January 2009}} According to G.V. Rimlinger, one cannot speak of “fascist social policy” as a single concept with logical and internally consistent ideas and common identifiable goals.<ref>Rimlinger, G.V. ‘’Social Policy Under German Fascism’’ in by Martin Rein, Gosta Esping-Andersen, and Lee Rainwater, p. 61, M.E. Sharpe, 1987.</ref> | |||
| {{legend|#bc85be|]}}]] | |||
| Upon being appointed Prime Minister of Italy, Mussolini had to form a coalition government because the fascists did not have control over the Italian parliament.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=110}} Mussolini's coalition government initially pursued ] policies under the direction of liberal finance minister ], a member of the Center Party, including balancing the budget through deep cuts to the civil service.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=110}} Initially, little drastic change in government policy had occurred and repressive police actions were limited.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=110}} | |||
| The fascists began their attempt to entrench fascism in Italy with the ], which guaranteed a plurality of the seats in parliament to any party or coalition list in an election that received 25% or more of the vote.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=113}} Through considerable fascist violence and intimidation, the list won a majority of the vote, allowing many seats to go to the fascists.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=113}} In the aftermath of the election, a crisis and political scandal erupted after Socialist Party deputy ] was kidnapped and murdered by a Fascist.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=113}} The liberals and the leftist minority in parliament walked out in protest in what became known as the ].{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=114}} On 3 January 1925, Mussolini addressed the Fascist-dominated Italian parliament and declared that he was personally responsible for what happened, but insisted that he had done nothing wrong. Mussolini proclaimed himself dictator of Italy, assuming full responsibility over the government and announcing the dismissal of parliament.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=114}} From 1925 to 1929, fascism steadily became entrenched in power: opposition deputies were denied access to parliament, censorship was introduced and a December 1925 decree made Mussolini solely responsible to the King.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=115}} | |||
| Fascists spoke of creating a "new man" and a "new civilization" as part of their intention to transform society.<ref>Gentile, Emilio. The Struggle for Modernity: Nationalism, Futurism, and Fascism. p. 86. </ref> Mussolini promised a “social revolution” for “remaking” the Italian people.<ref>Knight, Patricia , p. 72, Routledge, 2003.</ref> ] promised to purge Germany of non-Aryan influences on society and to create a pure Aryan race through ]. | |||
| ==== |
====Catholic Church==== | ||
| In 1929, the fascist regime briefly gained what was in effect a blessing of the Catholic Church after the regime signed a concordat with the Church, known as the ], which gave the papacy state sovereignty and financial compensation for the seizure of Church lands by the liberal state in the 19th century, but within two years the Church had renounced fascism in the Encyclical '']'' as a "pagan idolatry of the state" which teaches "hatred, violence and irreverence".{{sfnp|Payne|1995|pp=119–120}} Not long after signing the agreement, by Mussolini's own confession, the Church had threatened to have him "excommunicated", in part because of his intractable nature, but also because he had "confiscated more issues of Catholic newspapers in the next three months than in the previous seven years."{{sfnp|Mack Smith|1983|p=162}} By the late 1930s, Mussolini became more vocal in his anti-clerical rhetoric, repeatedly denouncing the Catholic Church and discussing ways to depose the pope. He took the position that the "papacy was a malignant tumor in the body of Italy and must 'be rooted out once and for all,' because there was no room in Rome for both the Pope and himself."{{sfnp|Mack Smith|1983|pp=222–223}} In her 1974 book, Mussolini's widow Rachele stated that her husband had always been an atheist until near the end of his life, writing that her husband was "basically irreligious until the later years of his life."{{sfnp|Mussolini|1977|p=131}} | |||
| Fascist states pursued policies of social ] through ] in education and the media and regulation of the production of educational and media materials.<ref>Pauley, Bruce F. 2003. Hitler, Stalin, and Mussolini: Totalitarianism in the Twentieth Century Italy. Wheeling: Harlan Davidson, Inc. Pauley, p. 117.</ref><ref>Payne, Stanley G. 1996. ''A History of Fascism, 1914–1945''. Routledge </ref> Education was designed to glorify the fascist movement and inform students of its historical and political importance to the nation. It attempted to purge ideas that were not consistent with the beliefs of the fascist movement and to teach students to be obedient to the state.<ref>Pauley, 2003. 117–119.</ref> Therefore, fascism tends to be ].<ref>Griffin, Roger and Matthew Feldma , 2004 Taylor and Francis</ref> The Nazis, in particular, despised intellectuals and university professors. Hitler declared them unreliable, useless, and even dangerous.<ref>Evans, p. 299</ref> He said: "When I take a look at the intellectual classes we have – unfortunately, I suppose, they are necessary; otherwise one could one day, I don't know, exterminate them or something – but unfortunately they're necessary."<ref>Domarus, ''Hitler'' II. 251–252</ref> | |||
| The Nazis in Germany employed similar anti-clerical policies. The Gestapo confiscated hundreds of monasteries in Austria and Germany, evicted clergymen and laymen alike and often replaced crosses with swastikas.{{sfnp|von Lang|1979|p=221}} Referring to the swastika as "the Devil's Cross", church leaders found their youth organizations banned, their meetings limited and various Catholic periodicals censored or banned. Government officials eventually found it necessary to place "Nazis into editorial positions in the Catholic press."{{sfnp|Evans|2005|p=239}} Up to 2,720 clerics, mostly Catholics, were arrested by the Gestapo and imprisoned inside of Germany's Dachau concentration camp, resulting in over 1,000 deaths.{{sfnp|Berben|1975|pp=276–277}} | |||
| ====Abortion, eugenics and euthanasia==== | |||
| The Fascist government in Italy banned literature on ] and increased penalties for abortion in 1926, declaring both crimes against the state.<ref>De Grazia, Victoria. 2002. ''How Fascism Ruled Women: Italy, 1922–1945''. ]. p. 55.</ref> The Nazis decriminalized abortion in cases where fetuses had hereditary defects or were of a race the government disapproved of, while the abortion of healthy "pure" German, "]" fetuses remained strictly forbidden.<ref>Henry Friedlander, ''The Origins of Nazi Genocide: From Euthanasia to the Final Solution'' (Chapel Hill, N.C.: University of Northern Carolina Press, 1995): 30.</ref> For non-Aryans, abortion was often compelled. Their ] program also stemmed from the "progressive biomedical model" of ].<ref>McLaren, Angus, Twentieth-Century Sexuality p. 139 Blackwell Publishing 1999</ref> | |||
| ====Corporatist economic system==== | |||
| In 1935 Nazi Germany expanded the legality of ] by amending ], to promote abortion for women with hereditary disorders.<ref>{{cite book |last=Friedlander |first=Henry |title=The origins of Nazi genocide: from euthanasia to the final solution |publisher=] |location=] |year=1995 |page= |isbn=0-8078-4675-9 |oclc=60191622 |accessdate=2008-12-10}}</ref> The law allowed abortion if a woman gave her permission and the fetus was not yet viable,<ref>{{cite book |last=Proctor |first=Robert E. |title=Racial Hygiene: Medicine Under the Nazis |publisher=] |location=] |year=1989 |page= |isbn=0-674-74578-7 |oclc=20760638 |quote=This emendation allowed abortion only if the woman granted permission, and only if the fetus was not old enough to survive outside the womb. It is unclear if either of these qualifications was enforced.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |first=Margaret |last=Arnot |coauthors=Cornelie Usborne |title=Gender and Crime in Modern Europe |publisher=] |location=] |year=1999 |page= |isbn=1-85728-745-2 |oclc=249726924 |accessdate=2008-12-10}}</ref> and for purposes of so-called ].<ref>{{cite book |last=Proctor |first=Robert E. |title=Racial Hygiene: Medicine Under the Nazis |publisher=] |location=] |year=1989 |pages=122–123 |isbn=0-674-74578-7 |oclc=20760638 |quote=Abortion, in other words, could be allowed if it was in the interest of racial hygiene... the Nazis did allow (and in some cases even required) abortions for women deemed racially inferior... On November 10, 1938, a Luneberg court declared abortion legal for Jews.}}</ref><ref>{{cite book |last=Tierney |first=Helen |title=Women's studies encyclopedia |publisher=] |location=] |year=1999 |page= |isbn=0-313-31072-6 |oclc=38504469 |accessdate=2008-12-10 |quote=In 1939, it was announced that Jewish women could seek abortions, but non-Jewish women could not.}}</ref> | |||
| The fascist regime created a corporatist economic system in 1925 with creation of ], in which the Italian employers' association ] and fascist trade unions agreed to recognize each other as the sole representatives of Italy's employers and employees, excluding non-fascist trade unions.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=150}} The Fascist regime first created a Ministry of Corporations that organized the Italian economy into 22 sectoral corporations, banned workers' strikes and lock-outs and in 1927 created the ], which established workers' rights and duties and created labour tribunals to arbitrate employer-employee disputes.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=150}} In practice, the sectoral corporations exercised little independence and were largely controlled by the regime, and the employee organizations were rarely led by employees themselves, but instead by appointed Fascist party members.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=150}} | |||
| ==== |
====Aggressive foreign policy==== | ||
| In the 1920s, Fascist Italy pursued an aggressive foreign policy that included ambitions to expand Italian territory.{{sfnp|Kallis|2000|p=132}} In response to revolt in the Italian colony of ], Fascist Italy abandoned previous liberal-era colonial policy of cooperation with local leaders. Instead, claiming that Italians were a superior race to African races and thereby had the right to colonize the "inferior" Africans, it sought to settle 10 to 15 million Italians in Libya.{{sfnp|Ahmida|1994|pp=134–135}} This resulted in an aggressive military campaign known as the ] against natives in Libya, including mass killings, the use of ]s and the forced starvation of thousands of people.{{sfnp|Ahmida|1994|pp=134–135}} Italian authorities committed ] by forcibly expelling 100,000 ] Cyrenaicans, half the population of Cyrenaica in Libya, from their settlements that was slated to be given to Italian settlers.{{sfnmp|Cardoza|2006|1p=109|2a1=Bloxham|2a2=Moses|2y=2010|2p=358}} | |||
| Fascism promoted principles of ] heroism, militarism, and discipline and rejected ] and ].<ref>Roger Griffin, The `post-fascism' of the Alleanza Nazionale: a case-study in ideological morphology, ''Journal of Political Ideologies'', Vol. 1, No. 2, 1996</ref> | |||
| ====Nazi adoption of the Italian model==== | |||
| ] stood in favour of expanding voting rights to women. In 1920, Benito Mussolini declared that "Fascists do not belong to the crowd of the vain and skeptical who undervalue women's social and political importance. Who cares about voting? You will vote!".<ref name=gg58>Gori, Gigliola. ''Italian fascism and the female body: sport, submissive women and strong mothers''. Routledge, 2004. p. 58</ref> In November 1925, women were given restricted voting rights, juxtaposed to the eliminaton of opposition parties and enabling of the Fascist government to rule with dictatorial powers. Fascist women's organizations, disgruntled at the lukewarm reforms, were then made subordinate to the secretariat of the party, headed by Fascist conservative and ] ], although gradual women's suffrage was retained.<ref name=gg58/><ref>Kevin Passmore ''Women, Gender and Fascism'', p. 16</ref> In the 1920s, the Italian Fascist government's '']'' (OND) allowed working women to attend various entertainment and recreation events, including sports that in the past had traditionally been played by men.<ref>Gori, Gigliola. ''Italian fascism and the female body: sport, submissive women and strong mothers''. Routledge, 2004. pp. 144–145.</ref> The regime was criticized by the ], which claimed that these activities were causing "masculinization" of women.<ref name=gg145>Gori, Gigliola. ''Italian fascism and the female body: sport, submissive women and strong mothers''. Routledge, 2004. p. 145.</ref> The Fascists responded to such criticism by restricting women to only being allowed to take part in "feminine" sports, forbidding them to be part of sports that were played mostly by men.<ref name=gg145/> | |||
| ] ]] | |||
| The March on Rome brought fascism international attention. One early admirer of the Italian fascists was ], who less than a month after the March had begun to model himself and the ] upon Mussolini and the Fascists.{{sfnp|Kershaw|2000|p=182}} The Nazis, led by Hitler and the German war hero ], attempted a "March on Berlin" modeled upon the March on Rome, which resulted in the failed ] in ] in November 1923.{{sfnp|Jablonsky|1989|pp=20–26, 30}} | |||
| ===International impact of the Great Depression and buildup to World War II=== | |||
| Mussolini perceived women's primary role as childbearers, while men were warriors; he once said, "war is to man what maternity is to the woman".<ref>Bollas, Christopher. 1993. Being a Character: Psychoanalysis and Self-Experience. Routledge. ISBN 9780415088152. p. 205.</ref> In an effort to increase birthrates, the Italian Fascist government gave financial incentives to women who raised large families and initiated policies designed to reduce the number of women employed.<ref>McDonald, Harmish. 1999. ''Mussolini and Italian Fascism''. Nelson Thornes. p. 27.</ref> Italian Fascism called for women to be honoured as "reproducers of the nation", and the Italian Fascist government held ritual ceremonies to honour women's role within the Italian nation.<ref>Mann, Michael. ''Fascists''. Cambridge University Press, 2004. p. 101.</ref> In 1934, Mussolini declared that employment of women was a "major aspect of the thorny problem of unemployment" that Italy was facing at the time and that for women, working was "incompatible with childbearing". Mussolini went on to say that the solution to unemployment for men was the "exodus of women from the work force".<ref>Durham, Martin. ''Women and fascism''. Routledge, 1998. p. 15.</ref> | |||
| The conditions of economic hardship caused by the ] brought about an international surge of social unrest.<ref>{{Cite news |last=Tenorio |first=Rich |date=2023-09-30 |title=Fascism in America: a long history that predates Trump |url=https://www.theguardian.com/books/2023/sep/30/fascism-in-america-book-trump |access-date=2024-02-26 |work=The Guardian |language=en-GB |issn=0261-3077}}</ref> Fascist propaganda blamed the problems of the long depression of the 1930s on minorities and ]s: "]-]-]" conspiracies, ] and the presence of immigrants.{{sfn|Chomsky|2003|p=46}} | |||
| In Germany, it contributed to the rise of the Nazi Party, which resulted in the demise of the ] and the establishment of the fascist regime, ], under the leadership of Adolf Hitler. With the rise of Hitler and the Nazis to power in 1933, ] was dissolved in Germany and the Nazis mobilized the country for war, with expansionist territorial aims against several countries. In the 1930s, the Nazis implemented racial laws that deliberately discriminated against, ] and persecuted Jews and other racial and minority groups. | |||
| Nazi policies toward women strongly encouraged them to stay at home to bear children and keep house.<ref>Evans, 331–332</ref> This policy was reinforced by bestowing the Cross of Honor of the German Mother on women bearing four or more babies. The unemployment rate was cut substantially, mostly through arms production and sending women home so that men could take their jobs. Nazi propaganda sometimes promoted premarital and extramarital sexual relations, unwed motherhood and divorce, but at other times the Nazis opposed such behaviour.<ref>Ann Taylor Allen. (broken link) H-German, H-Net Reviews, January 2006</ref> The growth of Nazi power, however, was accompanied by a breakdown of traditional sexual morals with regard to extramarital sex and licentiousness.<ref>Hau, Michael, Sex after Fascism: Memory and Morality in Twentieth-Century Germany (review) Modernism/modernity – Volume 14, Number 2, April 2007, pp. 378–380, The Johns Hopkins University Press</ref> | |||
| Fascist movements grew in strength elsewhere in Europe. Hungarian fascist ] rose to power as Prime Minister of ] in 1932 and attempted to entrench his ] throughout the country. He created an eight-hour work day and a forty-eight-hour work week in industry; sought to entrench a corporatist economy; and pursued ] claims on Hungary's neighbors.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=270}} The fascist ] movement in ] soared in political support after 1933, gaining representation in the Romanian government, and an Iron Guard member assassinated Romanian prime minister ].{{sfnp|Payne|1995|pp=282–288}} The Iron Guard was the only fascist movement outside Germany and Italy to ] without foreign assistance.<ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Q1zoXqTR_dAC&pg=PA35 |first1=Tom |last1=Gallagher |publisher=C. Hurst & Co. Publishers |date=2005 |title=Theft of a Nation: Romania Since Communism |page=35 |isbn=9781850657163 |via=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite book|url=https://books.google.com/books?id=8taGDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA66 |first1=D. |last1=Deletant |publisher=] |date=2006 |title=Hitler's Forgotten Ally: Ion Antonescu and his Regime, Romania 1940–1944 |page=66 |isbn=9780230502093 |via=]}}</ref> During the ], ] faced the greatest domestic political turmoil since the ] when the fascist ] and multiple far-right movements rioted '']'' in Paris against the French government resulting in major political violence.{{sfnp|Woolf|1983|p=311}} A variety of ] governments that borrowed elements from fascism were formed during the Great Depression, including those of ], ], ] and Yugoslavia.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=145}} In ], the ] was at its height in the 1930s due to the Great Depression, especially in 1935 when it won almost eight percent of votes, until the year 1937.{{sfnp|Rietbergen|2000|pp=160–161}} | |||
| Fascist movements and governments opposed ]. The Italian Fascist government declared it illegal in Italy in 1931.<ref>McDonald, 1999. p. 27.</ref> The Nazis thought homosexuality was degenerate, effeminate, perverted, and undermined the masculinity that they promoted, because it did not produce children.<ref>Evans, p. 529</ref> They considered homosexuality curable through therapy, citing modern ] and the study of ], which said that homosexuality could be felt by "normal" people and not just an abnormal minority.<ref>Ann Taylor Allen. Review of Dagmar Herzog, Sex after Fascism January 2006</ref> Critics have claimed that the Nazis' claim of scientific reasons behind their promotion of racism and hostility to homosexuals is ],<ref>Baumslag, Naomi; Pellgrino, Edmund D. 2005. ''Murderous medicine: Nazi doctors, human experimentation, and typhus''. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 37. Claims Nazi scientific reasoning for racial policy was pseudoscience</ref><ref>Lancaster, Roger N.''The Trouble of Nature: Sex in Science and Popular Culture''. University of California Press. p. 10. Claims that Nazi scientific reasoning for anti-homosexual policy was pseudoscience.</ref> Open homosexuals were among those interned in Nazi concentration camps.<ref>{{cite web|url=http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?ModuleId=10005261 |title=Persecution of Homosexuals in the Third Reich |publisher=Ushmm.org |accessdate=2010-06-04}}</ref> The British Union of Fascists opposed homosexuality and pejoratively questioned their opponents' heterosexuality.<ref>Gottlieb, Julie V., Linehan, Thomas P. p. 93.</ref> The Romanian ] opposed homosexuality as undermining society.<ref>Volovici, Nationalist Ideology, p. 98, citing N. Cainic, Ortodoxie şi etnocraţie, pp. 162–4.</ref> | |||
| ] marching in Brazil]] | |||
| ===Economic policies=== | |||
| {{See|Economics of fascism}} | |||
| In the Americas, the ] led by ] claimed as many as 200,000 members, although following coup attempts it faced a crackdown from the ] of ] in 1937.{{sfnp|Griffin|1991|pp=150–152}} In ], the fascist ] was a fascist political party which was in power 1931 to 1933. In the 1930s, the ] gained seats in ]'s parliament and attempted a coup d'état that resulted in the ] of 1938.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|pp=341–342}} | |||
| Fascists promoted their ideology as a "]" between capitalism and ].<ref name=pm168>Philip Morgan, ''Fascism in Europe, 1919–1945'', Taylor & Francis, 2003, p. 168. ISBN 0415169437</ref> Italian Fascism involved corporatism, a political system in which the economy is collectively managed by employers, workers, and state officials by formal mechanisms at the national level.<ref>''The Routledge Companion to Fascism and the Far Right'' (2002) by Peter Jonathan Davies and Derek Lynch, Routledge (UK), ISBN 0415214947 p. 143.</ref> Fascists advocated a new national class-based economic system, variously termed "national corporatism", "national socialism" or "national syndicalism".<ref name="deff"/> The common aim of all fascist movements was elimination of the autonomy or, in some cases, the existence of large-scale capitalism.<ref>Payne, Stanley (1996). ''A History of Fascism''. Routledge. ISBN 1857285956 p.10</ref> | |||
| During the Great Depression, Mussolini promoted active state intervention in the economy. He denounced the contemporary "]" that he claimed began in 1914 as a failure because of its alleged ], its support for unlimited ], and its intention to create the "standardization of humankind."{{sfnp|Berghaus|2000|pp=136–137}} Fascist Italy created the ] (IRI), a giant state-owned firm and holding company that provided state funding to failing private enterprises.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=189}} The IRI was made a permanent institution in Fascist Italy in 1937, pursued fascist policies to create national ] and had the power to take over private firms to maximize war production.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=189}} While Hitler's regime only nationalized 500 companies in key industries by the early 1940s,{{sfnp|Overy|1994|p=16}} Mussolini declared in 1934 that "hree-fourths of Italian economy, industrial and agricultural, is in the hands of the state."<ref>{{harvp|Toniolo|2013|p=59}}; Mussolini's speech to the Chamber of Deputies was on 26 May 1934.</ref> | |||
| Fascist governments exercised control over private property but did not nationalize it.<ref>Pauley. 2003. pp. 72, 84.</ref> They pursued economic policies to strengthen state power and spread ideology, such as consolidating trade unions to be state- or party-controlled.<ref>Pauley. 2003. p. 85.</ref> Attempts were made by both Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany to establish "]" (self-sufficiency) through significant economic planning, but neither achieved economic self-sufficiency.<ref>Pauley. 2003. p. 86.</ref> | |||
| Due to the worldwide depression, Mussolini's government was able to take over most of Italy's largest failing banks, who held controlling interest in many Italian businesses. The Institute for Industrial Reconstruction, a state-operated holding company in charge of bankrupt banks and companies, reported in early 1934 that they held assets of "48.5 percent of the share capital of Italy", which later included the capital of the banks themselves.{{sfnp|Toniolo|2013|p=59}} Political historian Martin Blinkhorn estimated Italy's scope of state intervention and ownership "greatly surpassed that in Nazi Germany, giving Italy a public sector second only to that of Stalin's Russia."{{sfnp|Blinkhorn|2006|p=46}} In the late 1930s, Italy enacted manufacturing cartels, tariff barriers, currency restrictions and massive regulation of the economy to attempt to balance payments.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=72}} Italy's policy of autarky failed to achieve effective economic autonomy.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=72}} Nazi Germany similarly pursued an economic agenda with the aims of autarky and rearmament and imposed ] policies, including forcing the German steel industry to use lower-quality German iron ore rather than superior-quality imported iron.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=190}} | |||
| ====National corporatism, socialism and syndicalism==== | |||
| Fascists supported the unifying of proletarian workers to their cause along corporatistic, socialistic, or syndicalistic lines, promoting the creation of a strong proletarian nation, but not a proletarian class.<ref>Payne, Stanley G. 1996. A History of Fascism, 1914–1945. Routledge. p. 64.</ref> Italian Fascism's economy was based on ], and a number of other fascist movements similarly promoted corporatism. ] of the ], describing fascist corporatism, said that "it means a nation organized as the human body, with each organ performing its individual function but working in harmony with the whole".<ref name=re208>Robert Eccleshall, Vincent Geoghegan, Richard Jay, Michael Kenny, Iain Mackenzie, Rick Wilford. ''Political Ideologies: an introduction''. 2nd ed. Routledge, 1994. p. 208.</ref> Fascists were not hostile to the '']'' or to small businesses, and they promised these groups, alongside the proletariat, protection from the upper-class bourgeoisie, big business, and Marxism. The promotion of these groups is the source of the term "extremism of the centre" to describe fascism.<ref name=gr101>Griffen, Roger (editor). Chapter 8: "Extremism of the Centre" – by Seymour Martin Lipset. ''International Fascism: Theories, Causes and the New Consensus.'' Arnold Readers. p. 101.</ref> | |||
| ===World War II (1939–1945)=== | |||
| Fascism blamed capitalist ] for creating class conflict and communists for exploiting it.<ref name="books.google.com">Welch, David. Modern European History, 1871–2000. . (Speaks of fascism opposing capitalism for creating class conflict and communism for exploiting class conflict).</ref> In Italy, the Fascist period presided over the creation of the largest number of state-owned enterprises in ], such as the nationalisation of ] companies into a single state enterprise called the Italian General Agency for Petroleum (''Azienda Generale Italiani Petroli'', AGIP).<ref>Schachter, Gustav; Engelbourg, Saul. 2005. ''Cultural Continuity In Advanced Economies: Britain And The U.S. Versus Continental Europe.'' Published by Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. .</ref> Fascists made populist appeals to the ], especially the lower middle class, by promising to protect small businesses and property owners from communism, and by promising an economy based on competition and profit while pledging to oppose big business.<ref name=gr101/> | |||
| ]}}, had boundaries derived from the plans of the {{lang|de|]}}, the ], and the {{lang|de|]}} (SS).<ref>{{Cite web |year=1999 |title=Utopia: The 'Greater Germanic Reich of the German Nation' |url=https://www.obersalzberg.de/en/exhibition/zweiter-weltkrieg/occupied-europe/utopie-grossgermanisches-reich/ |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180915155030/https://www.obersalzberg.de/en/exhibition/zweiter-weltkrieg/occupied-europe/utopie-grossgermanisches-reich/ |archive-date=2018-09-15 |access-date=2018-09-15 |publisher=] |location=Munich and Berlin}}</ref>]] | |||
| In Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany, both Mussolini and Hitler pursued territorial expansionist and ] agendas from the 1930s through the 1940s culminating in World War II. From 1935 to 1939, Germany and Italy escalated their demands for territorial claims and greater influence in world affairs. Italy ] resulting in its condemnation by the ] and its widespread diplomatic isolation. In 1936, Germany ], a region that had been ordered demilitarized by the ]. In 1938, Germany annexed ] and Italy assisted Germany in resolving the diplomatic crisis between Germany versus Britain and France over claims on ] by arranging the ] that gave Germany the ] and was perceived at the time to have averted a European war. These hopes faded when Czechoslovakia was dissolved by the proclamation of the German client state of ], followed by the next day of the occupation of the remaining ] and the proclamation of the German ]. At the same time from 1938 to 1939, Italy was demanding territorial and colonial concessions from France and Britain.{{sfnp|Rodogno|2006|p=47}} In 1939, Germany prepared for war with Poland, but attempted to gain territorial concessions from Poland through diplomatic means.{{sfnp|Davidson|2004|pp=371–372}} The Polish government did not trust Hitler's promises and refused to accept Germany's demands.{{sfnp|Davidson|2004|pp=371–372}} | |||
| In 1933, Benito Mussolini declared Italian Fascism's opposition to the "decadent capitalism" that he claimed prevailed in the world at the time, but he did not denounce capitalism entirely. Mussolini claimed that capitalism had degenerated in three stages, starting with dynamic or ] (1830–1870), followed by static capitalism (1870–1914), and reaching its final form of decadent capitalism or "]" beginning in 1914.<ref name=fz136>Falasca-Zamponi, Simonetta. ''Fascist Spectacle: The Aesthetics of Power in Mussolini's Italy''. University of California Press, 2000. p. 136.</ref> Mussolini argued that Italian Fascism was in favour of dynamic and heroic capitalism for its contribution to ] and its technical developments, but that it did not favour supercapitalism, which he claimed was incompatible with Italy's agricultural sector.<ref name=fz136/> | |||
| ] (the orange line delimits metropolitan Italy, the green line the borders of the enlarged ])]] | |||
| Thus Mussolini claimed that Italy under Fascist rule was not capitalist in the contemporary use of the term, which referred to supercapitalism.<ref name=fz136/> Mussolini denounced supercapitalism for causing the "standardization of humankind" and for causing excessive consumption.<ref>Falasca-Zamponi, Simonetta. ''Fascist Spectacle: The Aesthetics of Power in Mussolini's Italy''. University of California Press, 2000. p. 137.</ref> Mussolini claimed that at the stage of supercapitalism, "a capitalist enterprise, when difficulties arise, throws itself like a dead weight into the state's arms. It is then that state intervention begins and becomes more necessary. It is then that those who once ignored the state now seek it out anxiously."<ref>Mussolini, Benito; Schnapp, Jeffery Thompson (ed.); Sears, Olivia E. (ed.); Stampino, Maria G. (ed.). "Address to the National Corporative Council (14 November 1933) and Senate Speech on the Bill Establishing the Corporations (abridged; 13 January 1934)". ''A Primer of Italian Fascism''. University of Nebraska Press, 2000. p. 158.</ref> He saw Fascism as the next logical step to solve the problems of supercapitalism and claimed that this step could be seen as a form of earlier capitalism which involved state intervention, saying "our path would lead inexorably into ], which is nothing more nor less than ] turned on its head. In either event, the result is the bureaucratization of the economic activities of the nation."<ref name="mb158-159"/> | |||
| The invasion of Poland by Germany was deemed unacceptable by Britain, France and their allies, leading to their mutual declaration of war against Germany and the start of World War II. In 1940, Mussolini led Italy into World War II on the side of the Axis. During World War II, the Axis Powers in Europe led by Nazi Germany participated in the extermination of millions of Poles, Jews, Gypsies and others in the genocide known as the Holocaust. In 1943, after Italy faced multiple military failures, the complete reliance and subordination of Italy to Germany, the Allied invasion of Italy and the corresponding international humiliation, Mussolini ] on the order of King Victor Emmanuel III, who proceeded to dismantle the Fascist state and declared Italy's switching of allegiance to the Allied side. Mussolini was rescued from arrest by German forces and led the German client state, the Italian Social Republic from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany faced multiple losses and steady Soviet and Western Allied offensives from 1943 to 1945.<ref name="bi609">Bianchi (1963), p. 609</ref><ref name="bi704">Bianchi (1963), p. 704</ref> | |||
| Other fascist regimes were indifferent or hostile to ]. The Nazis initially attempted to form a corporatist economic system like that of Fascist Italy, creating the National Socialist Institute for Corporatism in May 1933, which included many major economists who argued that corporatism was consistent with National Socialism.<ref>Neocleous, Mark. Fascism. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1997. p. 47.</ref><ref>Peter Davies, Derek Lynch. The Routledge Companion to Fascism and the Far Right. Routledge, 2002. p. 103</ref> In '']'', Hitler spoke enthusiastically about the "National Socialist corporative idea" as one which would eventually "take the place of ruinous class warfare"<ref>The Fascism Reader by Aristotle A. Kallis.</ref> However, the Nazis later came to view corporatism as detrimental to Germany and institutionalizing and legitimizing social differences within the German nation. Instead, the Nazis began to promote economic organisation that emphasized the biological unity of the German national community.<ref>Neocleous, Mark. Fascism. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1997. p. 49.</ref> | |||
| On 28 April 1945, Mussolini was captured and executed by Italian communist partisans. On 30 April 1945, Hitler committed suicide. Shortly afterwards, Germany surrendered and the Nazi regime was ] by the occupying Allied powers. An International Military Tribunal was subsequently convened in ]. Beginning in November 1945 and lasting through 1949, numerous Nazi political, military and economic leaders were ] of ]s, with many of the worst offenders being sentenced to death and executed.<ref name=dg21>De Felice in Grandi (1983), p. 21</ref><ref name=def1391>De Felice (1996), p. 1391</ref> | |||
| Hitler continued to refer to corporatism in propaganda, but it was not put into place, even though a number of Nazi officials such as ], ], ], and ] were in favour of a ] form of corporatism, since corporations had been influential in German history in the ] era.<ref>Vincent, Andrew. ''Modern Political Ideologies.'' 3rd edition. John Wiley & Sons, 2009. pp. 158–159.</ref> | |||
| ===Post-World War II (1945–2008)=== | |||
| Spanish Falangist leader José Antonio Primo de Rivera did not believe that corporatism was effective and denounced it as a propaganda ploy, saying "this stuff about the corporative state is another piece of windbaggery".<ref>Vincent, Andrew. ''Modern Political Ideologies.'' 3rd edition. John Wiley & Sons, 2009. p. 160.</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Neo-fascism}} | |||
| ], ] from 1946 to 1955 and 1973 to 1974, admired ] and modelled his economic policies on those pursued by Fascist Italy.]] | |||
| The victory of the Allies over the Axis powers in ] led to the collapse of many fascist regimes in Europe. The ] convicted several Nazi leaders of crimes against humanity involving the Holocaust. However, there remained several movements and governments that were ideologically related to fascism.<ref>{{cite encyclopedia |title=Fascism as the Looming Shadow of Democracy: A Critique of the Xenophobic Reason |first=Henk |last=Oosterling |encyclopedia=Philosophy and Democracy in Intercultural Perspective/Philosophie et démocratie en perspective interculturelle |pages=235–252 |year=1997 |publisher=Rodopi |location=Amsterdam/Atlanta}}</ref><ref>{{cite journal |last=Deutsch |first=Sandra McGee |title=Fascism, Neo-Fascism, or Post-Fascism? Chile, 1945–1988 |journal=Diálogos-Revista do Departamento de História e do Programa de Pós-Graduação Em História 13.1 |year=2009 |pages=19–44}}</ref> | |||
| ====Economic planning==== | |||
| Fascists opposed the ] economic policies that were dominant in the era prior to the ].<ref>David Baker, "The political economy of fascism: Myth or reality, or myth and reality?", ''New Political Economy'', Volume 11, Issue 2 June 2006 , pages 227–250.</ref> After the Great Depression began, many people from across the ] blamed laissez-faire capitalism, and fascists promoted their ideology as a "]" between capitalism and ].<ref name=pm168/> | |||
| ]'s ] one-party state in Spain was officially neutral during World War II, although Franco's rise to power had been directly assisted by the militaries of Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany during the ]. The first years were characterized by a repression against the anti-fascist ideologies, deep censorship and the suppression of democratic institutions (elected Parliament, ], Regional Statutes of Autonomy). After World War II and a period of international isolation, Franco's regime normalized relations with the Western powers during the Cold War, until Franco's death in 1975 and the transformation of Spain into a liberal democracy.<ref name="libro.uca.edu">{{Cite book |url=http://libro.uca.edu/payne2/payne25.htm |last=Payne |first=Stanley G. |author-link=Stanley G. Payne |title=A History of Spain and Portugal |volume=2 |chapter=25 |page=632 |edition=Print |publisher=] |date=1973 |via=Library of Iberian Resources Online |access-date=30 May 2007}}</ref> | |||
| Fascists declared their opposition to ], ] charging, and profiteering.<ref>Frank Bealey & others. Elements of Political Science. Edinburgh University Press, 1999, p. 202</ref> ] and other anti-Semitic fascists considered finance capitalism a "]" "]".<ref>]. 1986. "Anti-Semitism and National Socialism." ''Germans and Jews Since the Holocaust: The Changing Situation in West Germany'', ed. Anson Rabinbach and Jack Zipes. New York: Homes & Meier.</ref> Fascist governments introduced ], wage controls and other types of ] measures.<ref name = "Andreski-p64">Stanislav Andreski, Wars, Revolutions, Dictatorships, Routledge 1992, page 64</ref> | |||
| Historian Robert Paxton observes that one of the main problems in defining fascism is that it was widely mimicked. Paxton says: "In fascism's heyday, in the 1930s, many regimes that were not functionally fascist borrowed elements of fascist decor in order to lend themselves an aura of force, vitality, and mass mobilization." He goes on to observe that ] "crushed Portuguese fascism after he had copied some of its techniques of popular mobilization."{{sfnp|Paxton|1998|pp=3, 17}} Paxton says: "Where Franco subjected Spain's fascist party to his personal control, Salazar abolished outright in July 1934 the nearest thing Portugal had to an authentic fascist movement, Rolão Preto's blue-shirted National Syndicalists. ... Salazar preferred to control his population through such 'organic' institutions traditionally powerful in Portugal as the Church. Salazar's regime was not only non-fascist, but 'voluntarily non-totalitarian,' preferring to let those of its citizens who kept out of politics 'live by habit.{{'"}}{{sfnp|Paxton|2004|p=150}} However, historians tend to view the ] as ] in nature,{{sfnp|Davies|Lynch|2002|p=}} possessing minimal fascist tendencies.{{sfnp|Passmore|2002|p=76}} Other historians, including ] and Manuel Villaverde Cabral, think that the Estado Novo should be considered fascist.<ref>{{Cite web |date=2024-04-26 |title=Inauguração do Museu de Peniche é um gesto antifascista atual contra a extrema-direita |url=https://www.esquerda.net/artigo/inauguracao-do-museu-de-peniche-e-um-gesto-antifascista-atual-contra-extrema-direita/90683 |access-date=2024-08-01 |website=Esquerda.net}}</ref> | |||
| Fascists thought that private property should be regulated to ensure that "benefit to the community precedes benefit to the individual."<ref>Richard Allen Epstein, ''Principles for a Free Society: Reconciling Individual Liberty With the Common Good'', De Capo Press 2002, p. 168</ref> Private ] rights were supported but were contingent upon service to the state.<ref>James A. Gregor, The Search for Neofascism: The Use and Abuse of Social Science, Cambridge University Press, 2006, p. 7</ref> For example, "an owner of agricultural land may be compelled to raise wheat instead of sheep and employ more labour than he would find profitable."<ref>Herbert Kitschelt, Anthony J. McGann. The Radical Right in Western Europe: a comparative analysis. 1996 University of Michigan Press. p. 30</ref> However, they promoted the interests of successful small businesses.<ref>De Grand, ''Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany'', pp. 48–51.</ref> Mussolini wrote approvingly of the notion that profits should not be taken away from those who produced them by their own labour, saying "I do not respect — I even hate — those men that leech a tenth of the riches produced by others".<ref>Benito Mussolini, Richard Washburn Child, Max Ascoli, Richard Lamb. ''My rise and fall''. Da Capo Press, 1998. p. 26.</ref> | |||
| ], leader of the ] from 1969 to 1987]] | |||
| According to historian Tibor Ivan Berend, '']'' was an inherent aspect of fascist economies.<ref>Tibor Ivan Berend, ''An Economic History of Twentieth-Century Europe'', Cambridge University Press, 2005, p. 93</ref> The ], promulgated by the ], stated in article 7: "The corporative State considers private initiative, in the field of production, as the most efficient and useful instrument of the Nation", then continued in article 9: "State intervention in economic production may take place only where private initiative is lacking or is insufficient, or when are at stakes the political interest of the State. This intervention may take the form of control, encouragement or direct management."<ref>Italian: ''Lo Stato corporativo considera l’iniziativa privata, nel campo della produzione, come lo strumento più utile ed efficiente della Nazione.''</ref> | |||
| The term neo-fascism refers to fascist movements after World War II. In Italy, the ] led by ] was a major neo-fascist movement that transformed itself into a self-described "post-fascist" movement called the ] (AN), which has been an ally of ]'s ] for a decade. In 2008, AN joined Forza Italia in Berlusconi's new party ], but in 2012 a group of politicians split from The People of Freedom, refounding the party with the name ]. In Germany, various neo-Nazi movements have been formed and banned in accordance with Germany's constitutional law which forbids Nazism. The ] (NPD) is widely considered a neo-Nazi party, although the party does not publicly identify itself as such. | |||
| ====Social welfare==== | |||
| Benito Mussolini promised a "social revolution" that would "remake" the ]. According to Patricia Knight, this was only achieved in part.<ref name=kp72>Knight, Patricia, Mussolini and Fascism, p. 72, Routledge, 2003.</ref> The people who primarily benefited from Italian fascist social policies were members of the ] and ]es, who filled jobs in the vastly expanded government workforce, which grew from about 500,000 to 1,000,000 jobs in 1930 alone.<ref name=kp72/> Health and welfare spending grew dramatically under Italian fascism, with welfare rising from 7% of the budget in 1930 to 20% in 1940.<ref>Pollard, John Francis, The Fascist Experience in Italy, p. 80 Routledge 1998</ref> | |||
| In Argentina, ], associated with the regime of ] from 1946 to 1955 and 1973 to 1974, was influenced by fascism.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=512}} Between 1939 and 1941, prior to his rise to power, Perón had developed a deep admiration of Italian Fascism and modelled his economic policies on Italian fascist policies.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=512}} However, not all historians agree with this identification,<ref>{{cite book |last=Page |first=Joseph A. |date=2014 |title=Perón: A biography |publisher=] |isbn=9789500748247 |page=10 and ss}}</ref> which they consider debatable<ref>{{citation |last=Romero |first=Ricardo |date=2015 |title=Perón, Reformism and Nazi fascism during the Second War World |publisher=Department of Social Sciences, National College of Buenos Aires, UBA |page=14 |quote=Although it is incorrect to define Peronism as Nazism, and it is debatable to conceptualize it as fascism, the truth is that in the University the Catholic sectors that received the support of the General did much to make the students consider as fascist to Perón.}}</ref> or even false,<ref>{{cite book |last=Galasso |first=Norberto |date=2003 |chapter=Peronismo y Liberación Nacional |trans-chapter=Peronism and National Liberation |title=Apuntes para otra historia |trans-title=Notes for another story |issn=1667-1635 |pages=2–3 |language=es}}</ref> biased by a pejorative political position.<ref>{{cite journal |last=Cucchetti |first=Humberto |date=2012 |url=https://gredos.usal.es/handle/10366/129373 |title=Readings and interpretations on the origins of Peronism: national-populism or fascist adaptation? |journal=Studia Historica. Contemporary History |volume=30 |issn=0213-2087 |publisher=] |pages=151–171}}</ref> Other authors, such as the Israeli ], categorically maintain that Perón was not a fascist and that this characterization was imposed on him because of his defiant stance against US hegemony.<ref>{{cite book |last=Rein |first=Raanan |date=2015 |title=Los muchachos judíos peronistas: Judeosargentinos y apoyo al Justicialismo |trans-title=The Peronist Jewish Boys: Judeo-sergeants and support for Justicialism |language=es |publisher=] |isbn=9789500753982}}</ref> | |||
| The '']'' (OND) or "National After-work Program" was one major social welfare initiative in Fascist Italy. Created in 1925, it was the state's largest recreational organisation for adults.<ref name=pauley3>Pauley, p. 113</ref> The ''Dopolavoro'' was responsible for establishing and maintaining 11,000 sports grounds, over 6,400 libraries, 800 movie houses, 1,200 theatres, and over 2,000 orchestras.<ref name=pauley3/> Membership of the ''Dopolavoro'' was voluntary, but it had high participation because of its nonpolitical nature.<ref name=pauley3/> It is estimated that, by 1936, the OND had organised 80% of salaried workers<ref>de Grazia, Victoria. ''The Culture of Consent: Mass Organizations of Leisure in Fascist Italy.'' Cambridge, 1981.</ref> and, by 1939, 40% of the industrial workforce. The sports activities proved popular with large numbers of workers. The OND had the largest membership of any of the mass Fascist organisations in Italy.<ref>Kallis, Aristotle, ed. (2003). ''The Fascism Reader,'' London: Routledge, pages 391–395.</ref> | |||
| ===Contemporary fascism (2008–present)=== | |||
| The enormous success of the ''Dopolavoro'' in Fascist Italy was the key factor in Nazi Germany's creation of its own version of the ''Dopolavoro'', the '']'' (KdF) or "Strength through Joy" program of the Nazi government's ], which became even more successful than the ''Dopolavoro''.<ref>Pauley, pp. 113–114</ref> KdF provided government-subsidized holidays for German workers.<ref>''Social Policy in the Third Reich. The Working Class and the 'National Community'' – Mason, T.W., Oxford: Berg. 1993, Page 160</ref> KdF was also responsible for the creation of the original ] ("People's Car"), a state-manufactured automobile that was meant to be cheap enough to allow all German citizens to be able to own one. | |||
| {{See also|Alt-right|Radical right (United States)|Fascism in the United States}} | |||
| ====Greece==== | |||
| While fascists promoted social welfare to ameliorate economic conditions affecting their nation or race as whole, they did not support social welfare for ] reasons. Fascists criticised egalitarianism as preserving the weak. They instead promoted ] views.<ref>Griffen, Roger; Feldman, Matthew. Fascism: Critical Concepts. p. 353. "When the Russian revolution occurred in 1917 and the 'Democratic' revolution spread after the First World War, anti-] and anti-egalitarianism rose as very strong "restoration movements" on the European scene. However, by the turn of that century no one could predict that fascism would become such a concrete, political reaction..."</ref><ref>Hawkins, Mike. ''Social Darwinism in European and American Thought, 1860–1945: Nature as Model and Nature as Threat''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997. p. 285. "Conflict is in fact the basic law of life in all social organisms, as it is of all biological ones; societies are formed, gain strength, and move forwards through conflict; the healthiest and most vital of them assert themselves against the weakest ans less well adapted through conflict; the natural evolution of nations and races takes place through conflict." Alfredo Rocco, Italian Fascist.</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Golden Dawn (Greece)|l1=Golden Dawn}} | |||
| Adolf Hitler was opposed to egalitarian and universal social welfare because, in his view, it encouraged the preservation of the degenerate and feeble.<ref>Adolf Hitler, ''Mein Kampf'', pp. 27–28</ref> While in power, the Nazis created social welfare programs to deal with the large numbers of unemployed. However, those programs were neither egalitarian nor universal, but instead residual, excluding multiple minority groups and certain other people whom they felt were incapable of helping themselves and pose a threat to the future health of the German people.<ref>Evans, pp. 491–492</ref> | |||
| ] | |||
| After the onset of the ] and economic crisis in Greece, a movement known as the ], widely considered a neo-Nazi party, soared in support out of obscurity and won seats in ], espousing a staunch hostility towards minorities, illegal immigrants and refugees. In 2013, after the murder of an anti-fascist musician by a person with links to Golden Dawn, the Greek government ordered the arrest of Golden Dawn's leader ] and other members on charges related to being associated with a criminal organization.<ref>{{cite news |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-24314319 |title=Greece's Golden Dawn leader Michaloliakos held in crackdown |publisher=] |date=28 September 2013 |access-date=28 September 2013 |archive-date=28 September 2013 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20130928063556/http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-24314319 |url-status=live}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|url=http://www.eek.gr/index.php/englishtext/79-articles/englishtext/1972-the-arrest-of-the-nazi-gangsters-of-golden-dawn-in-Greece |title=The Arrest of the Nazi Gangsters of Golden Dawn in Greece |first=Savvas |last=Michael |publisher=] |date=30 September 2013 |access-date=9 June 2020 |archive-date=13 June 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200613061925/http://www.eek.gr/index.php/englishtext/79-articles/englishtext/1972-the-arrest-of-the-nazi-gangsters-of-golden-dawn-in-Greece |url-status=live}}</ref> On 7 October 2020, Athens Appeals Court announced verdicts for 68 defendants, including the party's political leadership. Nikolaos Michaloliakos and six other prominent members and former members of parliament (MPs) were found guilty of running a criminal organization.<ref name="TheConversation">{{cite web|last=Samaras |first=Georgios |title=The end of Golden Dawn: has Greece shown us how to deal with neo-Nazis? |url=http://theconversation.com/the-end-of-golden-dawn-has-greece-shown-us-how-to-deal-with-neo-nazis-150239 |access-date=27 January 2021 |website=] |date=26 November 2020 |language=en |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201202120220/https://theconversation.com/the-end-of-golden-dawn-has-greece-shown-us-how-to-deal-with-neo-nazis-150239 |archive-date=2 December 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> Guilty verdicts were delivered on charges of murder, attempted murder, and violent attacks on immigrants and left-wing political opponents.<ref>{{cite news |title=Greece Golden Dawn: Neo-Nazi leaders guilty of running crime gang |publisher=] |date=7 October 2020 |url=https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-54433396 |access-date=7 October 2020 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20201010211224/https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-europe-54433396 |archive-date=10 October 2020 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| ==Racism and racialism== | |||
| Fascists are not unified on the issues of ] and ]. Mussolini, in a 1919 speech denouncing ], claimed that Jewish bankers in ] and ] were bound by the chains of ] to ] and that 80% of the ] leaders were Jews.<ref name=nm35>Neocleous, Mark. Fascism. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1997. p. 35.</ref> In his 1920 autobiography, he wrote, "Race and soil are strong influences upon us all", and said of ], "There were seers who saw in the European conflict not only national advantages but the possibility of a supremacy of race".<ref>Benito Mussolini, Richard Washburn Child, Max Ascoli, Richard Lamb. ''My rise and fall''. Da Capo Press, 1998. pp. 2, 38.</ref> In a 1921 speech in ], Mussolini stated that "Fascism was born... out of a profound, perennial need of this our ] and ]".<ref name=nm35/> Mussolini was concerned with the low birth rates of the ] in contrast to the African and Asian races. In 1928 he noted the high birth-rate of blacks in the ], and that they had surpassed the population of whites in certain areas, such as ] in ]. He described their greater racial consciousness in comparison with American whites as contributing to their growing strength.<ref name=ag43>Aaron Gillette. ''Racial theories in fascist Italy''. London, England, UK; New York, New York, USA. p. 43.</ref> On the issue of the low birth rate of whites, Mussolini said in 1928: | |||
| ====Post-Soviet Russia==== | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| {{Main|Rashism|Putinism}} | |||
| <nowiki></nowiki> city dies, the nation — deprived of the young life — blood of new generations — is now made up of people who are old and degenerate and cannot defend itself against a younger people which launches an attack on the now unguarded frontiers<nowiki></nowiki> This will happen, and not just to cities and nations, but on an infinitely greater scale: the whole White race, the Western race can be submerged by other coloured races which are multiplying at a rate unknown in our race.<ref>Griffen, Roger (ed.). ''Fascism''. Oxford University Press, 1995. p. 59.</ref></blockquote> | |||
| ], a French political scientist, contends in ''Is Russia Fascist?'' that the accusation of "fascist" has evolved into a strategic narrative of the existing world order. Geopolitical rivals might construct their own view of the world and assert the moral high ground by branding ideological rivals as fascists, regardless of their real ideals or deeds. Laruelle discusses the basis, significance, and veracity of accusations of fascism in and around Russia through an analysis of the domestic situation in Russia and the Kremlin's foreign policy justifications; she concludes that Russian efforts to brand its opponents as fascist is ultimately an attempt to determine the future of Russia in Europe as an antifascist force, influenced by its role in fighting fascism in World War II.<ref name="jstor">{{cite book |last=Laruelle |first=Marlene |url=http://www.jstor.org/stable/10.7591/j.ctv16t673d |title=Is Russia Fascist?: Unravelling Propaganda East and West |publisher=] |date=2021 |access-date=15 January 2023 |jstor=10.7591/j.ctv16t673d |isbn=9781501754135}}</ref> | |||
| During the ] Mussolini again expressed his alarm at the low birth rate among whites, saying "The singular, enormous problem is the destiny of the white race. Europe is truly towards the end of its destiny as the leader of civilization."<ref name=ag43/> He went on to say that under the circumstances, "the white race is sickly", "morally and physically in ruin", and that, in combination with the "progress in numbers and in expansion of yellow and black races, the civilization of the white man is destined to perish."<ref name=ag43/> According to Mussolini, only through promoting ] and ] could this be reversed.<ref name=ag43/> | |||
| According to ], an American historian and political scientist, Russian fascism has the following characteristics:<ref>{{cite journal |last=Motyl |first=Alexander J. |author-link=Alexander J. Motyl |date=March 2016 |title=Putin's Russia as a fascist political system |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/48610431 |journal=Communist and Post-Communist Studies |volume=49 |issue=1 |pages=25–36 |doi=10.1016/j.postcomstud.2016.01.002 |jstor=48610431 |issn=0967-067X}}</ref><ref>{{cite web |last=Motyl |first=Alexander J. |author-link=Alexander J. Motyl |date=30 March 2022 |title=Yes, Putin and Russia are fascist. How they meet the textbook definition |url=https://theconversation.com/yes-putin-and-russia-are-fascist-a-political-scientist-shows-how-they-meet-the-textbook-definition-179063 |website=]}}</ref> | |||
| Many Italian fascists held ] views, especially against neighbouring ] nations, whom the Italian fascists saw as being in competition with Italy, which had claims on territories of ], particularly ].<ref>Benito Mussolini, Richard Washburn Child, Max Ascoli, Richard Lamb. ''My rise and fall''. Da Capo Press, 1998. p. 106.</ref> Mussolini claimed that Yugoslavs posed a threat after Italy failed to receive territory along the ] coast at the end of World War I, as promised by the 1915 ]. He said: "The danger of seeing the Jugo-Slavians settle along the whole Adriatic shore had caused a bringing together in Rome of the cream of our unhappy regions. Students, professors, workmen, citizens—representative men—were entreating the ministers and the professional politicians.<ref>Benito Mussolini, Richard Washburn Child, Max Ascoli, Richard Lamb. ''My rise and fall''. Da Capo Press, 1998. pp. 105–106.</ref> Italian fascists accused ] of having "] impulses" and of being part of a "], ] ]ish internationalist plot".<ref>]. Italian foreign policy in the interwar period, 1918–1940. p. 43. Greenwood Publishing Group, 1997.</ref> The fascists accused Yugoslavs of conspiring together on behalf of "Grand ] masonry and its funds". | |||
| * An ], different from both traditional authoritarianism and totalitarianism; | |||
| * ] and ]; | |||
| * A hypermasculine ] (emphasis on his courage, militancy and physical prowess); | |||
| * General popular support for the regime and its leader.<ref>{{Cite web |url=https://www.wilsoncenter.org/event/systemic-transformations-and-the-drift-toward-fascism-russia |title=Systemic Transformations and the Drift Toward Fascism in Russia |publisher=] |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230902165844/https://www.wilsoncenter.org/event/systemic-transformations-and-the-drift-toward-fascism-russia |archive-date=2 September 2023}}</ref> | |||
| ] and ] as Nazis with a ] made of colours of the ] and a ] in the centre (], 2014)]] | |||
| In 1933, Mussolini contradicted his earlier statements on race, saying, "Race! It is a feeling, not a reality: ninety-five percent, at least, is a feeling. Nothing will ever make me believe that biologically pure races can be shown to exist today. ... National pride has no need of the delirium of race."<ref>{{cite book|last = Montagu|first =Ashley|title =Man's Most Dangerous Myth: The Fallacy of Race| publisher = Rowman Altamira| url =http://books.google.com/?id=tkHqP3vgYi4C&pg=PA187&lpg=PA187|isbn =0803946481|year = 1997}}</ref> | |||
| Yale historian ] has stated that "Putin's regime is ... the world center of fascism" and has written an article entitled ''"We Should Say It: Russia Is Fascist."''<ref name="Laruelle 2022">{{cite journal |title=So, Is Russia Fascist Now? Labels and Policy Implications |first=Marlene |last=Laruelle |date=2022 |journal=] |volume=45 |number=2 |pages=149–168 |doi=10.1080/0163660X.2022.2090760 |s2cid=250566287 |url=https://cpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com/blogs.gwu.edu/dist/1/2181/files/2022/07/Laruelle_45-2_TWQ-1.pdf |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220720185045/https://cpb-us-e1.wpmucdn.com/blogs.gwu.edu/dist/1/2181/files/2022/07/Laruelle_45-2_TWQ-1.pdf |archive-date=20 July 2022 |url-status=live}}</ref> Oxford historian ] compared Putin's Russia to the World War II-era ], saying that like Putin's Russia, it "emulated fascism in many ways, but was not fascist."<ref name="rferl-russia"/> Historian ] says Putin's Russia "is not equivalent to the fascist regimes of World War II, but it forms the nearest analogue to fascism found in a major country since that time" and argues that Putin's political system is "more a revival of the creed of Tsar ] in the 19th century that emphasized 'Orthodoxy, autocracy, and nationality' than one resembling the revolutionary, modernizing regimes of Hitler and Mussolini."<ref name="rferl-russia"/> According to Griffin, fascism is "a revolutionary form of nationalism" seeking to destroy the old system and remake society, and that Putin is a reactionary politician who is not trying to create a new order "but to recreate a modified version of the Soviet Union". German political scientist ] said genuine fascists in Russia, like deceased politician ] and activist and self-styled philosopher ], "describe in their writings a completely new Russia" controlling parts of the world that were never under tsarist or Soviet domination.<ref name="rferl-russia">{{cite news |title=Nasty, Repressive, Aggressive – Yes. But Is Russia Fascist? Experts Say 'No.' |url=https://www.rferl.org/a/russia-repressive-aggressive-not-fascist/31794918.html |access-date=7 May 2022 |first=Robert |last=Coalson |publisher=] |date=9 April 2022 |language=en |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20230723061728/https://www.rferl.org/a/russia-repressive-aggressive-not-fascist/31794918.html |archive-date=23 July 2023}}</ref> According to Marlene Laurelle writing in '']'', "applying the "fascism" label ... to the entirety of the Russian state or society short-circuits our ability to construct a more complex and differentiated picture."<ref name="Laruelle 2022"/> | |||
| At the 1934 Fascist International Congress, the issue of ] was debated amongst various fascist parties, with some more favourable to it, and others less favourable. Two final compromises were adopted, creating the official stance of the Fascist International: | |||
| ], collecting the opinions of experts on fascism, said that while Russia is repressive and authoritarian, it cannot be classified as a fascist state for various reasons, including Russia's government being more reactionary than revolutionary.<ref name="rferl-russia"/> In 2023, ], the chairman of the Board of Human Rights Center "]", claimed that ] had descended into fascism and that the army is ] "mass murder".<ref>{{cite web |last1=Papachristou |first1=Lucy |title=Rights campaigner calls Russia 'fascist' in court |url=https://www.reuters.com/world/europe/russian-prosecutor-seeks-nearly-3-years-jail-rights-campaigner-orlov-2024-02-26/ |date=26 February 2024 |website=]}}</ref><ref>{{cite news |last1=Ebel |first1=Francesca |title=Russian activist from Nobel-winning organization gets prison term |url=https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/2024/02/27/russia-orlov-memorial-prison-fascist/ |newspaper=] |date=27 February 2024}}</ref> On 7 March 2024, in his ], American President ] compared Russia under Vladimir Putin to ]'s ].<ref>{{cite web |title=Biden compares Putin to Hitler as he makes the case for continued aid to Ukraine in SOTU address |url=https://www.yahoo.com/news/biden-compares-putin-hitler-makes-100000473.html |website=], The New Voice of Ukraine |date=8 March 2024}}</ref> | |||
| <blockquote> | |||
| he ] cannot be converted into a universal campaign of hatred against the Jews Considering that in many places certain groups of Jews are installed in conquered countries, exercising in an open and occult manner an influence injurious to the material and moral interests of the country which harbors them, constituting a sort of state within a state, profiting by all benefits and refusing all duties, considering that they have furnished and are inclined to furnish, elements conducive to international revolution which would be destructive to the idea of patriotism and Christian civilization, the Conference denounces the nefarious action of these elements and is ready to combat them.<ref name="Pax Romanizing">"". TIME Magazine, 31 December 1934</ref> | |||
| </blockquote> | |||
| ==Tenets== | |||
| ==Relation to religion== | |||
| ] finds that even though fascism "maintained the existing regime of property and social hierarchy", it cannot be considered "simply a more muscular form of conservatism" because "fascism in power did carry out some changes profound enough to be called 'revolutionary.{{'"}}{{sfnp|Paxton|2004|p=11}} These transformations "often set fascists into conflict with conservatives rooted in families, churches, social rank, and property." Paxton argues: | |||
| The attitude of fascism toward religion has run the gamut from persecution, to denunciation, to cooperation<ref name = "oktyar">Laqueur, Walter, Fascism: Past, Present, Future p. 41 1996 Oxford University Press.</ref>, but is tyically anticlerical.<ref>Walter Laqueur. ''Fascism - a reader's guide: analyses, interpretations, bibliography''. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California, USA: University of California Press, 1976. Pp. 16.</ref> Stanley Payne notes that fundamental to fascism was the foundation of a purely materialistic "civic religion" that would "displace preceding structures of belief and relegate supernatural religion to a secondary role, or to none at all", and that "though there were specific examples of religious or would-be '] fascists,' fascism presupposed a post-Christian, post-religious, ], and immanent frame of reference."<ref>Payne, Stanley, A History of Fascism, 1914–1945, p. 9, Routledge 1996.</ref> | |||
| <blockquote>fascism redrew the frontiers between private and public, sharply diminishing what had once been untouchably private. It changed the practice of citizenship from the enjoyment of constitutional rights and duties to participation in mass ceremonies of affirmation and conformity. It reconfigured relations between the individual and the collectivity, so that an individual had no rights outside community interest. It expanded the powers of the executive—party and state—in a bid for total control. Finally, it unleashed aggressive emotions hitherto known in Europe only during war or social revolution.{{sfnp|Paxton|2004|p=11}}</blockquote> | |||
| According to Payne, fascisms own myth of secular transcendence only gains hold where traditional belief is weakened or absent, since fascism seeks to create new non-rationalist myth structures for those who no longer hold a traditional view.<ref name=ps9>Payne, Stanley , p. 9, Routledge 1996.</ref> The rise of modern secularism in Europe and Latin America, and the incursion and large-scale adoption of western secular culture in the mid-east, leave a void where this modern secular ideology, sometimes under a religious veneer, can take hold.<ref name=ps9/> | |||
| ===Nationalism with or without expansionism=== | |||
| Many fascists were ] in both private and public life.<ref>Laqueur, Walter; Fascism: Past, Present, Future p. 42 1996 Oxford University Press.</ref> Although both Hitler and Mussolini were anti-clerical, they both understood that it would be rash to begin their ]s prematurely; though possibly inevitable in the future, such clashes were put off while they dealt with other enemies.<ref>Laqueur, Walter, Fascism: Past, Present, Future pp. 31, 42, 1996 Oxford University Press.</ref> Hitler had a general plan, even before the Nazis' rise to power, to destroy Christianity within the Reich.<ref name=a4>Sharkey, , New York Times, January 13, 2002</ref><ref>, Rutgers Journal of Law and Religion, Winter 2001, publishing evidence compiled by the O.S.S. for the Nuremberg war-crimes trials of 1945 and 1946</ref><ref> Adherents.com</ref> Many Italian Fascists were disgusted by Mussolini's decision to abandon Fascism's anti-clericalism in favour of reconciliation with the Roman Catholic Church.<ref>Brendon, Piers. ''The dark valley : a panorama of the 1930s''. New York, New York, USA; Toronto, Ontario, Canada: Vintage Books, 2002 (2nd edition). p. 128.</ref> | |||
| {{Nationalism sidebar|Types}} | |||
| Ultranationalism, combined with the myth of national rebirth, is a key foundation of fascism.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006b|pp=451–453|loc="Nationalism"}} Robert Paxton argues that "a passionate nationalism" is the basis of fascism, combined with "a conspiratorial and Manichean view of history" which holds that "the chosen people have been weakened by political parties, social classes, unassimilable minorities, spoiled rentiers, and rationalist thinkers."{{sfnp|Paxton|2004|p=41}} Roger Griffin identifies the core of fascism as being ].{{sfnp|Griffin|1991|p=26}} | |||
| The leader of the ] stated, "the destruction of Christianity was explicitly recognized as a purpose of the National Socialist movement" from the start, but "considerations of expedience made it impossible" publicly to express this extreme position.<ref name=a4 /> In ], the ] were vehemently ], renounced religion, killed priests, and on one occasion gunned down Catholics as they left ].<ref>Krauze, Enrique, The Troubling Roots of Mexico's López Obrador: Tropical Messiah, The New Republic June 19, 2006.</ref><ref>Parsons, Wilfrid, Mexican Martyrdom, p. 238, 2003 Kessinger Publishing</ref><ref>"Garrido Canabal, Tomás". ''The Columbia Encyclopedia'' Sixth Edition (2005).</ref><ref>The New International Yearbook p. 442, Dodd, Mead and Co. 1966.</ref><ref>Millan, Verna Carleton, Mexico Reborn, p. 101, 1939 Riverside Press.</ref> | |||
| The fascist view of a nation is of a single organic entity that binds people together by their ancestry and is a natural unifying force of people.{{sfnp|Zimmer|2003|pp=80–107|loc=ch. 4}} Fascism seeks to solve economic, political and social problems by achieving a ] national rebirth, exalting the nation or ] above all else and promoting cults of unity, strength and purity.{{sfnp|Paxton|2004}}{{page needed|date=October 2021}}{{sfnp|Laqueur|1997|p=223}}{{sfnp|Encyclopedia Britannica ''Fascism''}} European fascist movements typically espouse a racist conception of non-Europeans being inferior to Europeans.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=11}} Beyond this, fascists in Europe have not held a unified set of racial views.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=11}} Historically, most fascists promoted imperialism, although there have been several fascist movements that were uninterested in the pursuit of new imperial ambitions.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|p=11}} For example, Nazism and Italian Fascism were ] and ]. Falangism in Spain envisioned the worldwide unification of Spanish-speaking peoples ({{lang|es|]}}). ] was ], though it did embrace the British Empire. | |||
| According to a biographer of Mussolini, "Initially, fascism was fiercely ]" — the Church being a competitor for dominion over the people's hearts.<ref>Farrell, Nicholas, Mussolini: A New Life p. 5 2004 Sterling Publishing Company, Inc.</ref> Mussolini, originally an ], published anti-Catholic writings and planned for the confiscation of Church property, but eventually moved to accommodation.<ref name = "oktyar"/> Mussolini endorsed the Roman Catholic Church for political legitimacy; during the ] talks, Fascist Party officials engaged in bitter arguments with ] officials and pressured them to accept terms that the regime deemed acceptable.<ref>Pollard, John F. (1985). ''The Vatican and Italian Fascism, 1929–32.'' Cambridge, USA: Cambridge University Press. p. 53.</ref> ] in Italy was not as significant as Catholicism, and the Protestant minority was persecuted.<ref>Rochat Giorgio, Regime fascista e chiese evangeliche, Torino, Claudiana, 1990.</ref> Mussolini's sub-secretary of Interior, Bufferini-Guidi, issued a memo closing all houses of worship of the Italian Pentecostals and ] and imprisoned their leaders.<ref>Bracco, Roberto. ''Persecuzione in Italia ''. Rome, n.d.</ref> In some instances, people were killed because of their faith.<ref>Rochat, Giorgio. ''Regime fascista e chiese evangeliche''. Torino: Claudiana, 1990.</ref> | |||
| ===Totalitarianism=== | |||
| The ] in ] had strong Catholic overtones, with some clerics in positions of power.<ref>Laqueur, Walter, Fascism: Past, Present, Future p. 148 1996 Oxford University Press.</ref> The fascist movement in Romania, known as the ] or the Legion of Archangel Michael, preceded its meetings with a church service, and their demonstrations were usually led by priests carrying icons and religious flags.{{Citation needed|date=January 2009}} The Romanian fascist movement promoted a cult of "suffering, sacrifice and martyrdom."<ref>source: Weber, E. "Rumania" in H. Rogger and E. Weber, eds., ''The European Right: A Historical Profile.'' Berkeley: University of California Press, 1965.</ref><ref>Nagy-Talavera, N. M. ''The Green Shirts and the Others. A History of Fascism in Hungary and Rumania''. Stanford: ], 1970; pp. 247, 266–70.</ref> | |||
| Fascism promotes the establishment of a ] state.{{sfnp|Griffin|2013|pp=1–6}}<!-- Page numbers may be for 2005 edition --> It opposes liberal democracy, rejects multi-party systems, and may support a ] so that it may synthesize with the nation.{{sfnp|Mussolini|2002|p=40}} Mussolini's ''The Doctrine of Fascism'' (1932), partly ] by philosopher ],{{sfnp|Lyttelton|1973|p=13|ps=: "The first half of the article was the work of Giovanni Gentile; only the second half was Mussolini's own work, though the whole article appeared under his name."}} who Mussolini described as "the philosopher of Fascism", states: "The Fascist conception of the State is all-embracing; outside of it no human or spiritual values can exist, much less have value. Thus understood, Fascism is totalitarian, and the Fascist State—a synthesis and a unit inclusive of all values—interprets, develops, and potentiates the whole life of a people."{{sfnp|Mussolini|1935|p=14}} In ''The Legal Basis of the Total State'', Nazi political theorist ] described the Nazi intention to form a "strong state which guarantees a totality of political unity transcending all diversity" in order to avoid a "disastrous pluralism tearing the German people apart."{{sfnp|Schmitt|1995|p=72}} | |||
| Fascist states pursued policies of social ] through ] in education and the media, and regulation of the production of educational and media materials.{{sfnmp|Pauley|2003|1p=117|Payne|1995|2p=220}} Education was designed to glorify the fascist movement and inform students of its historical and political importance to the nation. It attempted to purge ideas that were not consistent with the beliefs of the fascist movement and to teach students to be obedient to the state.{{sfnp|Pauley|2003|pp=117–119}} | |||
| In ], the most notable fascist movement was ]'s ]ian ]. Built on a network of lay religious associations, its vision was of an integral state that "comes from ], is inspired in Christ, acts for Christ, and goes toward Christ."<ref>''Turban for the Crown: The Islamic Revolution in Iran'' by Said Amir Arjomand. pp. 208–9.</ref><ref>Hilton, S. "Acao Integralista Brasiliera: Fascism in Brazil, 1932–38" ''Lusa Brazilian Review'', v.9, n.2, 1972: 12.</ref><ref>Williams, M.T. "Integralism and the Brazilian Catholic Church." ''Hispanic American Historical Review'', v.54, n.3, 1974: pp. 436–40.</ref> Salgado criticised the "dangerous ] tendencies of Hitlerism".<ref>Payne, Stanley , pp. 345–346, Routledge 1996.</ref> | |||
| ===Economy=== | |||
| Hitler and the Nazi regime attempted to found their own version of Christianity called ], which made major changes in its interpretation of the ], saying that ] was the son of God, but was not a Jew. They further claimed that Christ despised Jews, and that the Jews were solely responsible for his death.{{Citation needed|date=January 2009}} By 1940, however, it was public knowledge that Hitler had abandoned even the ] idea of a positive Christianity.<ref>Poewe, Karla O, , p. 30, Routledge 2006</ref> | |||
| {{Main|Economics of fascism}} | |||
| Historians and other scholars disagree on the question of whether a specifically ] type of ] can be said to exist. David Baker argues that there is an identifiable economic system in fascism that is distinct from those advocated by other ideologies, comprising essential characteristics that fascist nations shared.<ref>Baker, David (June 2006). "The political economy of fascism: Myth or reality, or myth and reality?" ''New Political Economy'' '''11''' (2): 227–250. {{doi|10.1080/13563460600655581}}.</ref> ], ], ] ''et al.'' argue that while fascist economies share some similarities, there is no distinctive form of fascist economic organization.<ref>Asheri, Maia; Sznajder; Mario; Zeev, Sternhell (1994) . ''The Birth of Fascist Ideology''. Translated by Maisel, David. Princeton: Princeton University Press. {{ISBN|9780691044866}}.</ref><ref>Payne, Stanley G. (1995). ''A History of Fascism, 1914–1945''. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press. {{ISBN|9780299148744}}.</ref><ref>] (2004). '']''. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. {{ISBN|9781400040940}}.</ref> ] and ] argue that fascism is distinguished by an absence of coherent economic ideology and an absence of serious economic thinking. They state that the decisions taken by fascist leaders cannot be explained within a logical economic framework.<ref>Woodley, Daniel (2009). ''Fascism and Political Theory: Critical Perspectives on Fascist Ideology''. London: Routledge. p. 161. {{ISBN|9781135248802}}.</ref> | |||
| The Catholic Church was suppressed by Nazis in ]. In addition to the deaths of some 3 million ]s, 2 million Polish Catholics were killed.<ref name=ctj/> Between 1939 and 1945, an estimated 3,000 polish clergy (18%) were murdered; of these, 1,992 died in ]s.<ref name=ctj>Craughwell, Thomas J., Catholic Culture. Retrieved July 18, 2008.</ref> In the annexed territory of ''Reichsgau Wartheland'', churches were systematically closed, and most priests were either killed, imprisoned, or deported to the ]. | |||
| Fascists presented their views as an alternative to both international ] and ].{{sfnp|Bastow|Martin|2003|p=36}} While fascism opposed mainstream socialism, fascists sometimes regarded their movement as a type of nationalist "socialism" to highlight their commitment to ], describing it as national ] and unity.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.historyguide.org/europe/duce.html |title=Benito Mussolini, Doctrine of Fascism (1932). |access-date=28 July 2016 |archive-date=31 July 2016 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20160731235010/http://www.historyguide.org/europe/duce.html |url-status=live}}</ref>{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=610}} Fascism had a complex relationship with ], both supporting and opposing different aspects of it at different times and in different countries. In general, fascists held an instrumental view of capitalism, regarding it as a tool that may be useful or not, depending on circumstances.<ref>Laqueur, Walter (1978). Fascism: A Reader's Guide: Analyses, Interpretations, Bibliography. University of California Press. p. 357. {{ISBN|978-0-520-03642-0}}</ref><ref>Overy, Richard (1994). War and Economy in the Third Reich. Oxford University Press. p. 1. {{ISBN|978-0-19-820290-5}}</ref> Fascists opposed international free market capitalism, but supported a type of productive capitalism.<ref>Laqueur, Walter (1978). ''Fascism: A Reader's Guide: Analyses, Interpretations, Bibliography''. University of California Press. p. 357. {{ISBN|978-0-520-03642-0}}</ref><ref>Overy, Richard (1994). ''War and Economy in the Third Reich''. Oxford University Press. p. 1. {{ISBN|978-0-19-820290-5}}</ref> Economic self-sufficiency, known as ], was a major goal of most fascist governments.{{sfnp|De Grand|1995|pp=60–61}} | |||
| The Germans also closed ] and ]s, persecuting monks and nuns throughout Poland. Eighty percent of the Catholic clergy and five of the bishops of ] were sent to concentration camps in 1939; in ], 48%.<ref name=ctj/> Of those murdered by the Nazi regime, 108 are regarded as blessed martyrs.<ref name=ctj/> Among them, ] was ] as a saint. Not only in Poland were Christians persecuted by the Nazis. In the ] alone, 2,600 Catholic priests from 24 different countries were killed.<ref name=ctj/> | |||
| Fascist governments advocated for the resolution of domestic ] within a nation in order to guarantee national unity.{{sfnp|Griffin|1991|pp=222–223}} This would be done through the state's mediating relations between the classes (contrary to the views of ]-inspired capitalists).{{sfnp|Hoover|1935|pp=13–20}} While fascism was opposed to domestic class conflict, it held that bourgeois-proletarian conflict existed primarily in international conflict between ] and ].{{sfnp|Neocleous|1997|pp=21–22}} Fascism condemned what it viewed as widespread character traits that it associated with the typical bourgeois mentality that it opposed, such as: materialism, crassness, cowardice, and the inability to comprehend the heroic ideal of the fascist "warrior"; and associations with liberalism, individualism and parliamentarianism.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=102}} In 1918, Mussolini defined what he viewed as the proletarian character, defining proletarian as being one and the same with producers, a ] perspective that associated all people deemed productive, including entrepreneurs, technicians, workers and soldiers as being proletarian. | |||
| One theory is that religion and fascism could never have a lasting connection because both are a "holistic weltanschauung" claiming the whole of the person.<ref name = "oktyar"/> Along these lines, ] political scientist, ] and others have noted that secularization had created a void which could be filled by a total ideology, making totalitarianism possible,<ref>Griffin, Roger, Fascism, Totalitarianism and Political Religion, p. 7 2005Routledge</ref><ref name=jb108>Maier, Hans and Jodi | |||
| Bruhn , p. 108, 2004 Routledge</ref> and Roger Griffin has characterized fascism as a type of anti-religious ].<ref>Eatwell, Roger 2004</ref> Such political religions vie with conventional, actual religions, and try to replace or eradicate them.<ref name=jb108/> | |||
| ]'' in German), its concept and its functional objectives were formulated by ].]] | |||
| ==Variations and subforms== | |||
| Movements identified by scholars as fascist hold a variety of views, and what qualifies as fascism is often a hotly contested subject. The first movement to self-identify as Fascist was the ] of ]. Strains which emerged after the original fascism, but are often placed under the wider usage of the term, self-identified their parties with different names. Major examples include ], ], ], and ].<ref>{{cite book|last = Mühlberger|first =Detlef|title =The Social Basis of European Fascist Movements| publisher =Routledge| url =http://books.google.com/?id=suENAAAAQAAJ&printsec=frontcover|isbn =0709935854|year = 1987}}</ref> | |||
| Because ] was key to creating a strong nationalist state, it criticized internationalist and Marxist socialism, advocating instead to represent a type of nationalist productivist socialism. Nevertheless, while condemning parasitical capitalism, was willing to accommodate productivist capitalism within it so long as it supported the nationalist objective.{{sfnp|Spektorowski|Ireni-Saban|2013|p=33}} The role of productivism was derived from ], whose ideas inspired the creation of ] and influenced other ideologies, that stressed solidarity rather than class war and whose conception of productive people in the economy included both productive workers and productive bosses to challenge the influence of the aristocracy and unproductive financial speculators.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=535}} Saint Simon's vision combined the traditionalist right-wing criticisms of the French Revolution with a left-wing belief in the need for association or collaboration of productive people in society.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=535}} Whereas Marxism condemned capitalism as a system of exploitative property relations, fascism saw the nature of the control of credit and money in the contemporary capitalist system as abusive.{{sfnp|Spektorowski|Ireni-Saban|2013|p=33}} | |||
| ''Para-fascism'' is a term used to describe authoritarian regimes with aspects that differentiate them from true fascist states or movements.<ref>Davies, Peter Jonathan and Derek | |||
| Lynch . p. 3, 2002 Routledge</ref> Para-fascists typically eschew radical change, and some view genuine fascists as a threat.<ref>Davies, Peter Jonathan and Derek Lynch . p. 326, 2002 Routledge</ref> | |||
| Unlike Marxism, fascism did not see class conflict between the Marxist-defined proletariat and the bourgeoisie as a given or as an engine of historical materialism.{{sfnp|Spektorowski|Ireni-Saban|2013|p=33}} Instead, it viewed workers and productive capitalists in common as productive people who were in conflict with parasitic elements in society including: corrupt political parties, corrupt financial capital and feeble people.{{sfnp|Spektorowski|Ireni-Saban|2013|p=33}} Fascist leaders such as Mussolini and Hitler spoke of the need to create a new managerial elite led by engineers and captains of industry—but free from the parasitic leadership of industries.{{sfnp|Spektorowski|Ireni-Saban|2013|p=33}} Hitler stated that the Nazi Party supported {{lang|de|bodenständigen Kapitalismus}} ("productive capitalism") that was based upon profit earned from one's own labour, but condemned unproductive capitalism or loan capitalism, which derived profit from speculation.{{sfnp|Friedman|2011|p=24}} | |||
| ===Europe=== | |||
| {{See also|European fascist ideologies}} | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ].]] | |||
| ] and German ] were the two most significant fascist movements in Europe during the 1920s and 30s. | |||
| Fascist economics supported a state-controlled economy that accepted a mix of ] and ] over the ].{{sfnp|Millward|2007|p=178}} ] was applied to both the public and private sector and the prosperity of private enterprise depended on its acceptance of synchronizing itself with the economic goals of the state.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=189}} Fascist economic ideology supported the ], but emphasized that industries must uphold the national interest as superior to private profit.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=189}} | |||
| ]' ] was created in the Hungarian city of ] in 1919. Its "Szeged fascism" has been considered a form of proto-fascism in its origins, but consolidated its fascist characteristics in the 1920s and 30s.<ref name=sgp112>Stanley G. Payne. Fascism: Comparison and Definition. Madison, Wisconsin, USA: Wisconsin University Press, 1980. p. 112.</ref> It came under the control of ] and was merged with Nazi and other far-right Hungarian groupings. Horthy allied with Germany and Italy during World War II but, after his support faltered in 1944, Germany invaded and installed the ] in government. | |||
| While fascism accepted the importance of material wealth and power, it condemned materialism which identified as being present in both communism and ] and criticized materialism for lacking acknowledgement of the role of the ].{{sfnp|Davies|Lynch|2002|p=103}} In particular, fascists criticized capitalism, not because of its competitive nature nor support of private property, which fascists supported—but due to its materialism, individualism, alleged bourgeois decadence and alleged indifference to the nation.{{sfnp|Paxton|2005|p=10}} Fascism denounced Marxism for its advocacy of materialist internationalist class identity, which fascists regarded as an attack upon the emotional and spiritual bonds of the nation and a threat to the achievement of genuine national solidarity.{{sfnp|Breuilly|1994|p=290}} | |||
| The ] was a fascist movement and political party in ] from 1927 to 1941.<ref>Spicer, Kevin P. 2007. Antisemitism, Christian ambivalence, and the Holocaust. Indiana University Press on behalf of the Center for Advanced Holocaust Studies. p. 142. </ref> It was briefly in power from September 1940 until January 1941. | |||
| In discussing the spread of fascism beyond Italy, historian Philip Morgan states: <blockquote>Since the Depression was a crisis of laissez-faire capitalism and its political counterpart, parliamentary democracy, fascism could pose as the 'third-way' alternative between capitalism and Bolshevism, the model of a new European 'civilization.' As Mussolini typically put it in early 1934, 'from 1929 ... fascism has become a universal phenomenon ... The dominant forces of the 19th century, democracy, socialism, liberalism have been exhausted ... the new political and economic forms of the twentieth-century are fascist'.{{sfnp|Morgan|2003|p=32}}</blockquote> | |||
| ] was a form of fascism founded by ] in 1934 during the ].<ref name="spanishfascism">{{cite book|last =Payne|first =Stanley G| title =Falange: A History of Spanish Fascism| publisher =Textbook Publisherss| url =http://books.google.com/?id=rsHyAAAACAAJ&dq=Spanish+Fascism| isbn =0758134452|date =1961-06-01}}</ref> Following the establishment of the ], General ], already the leader of the rebel Nationalists, became leader of the Falangists. A merger between the Falange and the ] took place in 1937, creating the ], a more traditionalist, conservative party than the original Falagnists, and one which was considered by some ] as a move away from the party's original fascist position.<ref name="spanishfascism"/><ref>{{cite book|last = Del Boca|first =Angelo| title =Fascism Today: A World Survey| publisher =Pantheon Books| url =http://books.google.com/?id=nadBAAAAIAAJ&q=%22authentic+Falangism%22&dq=%22authentic+Falangism%22|year = 1969}}</ref> Franco balanced several different interests of elements in his party in an effort to keep them united, especially in regard to the question of monarchy.<ref name="francoyears">{{cite book|last =Payne|first =Stanley G| title =The Franco Regime, 1936–1975| publisher =University of Wisconsin Press| url =http://books.google.com/?id=mgDWLYcTYIAC&dq=Francisco+Franco+payne| isbn =0299110702|year =1987}}</ref> | |||
| Fascists criticized egalitarianism as preserving the weak, and they instead promoted social Darwinist views and policies.{{sfnp|Griffin|Feldman|2004|p=353|ps=: "When the Russian revolution occurred in 1917 and the 'Democratic' revolution spread after the First World War, anti-] and anti-egalitarianism rose as very strong "restoration movements" on the European scene. However, by the turn of that century no one could predict that fascism would become such a concrete, political reaction ... ."}}{{sfnp|Hawkins|1997|p=285|ps=: "Conflict is in fact the basic law of life in all social organisms, as it is of all biological ones; societies are formed, gain strength, and move forwards through conflict; the healthiest and most vital of them assert themselves against the weakest and less well adapted through conflict; the natural evolution of nations and races takes place through conflict." Alfredo Rocco, Italian Fascist.}} They were in principle opposed to the idea of ], arguing that it "encouraged the preservation of the degenerate and the feeble."{{sfnp|Evans|2005|pp=483–484}} The Nazi Party condemned the welfare system of the Weimar Republic, as well as private charity and philanthropy, for supporting people whom they regarded as racially inferior and weak, and who should have been weeded out in the process of natural selection.{{sfnp|Evans|2005|p=484}} Nevertheless, faced with the mass unemployment and poverty of the Great Depression, the Nazis found it necessary to set up charitable institutions to help racially-pure Germans in order to maintain popular support, while arguing that this represented "racial self-help" and not indiscriminate charity or universal social welfare.{{sfnp|Evans|2005|pp=484–485}} Thus, Nazi programs such as the ] and the broader ] (NSV) were organized as quasi-private institutions, officially relying on private donations from Germans to help others of their race—although in practice those who refused to donate could face severe consequences.{{sfnp|Evans|2005|pp=486–487}} Unlike the social welfare institutions of the Weimar Republic and the Christian charities, the NSV distributed assistance on explicitly racial grounds. It provided support only to those who were "racially sound, capable of and willing to work, politically reliable, and willing and able to reproduce." Non-Aryans were excluded, as well as the "work-shy", "asocials" and the "hereditarily ill".{{sfnp|Evans|2005|p=489}} Under these conditions, by 1939, over 17 million Germans had obtained assistance from the NSV, and the agency "projected a powerful image of caring and support" for "those who were judged to have got into difficulties through no fault of their own."{{sfnp|Evans|2005|p=489}} Yet the organization was "feared and disliked among society's poorest" because it resorted to intrusive questioning and monitoring to judge who was worthy of support.{{sfnp|Evans|2005|pp=489–490}} | |||
| "Austrofascism" is a controversial category encompassing various para-fascist and semi-fascist movements in Austria in the 1930s.<ref>Davies, Peter Jonathan and Derek Lynch . p. 255, 2002 Routledge</ref> In particular it refers to the ], which became Austria's sole legal political party in 1934 and promoted ], but not along secular and totalitarian lines.<ref name=mp170>Morgan, Philip. ''Fascism in Europe, 1919–1945''. London, UK; New York, USA: Routledge, 2003. p. 170.</ref> | |||
| ===Direct action=== | |||
| The ] ("New State") regime in Portugal from 1933 to 1974 has been described as having close similarities to fascism as well as significant differences. ] rose to power in Portugal as Prime Minister in an army coup in 1932, creating an authoritarian ] ].<ref name=bm164>Blinkhorn, Martin. ''Fascists and Conservatives''. Abingdon, England, UK: Routledge, 2001 (2nd edition). p. 164.</ref> Salazar also instituted economic ] and substantial state control over the economy,<ref>Blinkhorn, Martin. ''Fascists and Conservatives''. Abingdon, England, UK: Routledge, 2001 (2nd edition). p. 161.</ref> and, like fascist leaders, he denounced democracy as detrimental to nations.<ref name=bm164/> | |||
| Fascism emphasizes ], including supporting the legitimacy of political violence, as a core part of its politics.{{sfnmp|Payne|1995|1p=106|Breuilly|1994|2p=294}} Fascism views violent action as a necessity in politics that fascism identifies as being an "endless struggle";{{sfnp|Woodley|2010|p=106}} this emphasis on the use of political violence means that most fascist parties have also created their own private ] (e.g. the Nazi Party's ] and Fascist Italy's ]). The basis of fascism's support of violent action in politics is connected to social Darwinism.{{sfnp|Woodley|2010|p=106}} Fascist movements have commonly held social Darwinist views of nations, races and societies.{{sfnp|Payne|1995|pp=485–486}} They say that nations and races must purge themselves of socially and biologically weak or ] people, while simultaneously promoting the creation of strong people, in order to survive in a world defined by perpetual national and racial conflict.{{sfnp|Griffin|1995|p=59}} | |||
| ===Age and gender roles=== | |||
| ] from 1936 to 1941 was a constitutional monarchy whose government was controlled by General ]. He created an authoritarian state based loosely on German national socialism. | |||
| ] | |||
| ], an organization for girls within the Nazi Party in Germany]] | |||
| Fascism emphasizes ] both in a physical sense of age and in a spiritual sense as related to virility and commitment to action.{{sfnp|Antliff|2007|p=171}} The Italian Fascists' political anthem was called '']'' ("The Youth").{{sfnp|Antliff|2007|p=171}} Fascism identifies the physical age period of youth as a critical time for the moral development of people who will affect society.{{sfnp|Quine|1996|p=47}} ] argues that "he corollaries of the cult of war and physical danger were the cult of brutality, strength, and sexuality ... a true counter-civilization: rejecting the sophisticated rationalist humanism of Old Europe, fascism sets up as its ideal the primitive instincts and primal emotions of the barbarian."{{sfnp|Laqueur|1978|p=341}} | |||
| Italian fascism pursued what it called "moral hygiene" of youth, particularly regarding ].{{sfnp|Quine|1996|pp=46–47}} Fascist Italy promoted what it considered normal sexual behaviour in youth while denouncing what it considered deviant sexual behaviour.{{sfnp|Quine|1996|pp=46–47}} It condemned ], most forms of ] and contraceptive devices (with the exception of the ]), ] and ] as deviant sexual behaviour, although enforcement of laws opposed to such practices was erratic and authorities often turned a blind eye.{{sfnp|Quine|1996|pp=46–47}} Fascist Italy regarded the promotion of male sexual excitation before ] as the cause of criminality amongst male youth, declared homosexuality a social disease and pursued an aggressive campaign to reduce prostitution of young women.{{sfnp|Quine|1996|pp=46–47}} | |||
| During World War II, a number of countries that came under Nazi occupation had fascist puppet regimes installed. In France, the ] controlled part of the country from 1940 to 1944. Part of Yugoslavia was ruled by the ] from 1941 to 1945. | |||
| Mussolini perceived women's primary role as primarily child bearers, while that of men as warriors, once saying: "War is to man what maternity is to the woman."{{sfnp|Bollas|1993|p=205}} In an effort to increase birthrates, the Italian Fascist government gave financial incentives to women who raised large families and initiated policies intended to reduce the number of women employed.{{sfnp|McDonald|1999|p=27}} Italian Fascism called for women to be honoured as "reproducers of the nation" and the Italian Fascist government held ritual ceremonies to honour women's role within the Italian nation.{{sfnp|Mann|2004|p=101}} In 1934, Mussolini declared that employment of women was a "major aspect of the thorny problem of unemployment" and that for women, working was "incompatible with childbearing"; Mussolini went on to say that the solution to unemployment for men was the "exodus of women from the work force."{{sfnp|Durham|1998|p=15}} | |||
| Fascist movements emerged in other European countries in the 1920s and 1930s without gaining significant political power. These included the ] in Finland, the ] in Sweden, the ] in the United Kingdom and the parafascist ] in the Republic of Ireland. The traditionalist ] in France and the ] in Belgium are also sometimes regarded as fascist. | |||
| The German Nazi government strongly encouraged women to stay at home to bear children and keep house.{{sfnp|Evans|2005|pp=331–332}} This policy was reinforced by bestowing the ] on women bearing four or more children. The unemployment rate was cut substantially, mostly through arms production and sending women home so that men could take their jobs. Nazi propaganda sometimes promoted premarital and extramarital sexual relations, unwed motherhood and divorce, but at other times the Nazis opposed such behaviour.<ref>{{Cite journal |last=Heineman |first=Elizabeth D. |date=2002 |title=Sexuality and Nazism: The Doubly Unspeakable? |url=https://www.jstor.org/stable/3704551 |journal=Journal of the History of Sexuality |volume=11 |issue=1/2 |pages=22–66 |doi=10.1353/sex.2002.0006 |jstor=3704551 |s2cid=142085835 |issn=1043-4070}}</ref> | |||
| ===East Asia=== | |||
| The Nazis decriminalized abortion in cases where fetuses had hereditary defects or were of a race the government disapproved of, while the abortion of healthy pure German, ] fetuses remained strictly forbidden.{{sfnp|Friedlander|1995|p=}} For non-Aryans, abortion was often compulsory. Their ] program also stemmed from the "progressive biomedical model" of ].{{sfnp|McLaren|1999|p=139}} In 1935, Nazi Germany expanded the legality of ] by amending ], to promote abortion for women with hereditary disorders.{{sfnp|Friedlander|1995|p=}} The law allowed abortion if a woman gave her permission and the fetus was not yet viable{{sfnp|Proctor|1989|p=366|ps=: "This emendation allowed abortion only if the woman granted permission, and only if the fetus was not old enough to survive outside the womb. It is unclear if either of these qualifications was enforced."}}{{sfnp|Arnot|Usborne|1999|p=}} and for purposes of so-called ].{{sfnp|Proctor|1989|pp=122–123|ps=: "Abortion, in other words, could be allowed if it was in the interest of racial hygiene. ... the Nazis did allow (and in some cases even required) abortions for women deemed racially inferior. ... On 10 November 1938, a Luneberg court declared abortion legal for Jews."}}{{sfnp|Tierney|1999|p=|ps=: "In 1939, it was announced that Jewish women could seek abortions, but non-Jewish women could not."}} | |||
| The ] was a Japanese fascist movement of the late 1920s and early 1930s, led by the prominent politician ]. Hiranuma ordered it dissolved after the ]. | |||
| The Nazis said that homosexuality was degenerate, effeminate, perverted and undermined masculinity because it did not produce children.{{sfnp|Evans|2005|p=529}} They considered homosexuality curable through therapy, citing modern ] and the study of ]. Open homosexuals were interned in Nazi concentration camps.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?ModuleId=10005261 |title=Persecution of Homosexuals in the Third Reich |author=] |publisher=Ushmm.org |access-date=4 June 2010 |archive-date=6 October 2008 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20081006104442/http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?ModuleId=10005261 |url-status=live}}</ref> | |||
| The ] (''Taisei Yokusankai'') was a Japanese coalition of fascist and ] political movements, such as the ] (''Kōdōha'') and the ] (''Tōhōkai''), formed in 1940 under the guidance of ] ].<ref name=tc244>Tsuzuki, Chushichi. ''The Pursuit of Power in Japan 1825–1995.'' Oxford University Press, 2000. p. 244.</ref><ref name=ni234>Nish, Ian. Japanese Foreign Policy. Routledge, 2001. p. 234.</ref> Konoe's successor, ], entrenched the IRAA as the country's ruling political movement and attempted to establish himself as the absolute leader, or '']'', of Japan. The IRAA created '']'' (Neighbourhood Association) and youth organisations, in which participation was mandatory. After 1942, Japan became a single-party state which promoted Japanese expansionism and imperialism.<ref>Tsuzuki, Chushichi. ''The Pursuit of Power in Japan 1825–1995.'' Oxford University Press, 2000. P. 245.</ref> | |||
| ===Palingenesis and modernism=== | |||
| The ] was a secret faction within the Chinese army which existed under the leadership of ] in the early 1930s. It was heavily influenced by European fascism. | |||
| {{Main article|Reactionary modernism}} | |||
| Fascism emphasizes both palingenesis (national rebirth or re-creation) and ].{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=168}} In particular, fascism's nationalism ].{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=451–453}} Fascism promotes the regeneration of the nation and purging it of decadence.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|p=168}} Fascism accepts forms of modernism that it deems promotes national regeneration while rejecting forms of modernism that are regarded as antithetical to national regeneration.{{sfnp|Blamires|2006|pp=168–169}} Fascism aestheticized modern technology and its association with speed, power and violence.{{sfnp|Neocleous|1997|p=63}} Fascism admired advances in the economy in the early 20th century, particularly ] and ].{{sfnp|Neocleous|1997|p=65}} Fascist modernism has been recognized as inspired or developed by various figures—such as ], ], ], ], ], ] and ].{{sfnp|Welge|2007|p=547}} | |||
| In Italy, such modernist influence was exemplified by Marinetti who advocated a palingenetic modernist society that condemned liberal-bourgeois values of tradition and psychology, while promoting a technological-martial religion of national renewal that emphasized militant nationalism.{{sfnp|Welge|2007|p=550}} In Germany, it was exemplified by Jünger who was influenced by his observation of the technological warfare during World War I and claimed that a new social class had been created that he described as the "warrior-worker";{{sfnp|Welge|2007|p=553}} Like Marinetti, Jünger emphasized the revolutionary capacities of technology. He emphasized an "organic construction" between human and machine as a liberating and regenerative force that challenged liberal democracy, conceptions of individual autonomy, bourgeois nihilism and decadence.{{sfnp|Welge|2007|p=553}} He conceived of a society based on a totalitarian concept of "total mobilization" of such disciplined warrior-workers.{{sfnp|Welge|2007|p=553}} | |||
| A number of left-wing anti-Communists in China during the late 1930s, including ], spoke and wrote positively of European fascism. | |||
| == |
==Culture== | ||
| ===Aesthetics=== | |||
| ] | |||
| ]]] | |||
| ] | |||
| In '']'' (1935), ] identifies ] as a key ingredient in fascist regimes.<ref>{{cite journal|last=Jay|first=Martin|year=1992|title='The Aesthetic Ideology' as Ideology; Or, What Does It Mean to Aestheticize Politics?|journal=Cultural Critique|publisher=University of Minnesota Press|issue=21|pages=41–61|doi=10.2307/1354116|jstor=1354116}}</ref> On this point he quotes ], founder of the ] art movement and co-author of the ] (1919), who ] in his writings and claims that "war is beautiful."<ref>{{Cite book |last=Benjamin |first=Walter |title=The Work of Art in the Age of Mechanical Reproduction |date=2008 |orig-year=1935 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-14-103619-9 |location=London |pages=36–37}}</ref> | |||
| Brazilian Integralism (Ação Integralista Brasileira) was a form of fascism founded by ] in Brazil in 1932. By 1937 they were one of the most important parties in Latin America, with around one million members. Integralist principles included corporativism and ], and, like other fascist movements, they exhibited an ] and ] agenda. They also formed armed squads, nicknamed ]. During the later years of the ], from 1937 to 1945, Brazil was governed according to principles that drew heavily on fascism. | |||
| In '']'' (1981), ] interprets fascism as a "political aesthetic of death" and a vehement ] against the increasing rationalism, secularism, and pacifism of the modern Western world.<ref>{{Cite book |last=Baudrillard |first=Jean |author-link=Jean Baudrillard |title=Simulacra and Simulation |date=1994 |orig-date=1981 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-472-06521-9 |location=Ann Arbor |quote=Fascism itself, the mystery of its appearance and of its collective energy, ... can already be interpreted as the 'irrational' excess of mythic and political referentials, the mad intensification of collective value (blood, race, people, etc.), the reinjection of death, of a 'political aesthetic of death' at a time when the process of the disenchantment of value and of collective values, of the rational secularization and unidimensionalization of all life, of the operationalization of all social and individual life already makes itself strongly felt in the West. Yet again, everything seems to escape this catastrophe of value, this neutralization and pacification of life. Fascism is a resistance to this, even if it is a profound, irrational, demented resistance, it would not have tapped into this massive energy if it hadn't been a resistance to something much worse. Fascism's cruelty, its terror is on the level of ''this other terror that is the confusion of the real and the rational,'' which deepened in the West, and it is a response to that.}}</ref> | |||
| ], due to its Spanish origins, also composed much of the fascist ideology prevalent in Latin America, particularly South America. | |||
| The standard definition of fascism, given by ], focuses on three concepts, one of which is a "fascist style" with an aesthetic structure of meetings, symbols, and political liturgy, stressing emotional and mystical aspects.{{sfnp|Payne|1980|p=7}} | |||
| ] in ] is often characterized as being fascist or at least para-fascist in nature, as encompassed by many of the economic and social policies pursued, encouraged and enacted by ], his wife ] and other leading members. Juan Peron expressed an admiration for the fascist systems of such nations as Italy, openly praising Benito Mussolini following a state visit there. Following WWII, Peron also provided asylum to several Nazis, and habilitated the underground organization ], composed of former members of the SS. | |||
| ] argues that fascism expresses itself aesthetically more than theoretically by means of a new political style with myths, rites, and symbols as a lay religion designed to acculturate, socialize, and integrate the faith of the masses with the goal of creating a "]".<ref>{{cite book |last1=Payne |first1=Stanley G. |author1-link=Stanley G. Payne |year=1996 |title=A History of Fascism, 1914–1945 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=x_MeR06xqXAC |location=Madison, WI |publisher=] |isbn=9780299148737 |via=] |pages=5–6}}</ref> | |||
| ], the ], founded an anti-Catholic fascist organization and paramilitary known as the ] in the state of ], ] in 1931. | |||
| Cultural critic ] writes: | |||
| The ] was established in 1932 and merged into the ] in 1938. There was an attempt to revive it during the 1970s. | |||
| {{Blockquote|Fascist aesthetics ... flow from (and justify) a preoccupation with situations of control, submissive behavior, extravagant effort, and the endurance of pain; they endorse two seemingly opposite states, egomania and servitude. The relations of domination and enslavement take the form of a characteristic pageantry: the massing of groups of people; the turning of people into things; the multiplication or replication of things; and the grouping of people/things around an all-powerful, hypnotic leader-figure or force. The fascist dramaturgy centers on the orgiastic transactions between mighty forces and their puppets, uniformly garbed and shown in ever swelling numbers. Its choreography alternates between ceaseless motion and a congealed, static, 'virile' posing. Fascist art glorifies surrender, it exalts mindlessness, it glamorizes death.{{sfnp|Sontag|1975}}}} | |||
| ===Middle East=== | |||
| Sontag also enumerates some commonalities between fascist art and the official art of communist countries, such as the obeisance of the masses to the hero, and a preference for the monumental and the "grandiose and rigid" choreography of mass bodies. But whereas official communist art "aims to expound and reinforce a utopian morality", the art of fascist countries such as Nazi Germany "displays a utopian aesthetics – that of physical perfection", in a way that is "both prurient and idealizing".{{sfnp|Sontag|1975}} | |||
| Phalangism (or Falangism) was a significant influence in ] through the ] and its founder ],<ref>{{cite book|last =Robertson| first =David| title =A Dictionary of Modern Politics| publisher =Routledge| url =http://books.google.com/?id=qHXbGOUuF9YC&pg=PA181&dq=Falange+lebanon|isbn=185743093X|date =2002-10}}</ref> who won national independence in 1943. | |||
| According to Sontag, fascist aesthetics "is based on the containment of vital forces; movements are confined, held tight, held in." Its appeal is not necessarily limited to those who share the fascist political ideology because fascism "stands for an ideal or rather ideals that are persistent today under the other banners: the ideal of life as art, the cult of beauty, the fetishism of courage, the dissolution of alienation in ecstatic feelings of community; the repudiation of the intellect; the family of man (under the parenthood of leaders)."{{sfnp|Sontag|1975}} | |||
| In ], the ] was a fascist faction of the ], active in the early 1930s. It opposed liberal Zionism and proposed the creation of a fascist Jewish state. | |||
| ===Popular culture=== | |||
| In the late 1930s, the Iraqi and pan-Arab ] became a significant pro-fascist force and was linked to the ], whose failed coup attempt of 1941 provoked the ]. It had a youth wing, the ]. | |||
| {{Further|Art in Nazi Germany|Reich Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda}} | |||
| ] in 1937]] | |||
| In Italy, the Mussolini regime created the {{lang|it|Direzione Generale per la Cinematografi}} to encourage film studios to glorify fascism. Italian cinema flourished because the regime stopped the import of Hollywood films in 1938, subsidized domestic production, and kept ticket prices low. It encouraged international distribution to glorify its African empire and to belie the charge that Italy was backward.<ref>{{cite journal |first=Ruth |last=Ben-Ghiat |title=The Imperial Moment in Fascist Cinema |journal=Journal of Modern European History |volume=13 |number=1 |date=2015 |pages=59–78|doi=10.17104/1611-8944_2015_1_59 |s2cid=147023860}}</ref> The regime censored criticism and used the state-run Luce Institute film company to laud the Duce through newsreels, documentaries, and photographs.<ref>{{cite journal |first=Pierre |last=Sorlin |title=A Mirror for Fascism. How Mussolini Used Cinema to Advertise his Person and Regime |journal=Historical Journal of Film, Radio and Television |date=2007 |volume=27 |number=1 |pages=111–117 |doi=10.1080/01439680601177163 |s2cid=192025081}}</ref> The regime promoted Italian opera and theatre as well, making sure that political enemies did not have a voice on stage.<ref>{{cite journal |first=Mabel |last=Berezin |title=The organization of political ideology: Culture, state, and theater in fascist Italy |journal=] |date=1991 |volume=56 |issue=5 |pages=639–651 |doi=10.2307/2096085 |jstor=2096085}}</ref> | |||
| In Nazi Germany the new ] was under the control of ], Hitler's powerful Reich Minister for Public Enlightenment and Propaganda.<ref name="overy361">{{cite book |first=Richard |last=Overy |title=The Dictators: Hitler's Germany, Stalin's Russia |page=361}}</ref> The goal was to stimulate the ] of German culture and to prohibit postmodern trends such as ] and ].<ref>{{cite book |first=Alan E. |last=Steinweis |title=Art, ideology, & economics in Nazi Germany: the Reich chambers of music, theater, and the visual arts |publisher=] |date=1996}}</ref> | |||
| The founder of the ], ], came under criticism in the 1930s as being influenced by Nazism, which he strongly denied.<ref name=goetz>{{cite book | title = Nazism in Syria and Lebanon: The Ambivalence of the German Option, 1933-1945 | author = ] | publisher = ] | year = 2009 | isbn = 0203888561, 9780203888568 | url = http://books.google.com/books?id=iAWBkDAv4TkC&pg=PA45&dq=Syrian+social+nationalist+nazi+fascist}}</ref>{{rp|43}} | |||
| ==Criticism== | ==Criticism== | ||
| Fascist parties were closely contested by ] movements from the ] and ] throughout the ]. The defeat of the ] in ] and subsequent revelation of the ] committed during the Holocaust by Germany have led to an almost universal condemnation of both past and present forms of fascism in the modern era. "Fascism" is today used across the political spectrum as a pejorative or byword for perceived authoritarianism and other forms of political evil. | |||
| Fascism has been widely criticized since the end of World War II for a variety of reasons. | |||
| ===Anti-democratic and tyrannical=== | |||
| One view of fascism is that it is not an actual ideology;<ref name=rg222>Roger Griffin, Matthew Feldman. Fascism: The nature of fascism. Routledge, 2004. p. 222.</ref> this view claims that fascism is a form of opportunistic politics, and that its ideological components are often tools of propaganda. | |||
| {{See also|Criticism of democracy}} | |||
| ] in ], on 23 October 1940]] | |||
| One of the most common and strongest criticisms of fascism is that it is a ].{{sfnp|Boesche|2010|p=11}} Fascism is deliberately and entirely non-democratic and anti-democratic.{{sfnmp|1a1=Clarke|1a2=Foweraker|1y=2001|1p=540|Pollard|1998|2p=121|Griffin|1991|3p=42}} | |||
| Fascism's extreme authoritarianism and nationalism often manifest as a belief in ] or a ], usually blended with some variant of ] or ] against a demonized "]", such as ], ], ], ], or ]. These ideas have motivated fascist regimes to commit ]s, ], ]s, and ]s.{{sfnmp|1a1=Kallis|1y=2011|2a1=Paxton|2y=1998|3a1=Lancaster|3y=2011}} During ], the genocidal and imperialist ambitions of the fascist ] resulted in the murder of millions of people. ] wrote that fascism {{blockquote|...encompassed ], ], ], ] and, in the German case, the most radical genocide of the last century: the ]. Fascism, in its many forms, did not hesitate to kill its own citizens as well as its colonial subjects in its search for ideological and political closure. Millions of civilians perished on a global scale during the apogee of fascist ideologies in Europe and beyond.<ref name="Finchelstein2008">{{cite journal |last=Finchelstein |first=Federico |title=On Fascist Ideology |journal=] |publisher=Wiley |volume=15 |issue=3 |date=20 August 2008 |issn=1351-0487 |doi=10.1111/j.1467-8675.2008.00494.x |pages=320–331}}</ref>}} | |||
| ] accuse fascism of being a ] ] that attempts to make ] ] popular to the ] but in practice represses the working class.<ref name=rg231>Roger Griffin, Matthew Feldman. Fascism: The nature of fascism. Routledge, 2004. p. 231.</ref> ] interpretations condemn fascism as a "political offensive of the bourgeosie against the working class"; a servant of "big business", "large landowners", and ] and ] capitalism.<ref name=ajg131-132>Anthony James Gregor. ''Interpretations of fascism''. 6th ed. New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA: Transaction Publishers, 2006 pp. 131–132.</ref> ] claimed that "Fascism is capitalism in decay."<ref>''The Book of Poisonous Quotes'', by Colin Jarman, McGraw-Hill Professional, 1993, ISBN 0809236818, p. 245.</ref> | |||
| ===Unprincipled opportunism=== | |||
| Hungarian ] Djula Sas in 1923 made a more detailed critique of fascism, in which he noted that, six months after rising to power, Italian Fascists had dismantled working-class organizations, significantly reduced wages in certain areas, abolished taxes on inheritance and war profits, and emphasized the need for "national production".<ref name=ajg131-132/> According to Sas, these actions clearly indicated that fascism was in the service of ].<ref>Anthony James Gregor. ''Interpretations of fascism''. 6th ed. New Brunswick, New Jersey, USA: Transaction Publishers, 2006 p. 135.</ref> | |||
| Some critics of Italian fascism have said that much of the ideology was merely a by-product of unprincipled ] by Mussolini and that he changed his political stances merely to bolster his personal ambitions while he disguised them as being purposeful to the public.{{sfnp|Schreiber|Stegemann|Vogel|1995|p=111}} ], the American ambassador to Italy who worked with Mussolini and became his friend and admirer, defended Mussolini's opportunistic behaviour by writing: <blockquote>Opportunist is a term of reproach used to brand men who fit themselves to conditions for the reasons of self-interest. Mussolini, as I have learned to know him, is an opportunist in the sense that he believed that mankind itself must be fitted to changing conditions rather than to fixed theories, no matter how many hopes and prayers have been expended on theories and programmes.<ref>{{harvp|Mussolini|1998|p=ix}}. (Note: Mussolini wrote the second volume about his fall from power as head of government of the Kingdom of Italy in 1943, though he was restored to power in northern Italy by the German military.)</ref></blockquote> Child quoted Mussolini as saying: "The sanctity of an ism is not in the ism; it has no sanctity beyond its power to do, to work, to succeed in practice. It may have succeeded yesterday and fail to-morrow. Failed yesterday and succeed to-morrow. The machine, first of all, must run!"{{sfnp|Mussolini|1998|p=ix}} | |||
| Some have criticized Mussolini's actions during the outbreak of World War I as opportunistic for seeming to suddenly abandon Marxist egalitarian internationalism for non-egalitarian ] and note, to that effect, that upon Mussolini endorsing Italy's intervention in the war against Germany and Austria-Hungary, he and the new fascist movement received financial support from Italian and foreign sources, such as ] (an armaments firm) and other companies{{sfnp|Mack Smith|1997|p=284}} as well as the British Security Service ].<ref name="Guardian2009-10-13">{{cite news |url=https://www.theguardian.com/world/2009/oct/13/benito-mussolini-recruited-mi5-italy |work=] |location=UK |title=Recruited by MI5: the name's Mussolini. Benito Mussolini – Documents reveal Italian dictator got start in politics in 1917 with help of £100 weekly wage from MI5 |date=13 October 2009 |access-date=14 October 2009 |first=Tom |last=Kington |archive-date=19 May 2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190519191439/https://www.theguardian.com/world/2009/oct/13/benito-mussolini-recruited-mi5-italy |url-status=live}}</ref> Some, including Mussolini's socialist opponents at the time, have noted that regardless of the financial support he accepted for his pro-interventionist stance, Mussolini was free to write whatever he wished in his newspaper {{lang|it|Il Popolo d'Italia}} without prior sanctioning from his financial backers.{{sfnp|O'Brien|2014|p=37}} Furthermore, the major source of financial support that Mussolini and the fascist movement received in World War I was from France and is widely believed to have been French socialists who supported the French government's war against Germany and who sent support to Italian socialists who wanted Italian intervention on France's side.{{sfnp|Gregor|1979|p=200}} | |||
| Marxist interpretations of fascism are typically based on a developmental approach.<ref name=rg231/> The Marxist developmental perspective on fascism has been criticized for failing to explain why fascism has not appeared in developing countries.<ref name=rg231/> Furthermore, Marxist interpretations of fascism have categorized multiple movements with significant differences to fascism as simply "fascist".<ref name=rg231/> As a result, even some communist regimes have been declared "fascist" under such interpretations, including those of ] under ] and ] under ].<ref name=rg231/> | |||
| Mussolini’s transformation away from Marxism into what eventually became fascism began prior to World War I, as Mussolini had grown increasingly pessimistic about Marxism and egalitarianism while becoming increasingly supportive of figures who opposed egalitarianism, such as Friedrich Nietzsche.{{sfnp|Golomb|Wistrich|2002|p=249}} By 1902, Mussolini was studying Georges Sorel, Nietzsche and ].{{sfnp|Delzel|1970|p=96}} Sorel's emphasis on the need for overthrowing decadent liberal democracy and capitalism by the use of violence, direct action, general strikes and ] appeals to emotion impressed Mussolini deeply.{{sfnp|Delzel|1970|p=3}} Mussolini's use of Nietzsche made him a highly unorthodox socialist, due to Nietzsche's promotion of elitism and anti-egalitarian views.{{sfnp|Golomb|Wistrich|2002|p=249}} Prior to World War I, Mussolini's writings over time indicated that he had abandoned the Marxism and egalitarianism that he had previously supported in favour of Nietzsche's {{lang|de|übermensch}} concept and anti-egalitarianism.{{sfnp|Golomb|Wistrich|2002|p=249}} In 1908, Mussolini wrote a short essay called "Philosophy of Strength" based on his Nietzschean influence, in which Mussolini openly spoke fondly of the ramifications of an impending war in Europe in challenging both religion and ]: " new kind of free spirit will come, strengthened by the war, ... a spirit equipped with a kind of sublime perversity, ... a new free spirit will triumph over God and over Nothing."{{sfnp|Gori|2004|p=14}} | |||
| ===Ideological dishonesty=== | |||
| Fascism has been criticized for being ideologically dishonest. Major examples of ideological dishonesty have been identified in Italian fascism's changing relationship with German Nazism.{{sfnmp|Gillette|2001|1p=17|Pollard|1998|2p=129}} Fascist Italy's official foreign policy positions commonly used rhetorical ideological ] to justify its actions, although during ]'s tenure as Italy's foreign minister the country engaged in {{lang|de|]}} free of such fascist hyperbole.{{sfnp|Burgwyn|1997|p=58}} Italian fascism's stance towards German Nazism fluctuated from support from the late 1920s to 1934, when it celebrated Hitler's rise to power and Mussolini's first meeting with Hitler in 1934; to opposition from 1934 to 1936 after the assassination of Italy's allied leader in Austria, ], by Austrian Nazis; and again back to support after 1936, when Germany was the only significant power that did not denounce ]. | |||
| After antagonism exploded between Nazi Germany and ] over the assassination of Austrian Chancellor Dollfuss in 1934, Mussolini and Italian fascists denounced and ridiculed Nazism's racial theories, particularly by denouncing its ], while promoting ].{{sfnp|Pollard|1998|p=129}} Mussolini himself responded to Nordicists' claims of Italy being divided into Nordic and Mediterranean racial areas due to Germanic invasions of Northern Italy by claiming that while Germanic tribes such as the ] took control of Italy after the ], they arrived in small numbers (about 8,000) and quickly assimilated into Roman culture and spoke the ] language within fifty years.{{sfnp|Gillette|2001|p=93}} Italian fascism was influenced by the tradition of ] scornfully looking down upon Nordicists' claims and taking pride in comparing the age and sophistication of ] as well as the classical revival in the ] to that of Nordic societies that Italian nationalists described as "newcomers" to civilization in comparison.{{sfnp|Gillette|2001|p=17}} At the height of antagonism between the Nazis and Italian fascists over race, Mussolini claimed that the Germans themselves were not a pure race and noted with irony that the Nazi theory of German racial superiority was based on the theories of non-German foreigners, such as Frenchman Arthur de Gobineau.{{sfnp|Gillette|2001|p=45}} After the tension in ] diminished during the late 1930s, Italian fascism sought to harmonize its ideology with German Nazism and combined Nordicist and Mediterranean racial theories, noting that Italians were members of the Aryan Race, composed of a mixed Nordic-Mediterranean subtype.{{sfnp|Pollard|1998|p=129}} | |||
| In 1938, Mussolini declared upon Italy's adoption of antisemitic laws that Italian fascism had always been antisemitic.{{sfnp|Pollard|1998|p=129}} However, Italian fascism did not endorse ] until the late 1930s when Mussolini feared alienating antisemitic Nazi Germany, whose power and influence were growing in Europe. Prior to that period, there had been notable ] who had been senior Italian fascist officials, including ], who had also been Mussolini's mistress.{{sfnp|Pollard|1998|p=129}} Also contrary to Mussolini's claim in 1938, only a small number of Italian fascists were staunchly antisemitic (such as ] and Giuseppe Preziosi), while others such as ], who came from ] which had one of Italy's largest Jewish communities, were disgusted by the antisemitic laws and opposed them.{{sfnp|Pollard|1998|p=129}} Fascism scholar Mark Neocleous notes that while Italian fascism did not have a clear commitment to antisemitism, there were occasional antisemitic statements issued prior to 1938, such as Mussolini in 1919 declaring that the Jewish bankers in London and New York were connected by race to the Russian Bolsheviks and that eight percent of the Russian Bolsheviks were Jews.{{sfnp|Neocleous|1997|pp=35–36}} | |||
| ==Anti-fascism== | |||
| {{main|Anti-fascism}} | |||
| ] in ], 14 August 1944, during the ]]] | |||
| ] is a ] in opposition to ] ideologies, groups and individuals. Beginning in European countries in the 1920s, it was at its most significant shortly before and during ], where the ] were opposed by many countries forming the ] and dozens of ]s worldwide. Anti-fascism has been an element of movements across the political spectrum and holding many different political positions such as ], ], ], ], ], ] and ] as well as ], ], ] and ] viewpoints. | |||
| Fascism, a ] ] ideology best known for its use by the ] and the ], became prominent beginning in the 1910s. Organization against fascism began around 1920. Fascism became the state ideology of Italy in 1922 and of Germany in 1933, spurring a large increase in anti-fascist action, including ] and the ]. Anti-fascism was a major aspect of the ], which foreshadowed World War II. | |||
| Before World War II, ] had not taken seriously the threat of fascism, and anti-fascism was sometimes associated with communism. However, the ] greatly changed Western perceptions, and fascism was seen as an existential threat by not only the ] Soviet Union but also by the ] United States and United Kingdom. The Axis Powers of World War II were generally fascist, and the fight against them was characterized in anti-fascist terms. ] to fascism occurred in every occupied country, and came from across the ideological spectrum. The defeat of the Axis powers generally ended fascism as a state ideology. | |||
| After World War II, the anti-fascist movement continued to be active in places where organized fascism continued or re-emerged. There was a resurgence of ] in the 1980s, as a response to the invasion of the ] by ]. This influenced the ] in the late 1980s and 1990s, which was similarly carried by punks. In the 21st century, this greatly increased in prominence as a response to the resurgence of the ], especially after the ].<ref>{{cite web|last=Beinart|first=Peter|date=2017-08-06|title=The Rise of the Violent Left|url=https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2017/09/the-rise-of-the-violent-left/534192/|access-date=2020-10-21|website=The Atlantic|language=en-US}}</ref><ref>{{Cite web|last=Beauchamp|first=Zack|date=2020-06-08|title=Antifa, explained|url=https://www.vox.com/policy-and-politics/2020/6/8/21277320/antifa-anti-fascist-explained|access-date=2020-10-21|website=Vox|language=en}}</ref> | |||
| ==See also== | |||
| {{Portal|Politics|History}} | |||
| {{div-col}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * ] | |||
| * '']'' | |||
| * ] | |||
| {{div-col-end}} | |||
| ==References== | ==References== | ||
| {{reflist}} | |||
| ===Notes=== | |||
| {{Reflist|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| ==Bibliography== | |||
| ===Primary sources=== | ===Primary sources=== | ||
| {{refbegin|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| <div class="references-small" style="-moz-column-count:2; column-count:2;"> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Galeazzo |first=Ciano |author-link=Galeazzo Ciano |year=2001 |title=The Ciano Diaries, 1939–1943 |publisher=Simon Publications |isbn=978-1-931313-74-2}} | |||
| *]. 1932. '']''. ]. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gentile |first=Giovanni |author-link=Giovanni Gentile |year=1932 |title=The Doctrine of Fascism |title-link=The Doctrine of Fascism}} | |||
| *]. 1939. ''Doctrine and Action: Internal and Foreign Policy of the New Portugal, 1928–1939.'' Faber and Faber. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Goebbels |first=Joseph |author-link=Joseph Goebbels |editor-last=Dalton |editor-first=Thomas |title=Goebbels on the Jews: The Complete Diary Entries – 1923 to 1945 |year=2019}} | |||
| *]. 1968. '']''. Nelson Publications. | |||
| ** {{cite book |editor-last=Taylor |editor-first=Fred |title=The Goebbels Diaries 1939–1941 |year=1983}} | |||
| *]. 1971. ''Textos de Doctrina Politica''. Madrid. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hitler |first=Adolf |author-link=Adolf Hitler |title=] |year=1925}} | |||
| *]. 1998. ''My Rise And Fall ''. Da Capo Press. ISBN 0306808641 | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Hoover |first=Calvin B. |author-link=Calvin B. Hoover |title=The Paths of Economic Change: Contrasting Tendencies in the Modern World |journal=The American Economic Review |volume=25 |number=1 |date=March 1935 |pages=13–20}}. Supplement, Papers and Proceedings of the Forty-Seventh Annual Meeting of the American Economic Association. | |||
| *]. 2001. ''The Ciano Diaries, 1939—1943''. Simon Publications. ISBN 1931313741 | |||
| * {{cite web |last=Hoover |first=J. Edgar |author-link=J. Edgar Hoover |url=http://www.milestonedocuments.com/documents/full-text/j-edgar-hoovers-testimony-before-the-house-un-american-activities-committee/ |title=Testimony before the House Un-American Activities Committee |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20100723195632/http://www.milestonedocuments.com/documents/full-text/j-edgar-hoovers-testimony-before-the-house-un-american-activities-committee/ |archive-date=23 July 2010 |year=1947}} | |||
| *Mussolini, Benito. 2006. ''My Autobiography: With "The Political and Social Doctrine of Fascism"''. Dover Publications. ISBN 0486447774 | |||
| * {{cite magazine |last=Matthews |first=Claudio |title=Fascism Is Not Dead ... |magazine=Nation's Business |year=1946}}{{full citation needed|date=October 2021}} | |||
| </div> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mosely |first=Oswald |author-link=Oswald Mosley |year=1968 |title=My Life |title-link=My Life (Sir Oswald Mosley autobiography) |publisher=Nelson Publications}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mussolini |first=Benito |author-link=Benito Mussolini |orig-date=1928 |date=2006 |title=My Autobiography with The Political and Social Doctrine of Fascism |location=Mineloa, NY |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-486-44777-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mussolini |first=Benito |author-link=Benito Mussolini |editor-last=Gregor |editor-first=Anthony James |editor-link=A. James Gregor |title=Origins and Doctrine of Fascism |url=https://archive.org/details/OriginsAndDoctrineOfFascismGiovanniGentile/page/n49/mode/2up |year=2002 |orig-date=1934 |publisher=Transaction Publishers |location=New Brunswick (US); London |isbn=978-0-7658-0130-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mussolini |first=Benito |author-link=Benito Mussolini |title=Fascism: Doctrine and Institutions |location=Rome |publisher=Ardita Publishers |year=1935}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mussolini |first=Benito |author-link=Benito Mussolini |year=1998 |title=My Rise And Fall |publisher=Da Capo Press |isbn=978-0-306-80864-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=de Oliveira Salazar |first=António |author-link=António de Oliveira Salazar |year=1939 |title=Doctrine and Action: Internal and Foreign Policy of the New Portugal, 1928–1939 |publisher=Faber and Faber}} | |||
| * {{cite magazine |last=Orwell |first=George |author-link=George Orwell |date=29 December 2019 |orig-date=26 March 1944 |url=http://orwell.ru/library/articles/As_I_Please/english/efasc |title=What is Fascism? |magazine=]}}, republished in {{cite book |title=The Collected Essays, Journalism and Letters of George Orwell |year=1968 |url=https://orwell.ru/home.html}} | |||
| * {{cite magazine |last=Orwell |first=George |author-link=George Orwell |date=April 1946 |url=https://www.orwellfoundation.com/the-orwell-foundation/orwell/essays-and-other-works/politics-and-the-english-language/ |title=Politics and the English Language |magazine=]}}; link via '']'' | |||
| * {{cite book |last=de Rivera |first=José Antonio Primo |author-link=José Antonio Primo de Rivera |year=1971 |title=Textos de Doctrina Política |trans-title=Political Doctrine Texts |location=Madrid |publisher=Delegación Nacional de la Sección Femenina del Movimiento |language=es}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ===Secondary sources=== | ===Secondary sources=== | ||
| {{refbegin|colwidth=30em}} | |||
| <div class="references-small" style="-moz-column-count:2; column-count:2;"> | |||
| <!-- A --> | |||
| *Cyprian Blamires. World fascism: a historical encyclopedia, Volume 1. Santa Barbara, California, USA: ABC-CLIO, Inc., 2006. | |||
| * {{cite web |last1=Acemoğlu |first1=Daron |author1-link=Daron Acemoglu |last2=De Feo |first2=Giuseppe |last3=De Luca |first3=Giacomo |last4=Russo |first4=Gianluca |date=28 October 2020 |url=https://voxeu.org/article/revisiting-rise-italian-fascism |title=Revisiting the rise of Italian fascism |publisher=] |access-date=5 August 2021}} | |||
| * Costa Pinto, Antonio, ed. ''Rethinking the Nature of Fascism: Comparative Perspectives'' (Palgrave Macmillan; 2011) 287 pages | |||
| * {{cite book |first=Ian |last=Adams |title=Political Ideology Today |publisher=] |location=Manchester, England |date=1993 |isbn=978-0-7190-6020-5}} | |||
| *], ''The Third Reich in Power: 1933–1939'', The Penguin Press HC, 2005 | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Ahmida |first=Ali Abdullatif |title=The Making of Modern Libya: State Formation, Colonization, and Resistance, 1830–1922 |location=Albany, New York |publisher=] |year=1994}} | |||
| *]. 1976. ''''. Transaction Books. ISBN 0878556192 | |||
| * {{cite journal |last1=Amann |first1=Peter H. |title=A 'Dog in the Nighttime' Problem: American Fascism in the 1930s |journal=The History Teacher |date=1986 |volume=19 |issue=4 |pages=559–584 |doi=10.2307/493879 |jstor=493879 |issn=0018-2745}} | |||
| *De Felice, Renzo. 1977. ''''. Harvard University Press. ISBN 0674459628. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Antliff |first=Mark |title=Avant-Garde Fascism: The Mobilization of Myth, Art, and Culture in France, 1909–1939 |publisher=] |year=2007}} | |||
| *]. 2005. ''Pour une étude scientifique du fascisme''. Ars Magna Editions. ISBN 2-912164-11-7. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Arnot |first1=Margaret |last2=Usborne |first2=Cornelie |title=Gender and Crime in Modern Europe |publisher=] |location=New York |year=1999 |isbn=978-1-85728-745-5 |oclc=249726924}} | |||
| *Kitsikis, Dimitri. 2006. ''Jean-Jacques Rousseau et les origines françaises du fascisme''. Ars Magna Editions. ISBN 2-912164-46-X. | |||
| <!-- B --> | |||
| *Ben-Am, Shlomo. 1983. . Oxford University Press. ISBN 0198225962 | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Baker |first=David |title=The political economy of fascism: Myth or reality, or myth and reality? |journal=New Political Economy |volume=11 |issue=2 |date=June 2006 |pages=227–250|doi=10.1080/13563460600655581 |s2cid=155046186}} | |||
| *]. 1987. ''''. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 0299110702 | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Ball |first1=Terence |last2=Bellamy |first2=Richard |title=The Cambridge History of Twentieth-Century Political Thought |year=2003 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-521-56354-3 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=N1h4_NqTOFoC |language=en |via=]}} <!-- This may not be the correct edition; not specified in original citation --> | |||
| *Vatikiotis, Panayiotis J. 1988. ''''. Routledge. ISBN 0714648698 | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Baranski |first1=Zygmunt G. |last2=West |first2=Rebecca J. |title=The Cambridge Companion to Modern Italian Culture |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1hVfHLOGAxwC&pg=PA50 |year=2001 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-521-55982-9 |access-date=7 October 2017 |via=]}} | |||
| *Payne, Stanley G. 1995. ''''. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 0299148742 | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bastow |first1=Steve |last2=Martin |first2=James |title=Third Way Discourse: European Ideologies in the Twentieth Century |publisher=] Ltd. |year=2003}} | |||
| *Costa Pinto, António. 1995. ''''. Social Science Monographs. ISBN 0880339683 | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Ben-Ami |first=Shlomo |author-link=Shlomo Ben-Ami |year=1983 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=yvSEAAAAIAAJ |title=Fascism from Above: The Dictatorship of Primo de Rivera in Spain, 1923–1930 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-19-822596-6 |via=]}} | |||
| *Griffiths, Richard. 2001. ''''. Duckworth. ISBN 0715629182 | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Berben |first=Paul |title=Dachau, 1933–1945: The Official History |publisher=Norfolk Press |year=1975}} | |||
| *Lewis, Paul H. 2002. ''''. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 027597880X | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Berghaus |first=Günter |title=Fascism and Theatre: Comparative Studies on the Aesthetics and Politics of Performance |location=Berkeley and Los Angeles, CA |publisher=] |year=2000}} | |||
| *Payne, Stanley G. 2003. ''''. Textbook Publishers. ISBN 0758134452 | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Blamires |first=Cyprian |title=World Fascism: A Historical Encyclopedia |volume=1 |location=Santa Barbara, CA |publisher=], Inc. |year=2006}} | |||
| *]. 2005. ''''. Vintage Books. ISBN 1400033918 | |||
| ** {{cite book |last=Blamires |first=Cyprian |title=World Fascism: A Historical Encyclopedia |volume=2 |location=Santa Barbara, CA |publisher=], Inc. |year=2006b}} | |||
| *]. 1996. ''Fascism: A History.'' New York: Allen Lane. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Blinkhorn |first1=Martin |title=Fascists and Conservatives: The Radical Right and the Establishment in Twentieth-Century Europe |date=2003 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-134-99712-1 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zr6JAgAAQBAJ |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| *] ''The Three Faces Of Fascism: Action Française, Italian Fascism, National Socialism'', translated from the German by Leila Vennewitz, London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson, 1965. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Blinkhorn |first=Martin |title=Mussolini and Fascist Italy |edition=3rd |location=New York |year=2006 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-134-50572-2 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KQ-CAgAAQBAJ |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| *]. 1970. ''The Mass Psychology of Fascism''. New York: Farrar, Straus & Giroux. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Bloxham |first1=Donald |author1-link=Donald Bloxham |last2=Moses |first2=A. Dirk |editor1-first=Donald |editor1-last=Bloxham |editor2-first=A. Dirk |editor2-last=Moses |author2-link=A. Dirk Moses |title=The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies |location=Oxford, England |publisher=] |year=2010 |isbn=9780199232116 |doi=10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199232116.001.0001}} | |||
| *]. 1935. ''Sawdust Caesar: The Untold History of Mussolini and Fascism''. New York and London: Harper and Brothers. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Bollas |first=Christopher |author-link=Christopher Bollas |title=Being a Character: Psychoanalysis and Self-Experience |publisher=] |year=1993 |isbn=978-0-415-08815-2}} | |||
| *]. {{cite book|title = Facts and Fascism|year = 1943, reprinted 2009|page = 288|location = New York|publisher = In Fact|isbn = 0-930852-43-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Boesche |first1=Roger |author1-link=Roger Boesche |title=Theories of Tyranny: From Plato to Arendt |year=2010 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-271-04405-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=6l5mfnfqHdgC |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| *] ''Economy and Class Structure of German Fascism'', London, CSE Bks, 1978 ISBN 0906336007 | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Borsella |first1=Cristogianni |last2=Caso |first2=Adolph |title=Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative |location=Wellesley, Massachusetts |publisher=Branden Books |year=2007 |isbn=978-0828321556}} | |||
| *Kallis, Aristotle A. ," To Expand or Not to Expand? Territory, Generic Fascism and the Quest for an 'Ideal Fatherland'" Journal of Contemporary History, Vol. 38, No. 2. (Apr., 2003), pp. 237–260. | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Brennan |first=T Corey |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Dr-CEAAAQBAJ |title=The fasces: a history of ancient Rome's most dangerous political symbol |date=2022 |publisher=Oxford University Press |isbn=978-0-19-764488-1 }} | |||
| *]. 1990. ''Rehearsals for Fascism: Populism and Political Mobilization in Weimar Germany''. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-505780-5 | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Breuilly |first=John |author-link=John Breuilly |title=Nationalism and the State |publisher=] |year=1994}} | |||
| *]. 2000. "Revolution from the Right: Fascism," chapter in David Parker (ed.) ''Revolutions and the Revolutionary Tradition in the West 1560–1991'', Routledge, London. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Burgwyn |first=H. James |author-link=H. James Burgwyn |title=Italian Foreign Policy in the Interwar Period, 1918–1940 |publisher=] |year=1997 |isbn=978-0275948771}} | |||
| *]. 1966. ''Fascism: Past, Present, Future,'' New York: Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1997. ISBN 0-19-511793-X | |||
| <!-- C --> | |||
| *Sauer, Wolfgang "National Socialism: totalitarianism or fascism?" pages 404–424 from ''The American Historical Review'', Volume 73, Issue #2, December 1967. | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Caforio |first=Giuseppe |title=Handbook of the sociology of the military <!-- Handbooks of Sociology and Social Research --> |location=New York |publisher=] |year=2006}} | |||
| *] with ] and ]. 1994. ''The Birth of Fascist Ideology, From Cultural Rebellion to Political Revolution.'', Trans. David Maisei. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Camus |first1=Jean-Yves |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_j5YDgAAQBAJ |title=Far-Right Politics in Europe |last2=Lebourg |first2=Nicolas |date=2017 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-674-97153-0 |language=en |access-date=9 May 2020 |via=]}} | |||
| *Baker, David. "The political economy of fascism: Myth or reality, or myth and reality?" New Political Economy, Volume 11, Issue 2 June 2006 , pages 227 – 250 | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Cardoza |first=Anthony L. |title=Benito Mussolini: the First Fascist |publisher=] |year=2006}} | |||
| *Griffin, Roger. 1991. ''The Nature of Fascism''. New York: ]. | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Carroll |first1=David |title=French Literary Fascism: Nationalism, Anti-Semitism, and the Ideology of Culture |date=1998 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-691-05846-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=XccGLKte38gC |language=en |via=]}} <!-- May be the wrong edition for the cited page --> | |||
| *]. 1985. ''Varieties of Fascism: Doctrines of Revolution in the Twentieth Century,'' New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, (Contains chapters on fascist movements in different countries.) | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Chomsky |first1=Noam |author-link=Noam Chomsky |title=Hegemony or survival : America's quest for global dominance |date=2003 |publisher=Henry Holt and Company, LLC |isbn=0-8050-7400-7}} | |||
| *]. 2005. ''The Origins of Fascist Ideology, 1918–1925: The First Complete Study of the Origins of Italian Fascism,'' New York: Enigma Books, ISBN 978-1-929631-18-6 | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Clarke |first1=Paul Barry |last2=Foweraker |first2=Joe |title=Encyclopedia of Democratic Thought |publisher=] |year=2001}} | |||
| *] Routledge, 2004. ''Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany: the 'fascist' style of rule'' | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Copsey |first=Nigel |title=Contemporary British Fascism: The British National Party and the Quest for Legitimacy |publisher=] |year=2008 |isbn=978-0-230-57437-3 |edition=second |location=London and New York}} | |||
| </div> | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Costa Pinto |editor-first=Antonio |title=Rethinking the Nature of Fascism: Comparative Perspectives |publisher=Palgrave Macmillan |year=2011}} <!--287 pages--> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Costa Pinto |first=António |year=1995 |title=Salazar's Dictatorship and European Fascism: Problems of Interpretation |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Z8Y9AAAACAAJ |publisher=Social Science Monographs |isbn=978-0-88033-968-1 |via=]}} | |||
| <!-- D --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Davidson |first=Eugene |title=The Unmaking of Adolf Hitler |location=Columbia, Missouri |publisher=University of Missouri Press |year=2004}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last1=Davies |editor-first1=Peter |editor-last2=Lynch |editor-first2=Derek |title=The Routledge Companion to Fascism and the Far Right |year=2002 |publisher=Routledge |isbn=978-1-134-60952-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=1-iXGKN1AK4C |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=De Felice |first=Renzo |author-link=Renzo De Felice |year=1977 |url=https://archive.org/details/interpretationso00defe |title=Interpretations of Fascism |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-674-45962-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=De Felice |first=Renzo |author-link=Renzo De Felice |year=1976 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=ia2BdNGHRYoC&pg=PP1 |title=Fascism: An Informal Introduction to Its Theory and Practice |publisher=Transaction Books |isbn=978-0-87855-619-9 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=De Grand |first=Alexander J. |title=Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany |year=1995}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=De Grand |first=Alexander |title=Italian Fascism: its Origins and Development |edition=3rd |publisher=] |year=2000}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Delzel |editor-first=Charles F. |title=Mediterranean Fascism 1919–1945 |publisher=Harper Rowe |year=1970}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Dierkes |first=Julian |title=Postwar Historical Education in Japan and the Germanies |publisher=] |year=2010}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Doordan |first=Dennis P. |title=In the Shadow of the Fasces: Political Design in Fascist Italy |publisher=The ] |isbn=978-0-299-14874-4 |year=1995 |url=https://archive.org/details/isbn_9780299148744}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Durham |first=Martin |title=Women and Fascism |publisher=Routledge |year=1998}} | |||
| <!-- E --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Eatwell |first=Roger |author-link=Roger Eatwell |year=1996 |title=Fascism: A History |location=New York |publisher=Allen Lane |isbn=978-0-7139-9147-5 |url=https://archive.org/details/fascismhistory00eatw |url-access=registration}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Elazar |first=Dahlia S. |title=The Making of Fascism: Class, State, and Counter-Revolution, Italy 1919–1922 |location=Westport, Connecticut |publisher=] |year=2001}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Eley |first=Geoff |author-link=Geoff Eley |title=Nazism as Fascism: Violence, Ideology, and the Ground of Consent in Germany 1930–1945 |publisher=] |year=2013 |isbn=978-0-203-69430-5 |location=London and New York}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Evans |first=Richard J |author-link=Richard J. Evans |title=The Third Reich in Power: 1933–1939 |publisher=The Penguin Press HC |year=2005}} | |||
| <!-- F --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Falasca-Zamponi |first=Simonetta |title=Fascist Spectacle: The Aesthetics of Power in Mussolini's Italy |publisher=] |location=Oakland, California |date=2000 |isbn=978-0-520-22677-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Ferrandi |first1=Maurizio |last2=Obermair |first2=Hannes |title=Camicie nere in Alto Adige (1921–1928) |trans-title=Blackshirts in South Tyrol (1921–1928) |year=2023 |publisher=Alphabeta |location=Merano |language=it |isbn=978-88-7223-419-8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Friedlander |first=Henry |title=The origins of Nazi genocide: from euthanasia to the final solution |publisher=] |location=] |year=1995 |isbn=978-0-8078-4675-9 |oclc=60191622}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Friedman |first=Jonathan C. |title=The Routledge History of the Holocaust |publisher=] |year=2011}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Fritzsche |first=Peter |title=Rehearsals for Fascism: Populism and Political Mobilization in Weimar Germany |publisher=] |year=1990 |isbn=978-0-19-505780-5}} | |||
| <!-- G --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gentile |first=Emilio |author-link=Emilio Gentile |title=The Struggle for Modernity: Nationalism, Futurism, and Fascism |location=Westport, Connecticut |publisher=] |year=2003}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gentile |first=Emilio |author-link=Emilio Gentile |year=2005 |title=The Origins of Fascist Ideology, 1918–1925: The First Complete Study of the Origins of Italian Fascism |location=New York |publisher=Enigma Books |isbn=978-1-929631-18-6}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gerwarth |first=Robert |title=The Bismarck Myth |publisher=] |year=2005}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gillette |first=Aaron |title=Racial Theories in Fascist Italy |location=London; New York |publisher=] |year=2001}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Golomb |first1=Jacob |last2=Wistrich |first2=Robert S |year=2002 |title=Nietzsche, Godfather of Fascism? On the Uses and Abuses of a Philosophy |location=Princeton, New Jersey |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Goodwin |first=Matthew J. |author-link=Matthew Goodwin |title=New British Fascism: Rise of the British National Party |publisher=] |year=2011 |isbn=978-0-415-46500-7 |location=London and New York}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gori |first=Gigliola |year=2004 |title=Italian Fascism and the Female Body: Submissive Women and Strong Mothers |location=Oxfordshire; New York |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Grant |first1=Moyra |title=Key Ideas in Politics |date=2003 |publisher=Nelson Thornes |isbn=978-0-7487-7096-0 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Ml1Wn6S54n4C |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Grčić |first=Joseph |title=Ethics and Political Theory |location=Lanham, Maryland |publisher=University of America, Inc |year=2000}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gregor |first=Anthony James |year=1979 |title=Young Mussolini and the Intellectual Origins of Fascism |location=Berkeley and Los Angeles, California; London |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-520-03799-1}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gregor |first=Anthony James |title=Mussolini's Intellectuals: Fascist Social and Political Thought |publisher=] |year=2005 |isbn=978-0-691-12009-6}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Gregor |first=Anthony James |year=2009 |title=Phoenix: Fascism in Our Time |location=New Brunswick |publisher=Transaction Press}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Griffin |first1=Roger |author1-link=Roger Griffin |title=The Nature of Fascism |year=1991 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-312-07132-5 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=fcn5ZtaPc7oC |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Griffin |first=Roger |author-link=Roger Griffin |title=Fascism |location=Oxford, England |publisher=] |year=1995}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Griffin |first=Roger |author-link=Roger Griffin |year=2000 |chapter=Revolution from the Right: Fascism" |editor-first=David |editor-last=Parker |title=Revolutions and the Revolutionary Tradition in the West 1560–1991 |publisher=] |location=London}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Griffin |first=Roger |author-link=Roger Griffin |url=http://ah.brookes.ac.uk/history/staff/griffin/coreoffascism.pdf |chapter=The palingenetic core of generic fascist ideology |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20040729040842/http://ah.brookes.ac.uk/history/staff/griffin/coreoffascism.pdf |archive-date=29 July 2004 |editor-first=Alessandro |editor-last=Campi |title=Che cos'è il fascismo? Interpretazioni e prospettive di ricerche |trans-title=What is fascism? Interpretations and research perspectives |language=it |publisher=Ideazione editrice |location=Rome |year=2003 |pages=97–122 |url-status=dead}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor1-last=Griffin |editor1-first=Roger |editor2-last=Feldman |editor2-first=Matthew |editor1-link=Roger Griffin |editor2-link=Matthew Feldman (historian) |title=Fascism: Critical Concepts in Political Science |year=2004 |publisher=]}} | |||
| ** {{cite book |editor1-last=Griffin |editor1-first=Roger |editor2-last=Feldman |editor2-first=Matthew |editor1-link=Roger Griffin |editor2-link=Matthew Feldman (historian) |volume=1 |title=The nature of fascism |year=2004a |publisher=]}} | |||
| ** {{cite book |editor1-last=Griffin |editor1-first=Roger |editor2-last=Feldman |editor2-first=Matthew |editor1-link=Roger Griffin |editor2-link=Matthew Feldman (historian) |title=Fascism and Culture |volume=3 |location=London and New York |publisher=] |year=2004c}} | |||
| * {{cite book |first1=Roger |last1=Griffin |author1-link=Roger Griffin |title=A Fascist Century |editor1-first=Matthew |editor1-last=Feldman |date=2008 |publisher=] |location=London |isbn=978-0-230-20518-5 |oclc=226357121}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Griffin |first1=Roger |author1-link=Roger Griffin |title=Fascism, Totalitarianism and Political Religion |date=2013 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-136-87168-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=uWfaAAAAQBAJ |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Griffiths |first=Richard |year=2000 |url=https://archive.org/details/intelligentperso0000grif |title=An Intelligent Person's Guide to Fascism |publisher=Duckworth |isbn=978-0-7156-2918-5 |via=]}} | |||
| <!-- H --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hartley |first=John |author-link=John Hartley (academic) |title=Communication, Cultural and Media Studies: The Key Concepts |year=2004 |edition=3rd |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-521-55982-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Hawkesworth |first1=Mary |author1-link=Mary Hawkesworth |last2=Kogan |first2=Maurice |title=Encyclopaedia of Government and Politics: Vol. 1 |year=1992 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-203-71288-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hawkins |first=Mike |title=Social Darwinism in European and American Thought, 1860–1945: Nature as Model and Nature as Threat |location=Cambridge |publisher=] |year=1997}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Held |first=David |year=1980 |title=Introduction to Critical Theory: Horkheimer to Habermas |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-520-04175-2}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hewitt |first=Andrew |title=Fascist Modernism: Aesthetics, Politics, and the Avant-Garde |location=Stanford, California |publisher=] |year=1993}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Holmes |first=Douglas R. |title=Integral Europe: Fast-Capitalism, Multiculturalism, Neofascism |location=Princeton, New Jersey |publisher=] |year=2000}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Horne |first=John |title=State, Society and Mobilization in Europe During the First World War |date=2002 |publisher=] |location=Cambridge |isbn=978-0-521-52266-3}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Hüppauf |first=Bernd-Rüdiger |title=War, Violence, and the Modern Condition |location=Berlin |publisher=] |year=1997}} | |||
| <!-- I --> | |||
| <!-- J --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Jablonsky |first=David |title=The Nazi Party in dissolution: Hitler and the Verbotzeit, 1923–1925 |location=London; Totowa, NJ |publisher=Frank Cass and Company Ltd. |year=1989}} | |||
| <!-- K --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kallis |first=Aristotle A. |author-link=Aristotle Kallis |year=2000 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=BeeRQHDOKXQC |title=Fascist ideology: territory and expansionism in Italy and Germany, 1922–1945 |location=London |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-415-21612-8 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Kallis |first=Aristotle A. |author-link=Aristotle Kallis |title=To Expand or Not to Expand? Territory, Generic Fascism and the Quest for an 'Ideal Fatherland' |journal=Journal of Contemporary History |volume=38 |number=2 |date=April 2003a |pages=237–260|doi=10.1177/0022009403038002132 |s2cid=159641856}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Kallis |editor-first=Aristotle |author-link=Aristotle Kallis |year=2003b |title=The Fascism Reader |location=London |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kallis |first=Aristotle |author-link=Aristotle Kallis |year=2011|title=Genocide and Fascism: The Eliminationist Drive in Fascist Europe |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-415-89027-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kershaw |first=Ian |title=Hitler, 1889–1936: Hubris |location=New York; London |publisher=W.W. Norton & Co. |year=2000}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kershaw |first=Ian |author-link=Ian Kershaw |title=To Hell and Back: Europe 1914–1949 |year=2016 |location=New York |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-14-310992-1}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kertzer |first=David I. |author-link=David Kertzer |title=The Pope and Mussolini: The Secret History of Pius XI and the Rise of Fascism in Europe |year=2014 |publisher=] |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Xc3QAgAAQBAJ |isbn=978-0-19-871616-7 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kitchen |first=Martin |title=A History of Modern Germany, 1800–2000 |location=Malden, Massaschussetts; Oxford, England; Carlton, Victoria, Australia |publisher=], Inc. |year=2006}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kitsikis |first=Dimitri |year=2006 |title=Jean-Jacques Rousseau et les origines françaises du fascisme |language=fr |trans-title=Jean-Jacques Rousseau and the French origins of fascism |publisher=Ars Magna Editions. |isbn=978-2-912164-46-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Kitsikis |first=Dimitri |author-link=Dimitri Kitsikis |year=2005 |title=Pour une étude scientifique du fascisme |language=fr |trans-title=For a scientific study of fascism |publisher=Ars Magna Editions. |isbn=978-2-912164-11-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Knox |first=MacGregor |title=Mussolini unleashed, 1939–1941: Politics and Strategy in Fascist Italy's Last War |location=Cambridge |publisher=] |year=1999}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Koon |first=Tracy H. |title=Believe, obey, fight: political socialization of youth in fascist Italy, 1922–1943 |publisher=] |year=1985}} | |||
| <!-- L --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Laclau |first=Ernesto |author-link=Ernesto Laclau |title=Politics and Ideology in Marxist Theory: Capitalism, Fascism, Populism |date=1977 |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Lancaster |first=Guy |date=26 September 2011 |title=Genocide and Fascism: The Eliminationist Drive in Fascist Europe |journal=] |volume=13 |issue=3 |pages=366–369 |doi=10.1080/14623528.2011.595586 |s2cid=72839243}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Laqueur |first=Walter |title=Fascism: A Reader's Guide: Analyses, Interpretations, Bibliography |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=2s8OaLD7y_oC&pg=PA341 |year=1978 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-520-03642-0 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Laqueur |first=Walter |date=1997 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=KM3QCwAAQBAJ |title=Fascism: Past, Present, Future |publisher=] |location=Oxford |isbn=978-0-19-802527-6 |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last1=Larsen |editor-first1=Stein Ugelvik |editor-last2=Hagtvet |editor-first2=Bernt |editor-last3=Myklebust |editor-first3=Jan Petter |title=Who Were the Fascists: Social Roots of European Fascism |publisher=] |year=1984 |isbn=978-82-00-05331-6}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lewis |first=Paul H |year=2002 |title=Latin Fascist Elites: The Mussolini, Franco, and Salazar Regimes |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=z3fgxOPSBb4C&q=Latin+Fascist+Elites |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-275-97880-8 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lukacs |first=John |title=The Hitler of History |publisher=] |location=New York |date=1998 |isbn=978-0-375-70113-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Lyttelton |first=Adrian |year=1973 |title=Italian Fascisms: from Pareto to Gentile |location=London |publisher=Cape}} | |||
| <!-- M --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mack Smith |first=Denis |author-link=Denis Mack Smith |title=Mussolini |location=New York |publisher=Vintage Books |year=1983}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mack Smith |first=Denis |title=Modern Italy: A Political History |location=Ann Arbor |publisher=The ] |year=1997}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=McLaren |first=Angus |title=Twentieth-Century Sexuality |publisher=] |year=1999}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mann |first=Michael |title=Fascists |publisher=] |location=Cambridge, England |year=2004 |isbn=978-0-521-83131-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=McDonald |first=Harmish |title=Mussolini and Italian Fascism |publisher=Nelson Thornes |year=1999}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Millington |first=Chris |title=A History of Fascism in France: From the First World War to the National Front |publisher=] |year=2019}} . | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Millward |first1=Robert |title=Private and Public Enterprise in Europe: Energy, Telecommunications and Transport, 1830–1990 |date=2007 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-521-83524-4 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mQ-f1IFo4IsC |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Morgan |first=Philip |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=acGhRyqfuGIC&q=third+position&pg=PT203 |title=Fascism in Europe, 1919–1945 |publisher=] |location=London|date=2003 |isbn=978-1-134-74028-4 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Mudde |first1=Cas |author1-link=Cas Mudde |last2=Kaltwasser |first2=Cristóbal Rovira |title=Populism: A Very Short Introduction |location=Oxford, England |publisher=] |year=2017 |isbn=978-0-19-023487-4}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Mussolini |first=Rachele |title=Mussolini: An Intimate Biography |location=New York |publisher=Pocket Books |year=1977}} Originally published by William Morrow in 1974. | |||
| <!-- N --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Neocleous |first=Mark |title=Fascism |location=Minneapolis, MN |publisher=] |year=1997}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Neville |first=Peter |title=Mussolini |location=Oxon, England; New York |publisher=] |year=2004}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Nolte |first=Ernst |author-link=Ernst Nolte |title=The Three Faces of Fascism: Action Française, Italian Fascism, National Socialism |translator-first=Leila |translator-last=Vennewitz |location=London |publisher=Weidenfeld and Nicolson |year=1965}} | |||
| <!-- O --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=O'Brien |first1=Paul |title=Mussolini in the First World War: The Journalist, the Soldier, the Fascist |date=2014 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-84520-558-4 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_wLfBAAAQBAJ |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Overy |first=R. J. |title=War and Economy in the Third Reich |publisher=Clarendon Press (]) |year=1994 |isbn=9780198202905 |doi=10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198202905.001.0001}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Outhwaite |first=William |editor1-first=William |editor1-last=Outhwaite |title=The Blackwell Dictionary of Modern Social Thought |publisher=] |year=2006 |isbn=9780470999028 |doi=10.1002/9780470999028}} | |||
| <!-- P --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Parkins |first=Wendy |title=Fashioning the Body Politic: Dress, Gender, Citizenship |publisher=Berg Publishers |isbn=978-1-85973-587-9 |year=2002}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Passmore |first=Kevin |date=2002 |title=Fascism: A Very Short Introduction |publisher=] |location=Oxford |isbn=978-1-5366-6507-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Passmore |first1=Kevin |title=Women, Gender, and Fascism in Europe, 1919–45 |date=2003 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7190-6617-7 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=luwQ2I6K6xEC |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Pauley |first=Bruce F. |year=2003 |title=Hitler, Stalin, and Mussolini: Totalitarianism in the Twentieth Century Italy |location=Wheeling |publisher=Harlan Davidson, Inc.}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Paxton |first=Robert O. |author-link=Robert Paxton |title=The five stages of fascism |journal=Journal of Modern History |volume=70 |issue=1 |year=1998 |pages=1–23 |doi=10.1086/235001 |jstor=10.1086/235001 |s2cid=143862302}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Paxton |first=Robert O. |author-link=Robert Paxton |year=2004 |title=] |edition=First |location=New York |publisher=Alfred A. Knopf |isbn=978-1-4000-4094-0}} | |||
| ** {{cite book |last=Paxton |first=Robert O. |author-link=Robert Paxton |year=2005 |title=The Anatomy of Fascism |location=New York; Toronto |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-307-42812-7}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Payne |first=Stanley G. |author-link=Stanley G. Payne |title=Fascism: Comparison and Definition |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-299-08060-0 |year=1980}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Payne |first=Stanley G. |author-link=Stanley G. Payne |year=1995 |title=A History of Fascism, 1914–45 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-299-14874-4}} ; also . | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Payne |first=Stanley G. |author-link=Stanley G. Payne |year=2003 |title=Falange: A History of Spanish Fascism |publisher=Textbook Publishers. |isbn=978-0-7581-3445-5}} . | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Payne |first=Stanley G. |author-link=Stanley G. Payne |year=1987 |title=The Franco Regime, 1936–1975 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mgDWLYcTYIAC&q=Francisco+Franco+payne |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-299-11070-3 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Pollard |first=John |title=The Fascist Experience in Italy |publisher=] |year=1998}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Proctor |first=Robert E. |title=Racial Hygiene: Medicine Under the Nazis |url=https://archive.org/details/racialhygiene00robe |url-access=registration |publisher=] |location=] |year=1989 |isbn=978-0-674-74578-0 |oclc=20760638}} | |||
| <!-- Q --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Quarantotto |first1=Claudio |title=Tutti fascisti! |trans-title=All fascists! |date=1976 |publisher=Edizioni del Borghese |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=9BizAAAAIAAJ |language=it |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Quine |first1=Maria Sophia |title=Population Politics in Twentieth-century Europe: Fascist Dictatorships and Liberal Democracies |date=1996 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-415-08069-9 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=dRR3pR1NbhcC |language=en |via=]}} | |||
| <!-- R --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Ramswell |first=Prebble Q. |title=Euroscepticism and the Rising Threat from the Left and Right: The Concept of Millennial Fascism |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=_wNBDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA9 |year=2017 |publisher=Lexington Books |isbn=978-1-4985-4604-1 |access-date=8 March 2019 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Reich |first=Wilhelm |author-link=Wilhelm Reich |title=The Mass Psychology of Fascism |year=1970 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-285-64701-5}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Renton |first=David |title=Fascism: Theory and Practice |location=London |publisher=] |year=1999}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Richardson |first=John E. |title=British Fascism: A Discourse-Historical Analysis |publisher=Ibidem Press |year=2017 |isbn=978-3-8382-6491-2 |location=Stuttgart}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Rietbergen |first=P. J. A. N. |url=https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/52849131 |title=A Short History of the Netherlands: From Prehistory to the Present Day |publisher=Bekking |year=2000 |isbn=90-6109-440-2 |edition=4th |location=Amersfoort |oclc=52849131}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Rodogno |first=Davide |title=Fascism's European empire |location=Cambridge, England |publisher=] |year=2006}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Roel Reyes |first=Stefan |date=17 December 2019 |title=Antebellum Palingenetic Ultranationalism: The Case for including the United States in Comparative Fascist Studies |journal=Fascism |publisher=] |location=Leiden, Netherlands |language=en |volume=8 |issue=2 |pages=307–330 |doi=10.1163/22116257-00802005 |issn=2211-6257 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Rohkrämer |first=Thomas |title=A Single Communal Faith? The German Right from Conservatism to National Socialism |series=Monographs in German History |volume=20 |publisher=Berghahn Books |year=2007}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Rosas |first=Fernando |title=Salazar e os Fascismos: Ensaio Breve de História Comparada |trans-title=Salazar and the Fascisms: Brief Essay on Comparative History |year=2019 |publisher=Edições Tinta-da-China |language=pt |isbn=9789896714840}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Ross |first=Alexander Reid |year=2017 |title=Against the Fascist Creep |publisher=] |location=Chico, California |author-link=Alexander Reid Ross |isbn=978-1-84935-244-4}} | |||
| <!-- S --> | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Sauer |first=Wolfgang |date=December 1967 |title=National Socialism: totalitarianism or fascism? |journal=The American Historical Review |volume=73 |issue=2 |pages=404–424|doi=10.2307/1866167 |jstor=1866167}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Schmitt |first=Carl |chapter=The Legal Basis of the Total State |title=Fascism |editor-last=Griffin |editor-first=Roger |editor-link=Roger Griffin |year=1995 |location=New York |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Schnapp |first1=Jeffrey Thompson |first2=Olivia E. |last2=Sears |first3=Maria G. |last3=Stampino |title=A Primer of Italian Fascism |publisher=] |year=2000}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Schreiber |first1=Gerhard |author1-link=Gerhard Schreiber |last2=Stegemann |first2=Bernd |author2-link=Bernd Stegemann |last3=Vogel |first3=Detlef |author3-link=Detlef Vogel |title=Germany and the Second World War: Volume III: The Mediterranean, South-East Europe, and North Africa 1939–1941 (From Italy's Declaration of Non-Belligerence to the Entry of the United States into the War) |publisher=] |year=1995}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Seldes |first=George |author-link=George Seldes |year=1935 |title=Sawdust Caesar: The Untold History of Mussolini and Fascism |location=New York and London |publisher=Harper and Brothers}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Seldes |first=George |author-link=George Seldes |orig-date=1943 |year=2009 |title=Facts and Fascism |location=New York |publisher=In Fact |isbn=978-0-930852-43-6 |page=288}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Shirer |first=William |title=The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich |publisher=Mandarin |year=1960}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Sohn-Rethel |first=Alfred |author-link=Alfred Sohn-Rethel |title=Economy and Class Structure of German Fascism |location=London |publisher=CSE Bks |year=1978 |isbn=978-0-906336-00-7}} | |||
| * {{cite magazine |last=Sontag |first=Susan |author-link=Susan Sontag |date=6 February 1975 |url=https://www.nybooks.com/articles/1975/02/06/fascinating-fascism/ |title=Fascinating Fascism |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20200718114505/https://www.nybooks.com/articles/1975/02/06/fascinating-fascism/ |archive-date=18 July 2020 |magazine=] |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Spektorowski |first1=Alberto |last2=Ireni-Saban |first2=Liza |title=Politics of Eugenics: Productionism, Population, and National Welfare |publisher=] |year=2013}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Spielvogel |first=Jackson J. |title=Western Civilization |publisher=Wadsworth, ] |year=2012}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Stackelberg |first=Roderick |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GELM5-W_zMwC&pg=PA3 |title=Hitler's Germany |publisher=] |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-203-00541-5 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Sternhell |first=Zeev |date=1976 |title=Anatomie d'un mouvement fasciste en France: le faisceau de Georges Valois |language=fr |trans-title=Anatomy of a fascist movement in France: the beam of Georges Valois |journal=Revue française de science politique |volume=26 |issue=1 |pages=5–40 |doi=10.3406/rfsp.1976.393652}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Sternhell |first1=Zeev |last2=Sznajder |first2=Mario |last3=Ashéri |first3=Maia |author1-link=Zeev Sternhell |orig-date=1989 |year=1994 |title=The Birth of Fascist Ideology, From Cultural Rebellion to Political Revolution |translator-first=David |translator-last=Maisei |publisher=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Sternhell |first=Zeev |author-link=Zeev Sternhell |chapter=Crisis of Fin-de-siècle Thought |editor-last=Griffin |editor-first=Roger |editor-link=Roger Griffin |title=International Fascism: Theories, Causes and the New Consensus |location=London and New York |publisher=Bloomsbury Academic |year=1998 |isbn=978-0340706138}} | |||
| <!-- T --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Thomson |first=David |author-link=David Thomson (historian) |title=Europe Since Napoleon |publisher=Pelican |year=1966 |isbn=9780140135619}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Tierney |first=Helen |title=Women's studies encyclopedia |publisher=] |location=] |year=1999 |isbn=978-0-313-31072-0 |oclc=38504469}} | |||
| * {{cite book |editor-last=Toniolo |editor-first=Gianni |title=The Oxford Handbook of the Italian Economy Since Unification |location=Oxford |publisher=] |year=2013}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Turner |first=Henry Ashby |author-link=Henry Ashby Turner |title=Reappraisals of Fascism |publisher=New Viewpoints |year=1975 |isbn=978-0531053720}} | |||
| <!-- U --> | |||
| <!-- V --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Vatikiotis |first=Panayiotis J |year=1988 |title=Popular Autocracy in Greece, 1936–1941: A Political Biography of General Ioannis Metaxas |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=mT5DO_cVSfMC |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-7146-4869-9 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=von Lang |first=Jochen |title=The Secretary: Martin Bormann, The Man Who Manipulated Hitler |location=New York |publisher=Random House |year=1979}} | |||
| <!-- W --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Weber |first=Eugen |author-link=Eugen Weber |orig-date=1964 |year=1982 |title=Varieties of Fascism: Doctrines of Revolution in the Twentieth Century |location=New York |publisher=Van Nostrand Reinhold Company |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=23jZAAAAMAAJ |isbn=978-0-89874-444-6 |via=]}} Contains chapters on fascist movements in different countries. | |||
| * {{cite book |title=Webster's II New College Dictionary |publisher=Houghton Mifflin Reference Books |isbn=978-0-618-39601-6 |year=2005 |url-access=registration |url=https://archive.org/details/webstersnewcolle0000unse |ref={{sfnref|Websters}}}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Weiss |first=John |title=The Fascist Tradition: Radical Right-Wing Extremism in Modern Europe |publisher=] |location=New York City |date=1967 |asin=B0014D2EN8}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last1=Weiss-Wendt |first1=Anton |first2=Robert |last2=Krieken |first3=Alfred A. |last3=Cave |title=The Historiography of Genocide |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=NzIWDAAAQBAJ&pg=PA73 |year=2008 |publisher=] |location=New York |isbn=978-0-230-29778-4 |access-date=12 April 2019 |via=]}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Welge |first=Jobst |chapter=Fascist Modernism |editor-first1=Astradur |editor-last1=Eysteinsson |editor-first2=Vivian |editor-last2=Liska |title=Modernism, Volumes 1–2 |publisher=John Benjamins Publishing |year=2007}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Williams |first=Roger Lawrence |author-link=Roger Lawrence Williams |title=The Mortal Napoleon The Third |publisher=] |year=2015}} | |||
| * {{cite journal |last=Wistrich |first=Robert |date=October 1976 |title=Leon Trotsky's Theory of Fascism |journal=] |publisher=] |location=Thousand Oaks, California |volume=11 |issue=4 |pages=157–184 |doi=10.1177/002200947601100409 |jstor=260195 |s2cid=140420352}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Woodley |first=Daniel |title=Fascism and Political Theory: Critical Perspectives on Fascist Ideology |publisher=] |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-415-47354-5 |location=London and New York}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Woolf |first=Stuart |title=Fascism in Europe |publisher=Methuen |year=1981 |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=iaMOAAAAQAAJ&pg=PA18 |isbn=978-0-416-30240-0 |access-date=9 May 2020 |via=]}} | |||
| ** {{cite book |last=Woolf |first=Stuart Joseph |title=Fascism in Europe |edition=3rd |publisher=] |year=1983}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Woshinsky |first=Oliver |title=Explaining Politics: Culture, Institutions, and Political Behavior |location=Oxford, England; New York |publisher=] |year=2008 |isbn=9780415960786}} | |||
| <!-- X --> | |||
| <!-- Y --> | |||
| <!-- Z --> | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Zafirovski |first=Milan |title=Modern Free Society and Its Nemesis: Liberty Versus Conservatism in the New Millennium |year=2008 |publisher=Lexington Books |isbn=978-0-7391-1516-9}} | |||
| * {{cite book |last=Zimmer |first=Oliver |title=Nationalism in Europe, 1890–1940 |series=Studies in European History |location=London |publisher=] |year=2003 |doi=10.1007/978-1-4039-4388-0 |isbn=978-1-4039-4388-0}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ===Tertiary sources=== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia |url=http://search.eb.com/eb/article-9117286 |encyclopedia=] |title=Fascism |date=8 January 2008|ref={{sfnref|Encyclopedia Britannica ''Fascism''}}}} | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia |url=https://www.britannica.com/place/Italy/The-Fascist-era |title=Italy: The Fascist Era |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20171007022510/https://www.britannica.com/place/Italy/The-Fascist-era |archive-date=7 October 2017 |url-status=live |encyclopedia=Encyclopedia Britannica |access-date=5 August 2021|ref={{sfnref|Encyclopedia Britannica ''The fascist era''}}}} | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia |title=Volksgemeinschaft |url=https://www.britannica.com/topic/fascism/Volksgemeinschaft#ref742146 |encyclopedia=Encyclopedia Britannica |year=2019 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190331074936/https://www.britannica.com/topic/fascism/Volksgemeinschaft#ref742146 |archive-date=31 March 2019 |url-status=live |ref={{sfnref|Encyclopedia Britannica ''Volksgemeinschaft''}}}} | |||
| * {{cite web |url=http://www.treccani.it/enciclopedia/neofascismo/ |title=Neofascismo |trans-title=Neofascism |website=Treccani |publisher=Enciclopedia Italiana |language=it |date=31 October 2014 |access-date=31 October 2014 |archive-date=6 November 2014 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20141106235833/http://www.treccani.it/enciclopedia/neofascismo/ |url-status=live |ref={{sfnref|Enciclopedia Italiana ''Neofascismo''}}}} | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia |encyclopedia=International Encyclopedia of Political Science |title=Fascism |editor1-first=Bertrand |editor1-last=Badie |editor1-link=Bertrand Badie |editor2-first=Dirk |editor2-last=Berg-Schlosser |editor2-link=Dirk Berg-Schlosser |editor3-first=Leonardo |editor3-last=Morlino |editor3-link=Leonardo Morlino |date=2011 |publisher=] |ref={{sfnref|International Encyclopedia of Political Science}} |doi=10.4135/9781412994163 |isbn=9781412959636 |last1=Badie |first1=Bertrand |author1-link=Bertrand Badie |last2=Berg-Schlosser |first2=Dirk |author2-link=Dirk Berg-Schlosser |last3=Morlino |first3=Leonardo |author3-link=Leonardo Morlino}} | |||
| * {{cite encyclopedia |last=Staudenmaier |first=Peter |encyclopedia=Encyclopedia of World Environmental History |title=Fascism |pages=517–521 |editor1-first=Shepard |editor1-last=Krech III |editor2-first=John |editor2-last=McNeill |editor3-first=Carolyn |editor3-last=Merchant |date=2004 |publisher=] |isbn=0-415-93733-7 |url=https://epublications.marquette.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1097&context=hist_fac}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ===Further reading=== | |||
| {{refbegin|30em}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Ahmed |first=Saladdin |date=July 2023 |title=Fascism as an Ideological Form: A Critical Theory |url=https://www.researchgate.net/publication/362039222 |journal=Critical Sociology |language=en |volume=49 |issue=4–5 |pages=669–687 |doi=10.1177/08969205221109869 |issn=0896-9205}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Albright |first=Madeleine |author-link=Madeleine Albright |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Zzs2DwAAQBAJ |title=Fascism: a warning |date=2018 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-00-828227-1 |location=London |oclc=1031976003}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Alcalde |first=Ángel |date=May 2020 |title=The Transnational Consensus: Fascism and Nazism in Current Research |journal=] |volume=29 |issue=2 |pages=243–252 |doi=10.1017/S0960777320000089 |issn=0960-7773 |s2cid=213889043}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=Berezin |first=Mabel |date=30 July 2019 |title=Fascism and Populism: Are They Useful Categories for Comparative Sociological Analysis? |journal=Annual Review of Sociology |language=en |volume=45 |issue=1 |pages=345–361 |doi=10.1146/annurev-soc-073018-022351 |issn=0360-0572 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| * {{Cite magazine |last=Churchwell |first=Sarah |date=22 June 2020 |title=American Fascism: It Has Happened Here |url=http://termushistory.pbworks.com/w/file/fetch/140610243/Fascism%20in%20America%20today%20-%20New%20York%20Review%20of%20Books.pdf |magazine=] |page=22 |issn=0028-7504}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last1=Esposito |first1=Fernando |last2=Zentrum Für Zeithistorische Forschung Potsdam |date=August 2017 |title=Fascism – Concepts and Theories |url=https://docupedia.de/zg/Esposito_fascism_v1_en_2017 |journal=Docupedia-Zeitgeschichte |language=en |volume=31 |doi=10.14765/ZZF.DOK.2.1111.V1 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Finchelstein |first=Federico |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=h4qdDwAAQBAJ |title=From Fascism to populism in history: with a new preface |date=2019 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-520-30935-7 |location=Oakland, California}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=qoFTCgAAQBAJ |title=Rethinking antifascism: history, memory and political uses, 1922 to the present |date=2016 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-78533-138-1 |location=New York (N.Y.)}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Hayes |first=Paul M. |author-link=Paul Hayes (historian) |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CoXxDwAAQBAJ |title=Fascism |date=2016 |publisher=] |isbn=978-1-138-93837-3 |series=Routledge library editions Racism and fascism |location=London}} | |||
| * {{Cite web |last=Illing |first=Sean |date=19 September 2018 |title=How Fascism Works: A Yale philosopher on fascism, truth, and Donald Trump |url=https://www.vox.com/2018/9/19/17847110/how-fascism-works-donald-trump-jason-stanley |website=]}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last1=Joes |first1=Anthony James |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=GKubDwAAQBAJ |title=Fascism in the contemporary world: ideology, evolution, resurgence |last2=Gregor |first2=A. James |date=2019 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-367-01749-1 |location=London; New York}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Kagan |first=Robert |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=es6gDwAAQBAJ |title=Ideals and ideologies: a reader |date=2020 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-367-23504-8 |editor-last=Ball |editor-first=Terence |edition=11th |location=New York |pages=369–371 |chapter=This is how fascism comes to America |editor-last2=Dagger |editor-first2=Richard |editor-last3=O'Neill |editor-first3=Daniel L |chapter-url=https://www.salidalibrary.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/04/How-Fascism-Comes-To-America-Bob-Kagan.pdf}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Kuklick |first=Bruce |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=CwGWEAAAQBAJ |title=Fascism comes to America: a century of obsession in politics and culture |date=2022 |publisher=] |isbn=978-0-226-82146-7 |location=Chicago; London}} | |||
| * {{Cite journal |last=McGaughey |first=Ewan |date=30 December 2018 |title=Fascism-lite in America (or The Social Ideal of Donald Trump) |journal=] |volume=7 |issue=2 |pages=291–315 |doi=10.2478/bjals-2018-0012 |issn=2049-4092 |s2cid=195842347 |ssrn=2773217 |doi-access=free}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Riley |first=Dylan J. |author-link=Dylan John Riley |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=Lc_KTSUOQPkC |title=The civic foundations of fascism in Europe: Italy, Spain, and Romania, 1870-1945 |publisher=] |year=2010 |isbn=978-0-8018-9427-5 |location=Baltimore |oclc=370387631}} | |||
| * {{Cite book |last=Stanley |first=Jason |url=https://books.google.com/books?id=oYsPEQAAQBAJ |title=Erasing history: how fascists rewrite the past to control the future |date=2024 |publisher=One Signal Publishers |isbn=978-1-6680-5691-2 |location=New York |oclc=on1450005012}} | |||
| * {{Cite magazine |last=Wiskemann |first=Elizabeth |author-link=Elizabeth Wiskemann |date=December 1967 |title=The Origins of Fascism |url=https://www.historytoday.com/archive/origins-fascism |magazine=] |pages=812–818 |volume=17 |issue=12}} | |||
| {{refend}} | |||
| ==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| {{Wiktionary|fascism}} | {{Wiktionary|fascism}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Wikiquote}} | ||
| {{ |
{{Commons category|Fascism}} | ||
| * {{Britannica|202210}} | |||
| * | |||
| * {{Internet Archive author|sname=Fascism}} | |||
| * | |||
| * by Benito Mussolini (1932) {{in lang|en}} | |||
| {{Ideologies}} | |||
| * (PDF) media.wix.com | |||
| {{fascism footer}} | |||
| * ] | |||
| * – ]'s list of 14 characteristics of Fascism, originally published 1995 | |||
| {{fascism}} | |||
| ] | |||
| {{navboxes | |||
| ] | |||
| |list= | |||
| {{nazism}} | |||
| {{ideologies}} | |||
| {{political philosophy}} | |||
| {{authoritarian types of rule}} | |||
| {{World topic| prefix = Fascism in | title= ] |noredlinks=yes}} | |||
| {{Continent topic| prefix= Fascism in | title = ] }} | |||
| }} | |||
| {{authority control}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | ] | ||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| {{Link GA|de}} | |||
| {{Link GA|zh}} | |||
| {{Link FA|es}} | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
| ] | |||
Latest revision as of 07:27, 6 January 2025
Far-right, authoritarian, ultranationalistic political ideology For other uses, see Fascism (disambiguation).

Fascism (/ˈfæʃɪzəm/ FASH-iz-əm) is a far-right, authoritarian, and ultranationalist political ideology and movement, characterized by a dictatorial leader, centralized autocracy, militarism, forcible suppression of opposition, belief in a natural social hierarchy, subordination of individual interests for the perceived good of the nation or race, and strong regimentation of society and the economy. Opposed to anarchism, democracy, pluralism, egalitarianism, liberalism, socialism, and Marxism, fascism is at the far right of the traditional left–right spectrum.
Fascism rose to prominence in early-20th-century Europe. The first fascist movements emerged in Italy during World War I, before spreading to other European countries, most notably Germany. Fascism also had adherents outside of Europe. Fascists saw World War I as a revolution that brought massive changes to the nature of war, society, the state, and technology. The advent of total war and the mass mobilization of society erased the distinction between civilians and combatants. A military citizenship arose, in which all citizens were involved with the military in some manner. The war resulted in the rise of a powerful state capable of mobilizing millions of people to serve on the front lines, providing logistics to support them, and having unprecedented authority to intervene in the lives of citizens.
Fascism rejects the view that violence is inherently negative or pointless but rather views imperialism, political violence, and war as means to national rejuvenation. Fascists often advocate for the establishment of a totalitarian one-party state, and for a dirigiste economy (a market economy in which the state plays a strong directive role through economic interventionist policies), with the principal goal of achieving autarky (national economic self-sufficiency). Fascism's extreme authoritarianism and nationalism centres around the own group, but that can manifest as a belief in Manifest Destiny, revival of historical greatness (like Mussolini seeking to restore the Roman Empire) or in case of Nazism, racial purity or a master race which blended with some variant of racism or discrimination against a demonized "Other", such as Jews, homosexuals, transgender people, ethnic minorities, or immigrants. These ideas have motivated fascist regimes to commit massacres, forced sterilizations, deportations, and genocides. During World War II, the genocidal and imperialist ambitions of the fascist Axis powers resulted in the murder of millions of people.
Since the end of World War II in 1945, fascism has been largely disgraced, and few parties have openly described themselves as fascist; the term is often used pejoratively by political opponents. The descriptions neo-fascist or post-fascist are sometimes applied to contemporary parties with ideologies similar to, or rooted in, 20th-century fascist movements. Some opposition groups have adopted the label anti-fascist (often shortened to antifa) to signify their stance.
Etymology

The Italian term fascismo is derived from fascio, meaning 'bundle of sticks', ultimately from the Latin word fasces. This was the name given to political organizations in Italy known as fasci, groups similar to guilds or syndicates. According to Italian fascist dictator Benito Mussolini's own account, the Fasces of Revolutionary Action were founded in Italy in 1915. In 1919, Mussolini founded the Italian Fasces of Combat in Milan, which became the National Fascist Party two years later. The fascists came to associate the term with the ancient Roman fasces or fascio littorio, a bundle of rods tied around an axe, an ancient Roman symbol of the authority of the civic magistrate, carried by his lictors. The symbolism of the fasces suggested strength through unity: a single rod is easily broken, while the bundle is difficult to break. Similar symbols were developed by different fascist movements; for example, the symbol of Falangism is five arrows joined by a yoke.
Definitions
Main article: Definitions of fascismHistorian Ian Kershaw once wrote that "trying to define 'fascism' is like trying to nail jelly to the wall." Each group described as "fascist" has at least some unique elements, and frequently definitions of "fascism" have been criticized as either too broad or too narrow. According to many scholars, fascists—especially when they're in power—have historically attacked communism, conservatism, and parliamentary liberalism, attracting support primarily from the far-right.
Historian Stanley G. Payne's definition is frequently cited as standard by notable scholars, such as Roger Griffin, Randall Schweller, Bo Rothstein, Federico Finchelstein, and Stephen D. Shenfield, His definition of fascism focuses on three concepts:
- "Fascist negations" – anti-liberalism, anti-communism, and anti-conservatism.
- "Fascist goals" – the creation of a nationalist dictatorship to regulate economic structure and to transform social relations within a modern, self-determined culture, and the expansion of the nation into an empire.
- "Fascist style" – a political aesthetic of romantic symbolism, mass mobilization, a positive view of violence, and promotion of masculinity, youth, and charismatic authoritarian leadership.
Umberto Eco lists fourteen "features that are typical of what would like to call 'Ur-Fascism', or 'Eternal Fascism'. These features cannot be organized into a system; many of them contradict each other, and are also typical of other kinds of despotism or fanaticism. But it is enough that one of them be present to allow fascism to coagulate around it." Historian John Lukacs argues that there is no such thing as generic fascism. He claims that Nazism and communism are essentially manifestations of populism, and that states such as Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy are more different from each other than they are similar.

In his book How Fascism Works: The Politics of Us and Them (2018), Jason Stanley defined fascism thusly:
cult of the leader who promises national restoration in the face of humiliation brought on by supposed communists, Marxists and minorities and immigrants who are supposedly posing a threat to the character and the history of a nation ... The leader proposes that only he can solve it and all of his political opponents are enemies or traitors.
Stanley says recent global events as of 2020, including the COVID-19 pandemic and the 2020–2022 United States racial unrest, have substantiated his concern about how fascist rhetoric is showing up in politics and policies around the world.
Roger Griffin describes fascism as "a genus of political ideology whose mythic core in its various permutations is a palingenetic form of populist ultranationalism." Without palingenetic ultranationalism, there is no "genuine fascism" according to Griffin. Griffin further describes fascism as having three core components: "(i) the rebirth myth, (ii) populist ultra-nationalism, and (iii) the myth of decadence." In Griffin's view, fascism is "a genuinely revolutionary, trans-class form of anti-liberal, and in the last analysis, anti-conservative nationalism" built on a complex range of theoretical and cultural influences. He distinguishes an inter-war period in which it manifested itself in elite-led but populist "armed party" politics opposing socialism and liberalism, and promising radical politics to rescue the nation from decadence.
Kershaw argues that the difference between fascism and other forms of right-wing authoritarianism in the interwar period is that the latter generally aimed "to conserve the existing social order", whereas fascism was "revolutionary", seeking to change society and obtain "total commitment" from the population. In Against the Fascist Creep, Alexander Reid Ross writes regarding Griffin's view: "Following the Cold War and shifts in fascist organizing techniques, a number of scholars have moved toward the minimalist 'new consensus' refined by Roger Griffin: 'the mythic core' of fascism is 'a populist form of palingenetic ultranationalism.' That means that fascism is an ideology that draws on old, ancient, and even arcane myths of racial, cultural, ethnic, and national origins to develop a plan for the 'new man.'" Griffin himself explored this 'mythic' or 'eliminable' core of fascism with his concept of post-fascism to explore the continuation of Nazism in the modern era. Additionally, other historians have applied this minimalist core to explore proto-fascist movements.
Cas Mudde and Cristóbal Rovira Kaltwasser argue that although fascism "flirted with populism ... in an attempt to generate mass support", it is better seen as an elitist ideology. They cite in particular its exaltation of the Leader, the race, and the state, rather than the people. They see populism as a "thin-centered ideology" with a "restricted morphology" that necessarily becomes attached to "thick-centered" ideologies such as fascism, liberalism, or socialism. Thus populism can be found as an aspect of many specific ideologies, without necessarily being a defining characteristic of those ideologies. They refer to the combination of populism, authoritarianism and ultranationalism as "a marriage of convenience".
Robert Paxton says:
a form of political behavior marked by obsessive preoccupation with community decline, humiliation, or victimhood and by compensatory cults of unity, energy, and purity, in which a mass-based party of committed nationalist militants, working in uneasy but effective collaboration with traditional elites, abandons democratic liberties and pursues with redemptive violence and without ethical or legal restraints goals of internal cleansing and external expansion.
Roger Eatwell defines fascism as "an ideology that strives to forge social rebirth based on a holistic-national radical Third Way", while Walter Laqueur sees the core tenets of fascism as "self-evident: nationalism; social Darwinism; racialism, the need for leadership, a new aristocracy, and obedience; and the negation of the ideals of the Enlightenment and the French Revolution."
Historian Emilio Gentile has defined fascism thusly:
modern political phenomenon, revolutionary, anti-liberal, and anti-Marxist, organized in a militia party with a totalitarian conception of politics and the state, an activist and anti-theoretical ideology, with a mythical, virilistic and anti-hedonistic foundation, sacralized as a secular religion, which affirms the absolute primacy of the nation, understood as an ethnically homogeneous organic community, hierarchically organized in a corporate state, with a bellicose vocation to the politics of greatness, power, and conquest aimed at creating a new order and a new civilization.
Historian and cultural critic Ruth Ben-Ghiat has described fascism as "the original phase of authoritarianism, along with early communism, when a population has undergone huge dislocations or they perceive that there's been changes in society that are very rapid, too rapid for their taste".
Racism was a key feature of German fascism, for which the Holocaust was a high priority. According to The Historiography of Genocide, "In dealing with the Holocaust, it is the consensus of historians that Nazi Germany targeted Jews as a race, not as a religious group." Several historians, such as Umberto Eco, Kevin Passmore, and Moyra Grant, stress racism as a characteristic component of German fascism. Historian Robert Soucy stated that "Hitler envisioned the ideal German society as a Volksgemeinschaft, a racially unified and hierarchically organized body in which the interests of individuals would be strictly subordinate to those of the nation, or Volk." Kershaw noted that common factors of fascism included "the 'cleansing' of all those deemed not to belong—foreigners, ethnic minorities, 'undesirables'" and belief in its own nation's superiority, even if it was not biological racism like in Nazism. Fascist philosophies vary by application, but remain distinct by one theoretical commonality: all traditionally fall into the far-right sector of any political spectrum, catalyzed by afflicted class identities over conventional social inequities.
According to the Council on Foreign Relations, many experts see fascism as a mass political movement centered around extreme nationalism, militarism, and the placement of national interests above those of the individual. Fascist regimes often advocate for the overthrow of institutions that they view as "liberal decay" while simultaneously promoting traditional values. They believe in the supremacy of certain peoples and use it to justify the persecution of other groups. Fascist leaders often maintain a cult of personality and seek to generate enthusiasm for the regime by rallying massive crowds. This contrasts with authoritarian governments, which also centralize power and suppress dissent, but want their subjects to remain passive and demobilized.
Position on the political spectrum

Scholars place fascism on the far right of the political spectrum. Such scholarship focuses on its social conservatism and its authoritarian means of opposing egalitarianism. Roderick Stackelberg places fascism—including Nazism, which he says is "a radical variant of fascism"—on the political right by explaining: "The more a person deems absolute equality among all people to be a desirable condition, the further left he or she will be on the ideological spectrum. The more a person considers inequality to be unavoidable or even desirable, the further to the right he or she will be."
Fascism's origins are complex and include many seemingly contradictory viewpoints, ultimately centered on a mythos of national rebirth from decadence. Fascism was founded during World War I by Italian national syndicalists who drew upon both left-wing organizational tactics and right-wing political views. Italian fascism gravitated to the right in the early 1920s. A major element of fascist ideology that has been deemed to be far right is its stated goal to promote the right of a supposedly superior people to dominate, while purging society of supposedly inferior elements.
In the 1920s, Mussolini and Giovanni Gentile described their ideology as right-wing in the political essay The Doctrine of Fascism, stating: "We are free to believe that this is the century of authority, a century tending to the 'right,' a fascist century." Mussolini stated that fascism's position on the political spectrum was not a serious issue for fascists: "ascism, sitting on the right, could also have sat on the mountain of the center. ... These words in any case do not have a fixed and unchanged meaning: they do have a variable subject to location, time and spirit. We don't give a damn about these empty terminologies and we despise those who are terrorized by these words."
Major Italian groups politically on the right, especially rich landowners and big business, feared an uprising by groups on the left, such as sharecroppers and labour unions. They welcomed fascism and supported its violent suppression of opponents on the left. The accommodation of the political right into the Italian Fascist movement in the early 1920s created internal factions within the movement. The "fascist left" included Michele Bianchi, Giuseppe Bottai, Angelo Oliviero Olivetti, Sergio Panunzio, and Edmondo Rossoni, who were committed to advancing national syndicalism as a replacement for parliamentary liberalism in order to modernize the economy and advance the interests of workers and the common people. The "fascist right" included members of the paramilitary Blackshirts and former members of the Italian Nationalist Association (ANI). The Blackshirts wanted to establish fascism as a complete dictatorship, while the former ANI members, including Alfredo Rocco, sought to institute an authoritarian corporatist state to replace the liberal state in Italy while retaining the existing elites. Upon accommodating the political right, there arose a group of monarchist fascists who sought to use fascism to create an absolute monarchy under King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy.
A number of post-World War II fascist movements described themselves as a Third Position outside the traditional political spectrum. Falange Española de las JONS leader José Antonio Primo de Rivera said: "asically the Right stands for the maintenance of an economic structure, albeit an unjust one, while the Left stands for the attempt to subvert that economic structure, even though the subversion thereof would entail the destruction of much that was worthwhile."
Fascist as a pejorative
Main article: Fascist (insult)The term fascist has been used as a pejorative, regarding varying movements across the far right of the political spectrum. George Orwell noted in 1944 that the term had been used to denigrate diverse positions "in internal politics". Orwell said that while fascism is "a political and economic system" that was inconvenient to define, "as used, the word 'Fascism' is almost entirely meaningless. ... almost any English person would accept 'bully' as a synonym for 'Fascist'", and in 1946 wrote that "'Fascism' has now no meaning except in so far as it signifies something not desirable." Richard Griffiths of the University of Wales wrote in 2000 that "fascism" is the "most misused, and over-used word, of our times". Fascist is sometimes applied to post-World War II organizations and ways of thinking that academics more commonly term neo-fascist.
Despite fascist movements' history of anti-communism, Communist states have sometimes been referred to as fascist, typically as an insult. It has been applied to Marxist–Leninist regimes in Cuba under Fidel Castro and Vietnam under Ho Chi Minh. Chinese Marxists used the term to denounce the Soviet Union during the Sino-Soviet split, and the Soviets used the term to denounce Chinese Marxists, in addition to social democracy, coining a new term in social fascism. In the United States, Herbert Matthews of The New York Times asked in 1946: "Should we now place Stalinist Russia in the same category as Hitlerite Germany? Should we say that she is Fascist?" J. Edgar Hoover, longtime FBI director and ardent anti-communist, wrote extensively of red fascism. The Ku Klux Klan in the 1920s was sometimes called fascist. Historian Peter Amann states that, "Undeniably, the Klan had some traits in common with European fascism—chauvinism, racism, a mystique of violence, an affirmation of a certain kind of archaic traditionalism—yet their differences were fundamental ... never envisioned a change of political or economic system."
History
Further information: Fascism and ideologyBackground and 19th-century roots

Early influences that shaped the ideology of fascism have been dated back to ancient Greece. The political culture of ancient Greece and specifically the ancient Greek city state of Sparta under Lycurgus, with its emphasis on militarism and racial purity, were admired by the Nazis. Nazi Führer Adolf Hitler emphasized that Germany should adhere to Hellenic values and culture – particularly that of ancient Sparta.
Georges Valois, founder of the first non-Italian fascist party Faisceau, claimed the roots of fascism stemmed from the late 18th century Jacobin movement, seeing in its totalitarian nature a foreshadowing of the fascist state. Historian George Mosse similarly analyzed fascism as an inheritor of the mass ideology and civil religion of the French Revolution, as well as a result of the brutalization of societies in 1914–1918.
Historians such as Irene Collins and Howard C Payne see Napoleon III, who ran a 'police state' and suppressed the media, as a forerunner of fascism. According to David Thomson, the Italian Risorgimento of 1871 led to the 'nemesis of fascism'. William L Shirer sees a continuity from the views of Fichte and Hegel, through Bismarck, to Hitler; Robert Gerwarth speaks of a 'direct line' from Bismarck to Hitler. Julian Dierkes sees fascism as a 'particularly violent form of imperialism'.
Marcus Garvey, founder and leader of the Universal Negro Improvement Association, insisted that he and his organisation "were the first fascists". In 1938, C. L. R. James wrote "all the things that Hitler was to do so well later, Marcus Garvey was doing in 1920 and 1921".
Fin de siècle era and fusion of Maurrasism with Sorelianism (1880–1914)
See also: National syndicalismThe historian Zeev Sternhell has traced the ideological roots of fascism back to the 1880s and in particular to the fin de siècle theme of that time. The theme was based on a revolt against materialism, rationalism, positivism, bourgeois society, and democracy. The fin-de-siècle generation supported emotionalism, irrationalism, subjectivism, and vitalism. They regarded civilization as being in crisis, requiring a massive and total solution. Their intellectual school considered the individual as only one part of the larger collectivity, which should not be viewed as a numerical sum of atomized individuals. They condemned the rationalistic, liberal individualism of society and the dissolution of social links in bourgeois society.
The fin-de-siècle outlook was influenced by various intellectual developments, including Darwinian biology, Gesamtkunstwerk, Arthur de Gobineau's racialism, Gustave Le Bon's psychology, and the philosophies of Friedrich Nietzsche, Fyodor Dostoyevsky, and Henri Bergson. Social Darwinism, which gained widespread acceptance, made no distinction between physical and social life, and viewed the human condition as being an unceasing struggle to achieve the survival of the fittest. It challenged positivism's claim of deliberate and rational choice as the determining behaviour of humans, with social Darwinism focusing on heredity, race, and environment. Its emphasis on biogroup identity and the role of organic relations within societies fostered the legitimacy and appeal of nationalism. New theories of social and political psychology also rejected the notion of human behaviour being governed by rational choice and instead claimed that emotion was more influential in political issues than reason. Nietzsche's argument that "God is dead" coincided with his attack on the "herd mentality" of Christianity, democracy, and modern collectivism, his concept of the Übermensch, and his advocacy of the will to power as a primordial instinct, were major influences upon many of the fin-de-siècle generation. Bergson's claim of the existence of an élan vital, or vital instinct, centred upon free choice and rejected the processes of materialism and determinism; this challenged Marxism.
 Charles Maurras
Charles Maurras Georges Sorel
Georges Sorel
In his work The Ruling Class (1896), Gaetano Mosca developed the theory that claims that in all societies an "organized minority" would dominate and rule over an "disorganized majority", stating that there are only two classes in society, "the governing" (the organized minority) and "the governed" (the disorganized majority). He claims that the organized nature of the organized minority makes it irresistible to any individual of the disorganized majority.
French nationalist and reactionary monarchist Charles Maurras influenced fascism. Maurras promoted what he called integral nationalism, which called for the organic unity of a nation, and insisted that a powerful monarch was an ideal leader of a nation. Maurras distrusted what he considered the democratic mystification of the popular will that created an impersonal collective subject. He claimed that a powerful monarch was a personified sovereign who could exercise authority to unite a nation's people. Maurras' integral nationalism was idealized by fascists, but modified into a modernized revolutionary form that was devoid of Maurras' monarchism.
Fascist syndicalism
Main article: Fascist syndicalismFrench revolutionary syndicalist Georges Sorel promoted the legitimacy of political violence in his work Reflections on Violence (1908) and other works in which he advocated radical syndicalist action to achieve a revolution to overthrow capitalism and the bourgeoisie through a general strike. In Reflections on Violence, Sorel emphasized need for a revolutionary political religion. Also in his work The Illusions of Progress, Sorel denounced democracy as reactionary, saying "nothing is more aristocratic than democracy." By 1909, after the failure of a syndicalist general strike in France, Sorel and his supporters left the radical left and went to the radical right, where they sought to merge militant Catholicism and French patriotism with their views—advocating anti-republican Christian French patriots as ideal revolutionaries. Initially, Sorel had officially been a revisionist of Marxism, but by 1910 announced his abandonment of socialist literature and claimed in 1914, using an aphorism of Benedetto Croce that "socialism is dead" because of the "decomposition of Marxism". Sorel became a supporter of reactionary Maurrassian nationalism beginning in 1909 that influenced his works. Maurras held interest in merging his nationalist ideals with Sorelian syndicalism, known as Sorelianism, as a means to confront democracy. Maurras stated that "a socialism liberated from the democratic and cosmopolitan element fits nationalism well as a well made glove fits a beautiful hand."
The fusion of Maurrassian nationalism and Sorelian syndicalism influenced radical Italian nationalist Enrico Corradini. Corradini spoke of the need for a nationalist-syndicalist movement, led by elitist aristocrats and anti-democrats who shared a revolutionary syndicalist commitment to direct action and a willingness to fight. Corradini spoke of Italy as being a "proletarian nation" that needed to pursue imperialism in order to challenge the "plutocratic" French and British. Corradini's views were part of a wider set of perceptions within the right-wing Italian Nationalist Association (ANI), which claimed that Italy's economic backwardness was caused by corruption in its political class, liberalism, and division caused by "ignoble socialism".
The ANI held ties and influence among conservatives, Catholics, and the business community. Italian national syndicalists held a common set of principles: the rejection of bourgeois values, democracy, liberalism, Marxism, internationalism, and pacifism, and the promotion of heroism, vitalism, and violence. The ANI claimed that liberal democracy was no longer compatible with the modern world, and advocated a strong state and imperialism. They believed that humans are naturally predatory, and that nations are in a constant struggle in which only the strongest would survive.

Futurism was both an artistic-cultural movement and initially a political movement in Italy led by Filippo Tommaso Marinetti who founded the Manifesto of Futurism (1908), that championed the causes of modernism, action, and political violence as necessary elements of politics while denouncing liberalism and parliamentary politics. Marinetti rejected conventional democracy based on majority rule and egalitarianism, for a new form of democracy, promoting what he described in his work "The Futurist Conception of Democracy" as the following: "We are therefore able to give the directions to create and to dismantle to numbers, to quantity, to the mass, for with us number, quantity and mass will never be—as they are in Germany and Russia—the number, quantity and mass of mediocre men, incapable and indecisive."
Futurism influenced fascism in its emphasis on recognizing the virile nature of violent action and war as being necessities of modern civilization. Marinetti promoted the need of physical training of young men saying that, in male education, gymnastics should take precedence over books. He advocated segregation of the genders because womanly sensibility must not enter men's education, which he claimed must be "lively, bellicose, muscular and violently dynamic."
World War I and its aftermath (1914–1929)

At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, the Italian political left became severely split over its position on the war. The Italian Socialist Party (PSI) opposed the war but a number of Italian revolutionary syndicalists supported war against Germany and Austria-Hungary on the grounds that their reactionary regimes had to be defeated to ensure the success of socialism. Angelo Oliviero Olivetti formed a pro-interventionist fascio called the Revolutionary Fasces of International Action in October 1914. Benito Mussolini upon being expelled from his position as chief editor of the PSI's newspaper Avanti! for his anti-German stance, joined the interventionist cause in a separate fascio. The term "fascism" was first used in 1915 by members of Mussolini's movement, the Fasces of Revolutionary Action.
The first meeting of the Fasces of Revolutionary Action was held on 24 January 1915 when Mussolini declared that it was necessary for Europe to resolve its national problems—including national borders—of Italy and elsewhere "for the ideals of justice and liberty for which oppressed peoples must acquire the right to belong to those national communities from which they descended." Attempts to hold mass meetings were ineffective and the organization was regularly harassed by government authorities and socialists.

Similar political ideas arose in Germany after the outbreak of the war. German sociologist Johann Plenge spoke of the rise of a "National Socialism" in Germany within what he termed the "ideas of 1914" that were a declaration of war against the "ideas of 1789" (the French Revolution). According to Plenge, the "ideas of 1789"—such as the rights of man, democracy, individualism and liberalism—were being rejected in favor of "the ideas of 1914" that included "German values" of duty, discipline, law and order. Plenge believed that racial solidarity (Volksgemeinschaft) would replace class division and that "racial comrades" would unite to create a socialist society in the struggle of "proletarian" Germany against "capitalist" Britain. He believed that the Spirit of 1914 manifested itself in the concept of the People's League of National Socialism. This National Socialism was a form of state socialism that rejected the "idea of boundless freedom" and promoted an economy that would serve the whole of Germany under the leadership of the state. This National Socialism was opposed to capitalism because of the components that were against "the national interest" of Germany but insisted that National Socialism would strive for greater efficiency in the economy. Plenge advocated an authoritarian rational ruling elite to develop National Socialism through a hierarchical technocratic state.
Impact of World War I

Fascists viewed World War I as bringing revolutionary changes in the nature of war, society, the state and technology, as the advent of total war and mass mobilization had broken down the distinction between civilian and combatant, as civilians had become a critical part in economic production for the war effort and thus arose a "military citizenship" in which all citizens were involved to the military in some manner during the war. World War I had resulted in the rise of a powerful state capable of mobilizing millions of people to serve on the front lines or provide economic production and logistics to support those on the front lines, as well as having unprecedented authority to intervene in the lives of citizens. Fascists viewed technological developments of weaponry and the state's total mobilization of its population in the war as symbolizing the beginning of a new era fusing state power with mass politics, technology and particularly the mobilizing myth that they contended had triumphed over the myth of progress and the era of liberalism.
Impact of the Bolshevik Revolution
See also: The Struggle Against Fascism in Germany
The October Revolution of 1917, in which Bolshevik communists led by Vladimir Lenin seized power in Russia, greatly influenced the development of fascism. Leon Trotsky would later formulate a theory of fascism based on a dialectical interpretation of events to analyze the manifestation of Italian fascism and the early emergence of Nazi Germany from 1930 to 1933. In 1917, Mussolini, as leader of the Fasces of Revolutionary Action, praised the October Revolution, but later he became unimpressed with Lenin, regarding him as merely a new version of Tsar Nicholas II. After World War I, fascists commonly campaigned on anti-Marxist agendas.
Liberal opponents of both fascism and the Bolsheviks argue that there are various similarities between the two, including that they believed in the necessity of a vanguard leadership, showed contempt for bourgeois values, and had totalitarian ambitions. In practice, both have commonly emphasized revolutionary action, proletarian nation theories, one-party states, and party-armies; however, both draw clear distinctions from each other both in aims and tactics, with the Bolsheviks emphasizing the need for an organized participatory democracy (Soviet democracy) and an egalitarian, internationalist vision for society based on proletarian internationalism, while fascists emphasized hyper-nationalism and open hostility towards democracy, envisioning a hierarchical social structure as essential to their aims. With the antagonism between anti-interventionist Marxists and pro-interventionist fascists complete by the end of the war, the two sides became irreconcilable. The fascists presented themselves as anti-communists and as especially opposed to the Marxists. In 1919, Mussolini consolidated control over the fascist movement, known as Sansepolcrismo, with the founding of the Italian Fasces of Combat.
Fascist Manifesto and Charter of Carnaro
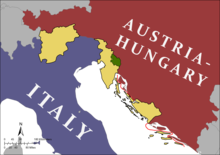
In 1919, Alceste De Ambris and futurist movement leader Filippo Tommaso Marinetti created "The Manifesto of the Italian Fasces of Combat". The Fascist Manifesto was presented on 6 June 1919 in the fascist newspaper Il Popolo d'Italia and supported the creation of universal suffrage, including women's suffrage (the latter being realized only partly in late 1925, with all opposition parties banned or disbanded); proportional representation on a regional basis; government representation through a corporatist system of "National Councils" of experts, selected from professionals and tradespeople, elected to represent and hold legislative power over their respective areas, including labour, industry, transportation, public health, and communications, among others; and abolition of the Senate of the Kingdom of Italy. The Fascist Manifesto supported the creation of an eight-hour work day for all workers, a minimum wage, worker representation in industrial management, equal confidence in labour unions as in industrial executives and public servants, reorganization of the transportation sector, revision of the draft law on invalidity insurance, reduction of the retirement age from 65 to 55, a strong progressive tax on capital, confiscation of the property of religious institutions and abolishment of bishoprics, and revision of military contracts to allow the government to seize 85% of profits. It also called for the fulfillment of expansionist aims in the Balkans and other parts of the Mediterranean, the creation of a short-service national militia to serve defensive duties, nationalization of the armaments industry, and a foreign policy designed to be peaceful but also competitive.

The next events that influenced the fascists in Italy were the raid of Fiume by Italian nationalist Gabriele d'Annunzio and the founding of the Charter of Carnaro in 1920. D'Annunzio and De Ambris designed the Charter, which advocated national-syndicalist corporatist productionism alongside D'Annunzio's political views. Many fascists saw the Charter of Carnaro as an ideal constitution for a fascist Italy. This behaviour of aggression towards Yugoslavia and South Slavs was pursued by Italian fascists with their persecution of South Slavs—especially Slovenes and Croats.
From populism to conservative accommodations
In 1920, militant strike activity by industrial workers reached its peak in Italy and 1919 and 1920 were known as the "Red Year" (Biennio Rosso). Mussolini and the fascists took advantage of the situation by allying with industrial businesses and attacking workers and peasants in the name of preserving order and internal peace in Italy.
Fascists identified their primary opponents as the majority of socialists on the left who had opposed intervention in World War I. The fascists and the Italian political right held common ground: both held Marxism in contempt, discounted class consciousness and believed in the rule of elites. The fascists assisted the anti-socialist campaign by allying with the other parties and the conservative right in a mutual effort to destroy the Italian Socialist Party and labour organizations committed to class identity above national identity.
Fascism sought to accommodate Italian conservatives by making major alterations to its political agenda—abandoning its previous populism, republicanism and anticlericalism, adopting policies in support of free enterprise and accepting the Catholic Church and the monarchy as institutions in Italy. To appeal to Italian conservatives, fascism adopted policies such as promoting family values, including policies designed to reduce the number of women in the workforce—limiting the woman's role to that of a mother. The fascists banned literature on birth control and increased penalties for abortion in 1926, declaring both crimes against the state.
Although fascism adopted a number of anti-modern positions designed to appeal to people upset with the new trends in sexuality and women's rights—especially those with a reactionary point of view—the fascists sought to maintain fascism's revolutionary character, with Angelo Oliviero Olivetti saying: "Fascism would like to be conservative, but it will by being revolutionary." The Fascists supported revolutionary action and committed to secure law and order to appeal to both conservatives and syndicalists.
Prior to fascism's accommodations to the political right, fascism was a small, urban, northern Italian movement that had about a thousand members. After Fascism's accommodation of the political right, the fascist movement's membership soared to approximately 250,000 by 1921. A 2020 article by Daron Acemoğlu, Giuseppe De Feo, Giacomo De Luca, and Gianluca Russo in the Center for Economic and Policy Research, exploring the link between the threat of socialism and Mussolini's rise to power, found "a strong association between the Red Scare in Italy and the subsequent local support for the Fascist Party in the early 1920s." According to the authors, it was local elites and large landowners who played an important role in boosting Fascist Party activity and support, which did not come from socialists' core supporters but from centre-right voters, as they viewed traditional centre-right parties as ineffective in stopping socialism and turned to the Fascists. In 2003, historian Adrian Lyttelton wrote: "The expansion of Fascism in the rural areas was stimulated and directed by the reaction of the farmers and landowners against the peasant leagues of both Socialists and Catholics."
Fascist violence
Beginning in 1922, fascist paramilitaries escalated their strategy from one of attacking socialist offices and the homes of socialist leadership figures, to one of violent occupation of cities. The fascists met little serious resistance from authorities and proceeded to take over several northern Italian cities. The fascists attacked the headquarters of socialist and Catholic labour unions in Cremona and imposed forced Italianization upon the German-speaking population of Bolzano. After seizing these cities, the fascists made plans to take Rome.

On 24 October 1922, the Fascist Party held its annual congress in Naples, where Mussolini ordered Blackshirts to take control of public buildings and trains and to converge on three points around Rome. The Fascists managed to seize control of several post offices and trains in northern Italy while the Italian government, led by a left-wing coalition, was internally divided and unable to respond to the Fascist advances. King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy perceived the risk of bloodshed in Rome in response to attempting to disperse the Fascists to be too high. Victor Emmanuel III decided to appoint Mussolini as Prime Minister of Italy and Mussolini arrived in Rome on 30 October to accept the appointment. Fascist propaganda aggrandized this event, known as "March on Rome", as a "seizure" of power because of Fascists' heroic exploits.
Fascist Italy
Historian Stanley G. Payne says:
primarily political dictatorship. ... The Fascist Party itself had become almost completely bureaucratized and subservient to, not dominant over, the state itself. Big business, industry, and finance retained extensive autonomy, particularly in the early years. The armed forces also enjoyed considerable autonomy. ... The Fascist militia was placed under military control. ... The judicial system was left largely intact and relatively autonomous as well. The police continued to be directed by state officials and were not taken over by party leaders ... nor was a major new police elite created. ... There was never any question of bringing the Church under overall subservience. ... Sizable sectors of Italian cultural life retained extensive autonomy, and no major state propaganda-and-culture ministry existed. ... The Mussolini regime was neither especially sanguinary nor particularly repressive.
Mussolini in power

Upon being appointed Prime Minister of Italy, Mussolini had to form a coalition government because the fascists did not have control over the Italian parliament. Mussolini's coalition government initially pursued economically liberal policies under the direction of liberal finance minister Alberto De Stefani, a member of the Center Party, including balancing the budget through deep cuts to the civil service. Initially, little drastic change in government policy had occurred and repressive police actions were limited.
The fascists began their attempt to entrench fascism in Italy with the Acerbo Law, which guaranteed a plurality of the seats in parliament to any party or coalition list in an election that received 25% or more of the vote. Through considerable fascist violence and intimidation, the list won a majority of the vote, allowing many seats to go to the fascists. In the aftermath of the election, a crisis and political scandal erupted after Socialist Party deputy Giacomo Matteotti was kidnapped and murdered by a Fascist. The liberals and the leftist minority in parliament walked out in protest in what became known as the Aventine Secession. On 3 January 1925, Mussolini addressed the Fascist-dominated Italian parliament and declared that he was personally responsible for what happened, but insisted that he had done nothing wrong. Mussolini proclaimed himself dictator of Italy, assuming full responsibility over the government and announcing the dismissal of parliament. From 1925 to 1929, fascism steadily became entrenched in power: opposition deputies were denied access to parliament, censorship was introduced and a December 1925 decree made Mussolini solely responsible to the King.
Catholic Church
In 1929, the fascist regime briefly gained what was in effect a blessing of the Catholic Church after the regime signed a concordat with the Church, known as the Lateran Treaty, which gave the papacy state sovereignty and financial compensation for the seizure of Church lands by the liberal state in the 19th century, but within two years the Church had renounced fascism in the Encyclical Non Abbiamo Bisogno as a "pagan idolatry of the state" which teaches "hatred, violence and irreverence". Not long after signing the agreement, by Mussolini's own confession, the Church had threatened to have him "excommunicated", in part because of his intractable nature, but also because he had "confiscated more issues of Catholic newspapers in the next three months than in the previous seven years." By the late 1930s, Mussolini became more vocal in his anti-clerical rhetoric, repeatedly denouncing the Catholic Church and discussing ways to depose the pope. He took the position that the "papacy was a malignant tumor in the body of Italy and must 'be rooted out once and for all,' because there was no room in Rome for both the Pope and himself." In her 1974 book, Mussolini's widow Rachele stated that her husband had always been an atheist until near the end of his life, writing that her husband was "basically irreligious until the later years of his life."
The Nazis in Germany employed similar anti-clerical policies. The Gestapo confiscated hundreds of monasteries in Austria and Germany, evicted clergymen and laymen alike and often replaced crosses with swastikas. Referring to the swastika as "the Devil's Cross", church leaders found their youth organizations banned, their meetings limited and various Catholic periodicals censored or banned. Government officials eventually found it necessary to place "Nazis into editorial positions in the Catholic press." Up to 2,720 clerics, mostly Catholics, were arrested by the Gestapo and imprisoned inside of Germany's Dachau concentration camp, resulting in over 1,000 deaths.
Corporatist economic system
The fascist regime created a corporatist economic system in 1925 with creation of the Palazzo Vidoni Pact, in which the Italian employers' association Confindustria and fascist trade unions agreed to recognize each other as the sole representatives of Italy's employers and employees, excluding non-fascist trade unions. The Fascist regime first created a Ministry of Corporations that organized the Italian economy into 22 sectoral corporations, banned workers' strikes and lock-outs and in 1927 created the Charter of Labour, which established workers' rights and duties and created labour tribunals to arbitrate employer-employee disputes. In practice, the sectoral corporations exercised little independence and were largely controlled by the regime, and the employee organizations were rarely led by employees themselves, but instead by appointed Fascist party members.
Aggressive foreign policy
In the 1920s, Fascist Italy pursued an aggressive foreign policy that included ambitions to expand Italian territory. In response to revolt in the Italian colony of Libya, Fascist Italy abandoned previous liberal-era colonial policy of cooperation with local leaders. Instead, claiming that Italians were a superior race to African races and thereby had the right to colonize the "inferior" Africans, it sought to settle 10 to 15 million Italians in Libya. This resulted in an aggressive military campaign known as the Pacification of Libya against natives in Libya, including mass killings, the use of concentration camps and the forced starvation of thousands of people. Italian authorities committed ethnic cleansing by forcibly expelling 100,000 Bedouin Cyrenaicans, half the population of Cyrenaica in Libya, from their settlements that was slated to be given to Italian settlers.
Nazi adoption of the Italian model

The March on Rome brought fascism international attention. One early admirer of the Italian fascists was Adolf Hitler, who less than a month after the March had begun to model himself and the Nazi Party upon Mussolini and the Fascists. The Nazis, led by Hitler and the German war hero Erich Ludendorff, attempted a "March on Berlin" modeled upon the March on Rome, which resulted in the failed Beer Hall Putsch in Munich in November 1923.
International impact of the Great Depression and buildup to World War II
The conditions of economic hardship caused by the Great Depression brought about an international surge of social unrest. Fascist propaganda blamed the problems of the long depression of the 1930s on minorities and scapegoats: "Judeo-Masonic-bolshevik" conspiracies, left-wing internationalism and the presence of immigrants.
In Germany, it contributed to the rise of the Nazi Party, which resulted in the demise of the Weimar Republic and the establishment of the fascist regime, Nazi Germany, under the leadership of Adolf Hitler. With the rise of Hitler and the Nazis to power in 1933, liberal democracy was dissolved in Germany and the Nazis mobilized the country for war, with expansionist territorial aims against several countries. In the 1930s, the Nazis implemented racial laws that deliberately discriminated against, disenfranchised and persecuted Jews and other racial and minority groups.
Fascist movements grew in strength elsewhere in Europe. Hungarian fascist Gyula Gömbös rose to power as Prime Minister of Hungary in 1932 and attempted to entrench his Party of National Unity throughout the country. He created an eight-hour work day and a forty-eight-hour work week in industry; sought to entrench a corporatist economy; and pursued irredentist claims on Hungary's neighbors. The fascist Iron Guard movement in Romania soared in political support after 1933, gaining representation in the Romanian government, and an Iron Guard member assassinated Romanian prime minister Ion Duca. The Iron Guard was the only fascist movement outside Germany and Italy to come to power without foreign assistance. During the 6 February 1934 crisis, France faced the greatest domestic political turmoil since the Dreyfus Affair when the fascist Francist Movement and multiple far-right movements rioted en masse in Paris against the French government resulting in major political violence. A variety of para-fascist governments that borrowed elements from fascism were formed during the Great Depression, including those of Greece, Lithuania, Poland and Yugoslavia. In the Netherlands, the National Socialist Movement in the Netherlands was at its height in the 1930s due to the Great Depression, especially in 1935 when it won almost eight percent of votes, until the year 1937.

In the Americas, the Brazilian Integralists led by Plínio Salgado claimed as many as 200,000 members, although following coup attempts it faced a crackdown from the Estado Novo of Getúlio Vargas in 1937. In Peru, the fascist Revolutionary Union was a fascist political party which was in power 1931 to 1933. In the 1930s, the National Socialist Movement of Chile gained seats in Chile's parliament and attempted a coup d'état that resulted in the Seguro Obrero massacre of 1938.
During the Great Depression, Mussolini promoted active state intervention in the economy. He denounced the contemporary "supercapitalism" that he claimed began in 1914 as a failure because of its alleged decadence, its support for unlimited consumerism, and its intention to create the "standardization of humankind." Fascist Italy created the Institute for Industrial Reconstruction (IRI), a giant state-owned firm and holding company that provided state funding to failing private enterprises. The IRI was made a permanent institution in Fascist Italy in 1937, pursued fascist policies to create national autarky and had the power to take over private firms to maximize war production. While Hitler's regime only nationalized 500 companies in key industries by the early 1940s, Mussolini declared in 1934 that "hree-fourths of Italian economy, industrial and agricultural, is in the hands of the state."
Due to the worldwide depression, Mussolini's government was able to take over most of Italy's largest failing banks, who held controlling interest in many Italian businesses. The Institute for Industrial Reconstruction, a state-operated holding company in charge of bankrupt banks and companies, reported in early 1934 that they held assets of "48.5 percent of the share capital of Italy", which later included the capital of the banks themselves. Political historian Martin Blinkhorn estimated Italy's scope of state intervention and ownership "greatly surpassed that in Nazi Germany, giving Italy a public sector second only to that of Stalin's Russia." In the late 1930s, Italy enacted manufacturing cartels, tariff barriers, currency restrictions and massive regulation of the economy to attempt to balance payments. Italy's policy of autarky failed to achieve effective economic autonomy. Nazi Germany similarly pursued an economic agenda with the aims of autarky and rearmament and imposed protectionist policies, including forcing the German steel industry to use lower-quality German iron ore rather than superior-quality imported iron.
World War II (1939–1945)

In Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany, both Mussolini and Hitler pursued territorial expansionist and interventionist foreign policy agendas from the 1930s through the 1940s culminating in World War II. From 1935 to 1939, Germany and Italy escalated their demands for territorial claims and greater influence in world affairs. Italy invaded Ethiopia in 1935 resulting in its condemnation by the League of Nations and its widespread diplomatic isolation. In 1936, Germany remilitarized the industrial Rhineland, a region that had been ordered demilitarized by the Treaty of Versailles. In 1938, Germany annexed Austria and Italy assisted Germany in resolving the diplomatic crisis between Germany versus Britain and France over claims on Czechoslovakia by arranging the Munich Agreement that gave Germany the Sudetenland and was perceived at the time to have averted a European war. These hopes faded when Czechoslovakia was dissolved by the proclamation of the German client state of Slovakia, followed by the next day of the occupation of the remaining Czech Lands and the proclamation of the German Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia. At the same time from 1938 to 1939, Italy was demanding territorial and colonial concessions from France and Britain. In 1939, Germany prepared for war with Poland, but attempted to gain territorial concessions from Poland through diplomatic means. The Polish government did not trust Hitler's promises and refused to accept Germany's demands.

The invasion of Poland by Germany was deemed unacceptable by Britain, France and their allies, leading to their mutual declaration of war against Germany and the start of World War II. In 1940, Mussolini led Italy into World War II on the side of the Axis. During World War II, the Axis Powers in Europe led by Nazi Germany participated in the extermination of millions of Poles, Jews, Gypsies and others in the genocide known as the Holocaust. In 1943, after Italy faced multiple military failures, the complete reliance and subordination of Italy to Germany, the Allied invasion of Italy and the corresponding international humiliation, Mussolini was removed as head of government and arrested on the order of King Victor Emmanuel III, who proceeded to dismantle the Fascist state and declared Italy's switching of allegiance to the Allied side. Mussolini was rescued from arrest by German forces and led the German client state, the Italian Social Republic from 1943 to 1945. Nazi Germany faced multiple losses and steady Soviet and Western Allied offensives from 1943 to 1945.
On 28 April 1945, Mussolini was captured and executed by Italian communist partisans. On 30 April 1945, Hitler committed suicide. Shortly afterwards, Germany surrendered and the Nazi regime was systematically dismantled by the occupying Allied powers. An International Military Tribunal was subsequently convened in Nuremberg. Beginning in November 1945 and lasting through 1949, numerous Nazi political, military and economic leaders were tried and convicted of war crimes, with many of the worst offenders being sentenced to death and executed.
Post-World War II (1945–2008)
Main article: Neo-fascism
The victory of the Allies over the Axis powers in World War II led to the collapse of many fascist regimes in Europe. The Nuremberg Trials convicted several Nazi leaders of crimes against humanity involving the Holocaust. However, there remained several movements and governments that were ideologically related to fascism.
Francisco Franco's Falangist one-party state in Spain was officially neutral during World War II, although Franco's rise to power had been directly assisted by the militaries of Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany during the Spanish Civil War. The first years were characterized by a repression against the anti-fascist ideologies, deep censorship and the suppression of democratic institutions (elected Parliament, Spanish Constitution of 1931, Regional Statutes of Autonomy). After World War II and a period of international isolation, Franco's regime normalized relations with the Western powers during the Cold War, until Franco's death in 1975 and the transformation of Spain into a liberal democracy.
Historian Robert Paxton observes that one of the main problems in defining fascism is that it was widely mimicked. Paxton says: "In fascism's heyday, in the 1930s, many regimes that were not functionally fascist borrowed elements of fascist decor in order to lend themselves an aura of force, vitality, and mass mobilization." He goes on to observe that Salazar "crushed Portuguese fascism after he had copied some of its techniques of popular mobilization." Paxton says: "Where Franco subjected Spain's fascist party to his personal control, Salazar abolished outright in July 1934 the nearest thing Portugal had to an authentic fascist movement, Rolão Preto's blue-shirted National Syndicalists. ... Salazar preferred to control his population through such 'organic' institutions traditionally powerful in Portugal as the Church. Salazar's regime was not only non-fascist, but 'voluntarily non-totalitarian,' preferring to let those of its citizens who kept out of politics 'live by habit.'" However, historians tend to view the Estado Novo as para-fascist in nature, possessing minimal fascist tendencies. Other historians, including Fernando Rosas and Manuel Villaverde Cabral, think that the Estado Novo should be considered fascist.

The term neo-fascism refers to fascist movements after World War II. In Italy, the Italian Social Movement led by Giorgio Almirante was a major neo-fascist movement that transformed itself into a self-described "post-fascist" movement called the National Alliance (AN), which has been an ally of Silvio Berlusconi's Forza Italia for a decade. In 2008, AN joined Forza Italia in Berlusconi's new party The People of Freedom, but in 2012 a group of politicians split from The People of Freedom, refounding the party with the name Brothers of Italy. In Germany, various neo-Nazi movements have been formed and banned in accordance with Germany's constitutional law which forbids Nazism. The National Democratic Party of Germany (NPD) is widely considered a neo-Nazi party, although the party does not publicly identify itself as such.
In Argentina, Peronism, associated with the regime of Juan Perón from 1946 to 1955 and 1973 to 1974, was influenced by fascism. Between 1939 and 1941, prior to his rise to power, Perón had developed a deep admiration of Italian Fascism and modelled his economic policies on Italian fascist policies. However, not all historians agree with this identification, which they consider debatable or even false, biased by a pejorative political position. Other authors, such as the Israeli Raanan Rein, categorically maintain that Perón was not a fascist and that this characterization was imposed on him because of his defiant stance against US hegemony.
Contemporary fascism (2008–present)
See also: Alt-right, Radical right (United States), and Fascism in the United StatesGreece
Main article: Golden Dawn
After the onset of the Great Recession and economic crisis in Greece, a movement known as the Golden Dawn, widely considered a neo-Nazi party, soared in support out of obscurity and won seats in Greece's parliament, espousing a staunch hostility towards minorities, illegal immigrants and refugees. In 2013, after the murder of an anti-fascist musician by a person with links to Golden Dawn, the Greek government ordered the arrest of Golden Dawn's leader Nikolaos Michaloliakos and other members on charges related to being associated with a criminal organization. On 7 October 2020, Athens Appeals Court announced verdicts for 68 defendants, including the party's political leadership. Nikolaos Michaloliakos and six other prominent members and former members of parliament (MPs) were found guilty of running a criminal organization. Guilty verdicts were delivered on charges of murder, attempted murder, and violent attacks on immigrants and left-wing political opponents.
Post-Soviet Russia
Main articles: Rashism and PutinismMarlene Laruelle, a French political scientist, contends in Is Russia Fascist? that the accusation of "fascist" has evolved into a strategic narrative of the existing world order. Geopolitical rivals might construct their own view of the world and assert the moral high ground by branding ideological rivals as fascists, regardless of their real ideals or deeds. Laruelle discusses the basis, significance, and veracity of accusations of fascism in and around Russia through an analysis of the domestic situation in Russia and the Kremlin's foreign policy justifications; she concludes that Russian efforts to brand its opponents as fascist is ultimately an attempt to determine the future of Russia in Europe as an antifascist force, influenced by its role in fighting fascism in World War II.
According to Alexander J. Motyl, an American historian and political scientist, Russian fascism has the following characteristics:
- An undemocratic political system, different from both traditional authoritarianism and totalitarianism;
- Statism and hypernationalism;
- A hypermasculine cult of the supreme leader (emphasis on his courage, militancy and physical prowess);
- General popular support for the regime and its leader.
Yale historian Timothy Snyder has stated that "Putin's regime is ... the world center of fascism" and has written an article entitled "We Should Say It: Russia Is Fascist." Oxford historian Roger Griffin compared Putin's Russia to the World War II-era Empire of Japan, saying that like Putin's Russia, it "emulated fascism in many ways, but was not fascist." Historian Stanley G. Payne says Putin's Russia "is not equivalent to the fascist regimes of World War II, but it forms the nearest analogue to fascism found in a major country since that time" and argues that Putin's political system is "more a revival of the creed of Tsar Nicholas I in the 19th century that emphasized 'Orthodoxy, autocracy, and nationality' than one resembling the revolutionary, modernizing regimes of Hitler and Mussolini." According to Griffin, fascism is "a revolutionary form of nationalism" seeking to destroy the old system and remake society, and that Putin is a reactionary politician who is not trying to create a new order "but to recreate a modified version of the Soviet Union". German political scientist Andreas Umland said genuine fascists in Russia, like deceased politician Vladimir Zhirinovsky and activist and self-styled philosopher Aleksandr Dugin, "describe in their writings a completely new Russia" controlling parts of the world that were never under tsarist or Soviet domination. According to Marlene Laurelle writing in The Washington Quarterly, "applying the "fascism" label ... to the entirety of the Russian state or society short-circuits our ability to construct a more complex and differentiated picture."
Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty, collecting the opinions of experts on fascism, said that while Russia is repressive and authoritarian, it cannot be classified as a fascist state for various reasons, including Russia's government being more reactionary than revolutionary. In 2023, Oleg Orlov, the chairman of the Board of Human Rights Center "Memorial", claimed that Russia under Vladimir Putin had descended into fascism and that the army is committing "mass murder". On 7 March 2024, in his 2024 State of the Union Address, American President Joe Biden compared Russia under Vladimir Putin to Adolf Hitler's conquests of Europe.
Tenets
Robert O. Paxton finds that even though fascism "maintained the existing regime of property and social hierarchy", it cannot be considered "simply a more muscular form of conservatism" because "fascism in power did carry out some changes profound enough to be called 'revolutionary.'" These transformations "often set fascists into conflict with conservatives rooted in families, churches, social rank, and property." Paxton argues:
fascism redrew the frontiers between private and public, sharply diminishing what had once been untouchably private. It changed the practice of citizenship from the enjoyment of constitutional rights and duties to participation in mass ceremonies of affirmation and conformity. It reconfigured relations between the individual and the collectivity, so that an individual had no rights outside community interest. It expanded the powers of the executive—party and state—in a bid for total control. Finally, it unleashed aggressive emotions hitherto known in Europe only during war or social revolution.
Nationalism with or without expansionism
Ultranationalism, combined with the myth of national rebirth, is a key foundation of fascism. Robert Paxton argues that "a passionate nationalism" is the basis of fascism, combined with "a conspiratorial and Manichean view of history" which holds that "the chosen people have been weakened by political parties, social classes, unassimilable minorities, spoiled rentiers, and rationalist thinkers." Roger Griffin identifies the core of fascism as being palingenetic ultranationalism.
The fascist view of a nation is of a single organic entity that binds people together by their ancestry and is a natural unifying force of people. Fascism seeks to solve economic, political and social problems by achieving a millenarian national rebirth, exalting the nation or race above all else and promoting cults of unity, strength and purity. European fascist movements typically espouse a racist conception of non-Europeans being inferior to Europeans. Beyond this, fascists in Europe have not held a unified set of racial views. Historically, most fascists promoted imperialism, although there have been several fascist movements that were uninterested in the pursuit of new imperial ambitions. For example, Nazism and Italian Fascism were expansionist and irredentist. Falangism in Spain envisioned the worldwide unification of Spanish-speaking peoples (Hispanidad). British Fascism was non-interventionist, though it did embrace the British Empire.
Totalitarianism
Fascism promotes the establishment of a totalitarian state. It opposes liberal democracy, rejects multi-party systems, and may support a one-party state so that it may synthesize with the nation. Mussolini's The Doctrine of Fascism (1932), partly ghostwritten by philosopher Giovanni Gentile, who Mussolini described as "the philosopher of Fascism", states: "The Fascist conception of the State is all-embracing; outside of it no human or spiritual values can exist, much less have value. Thus understood, Fascism is totalitarian, and the Fascist State—a synthesis and a unit inclusive of all values—interprets, develops, and potentiates the whole life of a people." In The Legal Basis of the Total State, Nazi political theorist Carl Schmitt described the Nazi intention to form a "strong state which guarantees a totality of political unity transcending all diversity" in order to avoid a "disastrous pluralism tearing the German people apart."
Fascist states pursued policies of social indoctrination through propaganda in education and the media, and regulation of the production of educational and media materials. Education was designed to glorify the fascist movement and inform students of its historical and political importance to the nation. It attempted to purge ideas that were not consistent with the beliefs of the fascist movement and to teach students to be obedient to the state.
Economy
Main article: Economics of fascismHistorians and other scholars disagree on the question of whether a specifically fascist type of economic policy can be said to exist. David Baker argues that there is an identifiable economic system in fascism that is distinct from those advocated by other ideologies, comprising essential characteristics that fascist nations shared. Payne, Paxton, Sternhell et al. argue that while fascist economies share some similarities, there is no distinctive form of fascist economic organization. Gerald Feldman and Timothy Mason argue that fascism is distinguished by an absence of coherent economic ideology and an absence of serious economic thinking. They state that the decisions taken by fascist leaders cannot be explained within a logical economic framework.
Fascists presented their views as an alternative to both international socialism and free-market capitalism. While fascism opposed mainstream socialism, fascists sometimes regarded their movement as a type of nationalist "socialism" to highlight their commitment to nationalism, describing it as national solidarity and unity. Fascism had a complex relationship with capitalism, both supporting and opposing different aspects of it at different times and in different countries. In general, fascists held an instrumental view of capitalism, regarding it as a tool that may be useful or not, depending on circumstances. Fascists opposed international free market capitalism, but supported a type of productive capitalism. Economic self-sufficiency, known as autarky, was a major goal of most fascist governments.
Fascist governments advocated for the resolution of domestic class conflict within a nation in order to guarantee national unity. This would be done through the state's mediating relations between the classes (contrary to the views of classical liberal-inspired capitalists). While fascism was opposed to domestic class conflict, it held that bourgeois-proletarian conflict existed primarily in international conflict between proletarian nations and bourgeois nations. Fascism condemned what it viewed as widespread character traits that it associated with the typical bourgeois mentality that it opposed, such as: materialism, crassness, cowardice, and the inability to comprehend the heroic ideal of the fascist "warrior"; and associations with liberalism, individualism and parliamentarianism. In 1918, Mussolini defined what he viewed as the proletarian character, defining proletarian as being one and the same with producers, a productivist perspective that associated all people deemed productive, including entrepreneurs, technicians, workers and soldiers as being proletarian.

Because productivism was key to creating a strong nationalist state, it criticized internationalist and Marxist socialism, advocating instead to represent a type of nationalist productivist socialism. Nevertheless, while condemning parasitical capitalism, was willing to accommodate productivist capitalism within it so long as it supported the nationalist objective. The role of productivism was derived from Henri de Saint Simon, whose ideas inspired the creation of utopian socialism and influenced other ideologies, that stressed solidarity rather than class war and whose conception of productive people in the economy included both productive workers and productive bosses to challenge the influence of the aristocracy and unproductive financial speculators. Saint Simon's vision combined the traditionalist right-wing criticisms of the French Revolution with a left-wing belief in the need for association or collaboration of productive people in society. Whereas Marxism condemned capitalism as a system of exploitative property relations, fascism saw the nature of the control of credit and money in the contemporary capitalist system as abusive.
Unlike Marxism, fascism did not see class conflict between the Marxist-defined proletariat and the bourgeoisie as a given or as an engine of historical materialism. Instead, it viewed workers and productive capitalists in common as productive people who were in conflict with parasitic elements in society including: corrupt political parties, corrupt financial capital and feeble people. Fascist leaders such as Mussolini and Hitler spoke of the need to create a new managerial elite led by engineers and captains of industry—but free from the parasitic leadership of industries. Hitler stated that the Nazi Party supported bodenständigen Kapitalismus ("productive capitalism") that was based upon profit earned from one's own labour, but condemned unproductive capitalism or loan capitalism, which derived profit from speculation.
Fascist economics supported a state-controlled economy that accepted a mix of private and public ownership over the means of production. Economic planning was applied to both the public and private sector and the prosperity of private enterprise depended on its acceptance of synchronizing itself with the economic goals of the state. Fascist economic ideology supported the profit motive, but emphasized that industries must uphold the national interest as superior to private profit.
While fascism accepted the importance of material wealth and power, it condemned materialism which identified as being present in both communism and capitalism and criticized materialism for lacking acknowledgement of the role of the spirit. In particular, fascists criticized capitalism, not because of its competitive nature nor support of private property, which fascists supported—but due to its materialism, individualism, alleged bourgeois decadence and alleged indifference to the nation. Fascism denounced Marxism for its advocacy of materialist internationalist class identity, which fascists regarded as an attack upon the emotional and spiritual bonds of the nation and a threat to the achievement of genuine national solidarity.
In discussing the spread of fascism beyond Italy, historian Philip Morgan states:
Since the Depression was a crisis of laissez-faire capitalism and its political counterpart, parliamentary democracy, fascism could pose as the 'third-way' alternative between capitalism and Bolshevism, the model of a new European 'civilization.' As Mussolini typically put it in early 1934, 'from 1929 ... fascism has become a universal phenomenon ... The dominant forces of the 19th century, democracy, socialism, liberalism have been exhausted ... the new political and economic forms of the twentieth-century are fascist'.
Fascists criticized egalitarianism as preserving the weak, and they instead promoted social Darwinist views and policies. They were in principle opposed to the idea of social welfare, arguing that it "encouraged the preservation of the degenerate and the feeble." The Nazi Party condemned the welfare system of the Weimar Republic, as well as private charity and philanthropy, for supporting people whom they regarded as racially inferior and weak, and who should have been weeded out in the process of natural selection. Nevertheless, faced with the mass unemployment and poverty of the Great Depression, the Nazis found it necessary to set up charitable institutions to help racially-pure Germans in order to maintain popular support, while arguing that this represented "racial self-help" and not indiscriminate charity or universal social welfare. Thus, Nazi programs such as the Winter Relief of the German People and the broader National Socialist People's Welfare (NSV) were organized as quasi-private institutions, officially relying on private donations from Germans to help others of their race—although in practice those who refused to donate could face severe consequences. Unlike the social welfare institutions of the Weimar Republic and the Christian charities, the NSV distributed assistance on explicitly racial grounds. It provided support only to those who were "racially sound, capable of and willing to work, politically reliable, and willing and able to reproduce." Non-Aryans were excluded, as well as the "work-shy", "asocials" and the "hereditarily ill". Under these conditions, by 1939, over 17 million Germans had obtained assistance from the NSV, and the agency "projected a powerful image of caring and support" for "those who were judged to have got into difficulties through no fault of their own." Yet the organization was "feared and disliked among society's poorest" because it resorted to intrusive questioning and monitoring to judge who was worthy of support.
Direct action
Fascism emphasizes direct action, including supporting the legitimacy of political violence, as a core part of its politics. Fascism views violent action as a necessity in politics that fascism identifies as being an "endless struggle"; this emphasis on the use of political violence means that most fascist parties have also created their own private militias (e.g. the Nazi Party's Brown shirts and Fascist Italy's Blackshirts). The basis of fascism's support of violent action in politics is connected to social Darwinism. Fascist movements have commonly held social Darwinist views of nations, races and societies. They say that nations and races must purge themselves of socially and biologically weak or degenerate people, while simultaneously promoting the creation of strong people, in order to survive in a world defined by perpetual national and racial conflict.
Age and gender roles


Fascism emphasizes youth both in a physical sense of age and in a spiritual sense as related to virility and commitment to action. The Italian Fascists' political anthem was called Giovinezza ("The Youth"). Fascism identifies the physical age period of youth as a critical time for the moral development of people who will affect society. Walter Laqueur argues that "he corollaries of the cult of war and physical danger were the cult of brutality, strength, and sexuality ... a true counter-civilization: rejecting the sophisticated rationalist humanism of Old Europe, fascism sets up as its ideal the primitive instincts and primal emotions of the barbarian."
Italian fascism pursued what it called "moral hygiene" of youth, particularly regarding sexuality. Fascist Italy promoted what it considered normal sexual behaviour in youth while denouncing what it considered deviant sexual behaviour. It condemned pornography, most forms of birth control and contraceptive devices (with the exception of the condom), homosexuality and prostitution as deviant sexual behaviour, although enforcement of laws opposed to such practices was erratic and authorities often turned a blind eye. Fascist Italy regarded the promotion of male sexual excitation before puberty as the cause of criminality amongst male youth, declared homosexuality a social disease and pursued an aggressive campaign to reduce prostitution of young women.
Mussolini perceived women's primary role as primarily child bearers, while that of men as warriors, once saying: "War is to man what maternity is to the woman." In an effort to increase birthrates, the Italian Fascist government gave financial incentives to women who raised large families and initiated policies intended to reduce the number of women employed. Italian Fascism called for women to be honoured as "reproducers of the nation" and the Italian Fascist government held ritual ceremonies to honour women's role within the Italian nation. In 1934, Mussolini declared that employment of women was a "major aspect of the thorny problem of unemployment" and that for women, working was "incompatible with childbearing"; Mussolini went on to say that the solution to unemployment for men was the "exodus of women from the work force."
The German Nazi government strongly encouraged women to stay at home to bear children and keep house. This policy was reinforced by bestowing the Cross of Honor of the German Mother on women bearing four or more children. The unemployment rate was cut substantially, mostly through arms production and sending women home so that men could take their jobs. Nazi propaganda sometimes promoted premarital and extramarital sexual relations, unwed motherhood and divorce, but at other times the Nazis opposed such behaviour.
The Nazis decriminalized abortion in cases where fetuses had hereditary defects or were of a race the government disapproved of, while the abortion of healthy pure German, Aryan fetuses remained strictly forbidden. For non-Aryans, abortion was often compulsory. Their eugenics program also stemmed from the "progressive biomedical model" of Weimar Germany. In 1935, Nazi Germany expanded the legality of abortion by amending its eugenics law, to promote abortion for women with hereditary disorders. The law allowed abortion if a woman gave her permission and the fetus was not yet viable and for purposes of so-called racial hygiene.
The Nazis said that homosexuality was degenerate, effeminate, perverted and undermined masculinity because it did not produce children. They considered homosexuality curable through therapy, citing modern scientism and the study of sexology. Open homosexuals were interned in Nazi concentration camps.
Palingenesis and modernism
Main article: Reactionary modernismFascism emphasizes both palingenesis (national rebirth or re-creation) and modernism. In particular, fascism's nationalism has been identified as having a palingenetic character. Fascism promotes the regeneration of the nation and purging it of decadence. Fascism accepts forms of modernism that it deems promotes national regeneration while rejecting forms of modernism that are regarded as antithetical to national regeneration. Fascism aestheticized modern technology and its association with speed, power and violence. Fascism admired advances in the economy in the early 20th century, particularly Fordism and scientific management. Fascist modernism has been recognized as inspired or developed by various figures—such as Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, Ernst Jünger, Gottfried Benn, Louis-Ferdinand Céline, Knut Hamsun, Ezra Pound and Wyndham Lewis.
In Italy, such modernist influence was exemplified by Marinetti who advocated a palingenetic modernist society that condemned liberal-bourgeois values of tradition and psychology, while promoting a technological-martial religion of national renewal that emphasized militant nationalism. In Germany, it was exemplified by Jünger who was influenced by his observation of the technological warfare during World War I and claimed that a new social class had been created that he described as the "warrior-worker"; Like Marinetti, Jünger emphasized the revolutionary capacities of technology. He emphasized an "organic construction" between human and machine as a liberating and regenerative force that challenged liberal democracy, conceptions of individual autonomy, bourgeois nihilism and decadence. He conceived of a society based on a totalitarian concept of "total mobilization" of such disciplined warrior-workers.
Culture
Aesthetics

In The Work of Art in the Age of Mechanical Reproduction (1935), Walter Benjamin identifies aestheticization of politics as a key ingredient in fascist regimes. On this point he quotes Filippo Tommaso Marinetti, founder of the Futurist art movement and co-author of the Fascist Manifesto (1919), who aestheticizes war in his writings and claims that "war is beautiful."
In Simulacra and Simulation (1981), Jean Baudrillard interprets fascism as a "political aesthetic of death" and a vehement countermovement against the increasing rationalism, secularism, and pacifism of the modern Western world.
The standard definition of fascism, given by Stanley G. Payne, focuses on three concepts, one of which is a "fascist style" with an aesthetic structure of meetings, symbols, and political liturgy, stressing emotional and mystical aspects.
Emilio Gentile argues that fascism expresses itself aesthetically more than theoretically by means of a new political style with myths, rites, and symbols as a lay religion designed to acculturate, socialize, and integrate the faith of the masses with the goal of creating a "new man".
Cultural critic Susan Sontag writes:
Fascist aesthetics ... flow from (and justify) a preoccupation with situations of control, submissive behavior, extravagant effort, and the endurance of pain; they endorse two seemingly opposite states, egomania and servitude. The relations of domination and enslavement take the form of a characteristic pageantry: the massing of groups of people; the turning of people into things; the multiplication or replication of things; and the grouping of people/things around an all-powerful, hypnotic leader-figure or force. The fascist dramaturgy centers on the orgiastic transactions between mighty forces and their puppets, uniformly garbed and shown in ever swelling numbers. Its choreography alternates between ceaseless motion and a congealed, static, 'virile' posing. Fascist art glorifies surrender, it exalts mindlessness, it glamorizes death.
Sontag also enumerates some commonalities between fascist art and the official art of communist countries, such as the obeisance of the masses to the hero, and a preference for the monumental and the "grandiose and rigid" choreography of mass bodies. But whereas official communist art "aims to expound and reinforce a utopian morality", the art of fascist countries such as Nazi Germany "displays a utopian aesthetics – that of physical perfection", in a way that is "both prurient and idealizing".
According to Sontag, fascist aesthetics "is based on the containment of vital forces; movements are confined, held tight, held in." Its appeal is not necessarily limited to those who share the fascist political ideology because fascism "stands for an ideal or rather ideals that are persistent today under the other banners: the ideal of life as art, the cult of beauty, the fetishism of courage, the dissolution of alienation in ecstatic feelings of community; the repudiation of the intellect; the family of man (under the parenthood of leaders)."
Popular culture
Further information: Art in Nazi Germany and Reich Ministry of Public Enlightenment and Propaganda
In Italy, the Mussolini regime created the Direzione Generale per la Cinematografi to encourage film studios to glorify fascism. Italian cinema flourished because the regime stopped the import of Hollywood films in 1938, subsidized domestic production, and kept ticket prices low. It encouraged international distribution to glorify its African empire and to belie the charge that Italy was backward. The regime censored criticism and used the state-run Luce Institute film company to laud the Duce through newsreels, documentaries, and photographs. The regime promoted Italian opera and theatre as well, making sure that political enemies did not have a voice on stage.
In Nazi Germany the new Reich Chamber of Culture was under the control of Joseph Goebbels, Hitler's powerful Reich Minister for Public Enlightenment and Propaganda. The goal was to stimulate the Aryanization of German culture and to prohibit postmodern trends such as surrealism and cubism.
Criticism
Fascist parties were closely contested by anti-fascist movements from the political centre and left wing throughout the Interwar period. The defeat of the Axis powers in World War II and subsequent revelation of the crimes against humanity committed during the Holocaust by Germany have led to an almost universal condemnation of both past and present forms of fascism in the modern era. "Fascism" is today used across the political spectrum as a pejorative or byword for perceived authoritarianism and other forms of political evil.
Anti-democratic and tyrannical
See also: Criticism of democracy
One of the most common and strongest criticisms of fascism is that it is a tyranny. Fascism is deliberately and entirely non-democratic and anti-democratic.
Fascism's extreme authoritarianism and nationalism often manifest as a belief in racial purity or a master race, usually blended with some variant of racism or discrimination against a demonized "Other", such as Jews, homosexuals, transgender people, ethnic minorities, or immigrants. These ideas have motivated fascist regimes to commit massacres, forced sterilizations, deportations, and genocides. During World War II, the genocidal and imperialist ambitions of the fascist Axis powers resulted in the murder of millions of people. Federico Finchelstein wrote that fascism
...encompassed totalitarianism, state terrorism, imperialism, racism and, in the German case, the most radical genocide of the last century: the Holocaust. Fascism, in its many forms, did not hesitate to kill its own citizens as well as its colonial subjects in its search for ideological and political closure. Millions of civilians perished on a global scale during the apogee of fascist ideologies in Europe and beyond.
Unprincipled opportunism
Some critics of Italian fascism have said that much of the ideology was merely a by-product of unprincipled opportunism by Mussolini and that he changed his political stances merely to bolster his personal ambitions while he disguised them as being purposeful to the public. Richard Washburn Child, the American ambassador to Italy who worked with Mussolini and became his friend and admirer, defended Mussolini's opportunistic behaviour by writing:
Opportunist is a term of reproach used to brand men who fit themselves to conditions for the reasons of self-interest. Mussolini, as I have learned to know him, is an opportunist in the sense that he believed that mankind itself must be fitted to changing conditions rather than to fixed theories, no matter how many hopes and prayers have been expended on theories and programmes.
Child quoted Mussolini as saying: "The sanctity of an ism is not in the ism; it has no sanctity beyond its power to do, to work, to succeed in practice. It may have succeeded yesterday and fail to-morrow. Failed yesterday and succeed to-morrow. The machine, first of all, must run!"
Some have criticized Mussolini's actions during the outbreak of World War I as opportunistic for seeming to suddenly abandon Marxist egalitarian internationalism for non-egalitarian nationalism and note, to that effect, that upon Mussolini endorsing Italy's intervention in the war against Germany and Austria-Hungary, he and the new fascist movement received financial support from Italian and foreign sources, such as Ansaldo (an armaments firm) and other companies as well as the British Security Service MI5. Some, including Mussolini's socialist opponents at the time, have noted that regardless of the financial support he accepted for his pro-interventionist stance, Mussolini was free to write whatever he wished in his newspaper Il Popolo d'Italia without prior sanctioning from his financial backers. Furthermore, the major source of financial support that Mussolini and the fascist movement received in World War I was from France and is widely believed to have been French socialists who supported the French government's war against Germany and who sent support to Italian socialists who wanted Italian intervention on France's side.
Mussolini’s transformation away from Marxism into what eventually became fascism began prior to World War I, as Mussolini had grown increasingly pessimistic about Marxism and egalitarianism while becoming increasingly supportive of figures who opposed egalitarianism, such as Friedrich Nietzsche. By 1902, Mussolini was studying Georges Sorel, Nietzsche and Vilfredo Pareto. Sorel's emphasis on the need for overthrowing decadent liberal democracy and capitalism by the use of violence, direct action, general strikes and neo-Machiavellian appeals to emotion impressed Mussolini deeply. Mussolini's use of Nietzsche made him a highly unorthodox socialist, due to Nietzsche's promotion of elitism and anti-egalitarian views. Prior to World War I, Mussolini's writings over time indicated that he had abandoned the Marxism and egalitarianism that he had previously supported in favour of Nietzsche's übermensch concept and anti-egalitarianism. In 1908, Mussolini wrote a short essay called "Philosophy of Strength" based on his Nietzschean influence, in which Mussolini openly spoke fondly of the ramifications of an impending war in Europe in challenging both religion and nihilism: " new kind of free spirit will come, strengthened by the war, ... a spirit equipped with a kind of sublime perversity, ... a new free spirit will triumph over God and over Nothing."
Ideological dishonesty
Fascism has been criticized for being ideologically dishonest. Major examples of ideological dishonesty have been identified in Italian fascism's changing relationship with German Nazism. Fascist Italy's official foreign policy positions commonly used rhetorical ideological hyperbole to justify its actions, although during Dino Grandi's tenure as Italy's foreign minister the country engaged in realpolitik free of such fascist hyperbole. Italian fascism's stance towards German Nazism fluctuated from support from the late 1920s to 1934, when it celebrated Hitler's rise to power and Mussolini's first meeting with Hitler in 1934; to opposition from 1934 to 1936 after the assassination of Italy's allied leader in Austria, Engelbert Dollfuss, by Austrian Nazis; and again back to support after 1936, when Germany was the only significant power that did not denounce Italy's invasion and occupation of Ethiopia.
After antagonism exploded between Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy over the assassination of Austrian Chancellor Dollfuss in 1934, Mussolini and Italian fascists denounced and ridiculed Nazism's racial theories, particularly by denouncing its Nordicism, while promoting Mediterraneanism. Mussolini himself responded to Nordicists' claims of Italy being divided into Nordic and Mediterranean racial areas due to Germanic invasions of Northern Italy by claiming that while Germanic tribes such as the Lombards took control of Italy after the fall of Ancient Rome, they arrived in small numbers (about 8,000) and quickly assimilated into Roman culture and spoke the Latin language within fifty years. Italian fascism was influenced by the tradition of Italian nationalists scornfully looking down upon Nordicists' claims and taking pride in comparing the age and sophistication of ancient Roman civilization as well as the classical revival in the Renaissance to that of Nordic societies that Italian nationalists described as "newcomers" to civilization in comparison. At the height of antagonism between the Nazis and Italian fascists over race, Mussolini claimed that the Germans themselves were not a pure race and noted with irony that the Nazi theory of German racial superiority was based on the theories of non-German foreigners, such as Frenchman Arthur de Gobineau. After the tension in German-Italian relations diminished during the late 1930s, Italian fascism sought to harmonize its ideology with German Nazism and combined Nordicist and Mediterranean racial theories, noting that Italians were members of the Aryan Race, composed of a mixed Nordic-Mediterranean subtype.
In 1938, Mussolini declared upon Italy's adoption of antisemitic laws that Italian fascism had always been antisemitic. However, Italian fascism did not endorse antisemitism until the late 1930s when Mussolini feared alienating antisemitic Nazi Germany, whose power and influence were growing in Europe. Prior to that period, there had been notable Jewish Italians who had been senior Italian fascist officials, including Margherita Sarfatti, who had also been Mussolini's mistress. Also contrary to Mussolini's claim in 1938, only a small number of Italian fascists were staunchly antisemitic (such as Roberto Farinacci and Giuseppe Preziosi), while others such as Italo Balbo, who came from Ferrara which had one of Italy's largest Jewish communities, were disgusted by the antisemitic laws and opposed them. Fascism scholar Mark Neocleous notes that while Italian fascism did not have a clear commitment to antisemitism, there were occasional antisemitic statements issued prior to 1938, such as Mussolini in 1919 declaring that the Jewish bankers in London and New York were connected by race to the Russian Bolsheviks and that eight percent of the Russian Bolsheviks were Jews.
Anti-fascism
Main article: Anti-fascism
Anti-fascism is a political movement in opposition to fascist ideologies, groups and individuals. Beginning in European countries in the 1920s, it was at its most significant shortly before and during World War II, where the Axis powers were opposed by many countries forming the Allies of World War II and dozens of resistance movements worldwide. Anti-fascism has been an element of movements across the political spectrum and holding many different political positions such as anarchism, communism, pacifism, republicanism, social democracy, socialism and syndicalism as well as centrist, conservative, liberal and nationalist viewpoints.
Fascism, a far-right ultra-nationalistic ideology best known for its use by the Italian Fascists and the Nazis, became prominent beginning in the 1910s. Organization against fascism began around 1920. Fascism became the state ideology of Italy in 1922 and of Germany in 1933, spurring a large increase in anti-fascist action, including German resistance to Nazism and the Italian resistance movement. Anti-fascism was a major aspect of the Spanish Civil War, which foreshadowed World War II.
Before World War II, the West had not taken seriously the threat of fascism, and anti-fascism was sometimes associated with communism. However, the outbreak of World War II greatly changed Western perceptions, and fascism was seen as an existential threat by not only the communist Soviet Union but also by the liberal-democratic United States and United Kingdom. The Axis Powers of World War II were generally fascist, and the fight against them was characterized in anti-fascist terms. Resistance during World War II to fascism occurred in every occupied country, and came from across the ideological spectrum. The defeat of the Axis powers generally ended fascism as a state ideology.
After World War II, the anti-fascist movement continued to be active in places where organized fascism continued or re-emerged. There was a resurgence of antifa in Germany in the 1980s, as a response to the invasion of the punk scene by neo-Nazis. This influenced the antifa movement in the United States in the late 1980s and 1990s, which was similarly carried by punks. In the 21st century, this greatly increased in prominence as a response to the resurgence of the radical right, especially after the election of Donald Trump.
See also
- Anti-fascism
- Christian fascism
- Clerical fascism
- Conservative Revolution
- Crypto-fascism
- Ecofascism
- Hindutva
- Islamofascism
- Neo-Nazism
- Post–World War II anti-fascism
- Political strongman
- Proto-fascism
- Right-wing authoritarianism
- Reactionary modernism
- Squadrismo
- Third Position
References
- Turner (1975), p. 162: "... goals of radical and authoritarian nationalism"; Larsen, Hagtvet & Myklebust (1984), p. 424: "... organized form of integrative radical nationalist authoritarianism"; Paxton (2004), pp. 32, 45, 173: (32) "... antiliberal values, more aggressive nationalism and racism, and a new aesthetic of instinct and violence", (173) "... overtly violent racism and nationalism. ... its defining elements—unlimited particular sovereignty, a relish for war, and a society based on violent exclusion"; Nolte (1965), p. 300: "National fascism, as we have shown, is distinguished from nationalism by, among other things, the fact it demands the destruction of a neighbouring state whose very existence appears to threaten its own position of power and the historic remains of its past dominant status in the area."
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica Fascism: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the rule of elites, and the desire to create a Volksgemeinschaft (German: "people's community"), in which individual interests would be subordinated to the good of the nation"
- ^ "fascism". Merriam-Webster Online. Archived from the original on 22 August 2017. Retrieved 22 August 2017.
- International Encyclopedia of Political Science, p. 889, Fascism.
- ^ "Fascism". Holocaust Encyclopedia. Retrieved 7 August 2022.
- ^ Davies & Lynch (2002), pp. 1–5
- ^ Griffin (1995), pp. 8, 307; Kallis (2003b), p. 71; Hartley (2004), p. 187; Reich (1970); Hawkesworth & Kogan (1992); Copsey (2008); Goodwin (2011); Woodley (2010); Blamires (2006); Richardson (2017); Eley (2013); Wistrich (1976); Staudenmaier (2004)
- International Encyclopedia of Political Science, p. 887–888, Fascism.
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica Fascism.
- ^ Blamires (2006), pp. 140–141, 670; Mann (2004), p. 65.
- Grčić (2000), p. 120; Griffin & Feldman (2004c), p. 185; Spielvogel (2012), p. 935; Payne (1995), p. 106.
- ^ Rietbergen (2000), pp. 160–161.
- ^ Griffin (2013), pp. 1–6.
- ^ Mussolini (2002), p. 40.
- Davies & Lynch 2002, p. 275: "Detailed and intrusive state direction of the economy and/or society. Dirigisme was central to both fascism and Communist systems. However, in the case of fascism, there was no requirement for outright state ownership of the means of production, as long as the economy could be harnessed to serve what fascists deemed to be the 'national interest'."
- Berend, Iván T. (2016). An Economic History of Twentieth-Century Europe: Economic Regimes from Laissez-Faire to Globalization. Cambridge University Press. p. 93.
- ^ Kallis (2011); Paxton (1998); Lancaster (2011).
- "New Research Reveals How the Nazis Targeted Transgender People".
- Enciclopedia Italiana Neofascismo.
- Bogel-Burroughs, Nicholas; Garcia, Sandra E. (28 September 2020). "What Is Antifa, the Movement Trump Wants to Declare a Terror Group?". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 7 September 2022.
- Mussolini (2006), p. 227.
- Falasca-Zamponi (2000), p. 95.
- Johnston, Peter (12 April 2013). "The Rule of Law: Symbols of Power". The Keating Center, Oklahoma Wesleyan University. Archived from the original on 30 March 2017. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- Watkins, Tom (2013). "Policing Rome: Maintaining Order in Fact and Fiction". Fictional Rome. Stockton, New Jersey: Stockton University. Archived from the original on 16 March 2014. Retrieved 28 April 2013.
- "Fasces". Britannica.com. Britannica. Retrieved 17 April 2024.
When carried inside Rome, the ax was removed (unless the magistrate was a dictator or general celebrating a triumph) as recognition of the right of a Roman citizen to appeal a magistrate's ruling.
- Brennan 2022, pp. 2, 12.
- Parkins, Wendy (2002). Fashioning the body politic: dress, gender, citizenship. Oxford; New York: Berg. p. 178.
- Kershaw (2016), p. 228.
- Payne (1980), p. 7; Griffiths (2000).
- Laqueur (1997), p. 223; Eatwell (1996), p. 39; Griffin (1991), pp. 185–201; Weber (1982), p. 8
- "Works citing Stanley Payne's Fascism: Comparison and Definition". Archived from the original on 2 August 2022 – via Google Scholar.
- Griffin, Roger (1993). The Nature of Fascism. London: Routledge (published 2013). doi:10.4324/9781315003627. ISBN 9781315003627.
- Schweller, Randall L. (2006). Unanswered Threats: Political Constraints on the Balance of Power. Princeton Studies in International History and Politics. Vol. 125. Princeton University Press. doi:10.1515/9781400837854. ISBN 978-1-4008-3785-4. S2CID 266074243.
- Rothstein, B (1996). "Political institutions: An Overview (Part II, Chapter 4)". In Klingemann, Hans-Dieter; Goodin, Robert E. (eds.). A New Handbook of Political Science. Oxford University Press. pp. 135, 164. ISBN 9780191521089.
- Finchelstein, Federico (2010). Transatlantic Fascism: Ideology, Violence, and the Sacred in Argentina and Italy, 1919-1945. Duke University Press. doi:10.1515/9780822391555. ISBN 978-0-8223-9155-5.
- Shenfield, Stephen (2001). Russian Fascism: Traditions Tendencies Movements (2nd ed.). New York: Routledge (published 2016). doi:10.4324/9781315500058. ISBN 9781315500058.
- ^ Payne (1980), p. 7.
- Ramswell (2017), p. 9; Griffin & Feldman (2004a), p. 258; Kallis (2003b), pp. 84–5; Renton (1999), p. 21.
- ^ Eco, Umberto (22 June 1995). "Eternal Fascism" (PDF). The New York Review of Books. New York: New York Times Company. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 November 2005 – via justicescholars.org.
- Lukacs (1998), p. 118.
- Silva, Christianna. "Fascism Scholar Says U.S. Is 'Losing Its Democratic Status'". NPR. Archived from the original on 7 September 2020. Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- ^ Griffin (1991), p. 26.
- Griffin, Roger (1996). "Chapter I: Staging the Nation's Rebirth: The Politics and Aesthetics of Performance in the Context of Fascist Studies". In Berghaus, Günter (ed.). Fascism and theater: comparative studies on the aesthetics and politics of performance in Europe, 1925–1945. Providence, RI: Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-1571819017. Retrieved 7 October 2013 – via Library of Social Science.
- Griffin (1991), p. 201.
- Griffin (2003), p. 3.
- ^ Kershaw (2016), p. 228-9.
- Ross (2017), p. 5.
- Griffin (2008), Chapter 8: Fascism's New Faces (and New Facelessness) in the 'Post-Fascist' Epoch.
- Roel Reyes (2019).
- Roel Reyes, Stefan (24 November 2021). "'Christian Patriots': The Intersection Between Proto-fascism and Clerical Fascism in the Antebellum South". International Journal for History, Culture and Modernity. -1 (aop): 82–110. doi:10.1163/22130624-00219121. ISSN 2213-0624. S2CID 244746966.
- Mudde & Kaltwasser (2017), pp. 6, 33–34: "... thin-centered ideologies have a restricted morphology, which necessarily appears attached to—and sometimes is even assimilated into—other ideologies. In fact, populism almost always appears attached to other ideological elements, which are crucial for the promotion of political projects that are appealing to a broader public. Consequently, by itself populism can offer neither complex nor comprehensive answers to the political questions that modern societies generate. ... is not so much a coherent ideological tradition as a set of ideas that, in the real world, appears in combination with quite different, and sometimes contradictory, ideologies." (p. 6)
- Paxton (2004), p. 216.
- Eatwell (1996), p. 24.
- Laqueur (1997), p. 96.
- Gentile, Emilio (2002). Fascismo: Storia e interpretazione [Fascism: History and interpretation] (in Italian). Editori Laterza. ISBN 978-88-581-0916-8 – via Google Books.
- "Who Are You Calling a Fascist?". The New Republic. 29 March 2023. ISSN 0028-6583. Archived from the original on 29 March 2023. Retrieved 13 July 2023.
- Weiss-Wendt, Krieken & Cave (2008), p. 73.
- Passmore (2002), p. 31.
- Grant (2003), pp. 60–61.
- Encyclopedia Britannica Volksgemeinschaft.
- "What Is Fascism?". CFR Education from the Council on Foreign Relations. 14 April 2023.
- "Franco's dictatorship". Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- Davies & Lynch (2002), pp. 126–127; Zafirovski (2008), pp. 137–138.
- Stackelberg (1999), pp. 4–6.
- Griffin (2003), p. 5.
- Gregor (2009), p. 191.
- Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 161; Borsella & Caso (2007), p. 76.
- Woshinsky (2008), p. 156.
- Schnapp, Sears & Stampino (2000), p. 57; Mussolini (1935), p. 26.
- Mussolini quoted in Gentile (2005), p. 205
- Baranski & West (2001), pp. 50–51.
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica The fascist era.
- ^ Payne (1995), p. 112.
- Neocleous (1997), p. 54.
- Gregor (2005), p. 4.
- Orwell (2019).
- Orwell (1946).
- Griffiths (2000).
- Woolf (1981), p. 18.
- Griffin & Feldman (2004a), p. 231.
- Quarantotto (1976).
- Matthews (1946).
- Hoover (1947).
- Amann (1986), p. 562.
- ^ Whiffen, Timothy (2013). "To what extent was Hitler's rule of Nazi Germany similar to life in Sparta?". Academia. Retrieved 15 April 2016.
- Anthony Grafton, Glenn W. Most, Salvatore Settis. The Classical Tradition. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press, 2010. pp. 353.
- Sternhell (1976).
- ^ Camus & Lebourg (2017), p. 20.
- Williams (2015), p. 28.
- Thomson (1966), p. 293.
- Shirer (1960), p. 97.
- Gerwarth (2005), p. 166.
- Dierkes (2010), p. 54.
- Gregor, A. James (27 March 2006). "5 - Black Nationalism and Neofascism: Marcus Garvey and the Universal Negro Improvement Association". The Search for Neofascism: The Use and Abuse of Social Science. Cambridge University Press. pp. 111–136. doi:10.1017/cbo9780511617225.006. ISBN 9780521859202.
- Gilroy, Paul (2000). "Black Fascism". Transition (81/82): 70–91. ISSN 0041-1191. JSTOR 3137450.
- Sternhell (1998), p. 169; Payne (1995), pp. 23–24.
- ^ Sternhell (1998), p. 170.
- Payne (1995), p. 24.
- ^ Sternhell (1998), p. 171.
- Payne (1995), p. 29.
- Payne (1995), pp. 24–25.
- Payne (1995), p. 25.
- Outhwaite (2006), p. 442; Koon (1985), p. 6.
- ^ Caforio (2006), p. 12.
- ^ Carroll (1998), p. 92.
- Antliff (2007), pp. 75–81.
- Antliff (2007), p. 81.
- Antliff (2007), p. 77.
- Antliff (2007), p. 82.
- ^ Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 78.
- Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 82.
- Holmes (2000), p. 60.
- ^ Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 163.
- ^ Blinkhorn (2006), p. 12.
- Blinkhorn (2006), p. 12–13.
- Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 32.
- Gentile (2003), p. 6.
- Hewitt (1993), p. 153.
- ^ Gori (2004), p. 14.
- Gori (2004), pp. 20–21.
- ^ Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 175.
- Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 214.
- O'Brien (2014), p. 52.
- ^ O'Brien (2014), p. 41.
- Gregor (1979), pp. 195–196.
- ^ Kitchen (2006), p. 205.
- ^ Hüppauf (1997), p. 92.
- Rohkrämer (2007), p. 130.
- Blamires (2006), pp. 140–141, 670.
- Carr, Edward Hallett (1986). The twilight of Comintern 1930–1935. Macmillan. p. 433. ISBN 978-0-333-40455-3.
Trotsky...maintained during the period of Hitler's rise to power so persistent and, for the most part, so prescient a commentary on the course of events in Germany as to deserve record.
- Ticktin, Hillel (1992). Brotherstone, Terence; Dukes, Paul (eds.). Trotsky's political economy of capitalism. Edinburgh University Press. p. 227. ISBN 978-0-7486-0317-6.
- ^ Blamires (2006), pp. 95–96.
- Wistrich 1976.
- Neville (2004), p. 36.
- Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 178.
- Elazar (2001), p. 73.
- Passmore (2003), p. 116.
- Borsella & Caso (2007), p. 69.
- Borsella & Caso (2007), pp. 69–70.
- Borsella & Caso (2007), p. 70.
- Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 186.
- Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 187.
- ^ Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 189.
- Borsella & Caso (2007), p. 73.
- Borsella & Caso (2007), p. 75.
- ^ Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 193.
- De Grand (2000), p. 145.
- Blinkhorn (2003), p. 14.
- Sternhell, Sznajder & Ashéri (1994), p. 190.
- Blinkhorn (2003), p. 22.
- Borsella & Caso (2007), p. 72.
- Borsella & Caso (2007), p. 76.
- Acemoğlu et al. (2020).
- ^ Paxton (2005), p. 87.
- Ferrandi & Obermair (2023), p. 127–167.
- Paxton (2005), p. 88.
- ^ Paxton (2005), p. 90.
- Payne (1995), p. 122.
- ^ Payne (1995), p. 110.
- ^ Payne (1995), p. 113.
- ^ Payne (1995), p. 114.
- Payne (1995), p. 115.
- Payne (1995), pp. 119–120.
- Mack Smith (1983), p. 162.
- Mack Smith (1983), pp. 222–223.
- Mussolini (1977), p. 131.
- von Lang (1979), p. 221.
- Evans (2005), p. 239.
- Berben (1975), pp. 276–277.
- ^ Blamires (2006), p. 150.
- Kallis (2000), p. 132.
- ^ Ahmida (1994), pp. 134–135.
- Cardoza (2006), p. 109; Bloxham & Moses (2010), p. 358.
- Kershaw (2000), p. 182.
- Jablonsky (1989), pp. 20–26, 30.
- Tenorio, Rich (30 September 2023). "Fascism in America: a long history that predates Trump". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 26 February 2024.
- Chomsky 2003, p. 46.
- Payne (1995), p. 270.
- Payne (1995), pp. 282–288.
- Gallagher, Tom (2005). Theft of a Nation: Romania Since Communism. C. Hurst & Co. Publishers. p. 35. ISBN 9781850657163 – via Google Books.
- Deletant, D. (2006). Hitler's Forgotten Ally: Ion Antonescu and his Regime, Romania 1940–1944. Springer. p. 66. ISBN 9780230502093 – via Google Books.
- Woolf (1983), p. 311.
- Payne (1995), p. 145.
- Griffin (1991), pp. 150–152.
- Payne (1995), pp. 341–342.
- Berghaus (2000), pp. 136–137.
- ^ Blamires (2006), p. 189.
- Overy (1994), p. 16.
- Toniolo (2013), p. 59; Mussolini's speech to the Chamber of Deputies was on 26 May 1934.
- Toniolo (2013), p. 59.
- Blinkhorn (2006), p. 46.
- ^ Blamires (2006), p. 72.
- Blamires (2006), p. 190.
- "Utopia: The 'Greater Germanic Reich of the German Nation'". Munich and Berlin: Institut für Zeitgeschichte. 1999. Archived from the original on 15 September 2018. Retrieved 15 September 2018.
- Rodogno (2006), p. 47.
- ^ Davidson (2004), pp. 371–372.
- Bianchi (1963), p. 609
- Bianchi (1963), p. 704
- De Felice in Grandi (1983), p. 21
- De Felice (1996), p. 1391
- Oosterling, Henk (1997). "Fascism as the Looming Shadow of Democracy: A Critique of the Xenophobic Reason". Philosophy and Democracy in Intercultural Perspective/Philosophie et démocratie en perspective interculturelle. Amsterdam/Atlanta: Rodopi. pp. 235–252.
- Deutsch, Sandra McGee (2009). "Fascism, Neo-Fascism, or Post-Fascism? Chile, 1945–1988". Diálogos-Revista do Departamento de História e do Programa de Pós-Graduação Em História 13.1: 19–44.
- Payne, Stanley G. (1973). "25". A History of Spain and Portugal. Vol. 2 (Print ed.). University of Wisconsin Press. p. 632. Retrieved 30 May 2007 – via Library of Iberian Resources Online.
- Paxton (1998), pp. 3, 17.
- Paxton (2004), p. 150.
- Davies & Lynch (2002), p. 237.
- Passmore (2002), p. 76.
- "Inauguração do Museu de Peniche é um gesto antifascista atual contra a extrema-direita". Esquerda.net. 26 April 2024. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ^ Blamires (2006), p. 512.
- Page, Joseph A. (2014). Perón: A biography. Penguin Random House Grupo Editorial Argentina. p. 10 and ss. ISBN 9789500748247.
- Romero, Ricardo (2015), Perón, Reformism and Nazi fascism during the Second War World, Department of Social Sciences, National College of Buenos Aires, UBA, p. 14,
Although it is incorrect to define Peronism as Nazism, and it is debatable to conceptualize it as fascism, the truth is that in the University the Catholic sectors that received the support of the General did much to make the students consider as fascist to Perón.
- Galasso, Norberto (2003). "Peronismo y Liberación Nacional" [Peronism and National Liberation]. Apuntes para otra historia [Notes for another story] (in Spanish). pp. 2–3. ISSN 1667-1635.
- Cucchetti, Humberto (2012). "Readings and interpretations on the origins of Peronism: national-populism or fascist adaptation?". Studia Historica. Contemporary History. 30. Universidad de Salamanca: 151–171. ISSN 0213-2087.
- Rein, Raanan (2015). Los muchachos judíos peronistas: Judeosargentinos y apoyo al Justicialismo [The Peronist Jewish Boys: Judeo-sergeants and support for Justicialism] (in Spanish). Penguin Random House Grupo Editorial Argentina. ISBN 9789500753982.
- "Greece's Golden Dawn leader Michaloliakos held in crackdown". BBC News. 28 September 2013. Archived from the original on 28 September 2013. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- Michael, Savvas (30 September 2013). "The Arrest of the Nazi Gangsters of Golden Dawn in Greece". EEK. Archived from the original on 13 June 2020. Retrieved 9 June 2020.
- Samaras, Georgios (26 November 2020). "The end of Golden Dawn: has Greece shown us how to deal with neo-Nazis?". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 2 December 2020. Retrieved 27 January 2021.
- "Greece Golden Dawn: Neo-Nazi leaders guilty of running crime gang". BBC News. 7 October 2020. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 7 October 2020.
- Laruelle, Marlene (2021). Is Russia Fascist?: Unravelling Propaganda East and West. Cornell University Press. ISBN 9781501754135. JSTOR 10.7591/j.ctv16t673d. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- Motyl, Alexander J. (March 2016). "Putin's Russia as a fascist political system". Communist and Post-Communist Studies. 49 (1): 25–36. doi:10.1016/j.postcomstud.2016.01.002. ISSN 0967-067X. JSTOR 48610431.
- Motyl, Alexander J. (30 March 2022). "Yes, Putin and Russia are fascist. How they meet the textbook definition". The Conversation.
- "Systemic Transformations and the Drift Toward Fascism in Russia". Wilson Center. Archived from the original on 2 September 2023.
- ^ Laruelle, Marlene (2022). "So, Is Russia Fascist Now? Labels and Policy Implications" (PDF). The Washington Quarterly. 45 (2): 149–168. doi:10.1080/0163660X.2022.2090760. S2CID 250566287. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 July 2022.
- ^ Coalson, Robert (9 April 2022). "Nasty, Repressive, Aggressive – Yes. But Is Russia Fascist? Experts Say 'No.'". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. Archived from the original on 23 July 2023. Retrieved 7 May 2022.
- Papachristou, Lucy (26 February 2024). "Rights campaigner calls Russia 'fascist' in court". Reuters.
- Ebel, Francesca (27 February 2024). "Russian activist from Nobel-winning organization gets prison term". Washington Post.
- "Biden compares Putin to Hitler as he makes the case for continued aid to Ukraine in SOTU address". Yahoo!, The New Voice of Ukraine. 8 March 2024.
- ^ Paxton (2004), p. 11.
- Blamires (2006b), pp. 451–453, "Nationalism".
- Paxton (2004), p. 41.
- Zimmer (2003), pp. 80–107, ch. 4.
- Paxton (2004).
- Laqueur (1997), p. 223.
- ^ Payne (1995), p. 11.
- Lyttelton (1973), p. 13: "The first half of the article was the work of Giovanni Gentile; only the second half was Mussolini's own work, though the whole article appeared under his name."
- Mussolini (1935), p. 14.
- Schmitt (1995), p. 72.
- Pauley (2003), p. 117; Payne (1995), p. 220.
- Pauley (2003), pp. 117–119.
- Baker, David (June 2006). "The political economy of fascism: Myth or reality, or myth and reality?" New Political Economy 11 (2): 227–250. doi:10.1080/13563460600655581.
- Asheri, Maia; Sznajder; Mario; Zeev, Sternhell (1994) . The Birth of Fascist Ideology. Translated by Maisel, David. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691044866.
- Payne, Stanley G. (1995). A History of Fascism, 1914–1945. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 9780299148744.
- Paxton, Robert O. (2004). The Anatomy of Fascism. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 9781400040940.
- Woodley, Daniel (2009). Fascism and Political Theory: Critical Perspectives on Fascist Ideology. London: Routledge. p. 161. ISBN 9781135248802.
- Bastow & Martin (2003), p. 36.
- "Benito Mussolini, Doctrine of Fascism (1932)". Archived from the original on 31 July 2016. Retrieved 28 July 2016.
- Blamires (2006), p. 610.
- Laqueur, Walter (1978). Fascism: A Reader's Guide: Analyses, Interpretations, Bibliography. University of California Press. p. 357. ISBN 978-0-520-03642-0
- Overy, Richard (1994). War and Economy in the Third Reich. Oxford University Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-19-820290-5
- Laqueur, Walter (1978). Fascism: A Reader's Guide: Analyses, Interpretations, Bibliography. University of California Press. p. 357. ISBN 978-0-520-03642-0
- Overy, Richard (1994). War and Economy in the Third Reich. Oxford University Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-19-820290-5
- De Grand (1995), pp. 60–61.
- Griffin (1991), pp. 222–223.
- Hoover (1935), pp. 13–20.
- Neocleous (1997), pp. 21–22.
- Blamires (2006), p. 102.
- ^ Spektorowski & Ireni-Saban (2013), p. 33.
- ^ Blamires (2006), p. 535.
- Friedman (2011), p. 24.
- Millward (2007), p. 178.
- Davies & Lynch (2002), p. 103.
- Paxton (2005), p. 10.
- Breuilly (1994), p. 290.
- Morgan (2003), p. 32.
- Griffin & Feldman (2004), p. 353: "When the Russian revolution occurred in 1917 and the 'Democratic' revolution spread after the First World War, anti-bolshevism and anti-egalitarianism rose as very strong "restoration movements" on the European scene. However, by the turn of that century no one could predict that fascism would become such a concrete, political reaction ... ."
- Hawkins (1997), p. 285: "Conflict is in fact the basic law of life in all social organisms, as it is of all biological ones; societies are formed, gain strength, and move forwards through conflict; the healthiest and most vital of them assert themselves against the weakest and less well adapted through conflict; the natural evolution of nations and races takes place through conflict." Alfredo Rocco, Italian Fascist.
- Evans (2005), pp. 483–484.
- Evans (2005), p. 484.
- Evans (2005), pp. 484–485.
- Evans (2005), pp. 486–487.
- ^ Evans (2005), p. 489.
- Evans (2005), pp. 489–490.
- Payne (1995), p. 106; Breuilly (1994), p. 294.
- ^ Woodley (2010), p. 106.
- Payne (1995), pp. 485–486.
- Griffin (1995), p. 59.
- ^ Antliff (2007), p. 171.
- Quine (1996), p. 47.
- Laqueur (1978), p. 341.
- ^ Quine (1996), pp. 46–47.
- Bollas (1993), p. 205.
- McDonald (1999), p. 27.
- Mann (2004), p. 101.
- Durham (1998), p. 15.
- Evans (2005), pp. 331–332.
- Heineman, Elizabeth D. (2002). "Sexuality and Nazism: The Doubly Unspeakable?". Journal of the History of Sexuality. 11 (1/2): 22–66. doi:10.1353/sex.2002.0006. ISSN 1043-4070. JSTOR 3704551. S2CID 142085835.
- ^ Friedlander (1995), p. 30.
- McLaren (1999), p. 139.
- Proctor (1989), p. 366: "This emendation allowed abortion only if the woman granted permission, and only if the fetus was not old enough to survive outside the womb. It is unclear if either of these qualifications was enforced."
- Arnot & Usborne (1999), p. 241.
- Proctor (1989), pp. 122–123: "Abortion, in other words, could be allowed if it was in the interest of racial hygiene. ... the Nazis did allow (and in some cases even required) abortions for women deemed racially inferior. ... On 10 November 1938, a Luneberg court declared abortion legal for Jews."
- Tierney (1999), p. 589: "In 1939, it was announced that Jewish women could seek abortions, but non-Jewish women could not."
- Evans (2005), p. 529.
- United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. "Persecution of Homosexuals in the Third Reich". Ushmm.org. Archived from the original on 6 October 2008. Retrieved 4 June 2010.
- ^ Blamires (2006), p. 168.
- Blamires (2006), p. 451–453.
- Blamires (2006), pp. 168–169.
- Neocleous (1997), p. 63.
- Neocleous (1997), p. 65.
- Welge (2007), p. 547.
- Welge (2007), p. 550.
- ^ Welge (2007), p. 553.
- Jay, Martin (1992). "'The Aesthetic Ideology' as Ideology; Or, What Does It Mean to Aestheticize Politics?". Cultural Critique (21). University of Minnesota Press: 41–61. doi:10.2307/1354116. JSTOR 1354116.
- Benjamin, Walter (2008) . The Work of Art in the Age of Mechanical Reproduction. London: Penguin Books. pp. 36–37. ISBN 978-0-14-103619-9.
- Baudrillard, Jean (1994) . Simulacra and Simulation. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press. ISBN 978-0-472-06521-9.
Fascism itself, the mystery of its appearance and of its collective energy, ... can already be interpreted as the 'irrational' excess of mythic and political referentials, the mad intensification of collective value (blood, race, people, etc.), the reinjection of death, of a 'political aesthetic of death' at a time when the process of the disenchantment of value and of collective values, of the rational secularization and unidimensionalization of all life, of the operationalization of all social and individual life already makes itself strongly felt in the West. Yet again, everything seems to escape this catastrophe of value, this neutralization and pacification of life. Fascism is a resistance to this, even if it is a profound, irrational, demented resistance, it would not have tapped into this massive energy if it hadn't been a resistance to something much worse. Fascism's cruelty, its terror is on the level of this other terror that is the confusion of the real and the rational, which deepened in the West, and it is a response to that.
- Payne, Stanley G. (1996). A History of Fascism, 1914–1945. Madison, WI: University of Wisconsin Press. pp. 5–6. ISBN 9780299148737 – via Google Books.
- ^ Sontag (1975).
- Ben-Ghiat, Ruth (2015). "The Imperial Moment in Fascist Cinema". Journal of Modern European History. 13 (1): 59–78. doi:10.17104/1611-8944_2015_1_59. S2CID 147023860.
- Sorlin, Pierre (2007). "A Mirror for Fascism. How Mussolini Used Cinema to Advertise his Person and Regime". Historical Journal of Film, Radio and Television. 27 (1): 111–117. doi:10.1080/01439680601177163. S2CID 192025081.
- Berezin, Mabel (1991). "The organization of political ideology: Culture, state, and theater in fascist Italy". American Sociological Review. 56 (5): 639–651. doi:10.2307/2096085. JSTOR 2096085.
- Overy, Richard. The Dictators: Hitler's Germany, Stalin's Russia. p. 361.
- Steinweis, Alan E. (1996). Art, ideology, & economics in Nazi Germany: the Reich chambers of music, theater, and the visual arts. University of North Carolina Press.
- Boesche (2010), p. 11.
- Clarke & Foweraker (2001), p. 540; Pollard (1998), p. 121; Griffin (1991), p. 42.
- Finchelstein, Federico (20 August 2008). "On Fascist Ideology". Constellations. 15 (3). Wiley: 320–331. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8675.2008.00494.x. ISSN 1351-0487.
- Schreiber, Stegemann & Vogel (1995), p. 111.
- Mussolini (1998), p. ix. (Note: Mussolini wrote the second volume about his fall from power as head of government of the Kingdom of Italy in 1943, though he was restored to power in northern Italy by the German military.)
- Mussolini (1998), p. ix.
- Mack Smith (1997), p. 284.
- Kington, Tom (13 October 2009). "Recruited by MI5: the name's Mussolini. Benito Mussolini – Documents reveal Italian dictator got start in politics in 1917 with help of £100 weekly wage from MI5". The Guardian. UK. Archived from the original on 19 May 2019. Retrieved 14 October 2009.
- O'Brien (2014), p. 37.
- Gregor (1979), p. 200.
- ^ Golomb & Wistrich (2002), p. 249.
- Delzel (1970), p. 96.
- Delzel (1970), p. 3.
- Gillette (2001), p. 17; Pollard (1998), p. 129.
- Burgwyn (1997), p. 58.
- ^ Pollard (1998), p. 129.
- Gillette (2001), p. 93.
- Gillette (2001), p. 17.
- Gillette (2001), p. 45.
- Neocleous (1997), pp. 35–36.
- Beinart, Peter (6 August 2017). "The Rise of the Violent Left". The Atlantic. Retrieved 21 October 2020.
- Beauchamp, Zack (8 June 2020). "Antifa, explained". Vox. Retrieved 21 October 2020.
Bibliography
Primary sources
- Galeazzo, Ciano (2001). The Ciano Diaries, 1939–1943. Simon Publications. ISBN 978-1-931313-74-2.
- Gentile, Giovanni (1932). The Doctrine of Fascism.
- Goebbels, Joseph (2019). Dalton, Thomas (ed.). Goebbels on the Jews: The Complete Diary Entries – 1923 to 1945.
- Taylor, Fred, ed. (1983). The Goebbels Diaries 1939–1941.
- Hitler, Adolf (1925). Mein Kampf.
- Hoover, Calvin B. (March 1935). "The Paths of Economic Change: Contrasting Tendencies in the Modern World". The American Economic Review. 25 (1): 13–20.. Supplement, Papers and Proceedings of the Forty-Seventh Annual Meeting of the American Economic Association.
- Hoover, J. Edgar (1947). "Testimony before the House Un-American Activities Committee". Archived from the original on 23 July 2010.
- Matthews, Claudio (1946). "Fascism Is Not Dead ...". Nation's Business.
- Mosely, Oswald (1968). My Life. Nelson Publications.
- Mussolini, Benito (2006) . My Autobiography with The Political and Social Doctrine of Fascism. Mineloa, NY: Dover Publications. ISBN 978-0-486-44777-3.
- Mussolini, Benito (2002) . Gregor, Anthony James (ed.). Origins and Doctrine of Fascism. New Brunswick (US); London: Transaction Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7658-0130-2.
- Mussolini, Benito (1935). Fascism: Doctrine and Institutions. Rome: Ardita Publishers.
- Mussolini, Benito (1998). My Rise And Fall. Da Capo Press. ISBN 978-0-306-80864-7.
- de Oliveira Salazar, António (1939). Doctrine and Action: Internal and Foreign Policy of the New Portugal, 1928–1939. Faber and Faber.
- Orwell, George (29 December 2019) . "What is Fascism?". Tribune., republished in The Collected Essays, Journalism and Letters of George Orwell. 1968.
- Orwell, George (April 1946). "Politics and the English Language". Horizon.; link via The Orwell Foundation
- de Rivera, José Antonio Primo (1971). Textos de Doctrina Política [Political Doctrine Texts] (in Spanish). Madrid: Delegación Nacional de la Sección Femenina del Movimiento.
Secondary sources
- Acemoğlu, Daron; De Feo, Giuseppe; De Luca, Giacomo; Russo, Gianluca (28 October 2020). "Revisiting the rise of Italian fascism". Center for Economic and Policy Research. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- Adams, Ian (1993). Political Ideology Today. Manchester, England: Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-0-7190-6020-5.
- Ahmida, Ali Abdullatif (1994). The Making of Modern Libya: State Formation, Colonization, and Resistance, 1830–1922. Albany, New York: State University of New York Press.
- Amann, Peter H. (1986). "A 'Dog in the Nighttime' Problem: American Fascism in the 1930s". The History Teacher. 19 (4): 559–584. doi:10.2307/493879. ISSN 0018-2745. JSTOR 493879.
- Antliff, Mark (2007). Avant-Garde Fascism: The Mobilization of Myth, Art, and Culture in France, 1909–1939. Duke University Press.
- Arnot, Margaret; Usborne, Cornelie (1999). Gender and Crime in Modern Europe. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-85728-745-5. OCLC 249726924.
- Baker, David (June 2006). "The political economy of fascism: Myth or reality, or myth and reality?". New Political Economy. 11 (2): 227–250. doi:10.1080/13563460600655581. S2CID 155046186.
- Ball, Terence; Bellamy, Richard (2003). The Cambridge History of Twentieth-Century Political Thought. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-56354-3 – via Google Books.
- Baranski, Zygmunt G.; West, Rebecca J. (2001). The Cambridge Companion to Modern Italian Culture. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-55982-9. Retrieved 7 October 2017 – via Google Books.
- Bastow, Steve; Martin, James (2003). Third Way Discourse: European Ideologies in the Twentieth Century. Edinburgh University Press Ltd.
- Ben-Ami, Shlomo (1983). Fascism from Above: The Dictatorship of Primo de Rivera in Spain, 1923–1930. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-822596-6 – via Google Books.
- Berben, Paul (1975). Dachau, 1933–1945: The Official History. Norfolk Press.
- Berghaus, Günter (2000). Fascism and Theatre: Comparative Studies on the Aesthetics and Politics of Performance. Berkeley and Los Angeles, CA: University of California Press.
- Blamires, Cyprian (2006). World Fascism: A Historical Encyclopedia. Vol. 1. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO, Inc.
- Blamires, Cyprian (2006b). World Fascism: A Historical Encyclopedia. Vol. 2. Santa Barbara, CA: ABC-CLIO, Inc.
- Blinkhorn, Martin (2003). Fascists and Conservatives: The Radical Right and the Establishment in Twentieth-Century Europe. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-99712-1 – via Google Books.
- Blinkhorn, Martin (2006). Mussolini and Fascist Italy (3rd ed.). New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-50572-2 – via Google Books.
- Bloxham, Donald; Moses, A. Dirk (2010). Bloxham, Donald; Moses, A. Dirk (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780199232116.001.0001. ISBN 9780199232116.
- Bollas, Christopher (1993). Being a Character: Psychoanalysis and Self-Experience. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-08815-2.
- Boesche, Roger (2010). Theories of Tyranny: From Plato to Arendt. Penn State Press. ISBN 978-0-271-04405-7 – via Google Books.
- Borsella, Cristogianni; Caso, Adolph (2007). Fascist Italy: A Concise Historical Narrative. Wellesley, Massachusetts: Branden Books. ISBN 978-0828321556.
- Brennan, T Corey (2022). The fasces: a history of ancient Rome's most dangerous political symbol. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-764488-1.
- Breuilly, John (1994). Nationalism and the State. University of Chicago Press.
- Burgwyn, H. James (1997). Italian Foreign Policy in the Interwar Period, 1918–1940. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0275948771.
- Caforio, Giuseppe (2006). Handbook of the sociology of the military. New York: Springer.
- Camus, Jean-Yves; Lebourg, Nicolas (2017). Far-Right Politics in Europe. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-97153-0. Retrieved 9 May 2020 – via Google Books.
- Cardoza, Anthony L. (2006). Benito Mussolini: the First Fascist. Pearson Longman.
- Carroll, David (1998). French Literary Fascism: Nationalism, Anti-Semitism, and the Ideology of Culture. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-05846-7 – via Google Books.
- Chomsky, Noam (2003). Hegemony or survival : America's quest for global dominance. Henry Holt and Company, LLC. ISBN 0-8050-7400-7.
- Clarke, Paul Barry; Foweraker, Joe (2001). Encyclopedia of Democratic Thought. Routledge.
- Copsey, Nigel (2008). Contemporary British Fascism: The British National Party and the Quest for Legitimacy (second ed.). London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-230-57437-3.
- Costa Pinto, Antonio, ed. (2011). Rethinking the Nature of Fascism: Comparative Perspectives. Palgrave Macmillan.
- Costa Pinto, António (1995). Salazar's Dictatorship and European Fascism: Problems of Interpretation. Social Science Monographs. ISBN 978-0-88033-968-1 – via Google Books.
- Davidson, Eugene (2004). The Unmaking of Adolf Hitler. Columbia, Missouri: University of Missouri Press.
- Davies, Peter; Lynch, Derek, eds. (2002). The Routledge Companion to Fascism and the Far Right. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-60952-9 – via Google Books.
- De Felice, Renzo (1977). Interpretations of Fascism. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-45962-5.
- De Felice, Renzo (1976). Fascism: An Informal Introduction to Its Theory and Practice. Transaction Books. ISBN 978-0-87855-619-9 – via Google Books.
- De Grand, Alexander J. (1995). Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany.
- De Grand, Alexander (2000). Italian Fascism: its Origins and Development (3rd ed.). University of Nebraska Press.
- Delzel, Charles F., ed. (1970). Mediterranean Fascism 1919–1945. Harper Rowe.
- Dierkes, Julian (2010). Postwar Historical Education in Japan and the Germanies. Routledge.
- Doordan, Dennis P. (1995). In the Shadow of the Fasces: Political Design in Fascist Italy. The MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-299-14874-4.
- Durham, Martin (1998). Women and Fascism. Routledge.
- Eatwell, Roger (1996). Fascism: A History. New York: Allen Lane. ISBN 978-0-7139-9147-5.
- Elazar, Dahlia S. (2001). The Making of Fascism: Class, State, and Counter-Revolution, Italy 1919–1922. Westport, Connecticut: Praeger Publishers.
- Eley, Geoff (2013). Nazism as Fascism: Violence, Ideology, and the Ground of Consent in Germany 1930–1945. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-203-69430-5.
- Evans, Richard J (2005). The Third Reich in Power: 1933–1939. The Penguin Press HC.
- Falasca-Zamponi, Simonetta (2000). Fascist Spectacle: The Aesthetics of Power in Mussolini's Italy. Oakland, California: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-22677-7.
- Ferrandi, Maurizio; Obermair, Hannes (2023). Camicie nere in Alto Adige (1921–1928) [Blackshirts in South Tyrol (1921–1928)] (in Italian). Merano: Alphabeta. ISBN 978-88-7223-419-8.
- Friedlander, Henry (1995). The origins of Nazi genocide: from euthanasia to the final solution. Chapel Hill, North Carolina: University of North Carolina Press. ISBN 978-0-8078-4675-9. OCLC 60191622.
- Friedman, Jonathan C. (2011). The Routledge History of the Holocaust. Routledge.
- Fritzsche, Peter (1990). Rehearsals for Fascism: Populism and Political Mobilization in Weimar Germany. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-505780-5.
- Gentile, Emilio (2003). The Struggle for Modernity: Nationalism, Futurism, and Fascism. Westport, Connecticut: Praeger Publishers.
- Gentile, Emilio (2005). The Origins of Fascist Ideology, 1918–1925: The First Complete Study of the Origins of Italian Fascism. New York: Enigma Books. ISBN 978-1-929631-18-6.
- Gerwarth, Robert (2005). The Bismarck Myth. Oxford University Press.
- Gillette, Aaron (2001). Racial Theories in Fascist Italy. London; New York: Routledge.
- Golomb, Jacob; Wistrich, Robert S (2002). Nietzsche, Godfather of Fascism? On the Uses and Abuses of a Philosophy. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
- Goodwin, Matthew J. (2011). New British Fascism: Rise of the British National Party. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-46500-7.
- Gori, Gigliola (2004). Italian Fascism and the Female Body: Submissive Women and Strong Mothers. Oxfordshire; New York: Routledge.
- Grant, Moyra (2003). Key Ideas in Politics. Nelson Thornes. ISBN 978-0-7487-7096-0 – via Google Books.
- Grčić, Joseph (2000). Ethics and Political Theory. Lanham, Maryland: University of America, Inc.
- Gregor, Anthony James (1979). Young Mussolini and the Intellectual Origins of Fascism. Berkeley and Los Angeles, California; London: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-03799-1.
- Gregor, Anthony James (2005). Mussolini's Intellectuals: Fascist Social and Political Thought. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-12009-6.
- Gregor, Anthony James (2009). Phoenix: Fascism in Our Time. New Brunswick: Transaction Press.
- Griffin, Roger (1991). The Nature of Fascism. Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-07132-5 – via Google Books.
- Griffin, Roger (1995). Fascism. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press.
- Griffin, Roger (2000). "Revolution from the Right: Fascism"". In Parker, David (ed.). Revolutions and the Revolutionary Tradition in the West 1560–1991. London: Routledge.
- Griffin, Roger (2003). "The palingenetic core of generic fascist ideology". In Campi, Alessandro (ed.). Che cos'è il fascismo? Interpretazioni e prospettive di ricerche [What is fascism? Interpretations and research perspectives] (PDF) (in Italian). Rome: Ideazione editrice. pp. 97–122. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 July 2004.
- Griffin, Roger; Feldman, Matthew, eds. (2004). Fascism: Critical Concepts in Political Science. Taylor & Francis.
- Griffin, Roger; Feldman, Matthew, eds. (2004a). The nature of fascism. Vol. 1. Taylor & Francis.
- Griffin, Roger; Feldman, Matthew, eds. (2004c). Fascism and Culture. Vol. 3. London and New York: Routledge.
- Griffin, Roger (2008). Feldman, Matthew (ed.). A Fascist Century. London: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-230-20518-5. OCLC 226357121.
- Griffin, Roger (2013). Fascism, Totalitarianism and Political Religion. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-136-87168-9 – via Google Books.
- Griffiths, Richard (2000). An Intelligent Person's Guide to Fascism. Duckworth. ISBN 978-0-7156-2918-5 – via Internet Archive.
- Hartley, John (2004). Communication, Cultural and Media Studies: The Key Concepts (3rd ed.). Routledge. ISBN 978-0-521-55982-9.
- Hawkesworth, Mary; Kogan, Maurice (1992). Encyclopaedia of Government and Politics: Vol. 1. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-203-71288-7.
- Hawkins, Mike (1997). Social Darwinism in European and American Thought, 1860–1945: Nature as Model and Nature as Threat. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Held, David (1980). Introduction to Critical Theory: Horkheimer to Habermas. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-04175-2.
- Hewitt, Andrew (1993). Fascist Modernism: Aesthetics, Politics, and the Avant-Garde. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press.
- Holmes, Douglas R. (2000). Integral Europe: Fast-Capitalism, Multiculturalism, Neofascism. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press.
- Horne, John (2002). State, Society and Mobilization in Europe During the First World War. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-52266-3.
- Hüppauf, Bernd-Rüdiger (1997). War, Violence, and the Modern Condition. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter & Co.
- Jablonsky, David (1989). The Nazi Party in dissolution: Hitler and the Verbotzeit, 1923–1925. London; Totowa, NJ: Frank Cass and Company Ltd.
- Kallis, Aristotle A. (2000). Fascist ideology: territory and expansionism in Italy and Germany, 1922–1945. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-21612-8 – via Google Books.
- Kallis, Aristotle A. (April 2003a). "To Expand or Not to Expand? Territory, Generic Fascism and the Quest for an 'Ideal Fatherland'". Journal of Contemporary History. 38 (2): 237–260. doi:10.1177/0022009403038002132. S2CID 159641856.
- Kallis, Aristotle, ed. (2003b). The Fascism Reader. London: Routledge.
- Kallis, Aristotle (2011). Genocide and Fascism: The Eliminationist Drive in Fascist Europe. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-89027-4.
- Kershaw, Ian (2000). Hitler, 1889–1936: Hubris. New York; London: W.W. Norton & Co.
- Kershaw, Ian (2016). To Hell and Back: Europe 1914–1949. New York: Penguin Books. ISBN 978-0-14-310992-1.
- Kertzer, David I. (2014). The Pope and Mussolini: The Secret History of Pius XI and the Rise of Fascism in Europe. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-871616-7 – via Google Books.
- Kitchen, Martin (2006). A History of Modern Germany, 1800–2000. Malden, Massaschussetts; Oxford, England; Carlton, Victoria, Australia: Blackwell Publishing, Inc.
- Kitsikis, Dimitri (2006). Jean-Jacques Rousseau et les origines françaises du fascisme [Jean-Jacques Rousseau and the French origins of fascism] (in French). Ars Magna Editions. ISBN 978-2-912164-46-9.
- Kitsikis, Dimitri (2005). Pour une étude scientifique du fascisme [For a scientific study of fascism] (in French). Ars Magna Editions. ISBN 978-2-912164-11-7.
- Knox, MacGregor (1999). Mussolini unleashed, 1939–1941: Politics and Strategy in Fascist Italy's Last War. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Koon, Tracy H. (1985). Believe, obey, fight: political socialization of youth in fascist Italy, 1922–1943. University of North Carolina Press.
- Laclau, Ernesto (1977). Politics and Ideology in Marxist Theory: Capitalism, Fascism, Populism. Verso Books.
- Lancaster, Guy (26 September 2011). "Genocide and Fascism: The Eliminationist Drive in Fascist Europe". Journal of Genocide Research. 13 (3): 366–369. doi:10.1080/14623528.2011.595586. S2CID 72839243.
- Laqueur, Walter (1978). Fascism: A Reader's Guide: Analyses, Interpretations, Bibliography. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-03642-0 – via Google Books.
- Laqueur, Walter (1997). Fascism: Past, Present, Future. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-802527-6 – via Google Books.
- Larsen, Stein Ugelvik; Hagtvet, Bernt; Myklebust, Jan Petter, eds. (1984). Who Were the Fascists: Social Roots of European Fascism. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-82-00-05331-6.
- Lewis, Paul H (2002). Latin Fascist Elites: The Mussolini, Franco, and Salazar Regimes. Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-275-97880-8 – via Google Books.
- Lukacs, John (1998). The Hitler of History. New York: Vintage Books. ISBN 978-0-375-70113-9.
- Lyttelton, Adrian (1973). Italian Fascisms: from Pareto to Gentile. London: Cape.
- Mack Smith, Denis (1983). Mussolini. New York: Vintage Books.
- Mack Smith, Denis (1997). Modern Italy: A Political History. Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press.
- McLaren, Angus (1999). Twentieth-Century Sexuality. Blackwell Publishing.
- Mann, Michael (2004). Fascists. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-83131-4.
- McDonald, Harmish (1999). Mussolini and Italian Fascism. Nelson Thornes.
- Millington, Chris (2019). A History of Fascism in France: From the First World War to the National Front. Bloomsbury. online review.
- Millward, Robert (2007). Private and Public Enterprise in Europe: Energy, Telecommunications and Transport, 1830–1990. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-83524-4 – via Google Books.
- Morgan, Philip (2003). Fascism in Europe, 1919–1945. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-74028-4 – via Google Books.
- Mudde, Cas; Kaltwasser, Cristóbal Rovira (2017). Populism: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford, England: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-023487-4.
- Mussolini, Rachele (1977). Mussolini: An Intimate Biography. New York: Pocket Books. Originally published by William Morrow in 1974.
- Neocleous, Mark (1997). Fascism. Minneapolis, MN: Minnesota University Press.
- Neville, Peter (2004). Mussolini. Oxon, England; New York: Routledge.
- Nolte, Ernst (1965). The Three Faces of Fascism: Action Française, Italian Fascism, National Socialism. Translated by Vennewitz, Leila. London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson.
- O'Brien, Paul (2014). Mussolini in the First World War: The Journalist, the Soldier, the Fascist. Bloomsbury Publishing. ISBN 978-1-84520-558-4 – via Google Books.
- Overy, R. J. (1994). War and Economy in the Third Reich. Clarendon Press (Oxford University Press). doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198202905.001.0001. ISBN 9780198202905.
- Outhwaite, William (2006). Outhwaite, William (ed.). The Blackwell Dictionary of Modern Social Thought. Wiley-Blackwell. doi:10.1002/9780470999028. ISBN 9780470999028.
- Parkins, Wendy (2002). Fashioning the Body Politic: Dress, Gender, Citizenship. Berg Publishers. ISBN 978-1-85973-587-9.
- Passmore, Kevin (2002). Fascism: A Very Short Introduction. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-1-5366-6507-9.
- Passmore, Kevin (2003). Women, Gender, and Fascism in Europe, 1919–45. Manchester University Press. ISBN 978-0-7190-6617-7 – via Google Books.
- Pauley, Bruce F. (2003). Hitler, Stalin, and Mussolini: Totalitarianism in the Twentieth Century Italy. Wheeling: Harlan Davidson, Inc.
- Paxton, Robert O. (1998). "The five stages of fascism". Journal of Modern History. 70 (1): 1–23. doi:10.1086/235001. JSTOR 10.1086/235001. S2CID 143862302.
- Paxton, Robert O. (2004). The Anatomy of Fascism (First ed.). New York: Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-1-4000-4094-0.
- Paxton, Robert O. (2005). The Anatomy of Fascism. New York; Toronto: Random House. ISBN 978-0-307-42812-7.
- Payne, Stanley G. (1980). Fascism: Comparison and Definition. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-08060-0.
- Payne, Stanley G. (1995). A History of Fascism, 1914–45. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-14874-4. online; also another copy.
- Payne, Stanley G. (2003). Falange: A History of Spanish Fascism. Textbook Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7581-3445-5. online.
- Payne, Stanley G. (1987). The Franco Regime, 1936–1975. University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-11070-3 – via Google Books.
- Pollard, John (1998). The Fascist Experience in Italy. Routledge.
- Proctor, Robert E. (1989). Racial Hygiene: Medicine Under the Nazis. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-74578-0. OCLC 20760638.
- Quarantotto, Claudio (1976). Tutti fascisti! [All fascists!] (in Italian). Edizioni del Borghese – via Google Books.
- Quine, Maria Sophia (1996). Population Politics in Twentieth-century Europe: Fascist Dictatorships and Liberal Democracies. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-08069-9 – via Google Books.
- Ramswell, Prebble Q. (2017). Euroscepticism and the Rising Threat from the Left and Right: The Concept of Millennial Fascism. Lexington Books. ISBN 978-1-4985-4604-1. Retrieved 8 March 2019 – via Google Books.
- Reich, Wilhelm (1970). The Mass Psychology of Fascism. HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-285-64701-5.
- Renton, David (1999). Fascism: Theory and Practice. London: Pluto Press.
- Richardson, John E. (2017). British Fascism: A Discourse-Historical Analysis. Stuttgart: Ibidem Press. ISBN 978-3-8382-6491-2.
- Rietbergen, P. J. A. N. (2000). A Short History of the Netherlands: From Prehistory to the Present Day (4th ed.). Amersfoort: Bekking. ISBN 90-6109-440-2. OCLC 52849131.
- Rodogno, Davide (2006). Fascism's European empire. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
- Roel Reyes, Stefan (17 December 2019). "Antebellum Palingenetic Ultranationalism: The Case for including the United States in Comparative Fascist Studies". Fascism. 8 (2). Leiden, Netherlands: Brill: 307–330. doi:10.1163/22116257-00802005. ISSN 2211-6257.
- Rohkrämer, Thomas (2007). A Single Communal Faith? The German Right from Conservatism to National Socialism. Monographs in German History. Vol. 20. Berghahn Books.
- Rosas, Fernando (2019). Salazar e os Fascismos: Ensaio Breve de História Comparada [Salazar and the Fascisms: Brief Essay on Comparative History] (in Portuguese). Edições Tinta-da-China. ISBN 9789896714840.
- Ross, Alexander Reid (2017). Against the Fascist Creep. Chico, California: AK Press. ISBN 978-1-84935-244-4.
- Sauer, Wolfgang (December 1967). "National Socialism: totalitarianism or fascism?". The American Historical Review. 73 (2): 404–424. doi:10.2307/1866167. JSTOR 1866167.
- Schmitt, Carl (1995). "The Legal Basis of the Total State". In Griffin, Roger (ed.). Fascism. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Schnapp, Jeffrey Thompson; Sears, Olivia E.; Stampino, Maria G. (2000). A Primer of Italian Fascism. University of Nebraska Press.
- Schreiber, Gerhard; Stegemann, Bernd; Vogel, Detlef (1995). Germany and the Second World War: Volume III: The Mediterranean, South-East Europe, and North Africa 1939–1941 (From Italy's Declaration of Non-Belligerence to the Entry of the United States into the War). Oxford University Press.
- Seldes, George (1935). Sawdust Caesar: The Untold History of Mussolini and Fascism. New York and London: Harper and Brothers.
- Seldes, George (2009) . Facts and Fascism. New York: In Fact. p. 288. ISBN 978-0-930852-43-6.
- Shirer, William (1960). The Rise and Fall of the Third Reich. Mandarin.
- Sohn-Rethel, Alfred (1978). Economy and Class Structure of German Fascism. London: CSE Bks. ISBN 978-0-906336-00-7.
- Sontag, Susan (6 February 1975). "Fascinating Fascism". The New York Review of Books. Archived from the original on 18 July 2020 – via Google Books.
- Spektorowski, Alberto; Ireni-Saban, Liza (2013). Politics of Eugenics: Productionism, Population, and National Welfare. Routledge.
- Spielvogel, Jackson J. (2012). Western Civilization. Wadsworth, Cengage Learning.
- Stackelberg, Roderick (1999). Hitler's Germany. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-203-00541-5 – via Google Books.
- Sternhell, Zeev (1976). "Anatomie d'un mouvement fasciste en France: le faisceau de Georges Valois" [Anatomy of a fascist movement in France: the beam of Georges Valois]. Revue française de science politique (in French). 26 (1): 5–40. doi:10.3406/rfsp.1976.393652.
- Sternhell, Zeev; Sznajder, Mario; Ashéri, Maia (1994) . The Birth of Fascist Ideology, From Cultural Rebellion to Political Revolution. Translated by Maisei, David. Princeton University Press.
- Sternhell, Zeev (1998). "Crisis of Fin-de-siècle Thought". In Griffin, Roger (ed.). International Fascism: Theories, Causes and the New Consensus. London and New York: Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 978-0340706138.
- Thomson, David (1966). Europe Since Napoleon. Pelican. ISBN 9780140135619.
- Tierney, Helen (1999). Women's studies encyclopedia. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Publishing Group. ISBN 978-0-313-31072-0. OCLC 38504469.
- Toniolo, Gianni, ed. (2013). The Oxford Handbook of the Italian Economy Since Unification. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Turner, Henry Ashby (1975). Reappraisals of Fascism. New Viewpoints. ISBN 978-0531053720.
- Vatikiotis, Panayiotis J (1988). Popular Autocracy in Greece, 1936–1941: A Political Biography of General Ioannis Metaxas. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-7146-4869-9 – via Google Books.
- von Lang, Jochen (1979). The Secretary: Martin Bormann, The Man Who Manipulated Hitler. New York: Random House.
- Weber, Eugen (1982) . Varieties of Fascism: Doctrines of Revolution in the Twentieth Century. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company. ISBN 978-0-89874-444-6 – via Google Books. Contains chapters on fascist movements in different countries.
- Webster's II New College Dictionary. Houghton Mifflin Reference Books. 2005. ISBN 978-0-618-39601-6.
- Weiss, John (1967). The Fascist Tradition: Radical Right-Wing Extremism in Modern Europe. New York City: Harper & Row. ASIN B0014D2EN8.
- Weiss-Wendt, Anton; Krieken, Robert; Cave, Alfred A. (2008). The Historiography of Genocide. New York: Springer. ISBN 978-0-230-29778-4. Retrieved 12 April 2019 – via Google Books.
- Welge, Jobst (2007). "Fascist Modernism". In Eysteinsson, Astradur; Liska, Vivian (eds.). Modernism, Volumes 1–2. John Benjamins Publishing.
- Williams, Roger Lawrence (2015). The Mortal Napoleon The Third. Princeton University Press.
- Wistrich, Robert (October 1976). "Leon Trotsky's Theory of Fascism". Journal of Contemporary History. 11 (4). Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publishing: 157–184. doi:10.1177/002200947601100409. JSTOR 260195. S2CID 140420352.
- Woodley, Daniel (2010). Fascism and Political Theory: Critical Perspectives on Fascist Ideology. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-47354-5.
- Woolf, Stuart (1981). Fascism in Europe. Methuen. ISBN 978-0-416-30240-0. Retrieved 9 May 2020 – via Google Books.
- Woolf, Stuart Joseph (1983). Fascism in Europe (3rd ed.). Taylor & Francis.
- Woshinsky, Oliver (2008). Explaining Politics: Culture, Institutions, and Political Behavior. Oxford, England; New York: Routledge. ISBN 9780415960786.
- Zafirovski, Milan (2008). Modern Free Society and Its Nemesis: Liberty Versus Conservatism in the New Millennium. Lexington Books. ISBN 978-0-7391-1516-9.
- Zimmer, Oliver (2003). Nationalism in Europe, 1890–1940. Studies in European History. London: Palgrave. doi:10.1007/978-1-4039-4388-0. ISBN 978-1-4039-4388-0.
Tertiary sources
- "Fascism". Encyclopedia Britannica. 8 January 2008.
- "Italy: The Fascist Era". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 7 October 2017. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- "Volksgemeinschaft". Encyclopedia Britannica. 2019. Archived from the original on 31 March 2019.
- "Neofascismo" [Neofascism]. Treccani (in Italian). Enciclopedia Italiana. 31 October 2014. Archived from the original on 6 November 2014. Retrieved 31 October 2014.
- Badie, Bertrand; Berg-Schlosser, Dirk; Morlino, Leonardo (2011). "Fascism". In Badie, Bertrand; Berg-Schlosser, Dirk; Morlino, Leonardo (eds.). International Encyclopedia of Political Science. Sage Publications. doi:10.4135/9781412994163. ISBN 9781412959636.
- Staudenmaier, Peter (2004). "Fascism". In Krech III, Shepard; McNeill, John; Merchant, Carolyn (eds.). Encyclopedia of World Environmental History. Routledge. pp. 517–521. ISBN 0-415-93733-7.
Further reading
- Ahmed, Saladdin (July 2023). "Fascism as an Ideological Form: A Critical Theory". Critical Sociology. 49 (4–5): 669–687. doi:10.1177/08969205221109869. ISSN 0896-9205.
- Albright, Madeleine (2018). Fascism: a warning. London: HarperCollins. ISBN 978-0-00-828227-1. OCLC 1031976003.
- Alcalde, Ángel (May 2020). "The Transnational Consensus: Fascism and Nazism in Current Research". Contemporary European History. 29 (2): 243–252. doi:10.1017/S0960777320000089. ISSN 0960-7773. S2CID 213889043.
- Berezin, Mabel (30 July 2019). "Fascism and Populism: Are They Useful Categories for Comparative Sociological Analysis?". Annual Review of Sociology. 45 (1): 345–361. doi:10.1146/annurev-soc-073018-022351. ISSN 0360-0572.
- Churchwell, Sarah (22 June 2020). "American Fascism: It Has Happened Here" (PDF). The New York Review of Books. p. 22. ISSN 0028-7504.
- Esposito, Fernando; Zentrum Für Zeithistorische Forschung Potsdam (August 2017). "Fascism – Concepts and Theories". Docupedia-Zeitgeschichte. 31. doi:10.14765/ZZF.DOK.2.1111.V1.
- Finchelstein, Federico (2019). From Fascism to populism in history: with a new preface. Oakland, California: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-30935-7.
- Rethinking antifascism: history, memory and political uses, 1922 to the present. New York (N.Y.): Berghahn Books. 2016. ISBN 978-1-78533-138-1.
- Hayes, Paul M. (2016). Fascism. Routledge library editions Racism and fascism. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-138-93837-3.
- Illing, Sean (19 September 2018). "How Fascism Works: A Yale philosopher on fascism, truth, and Donald Trump". Vox.
- Joes, Anthony James; Gregor, A. James (2019). Fascism in the contemporary world: ideology, evolution, resurgence. London; New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-367-01749-1.
- Kagan, Robert (2020). "This is how fascism comes to America" (PDF). In Ball, Terence; Dagger, Richard; O'Neill, Daniel L (eds.). Ideals and ideologies: a reader (11th ed.). New York: Routledge. pp. 369–371. ISBN 978-0-367-23504-8.
- Kuklick, Bruce (2022). Fascism comes to America: a century of obsession in politics and culture. Chicago; London: The University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-82146-7.
- McGaughey, Ewan (30 December 2018). "Fascism-lite in America (or The Social Ideal of Donald Trump)". British Journal of American Legal Studies. 7 (2): 291–315. doi:10.2478/bjals-2018-0012. ISSN 2049-4092. S2CID 195842347. SSRN 2773217.
- Riley, Dylan J. (2010). The civic foundations of fascism in Europe: Italy, Spain, and Romania, 1870-1945. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 978-0-8018-9427-5. OCLC 370387631.
- Stanley, Jason (2024). Erasing history: how fascists rewrite the past to control the future. New York: One Signal Publishers. ISBN 978-1-6680-5691-2. OCLC 1450005012.
- Wiskemann, Elizabeth (December 1967). "The Origins of Fascism". History Today. Vol. 17, no. 12. pp. 812–818.
External links
- Fascism at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- Works by or about Fascism at the Internet Archive
- The Doctrine of Fascism by Benito Mussolini (1932) (in English)
- Authorized translation of Mussolini's "The Political and Social Doctrine of Fascism" (1933) (PDF) media.wix.com
- Readings on Fascism and National Socialism by Various – Project Gutenberg
- "Eternal Fascism: Fourteen Ways of Looking at a Blackshirt" – Umberto Eco's list of 14 characteristics of Fascism, originally published 1995
| Links to related articles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Fascism
- Authoritarianism
- Anti-communism
- Anti-union sentiment
- Corporatism
- Dictatorship
- Economic ideologies
- Far-right politics
- Genocide
- Italian words and phrases
- Political ideologies
- Political science terminology
- Political systems
- Populism
- Right-wing ideologies
- Right-wing populism
- Syncretic political movements
- Totalitarianism
- Totalitarian ideologies
